Planting pits for soil fertilisation and moisture improvement [Uganda]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Wilson Bamwerinde
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
EBISANIYA (Runyankore language)
technologies_1587 - Uganda
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Itália1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
16/11/2013
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
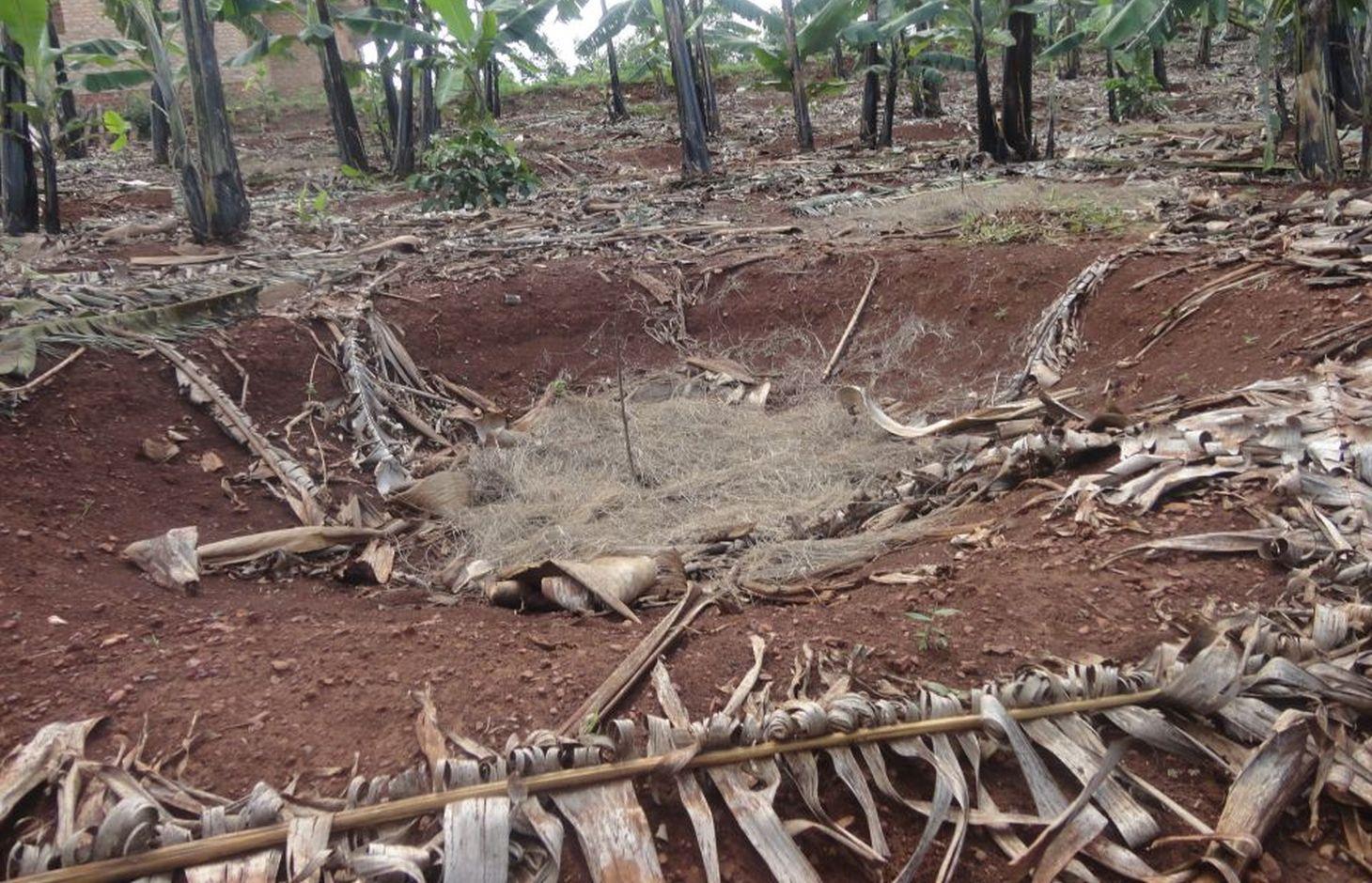
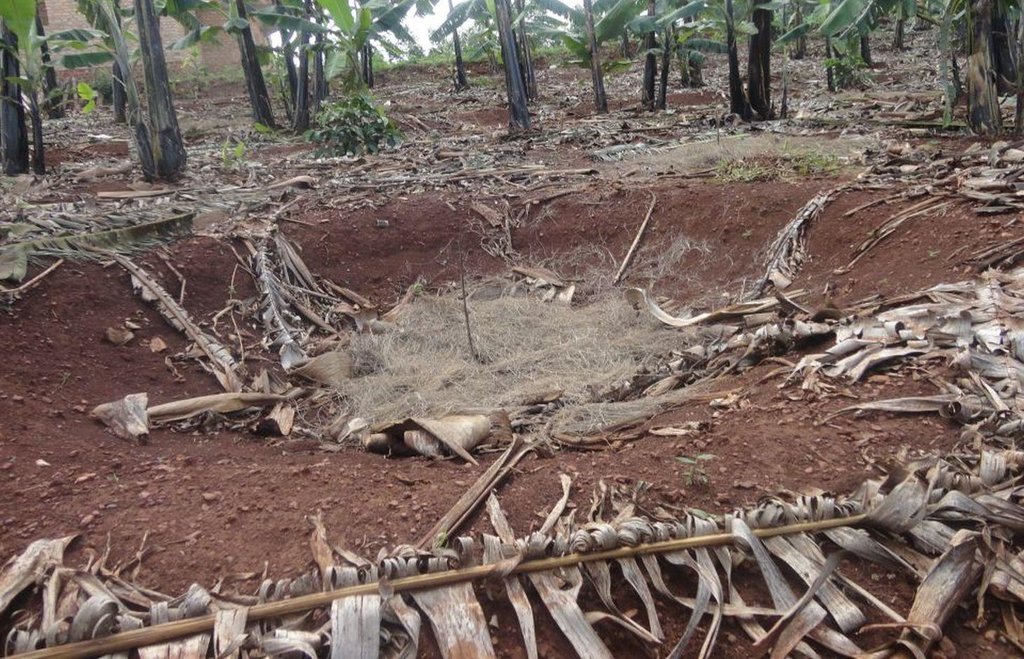
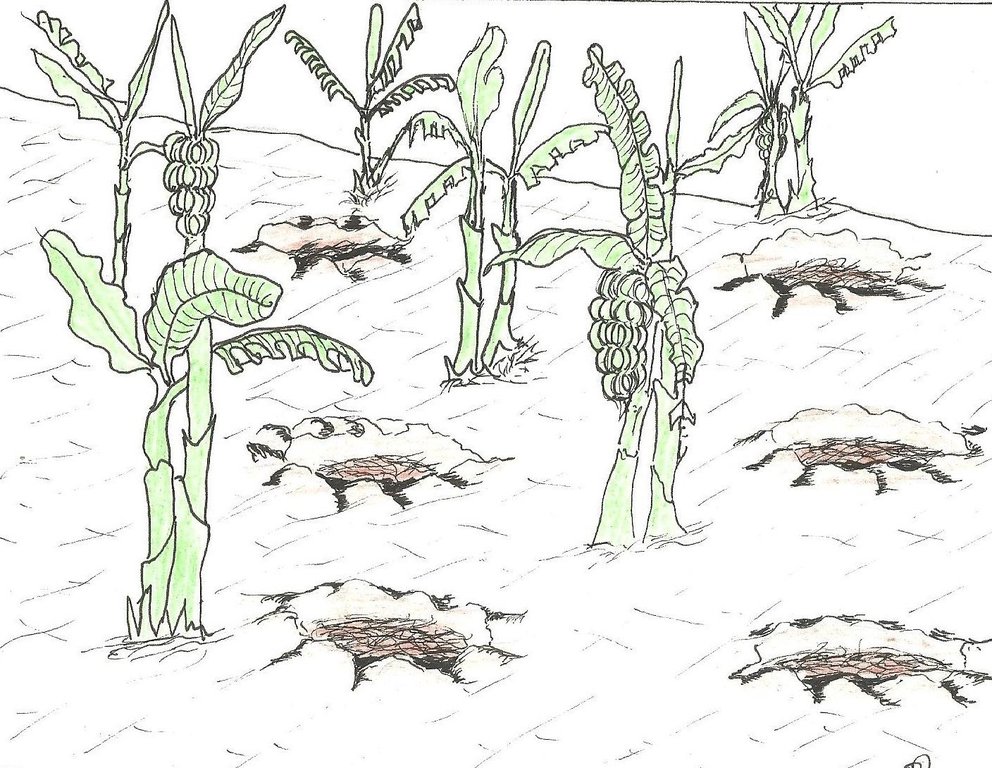
Planting pits in banana plantation filled with a mixture of manure, organic material and soil, to improve soil moisture and fertility and to enhance crop production and famer's income.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The planting pits are established between banana stems and filled with organic vegetative material mixed with decomposing manure to form a reservoir of nutrients for a long run. On gentle slopes covered with extensive banana plantations, the planting pits are dug at the center of banana stands. Before estbalishment of this technology, only the composting process was available for the conversion of organic domestic waste into manure. However, compost manure takes slightly longer to produce and is more bulky than conservation troughs making the latter easier to adopt. The technology can be applied to annual cropland as well. Application of the technology improves banana bunch size and plantation yield by over 300%.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objective is to improve soil fertility. The planting pits also check runoff thereby reducing soil erosion, improving moisture infiltration and retention, and enabling the plantation to withstand the dry months. Cabbages, beans and other high value vegetables can be grown directly on top of the trough.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The planting pits are established using simple tools such as the hand hoe, spade, panga and wheelbarrow. The hoe is used to dig up the soil and soften it. The soil is then scooped out using a spade, to create a bowl-shaped trough. The panga is used to chop the remains of harvested bananas (stems and leaves) which are then, carried to the troughs using a wheel barrow. The planting pit is 0.45 m to 0.60 m deep depending on the amount of manure available and 0.6 m wide. Each trough is about 0.60 m from the nearest banana stand. It is filled with chopped banana stems, followed by a layer of manure and then covered with mulch to prevent excessive evaporation of moisture. The planting pit is then covered with soil. After 3 to 4 months, the vigor of the banana stems improves. If the trough is opened by digging, roots are observed to have grown through the walls of the planting pit from all directions.
During the rainy season, the trough slowly fills with sediment from surface erosion. Weeding at the trough is done by uprooting the weeds using hands or a hand hoe.
Natural / human environment: Over time, the banana stands grow towards the trough. To maintain the distance between the stands, the suckers nearest to the trough are pruned.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Uganda
Região/Estado/Província:
Uganda
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mbarara
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86269 30.62587; -0.86275 30.62622; -0.86279 30.62631; -0.86405 30.62522; -0.86393 30.62539, -0.86387 30.62503
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
In 2012, Kagera TAMP introduced the Farmer Field School methodology. The members of these schools have been experimenting on several SLM technologies since then and the troughs are one of the successful innovations
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major cash crop: Banana
Major food crop: Banana
Major other crops: Maize, beans, peas, Irish potatoes
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The light, sandy loam soil on a hilly slope has very little capacity to hold water. The soils are dry a few days after it rains. The banana plantation therefore suffers two problems: inadequate soil water for plant growth and low nutrient retention. The problem of soil erosion is critical in the area but is addressed more adequately by fanya ju retention trenches stabilized with Napier grass strips.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity of the land compared to past seasons.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.04 km2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A6: Outros

Medidas estruturais
- S4: Valas de nível, fossos
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: Manure application (supp.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (No manure was being applied to replenish nutrients inspite of continuous banana harvesting)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Conservation troughs (0.4-0.6 m deep) are partially filled with a mixture of manure, undecomposed banana stems and other organic matter to add organic matter into the soil. They also capture rainfall runoff and help to maintain suitable soil moisture. The conservation trough should be dug about 0.6 m from banana plant so that the heat produced during decay does not affect the plant.
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara district. Uganda
Date: 29-Nov-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Self explanatory)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Basic training required on the construction methodology e.g. location selection, recommended dimentions of the trough (depth))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan)
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 3
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Reshaping surface
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Construction material (earth): Troughs are developed by excavating soil; soil mixed with manure is used to fill the pit partially.
Construction material (stone): n/a
Construction material (wood): n/a
Construction material (concrete): n/a
Construction material (other): n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): n/a%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: n/a%
Lateral gradient along the structure: n/a%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity n/am3
Catchment area: n/am2
Beneficial area: n/am2
Slope of dam wall inside: n/a%;
Slope of dam wall outside: n/a%
Dimensions of spillways: n/am
Other specifications: n/a
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:n/a
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
UGX
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
2500,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
4.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Measuring and marking pit positions | Estrutural | Wet season |
| 2. | Excavating pits | Estrutural | Wet season |
| 3. | Mixing top soil with animal manure, filling mixture into pits, putting domestic and field organic residues into pits, covering pits | Estrutural | Wet season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 91,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding by hand | Estrutural | Wet season |
| 2. | Addition of manure and residues | Estrutural | Once a year |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 34,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, wheel barrow
The calculations were made for the rainy season of September to November, 2013.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Availability of labour and animal manure are the most important factors affecting cost of the establishment activities. To reduce cost of labour it is recommended to apply Farmer Field Schools approach. To reduce cost of manure farmers can produce their own farmyard manure, e.g. by implementing zero-grazing technology.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
1400 mm spread over 2 seasons
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. Located at the Equator. A good supply of rain much of the year, but plenty of sunshine too
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1715 to 1740 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, concave) and ridges (ranked 2, convex)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Where the technology has been applied so far is on hilly slopes (< 30%) but the adjacent slopes where the technology is planned next is quite steep (> 45%))
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (The soils are generally shallow)
Soil fertility: Low
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (Mulching had already introduced topsoil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: >50 m (Boreholes have been sank before to great lengths but have invariably dried up)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (Available only as trapped runoff behind rocky formations, but soon dries up)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, runoff)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: n/a
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 20% of the land.
and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There has been an improvement in yields which translate into money generated per hectare. However, the farmers applying the technology have not yet diversified into other enterprises.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow)
Market orientation: Mixed (Surplus has grown to such a level that the commercial component has become inevitable)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Individual access to water rights is relatively new with the introduction of water harvesting.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
8 Kg
Quantidade posterior à GST:
25 Kg
Comentários/especificar:
Bunch of bananas is bigger and heavier at harvest
Risco de falha de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
20%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
67%
Comentários/especificar:
During the dry season or extended drought periods, only about 20% of the banana stands would have a fruiting stem; now well over two thirds of the stands do.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
80 US$
Quantidade posterior à GST:
200 US$
Comentários/especificar:
Monthly harvests for sale have increased from 20 to over 50 bunches
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
100%
Comentários/especificar:
Whereas extended drought posed food insecurity, this is no longer the case
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The earning power has increased greatly. Children are going to school because tuition fees are no longer burdensome and health needs are easily met. The farmers practicing the technology report making some savings from their incomes unlike before.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
The advantages of the technology to cropland are to be found underground. Therefore the technology is protected against most natural adversities above ground.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Costs at establishment are the only ones involved. There are no maintenance costs involved though pits need to be re-established every 2-3 years
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
22
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is a farmer initiative and no support has been received for the adoption of this technology.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
22 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This is a farmer field school initiative and the district facilitator for Kagera TAMP (and also an Agricultural officer of the local government) provided guidance on positioning the pits for maximum utility.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Noticing the results in only 3 seasons, the other farmers (not members of farmer field school) are also adopting the technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
The technology requires the use of only the simplest of farm tools such as a hand hoe, a spade and a wheel barrow. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Dissemination of the the technology through regular community meetings and a local language newsletter |
|
Demonstration of benefits is achieved quite quickly and therefore adoption by farmers is good. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Emphasize technology at farmer field school demonstration plots |
|
Technology bears similar benefits to composting but with a shorter list of activities How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption through demonstration |
|
Since the technology utilizes stem cuttings, whole stems are harvested reducing the risk of pests and diseases especially banana bacteria, that would be harbored by exposed rotting stems How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge dissemination through regular community meetings and local language newsletter |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The technology is labor intensive | Farmer Field Schools bring farmers together in a community level effort |
| The technology requires livestock manure in a predominantly cultivator community | Introduce zero-grazing livestock for manure production |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos