Gully plug [الأردن]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Mira Haddad
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
السدات
technologies_5862 - الأردن
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
الأردن
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Evett Steve
USDA Agricultural Research Service
الولايات المتحدة
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - لبنان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
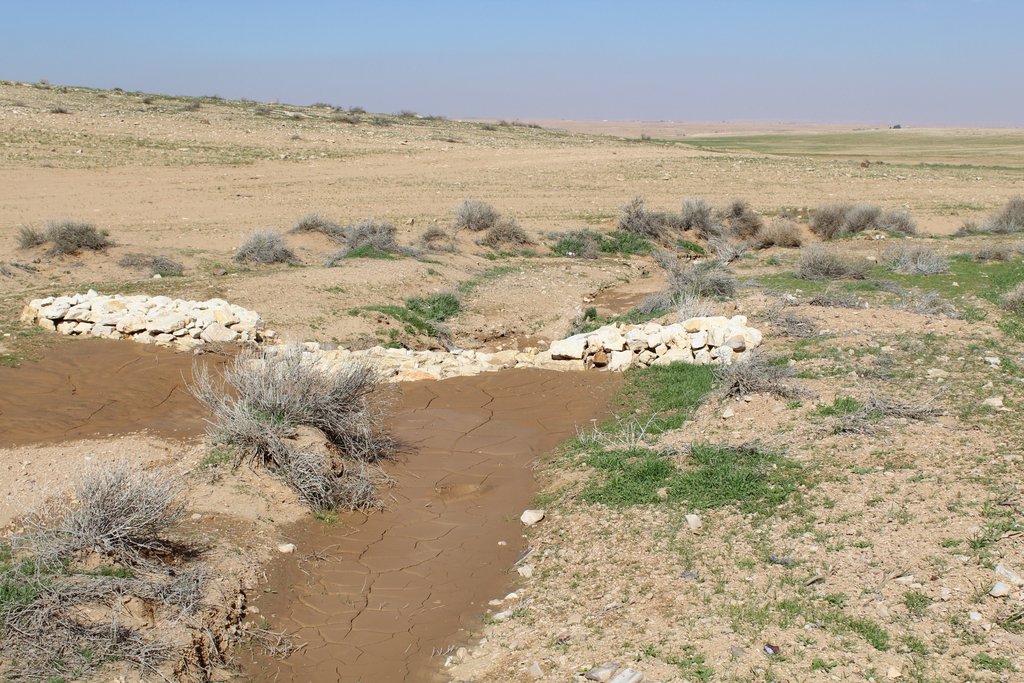
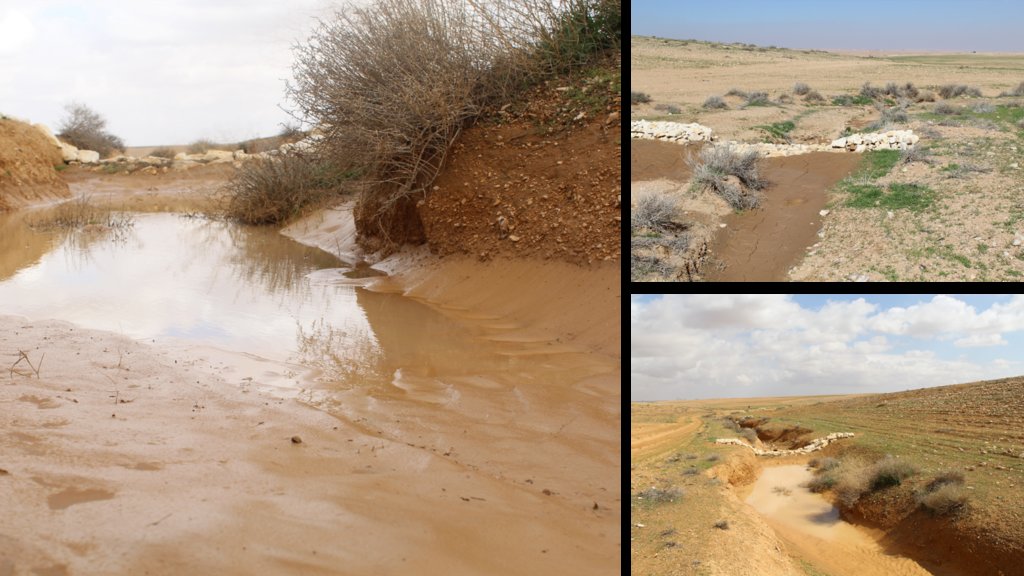
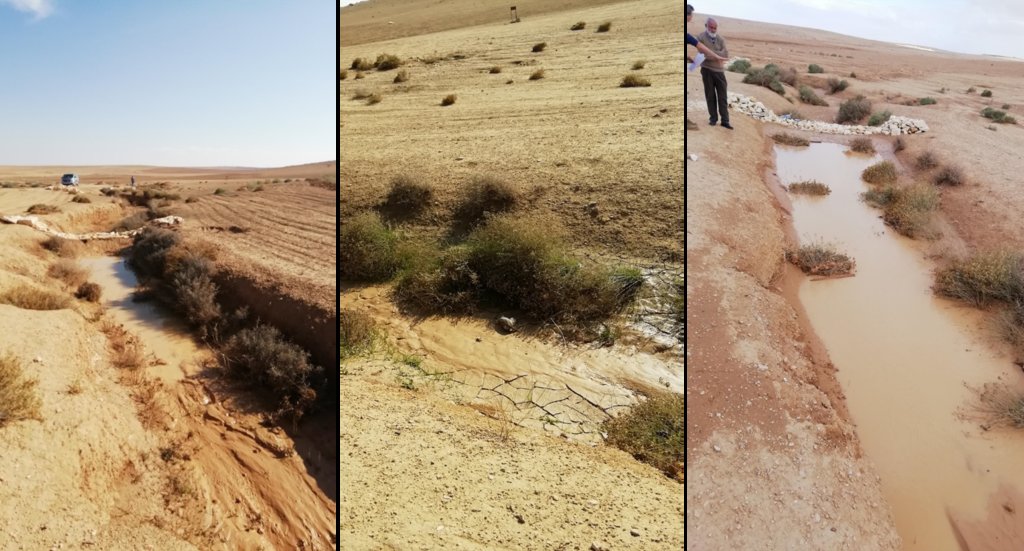
Gully plugs aim at rehabilitating active gullies in dryland watersheds, which are prone to erosion through concentrated surface runoff. Multiple gullies plugged in succession dissipate runoff energy, foster local water retention and infiltration, encourage sedimentation, assist in the stabilization of gully bed and side banks, and stimulate revegetation of flow paths; the channel measures must be combined with proper SLM in the catchments upstream.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
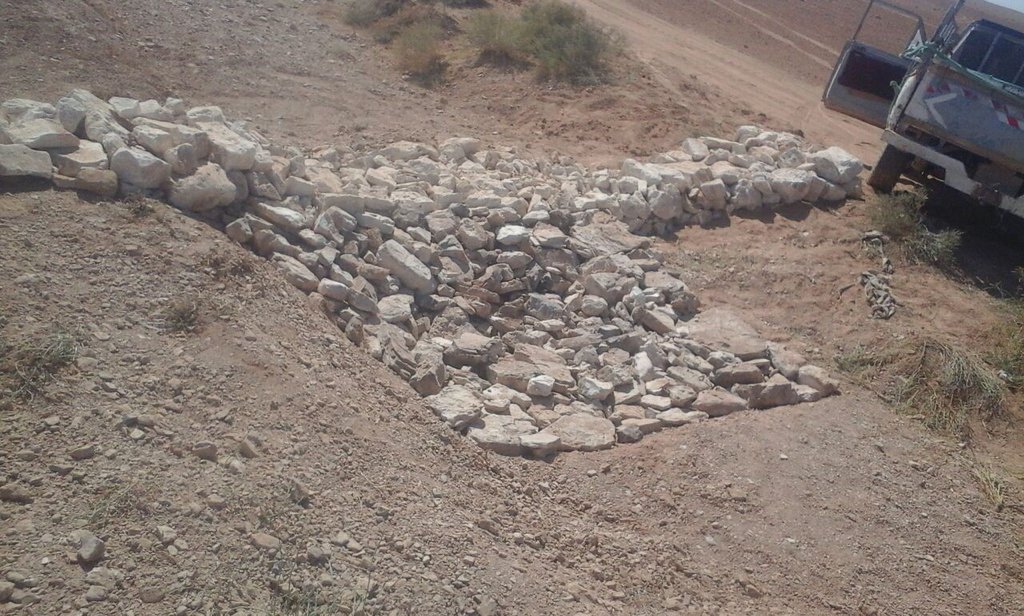
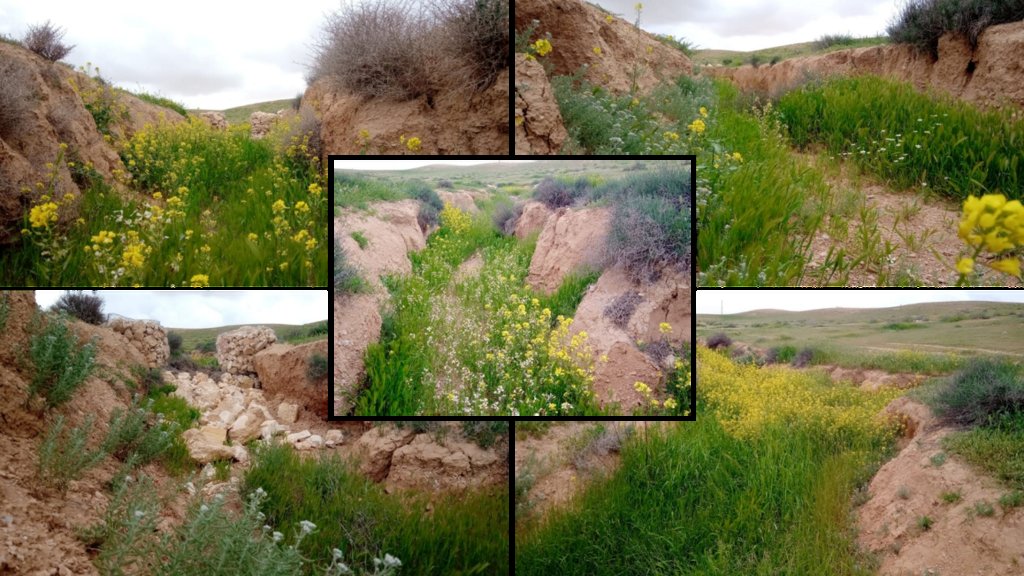
Characteristics: Multiple gully plugs positioned sequentially within a gully system interrupt concentrated surface runoff and reduce its erosive power. The plugs are each made of multiple cobbles/stones mostly ranging between 10 and 30 cm diameter and constructed to ensure a stable structure. The plugs started at the head of the gully (upstream) and ranges from 1.5 - 3.7 m in width with an average of 2.5 m. For heavily eroded and very unstable sections, gabions can be used also. The structures are around 1.0 to 1.5-m high, anchored into the sidewalls, and around 0.20 to 0.35 m deep into the gully bed, built up to around 1/3 to max. 1/2 of the gully depth - ensuring the concentrated flow stays within the channel and does not overflow the side banks. The top of the plug is U-shaped, with the sides built higher than the centre. Upslope, the plugs are packed with soil to trap sediments (stopping it flowing through the structure), and downslope the plugs have an apron to dissipate the energy of overflowing water, into a micro stilling basin. The downslope side of the gully plug is sloped rather than vertical. The large stones add roughness to the slope, creating a rough spillway that dissipates erosive energy. In the direction of gully flow, several gully plugs are placed such that the upper gully apron is set at approximately the height of the following downstream gully crest.
Environment: The technology is used in a watershed close to Al Majeddyeh village, located in the Middle Badia zone, approximately 30 km south-east of Amman. The climate is arid and warm (Palmer, 2013). The average annual rainfall is around 130 mm. The natural environment is labelled as steppe, “BSh” in the köppen classification. The human environment is characterized by agropastoralists. They are semi-nomadic and live in villages around the watershed, for example, Al Majeddyeh village.
Purpose: The measure interrupts the concentrated flow, reduces velocity, and dissipates energy. Multiple structures along the gully decrease the erosive power of runoff, retaining a fraction of the runoff, inducing sedimentation (upstream of the plug), thus protecting the gully bed from further deep-scouring, and strengthening the gully side banks, especially when this is linked with re-vegetation. Over time, the establishing vegetation (roots and surface cover) stabilizes the soil and protects it from concentrated flow erosion. To be effective, gully plug emplacement requires SLM in upland areas. These measures then jointly mitigate peak runoff generation and accordingly reduce downstream flooding.
Major activities: Upland SLM is essential. In the specific watershed rehabilitation context, upland SLM was achieved through micro water harvesting and re-vegetation through native shrubs (the “VALLERANI” method). Gully morphology assessment is required for gully plug design, and positioning and earthwork excavation is necessary for foundation preparation in the gully bed and wall anchors. Proper layering of various size stones and shaping of gully plugs is necessary as is the addition of a packed soil pack upstream of the stone structure, to semi-seal the surface and to pond water. Then gully walls are revegetated through native seedlings: these benefit from the water ponding upstream prior to sedimentation upstream of the gully and enhanced soil water storage in the sediments once the gully is filled.
Benefits: Stops ongoing land degradation and gully deepening, and achieves a certain degree of rehabilitation; retains a fraction of runoff water and sediments in the watershed – water mainly infiltrates and provides moisture to the gully vegetation; gully vegetation serves various purposes including livestock fodder, reduction of flow velocities in the gully, and retention of further sediment.
Land user's opinion: Land users benefit from the vegetation (e.g. fruit trees can potentially be out-planted), as well as ponded water for livestock; however, the technology is labor-intensive, and therefore costly, and landowners (at the local target site) require incentives to carry out the work.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الأردن
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Amman governorate/Al Jizza/Al Majeddyeh village
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2017
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
- خطوط الصرف، الممرات المائية
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
To convey and drain: Wd
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الرعي المرتحل
- رعي شبه مرتحل
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- الأغنام
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
كلا
المنتجات والخدمات:
- اللحوم
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
The measure mitigates the effect of surface runoff in concentrated flow areas - as a consequence of heavy rainfall events
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- water harvesting; surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea, riparian zone, riverbanks, seashore, lakeshore, spring shed); ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات

تدابير أخرى
حدد:
Specify tillage system: no tillage
Specify residue management: grazed and retained
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
- (Pu): فقدان الوظيفة الإنتاجية الحيوية بسبب أنشطة أخرى

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hw): تناقص القدرة التخفيفية للمناطق الرطبة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Emplacement in gully morphological system and watershed context: Determine the downstream starting point for the gully plugs and then extend upstream. The basic design is to keep the structure height maximum half the gully depth regardless of structure type. The spacing between structures is set as a gully depth function, structure crest height above the gully bed, and slope of the gully bed between structures. Additionally, the structure's final location will be shifted either upstream or downstream of the calculated gully bed level to place the structure in a more stable point if required. Following this methodology ensures variable spacing between structures to cope with both slope and depth of gully to ensure the sediment filling in between these structures occurs. In the case of distinct gully morphology and side banks that are very unstable, gabion structures can also be used/instead of a single stone pack.
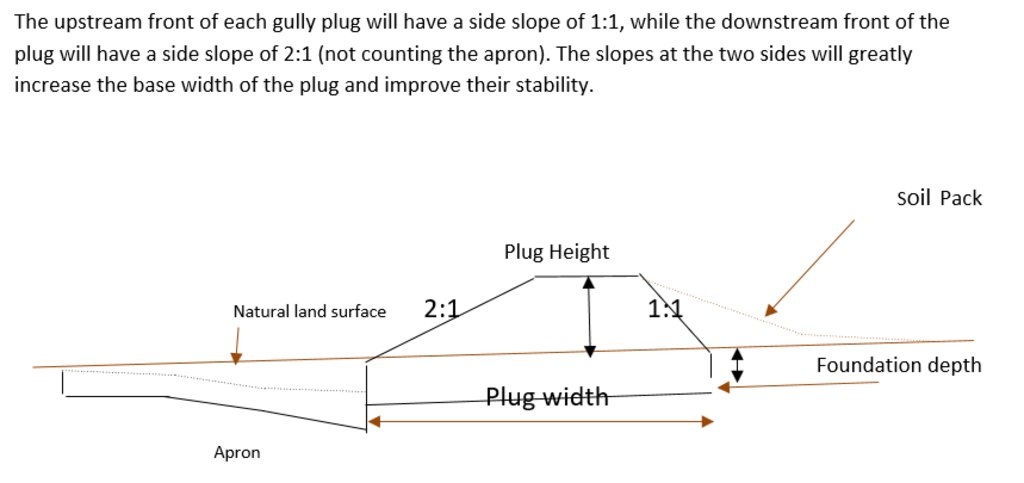
Design of the Structure: Gully plugs must be anchored strong enough to resist water flow and prevent bypass from the side banks. A foundation is also required for all structures, depending on their dimensions and the bed's nature. At the specific site, the foundation depth for the planned structures ranges between 0.2 to 0.35 meters. The anchoring of gully plugs ranges between 1 and 1.5 meters. This depends on the existing condition of the banks at each structure location. Gully plugs have a downstream apron with a length of around 3 to 4 times the height of structures. The apron starts from below the bottom level of the foundation and gradually level halfway down. All gully plugs were designed to have a height maximum of 0.5 the depth of the gully. So each structure will pass water flow downward but keeping it inside the gully. Gabion structures have a sort of spillway from the top but at the same time protecting the banks. The configuration slightly differs from the normal stone structure, but the idea is to protect the sides and a spillway in the middle. The upstream front of each gully plug has a side slope of 1:1, while the downstream front of the plug has a side slope of 2:1 (not counting the apron). The slopes at the two sides greatly increase the base width of the plug and improve their stability. The gully plugs are provided with an amount of soil resulting from the foundation to form a triangle of soil fill against the structure at the upstream side; this improves the function of the gully plugin holding more water and trapping sediments. On the other side of each structure, the downstream side's slope is meant to tackle the overflow of water along the drop to safely return to the gully bed level without causing additional erosion. The rock-filled apron catches the flow and acts to dissipate erosive energy.
المؤلف:
Steve Evett
التاريخ:
15/08/2017
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Gully plug
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implement upland watershed SLM (reference VALLERANI) | |
| 2. | Gully system/morphological assessment | |
| 3. | Determine plug design and implementation in the watershed | |
| 4. | Excavation earthworks for anchors and foundation | At least 2 months prior rainy season onset |
| 5. | Stone made construction of gully plugs (occasionally with gabions) | At least 1 month prior rainy season onset |
| 6. | Soil pack at upstream front | At least 1 month prior rainy season onset |
| 7. | Revegetation of gully side banks | At the onset of the rainy season |
التعليقات:
Gully plugs require proper SLM in the uplands. Revegetation of gully side banks is optional – depending on the recovery potential of the area.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Field technician (design and oversight) | Labour Day (LD) per structure | 0,2 | 50,0 | 10,0 | |
| العمالة | Workers (excavation/earthworks) | LD | 4,0 | 35,0 | 140,0 | |
| العمالة | Workers (stone layering/construction) | LD | 4,0 | 35,0 | 140,0 | |
| العمالة | Worker (out-planting of seedlings) | LD | 1,0 | 35,0 | 35,0 | |
| معدات | Shovel, Pickaxe, buckets, ruler | Lump sum | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | per item | 10,0 | 0,5 | 5,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Stones | m3 | 4,0 | 10,0 | 40,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Logistics (seedling transport, local stone transport) | lump sum | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 390,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 390,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
International research for the development project.
التعليقات:
Design is tailored for implementation through local workers (rural agro-pastoral community) and local materials. The engagement of local community workers as part of the specific project; if a professional contractor is hired costs can be significantly reduced.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inspect damage/status | After severe storms and runoff events |
| 2. | Maintain/repair/improve | After inspection |
التعليقات:
If optimally designed and connected with proper upland SLM the gully plug technology would not require maintenance; the measure induces nature-based (vegetation) protection of vulnerable gully zones over time.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Expert (investigation) | LD | 0,1 | 50,0 | 5,0 | |
| العمالة | LD | 0,5 | 35,0 | 17,5 | ||
| العمالة | LD | 1,0 | 35,0 | 35,0 | ||
| مواد البناء | stones | m3 | 0,5 | 10,0 | 5,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 62,5 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 62,5 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
It is 100% covered by the research project
التعليقات:
Maintenance might be needed in case of improper implementation and/or extreme event occurrence. Maintenance should be minimal - mostly after initial 1-2 rainy seasons. Thereafter, revegetated and rehabilitated gully system – and most importantly, the rehabilitated uplands - would take on hydrological buffering functions and withstand the erosive force of surface runoff.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most distinct cost factor is labor – which is especially significant when using local (community) labor; some technical training is required.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
130,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Jordan has a rainy season from September to May – but locally, the effective rainy season sets on later (November or December) and lasts until April.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Queen Alia international airport reference station reports long term average annual rainfall of about 150 mm A rainfall tipping bucket installed in the site in 2016.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Gully slope is 3.4% on average.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth is varying throughout the gully areas. At some points (mostly upstream) the gully bed reaches the bedrock
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
مرارًا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Gully plugs with out-planted vegetation create micro-climates; after recruitment and emergence of seed material, biodiversity increases.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
- شبه مرتحل
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
The entire watershed area affected by gully plugs is 160 hectares.
The total constructed plugs are 55.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some herbs (and fruits (trees) in the future)
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
enhanced biodiversity, shade and shelter
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through training/community participation
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Certain degree purification through infiltration in the sediment accumulation zone
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Effect on hydrology (distinctness of runoff peak)
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Certain deep-infiltration
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
more open water ponding – but also deep-infiltration and beneficial use for vegetation (transpiration)
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Side banks stabilized
تراكم التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
sediments trapped
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
sediment crust increased in the ponding area – but better soil structure at the side banks (revegetation) – overall positive impact.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through side bank stabilization.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
especially when combined with upland measure: reference VALLERANI
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less tributary channel development (connectivity of upland areas); less downstream siltation
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
less runoff peakiness and siltation
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان مفاجئ | جيدة جدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فترة نمو ممتدة | جيدة جدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
During the initial stage potential benefits through vegetation do not materialize; main effects are on water and sediment retention. Long-term, the technology fosters the rehabilitation nature-based retention functions (very limited long-term maintenance required).
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
1
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Gully side bank vegetation useable as (livestock) fodder source; some herbs (later fruit tree benefits) for human consumption. |
| Gully is stable and does not expand e.g. tributaries. Uplands remain connected and productive. |
| Ponded water for livestock watering (during the rainy season). |
| Shelter and shade through vegetation. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Sediments from the uplands are trapped; relatively fertile soil remains in the watershed. |
| Increased local soil moisture and consequential vegetation quantity and bio-diversity enhancement; increase carbon storage and other ecosystem services such as pollination. |
| Smoothened watershed hydrology is beneficial for downstream agriculture – especially when applied in a watershed context with downstream flood irrigation (MARAB) |
| Protection of downstream infrastructure (flooding and sediments). |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| implementation costs | Incentives (e.g. governmental) for communities to implement SLM; regulations and enforcement on environmental management – especially connected with entitlements of natural resources facilitation |
| Tensions between upstream and downstream watershed users (watershed hydrology) – especially affected through wrong design and failure (e.g. gully breakage) | Community-based and holistic watershed management – the share of benefits and commitment for maintenance. |
| Additional fodder supply might attract other foreign herders (overgrazing) | Community-based and holistic watershed management – and protection. |
| Technical skills needed for implementation | Rural communities’ capacity building programs |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Expert design and implementation support required | Governmental and environmental organizations in control of design and support to local communities (training). |
| Requires upland SLM | Integrated watershed management and empowerment of local communities to manage and facilitate – provision of support (e.g. government and/or international projects). |
| Increased vegetation in a fragile ecosystem can lead to local pressure | Integrated watershed management and empowerment of local communities – especially sustainable grazing plans |
| Risk of wrong lessons learned: large water harvesting in gully systems (dams) created by locals | Capacity development programs; regulations and enforcement on environmental management. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
The number of field visit is 5.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
The number of land users that were interviewed is 10.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
The number of SLM experts who were interviewed is 5.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
09/08/2020
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Steven, E. (2017). Report on Majiddya Watershed Rehabilitation Project - Gully Plugs Plan /August 2017.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Dimensioning of Marab in Majidyya.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
SEA. 1974. Les ouvrages en gabions – techniques rurales en Afrique. Secretariat d’Etat aux Affaires Etrangeres, Republique Francaise, 20, rue Monsieur, 75007 Paris.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
FAO. 1977. Guidelines for watershed management. FAO Conservation Guide 1. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Rome, 1977
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية