Indigenous knowledge transfer [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Godfrey Baraba
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Emikolele n'emyegesheleze. (HAYA)
approaches_2472 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Kaihura Fidelis
Kagera TAMP Project, National Project Manager
Tanzania, República Unida de
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - Tanzania, República Unida deNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - Italia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
25/05/2012
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST

Enhanced mulching in banana and coffee plantation [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Application of Thatch and Hyperrhenia Rufa grass mulch in banana and coffee plantation to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility and moisture and ensure high productivity
- Compilador: Iwona Piechowiak

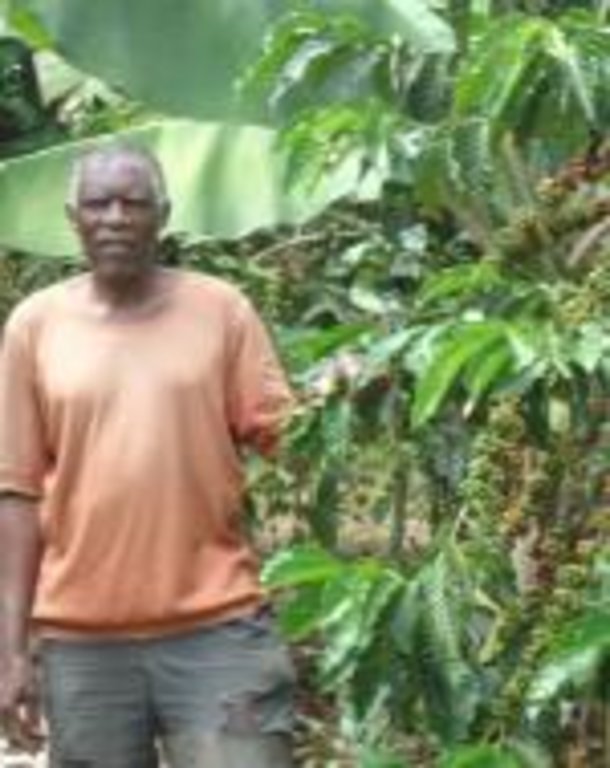
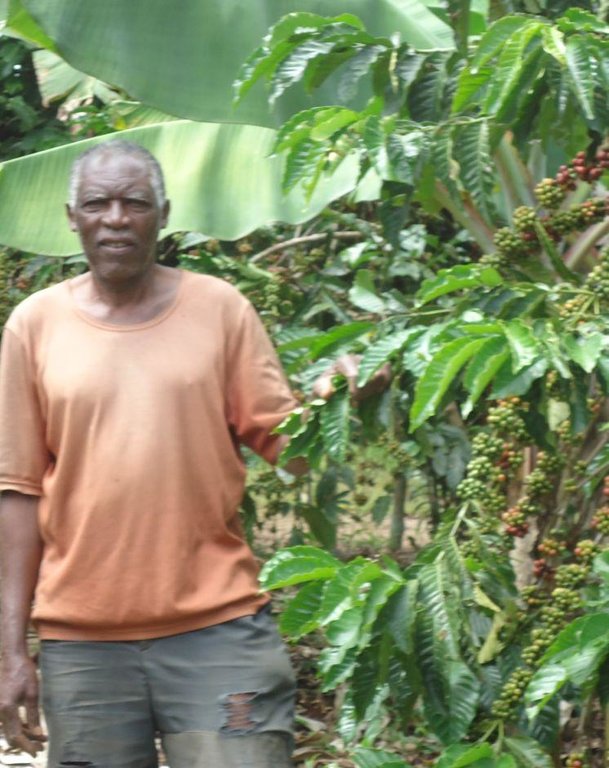
Buhaya agroforestry system [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Traditional agroforestry system comprising mixture of banana, coffee, fruit trees, biannual crops, annual crops and timber trees which together optimize the use of soil, moisture and space.
- Compilador: Godfrey Baraba
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: The main aim of this approach is to improve agricultural production through collaboration of households and the entire community. The approach ensures food security and income with land conservation. The approach is achieved by voluntary learning from the experienced elder farmers. This is achieved by creation of friendly environmental to implement the learning process. The approach is also characterized by traditional prons and norms of the young generation to inherit the elders property.
Methods: The elders spent evening hours to tell farming stories to the younger generation. These stories refer to the success of soil fertility improvement, water resources accessibility and utilization, land use type and farming practices in the community.
Also, practical aspect is attained by involving the younger generation in porting and allocating the land according to land use type.
Stages of implementation: 1. Experienced farmers telling farming stories to the younger while younger listen and ask questions.
2. The elders ask old sayings and elaborate their meaning.
3. Elders demonstrating to the younger, how farming activity are done.
4. The younger implement farming activity and plan for their future.
5.The land is allocated to the younger according to land use type.
6. The younger farmers now are in the position to train their successors.
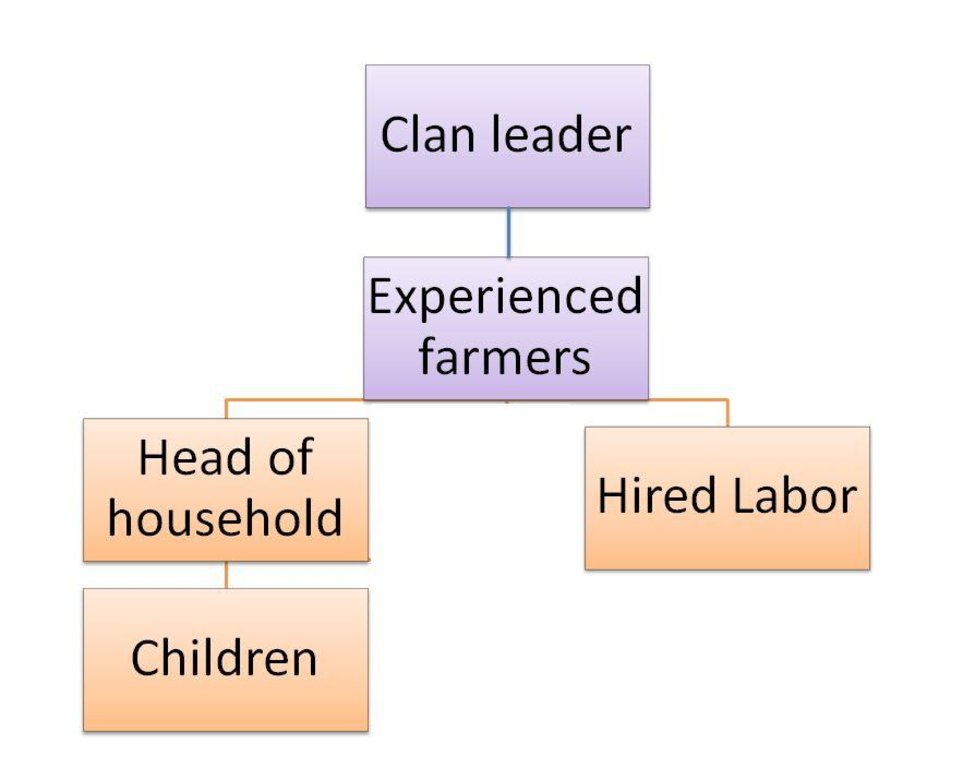
Role of stakeholders: The major stakeholders are Clan leaders, Head of households, mother, children and hired labour. The roles of Clan leaders are to organize the farming story sessions to the elders and reinforce traditional land norms and proms. The roles of Head of household are to conduct evening farming stories at homestead, encouraging the younger to practice farming by giving incentive according to performance. The roles of the children and hired labour is to work in the head of household farms and ensure proms and proms abides.
Other important information: Nowdays, the approach succeeded to expand cropland beyond grasslands and forestland.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tanzania
Especifique más el lugar :
Bukoba District
Map
×2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- tradicional/ local
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Products diversification, livelihood improvements and land resouces inheretence.)
The main aim of the approach is to improve productivity and ensure younger generations productive land ownership and user rights.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of knowledge and skills of farm technologies, collaboration between households and community, eroded/weakened traditional norms, land ownership inequalities.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
normas y valores sociales/ culturales/ religiosos
- impiden
Land ownership inequalities, whereby women and girls are not allowed to inheret the clan land.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Improve women participation in decision making
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
Farming activities regarded as volatile assets by most financial institutions
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Introduce and impliment subsidies policy.
entorno institucional
- impiden
The clan leaders not strong in terms of formal training. Weak reinforcement of laws and bylaws.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Use extension service staffs to promote informal training.
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Individual land ownership without lease smoothing the transfer of land from one parents to offspring. therefore assured perfect training grounds
- impiden
Community not well knowledgeable on land laws.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Train village land law to the community.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
Lack of farming technologies transfer.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Facilitate extension services.
otros
- impiden
Some plant spps habours pests
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Planting of pecit repelant species. eg Kajaye
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Household and hired laborers
Adoption farmers tends to use grups for socilization and participation. The difference between the participation of men and women is that, women train children only, while men can also train hired laborers. Hired labour normally spent the day while folk story conducted at night. Labourers including men and women are disposal to men trainings.Women participate in training at all stages but are not involved in land allocation to the younger generations. Women: Have the rights to produce annual crops and decide on the income from it.
Younger: Are assured of land inheritance from their parents.
laboures: Are paid at the market price.
Poor households: assured food security as work for food, informal land renting i.e paying back the prorate produce.
- gobierno local
Provides extension services for up scaling the aproach.
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | auto-movilización | Household members. To attend and particiapte in appropriate sessions. |
| planificación | auto-movilización | Clan leaders: To identify and select problems and find solutios Head of Household: Children. Siblings: Hired labour: |
| implementación | auto-movilización | Head of the clan: To organise the sittings. Head of Household:To inform the family and conduct the dialogue Children: To participate in farm production, aceptance of allocated land, Using the located land according to land use type. Siblings: To facilitate divison of labour Hired labor: |
| monitoreo y evaluación | ninguno | Clan head: To call the meeting Community leaders: To visit farms and other land, To observe and deliver the assessments. |
| Research | pasivo | Few farmers participated in adaptive resarch on Kibanja system 1n 1993. |
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
Explique:
Indigenous trainings are formalized by extension staffs. Coffee and Vanilla buyers tends to supervise farms for products assurance.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Extension staffs monitor, evaluate and advise the proper methods up scaling.
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
Describa/ comentarios:
Name of method used for advisory service: Train and Visit (T&V); Key elements: Subject Matter Specialist trin field staff on fortnight bases. Field staff visit Progressive farmers and train them, Field Staffs visit Farmers to assess the performance and give feed back to Subject Matter Specialist; The method is very effective under a strong economical situation.
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Farmer field schools can't reach farming communities with extension staffs based on Ward level.
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, un poco
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
- Agricultural advisory services.
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: activities according to the season.
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through measurements; indicators: Customary land law, land inheretance protocals.
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Harvesting season
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by other through measurements
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by None through observations
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Monitoring and Evaluation component took very minimal attention.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Proporcione detalles adicionales e indique quién hizo la investigación:
Research was carried out on station
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- < 2,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s): 100.0%
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
No
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
Mainly family labour is the major component of input.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
5.5 Otros incentivos o instrumentos
¿Se usaron otros incentivos o instrumentos para promover la implementación de Tecnologías MST?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Agricultural advisory services.
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
Diversification asure grand production
- incremento de la renta(bilidad), proporción mejorada de costo-beneficio
Implementation costs requires on family labour and commitments
- reglas y reglamentos (multas)/ aplicación
Farming land inheritance protocals and land norms enforcement are ver crucial components.
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- sí
Si respondió que sí, describa cómo:
It has been in application for very long time, and no signs of retardation observed.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Local resource person, obedience and committed community. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Kagera TAMP project website
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Enhanced mulching in banana and coffee plantation [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Application of Thatch and Hyperrhenia Rufa grass mulch in banana and coffee plantation to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility and moisture and ensure high productivity
- Compilador: Iwona Piechowiak

Buhaya agroforestry system [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Traditional agroforestry system comprising mixture of banana, coffee, fruit trees, biannual crops, annual crops and timber trees which together optimize the use of soil, moisture and space.
- Compilador: Godfrey Baraba
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos