Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure [Bangladesh]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: TUHIN SAMADDAR
- Editor: Anton Jöhr
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Hanspeter Liniger, Nicole Harari
দুর্যোগ সহনশীন অবকাঠামো উন্নয়ন (Durjog-shahonshil abokathamo unnayon)
technologies_664 - Bangladesh
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Emergency infrastructure, shelter and access: 28 de marzo de 2017 (inactive)
- Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure: 2 de agosto de 2017 (inactive)
- Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure: 10 de noviembre de 2017 (inactive)
- Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure: 5 de marzo de 2019 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Project Staff:
Mustafa Golam
+880 1718770373 / +880 1730799762
pmdrrwash16@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Project Manager, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Project staff:
Razzak Abdur
+880 1730 799763 / +880 1730 799763
razzak.pe@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Project Engineer, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Project Staff:
Islam Saiful
+880 1730 799746 / +880 1730 799746
saiful644@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Field Officer DRR and Training, DRRWASH Project Office, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Swiss Red Cross (Swiss Red Cross) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
04/10/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology presented has no direct bearing on land degradation.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Early Warning Message Dissemination [Bangladesh]
An effective system for dissemination of early warning messages was established among the vulnerable communities in Chars (riverine sandy islands) of Gaibandha district, Bangladesh, in order to strengthen their coping mechanisms and reduce loss and damage caused by floods.
- Compilador: TUHIN SAMADDAR
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
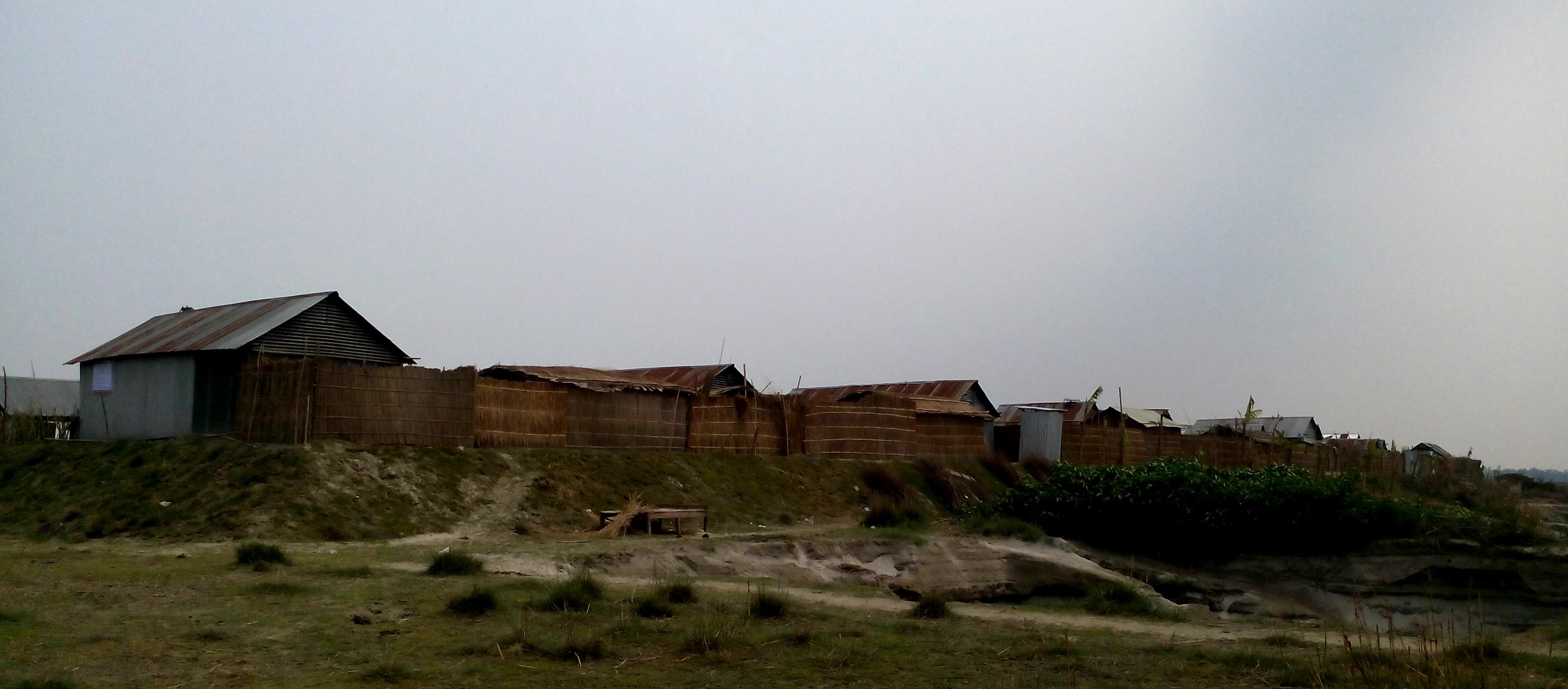
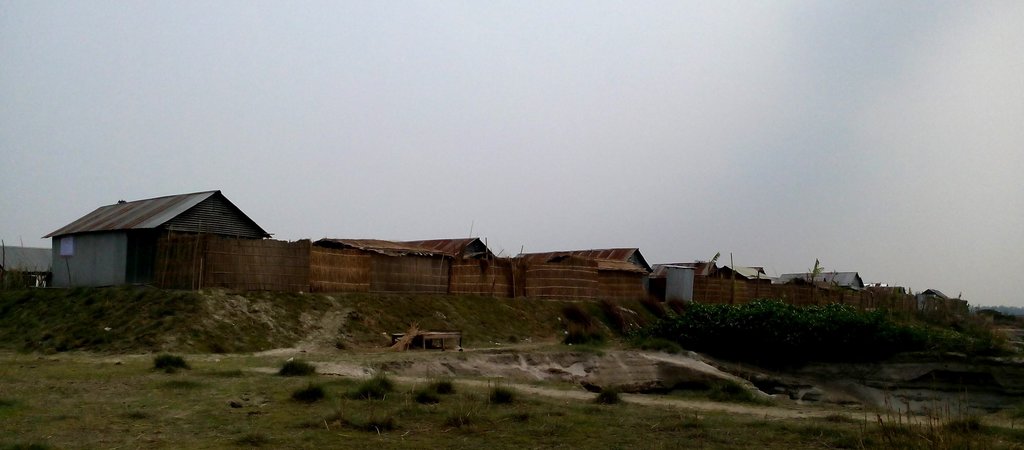
Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure, consists in establishing specific flood shelters (for people and animals) including flood-proof collective water sources and communication infrastructure as well as health and school facilities that may serve at the same time as emergency shelters during floods.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The technology applies to the specific context of the ‘Char’ land in Bangladesh, characterised as riverine sandy Islands along the Jamuna River. More than 80% of the land in the intervention area can be classified as 'Char' and is inhabited by 60% of the population served by the project. Every year, especially during floods, the rivers deposit huge amount of silt sediment that makes the land fertile. At the same time, river action washes away some portion of the 'Char' which at times can be quite large and has a strong impact on people's lives and livelihoods. Before the intervention, people living on 'Char' land depended on their traditional early warning mechanisms and were frequently surprised by floods that destroyed their crops and put their lives in danger. Due to recurring floods, people didn’t have the means to improve their built environment. The 'Char' land is furthermore characterised by its lack of public infrastructure and remoteness to public services.
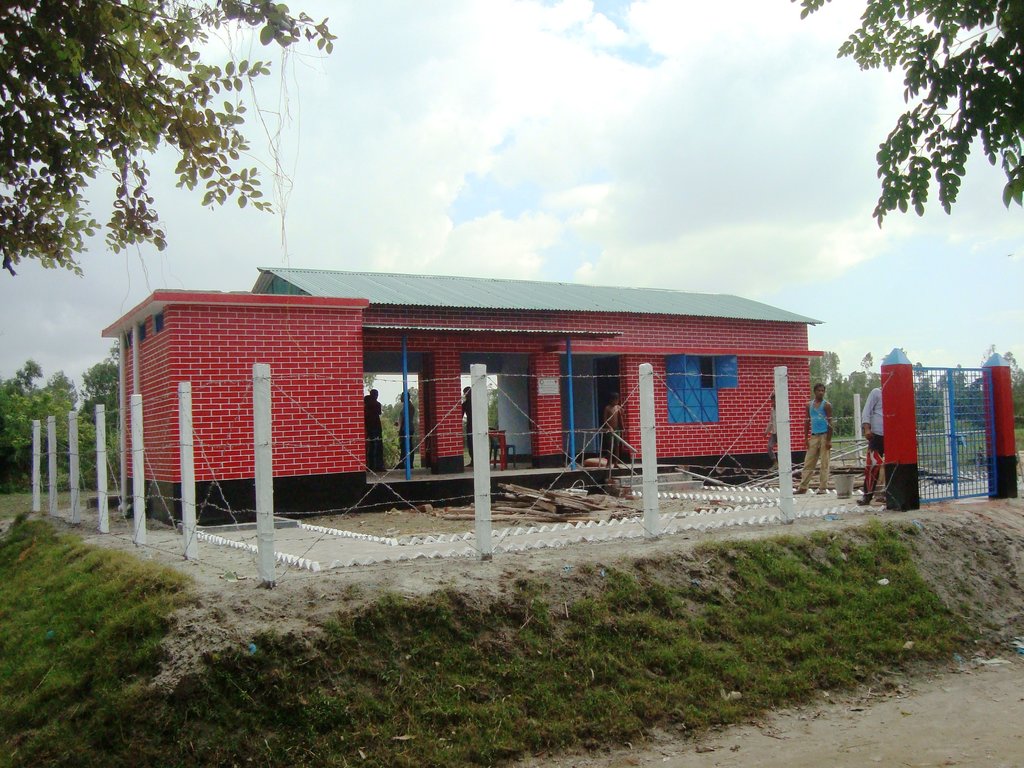
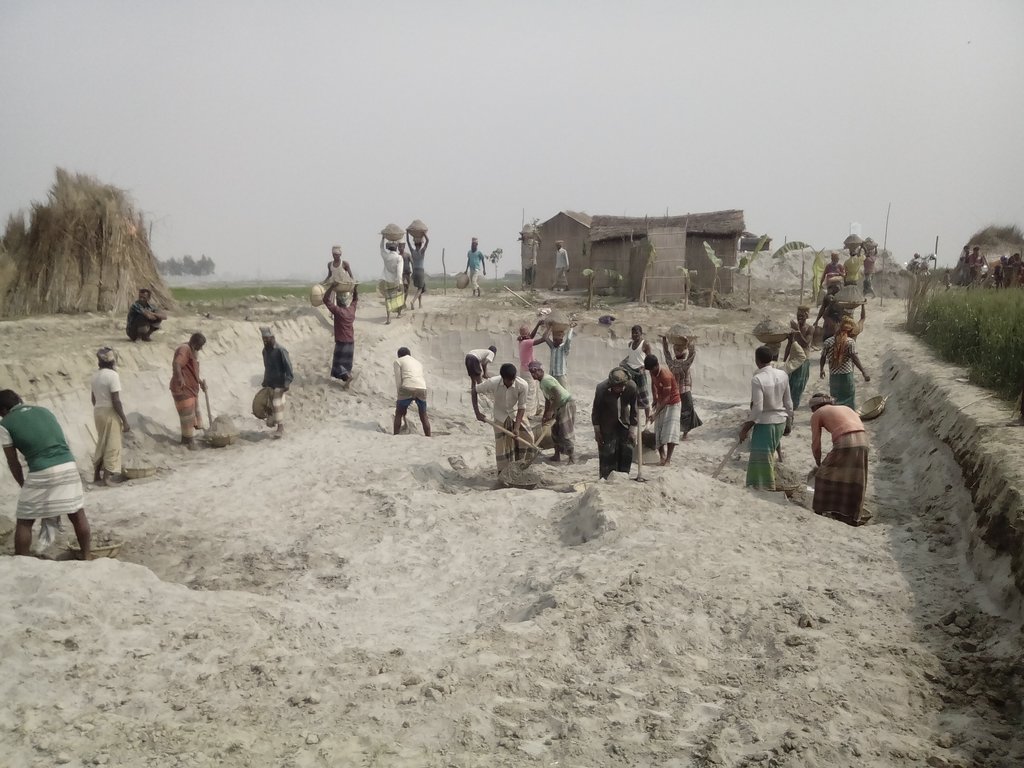
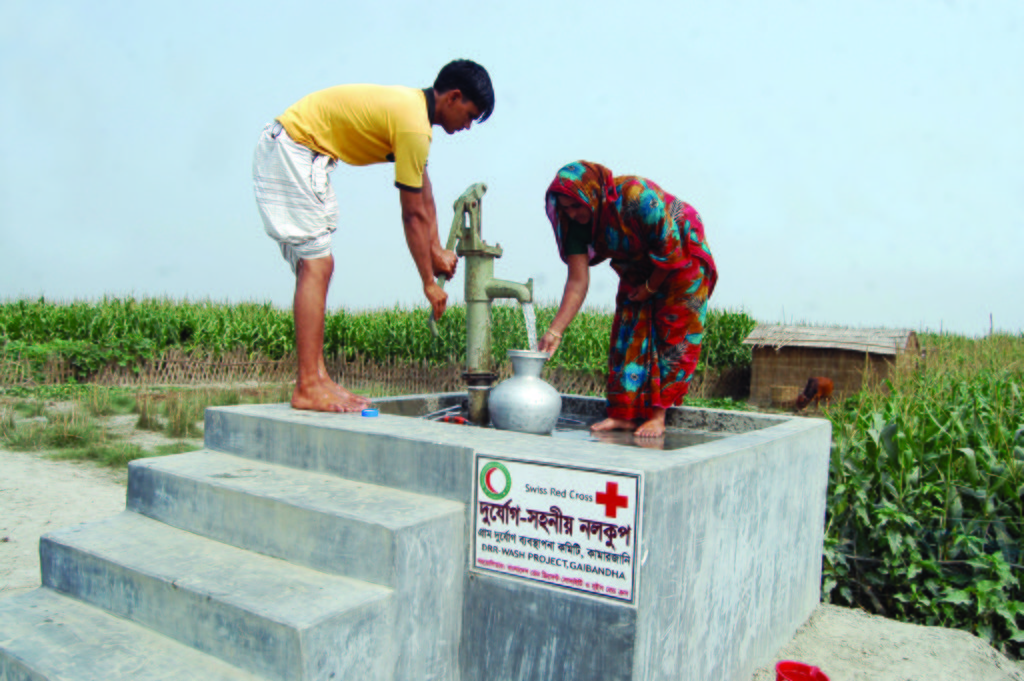
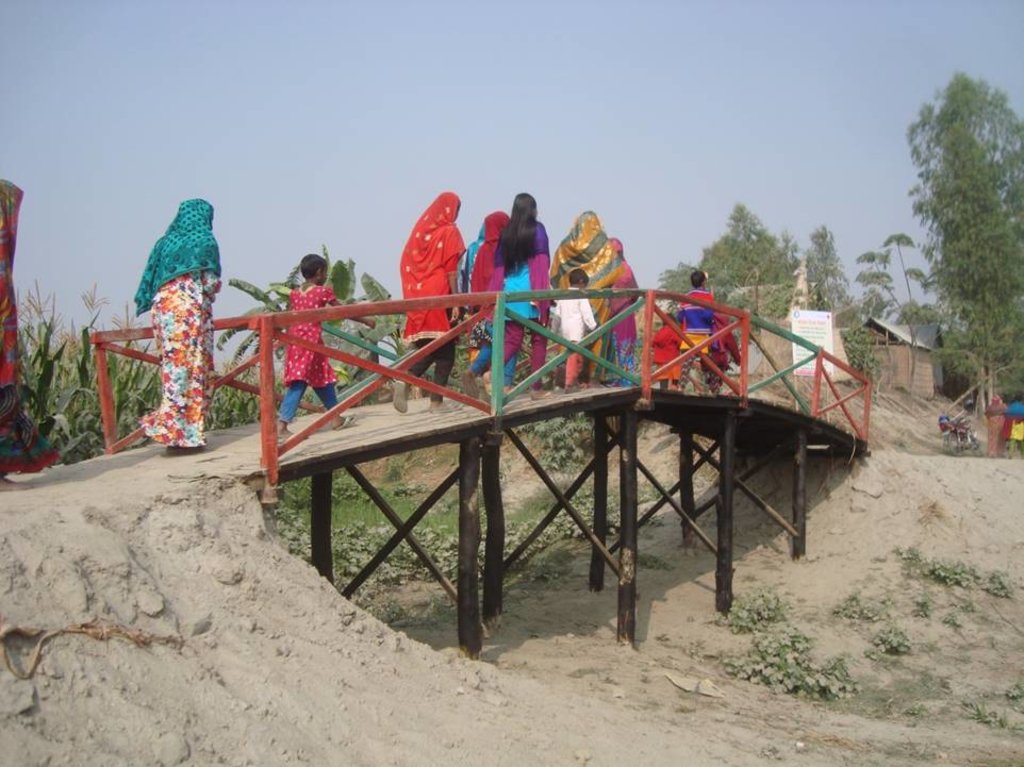
The technology consists of setting up an emergency infrastructure and ensuring community access to these infrastructures during times of floods. It has to be understood in close interrelation with the approach of setting up an early warning system. The emergency infrastructure includes specific flood shelters (for people and animals), flood-proof collective water sources and sanitation systems, transport infrastructure such as foot bridges and elevated rural roads, as well as flood-proof health and school facilities that also serve as emergency shelters during floods. The flood shelters are built on a raised bed of soil and located at sites selected by the communities that are relatively better protected from flood and river erosion within the 'Chars'. The purpose of the technology is to ensure safety of life and protection of assets during times of emergency and also to mitigate sufferings related to floods. The flood shelter is an elevated plane land which is on an average 220 square feet by size and at least five feet high from the existing ground level. The site is selected by the community and should be connected through an elevated road to the nearest community. This arrangement helps people to get easy access during times of floods. The shelter has collective hygienic latrine facilities and safe water sources. People generally dismantle their housing while evacuating and reinstall it on the flood shelter.
The major activities include facilitating the development of community-led risk reduction action plans and their implementation through community participation and engagement of local governance institutions. This includes maintenance of the built infrastructure as the joint responsibility of the community and the local government. Land use, especially sowing and harvesting, is increasingly linked to flood related forecasting measures which has led to significant adaptation in the timing of farming activities. This coupled with the creation and access to emergency infrastructure allows for a relatively safe and healthy living. The adopted technology and approach has led to adapted livelihoods, reduced health costs and increased income. The technology has furthermore led to mainstreaming disaster risk management in policies and approach of local government institutions. Increasingly the local government’s cash and food for work programmes are targeting establishment and/or reinforcement of emergency infrastructure that can cater to larger population. Increased investments are made especially towards flood shelters and improving communication and access to emergency infrastructure. Since the technology is based on local knowledge and has been developed in consultation with the involved communities, it is generally well accepted with a fair degree of ownership and involvement. However, parts of the region are also prone to river erosion and this has a destructive impact on built infrastructures. The technology does not assure any safeguard against this form of uncertain river action.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
Glimpse of few technologies that served as emergency infrastructure, shelter and access to health and water and sanitation facilities.
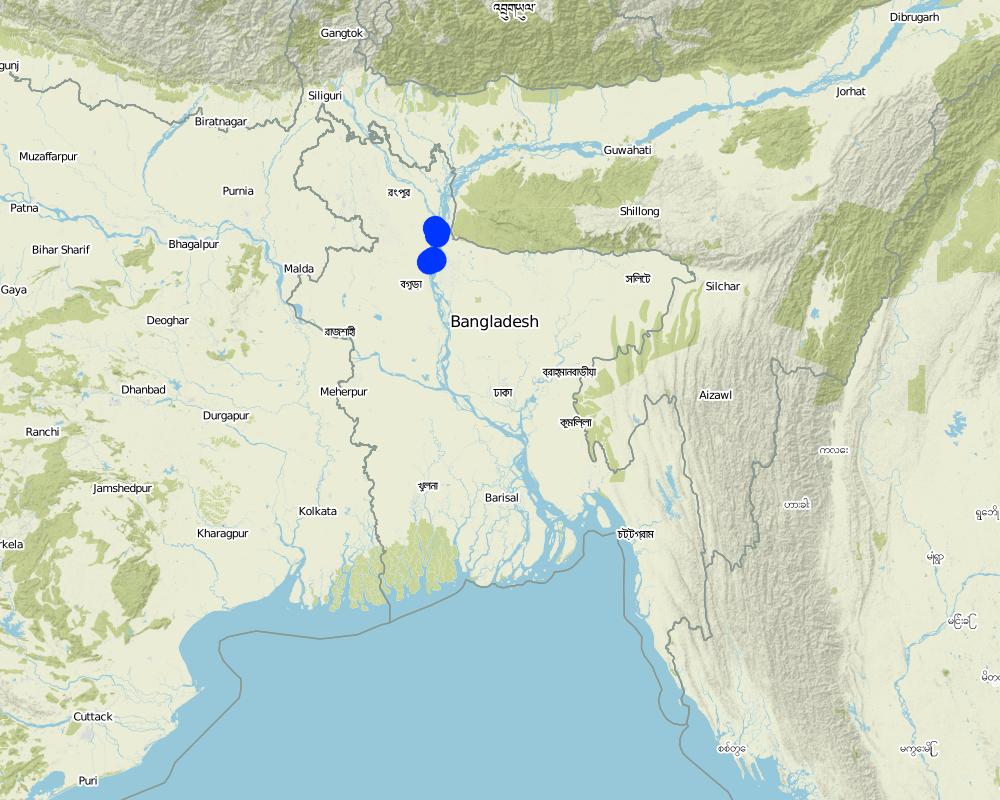
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Bangladesh
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
North-Bengal
Especifique más el lugar :
Kamarjani and Mollar Char Union (i.e. municipality) in Sadar Upazila and Haldia Union in Shaghata Upazila of Gaibandha District
Comentarios:
Since the disaster resilient infrastructure set up by the project is installed at a huge number of sites (as indicated in the description above), only a sample of the various emergency infrastructures are indicated on the map above (If needed a comprehensive GPS reading of all infrastructure built by the project can be provided separately).
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2014
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology has elements of traditional practice (raised plinths for flood protection) and project promoted interventions (emergency shelter and access infrastructure).
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Paddy, Wheat, maize, jute, chilli, pulse, sweet potato

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Asentamientos, edificios
- Tráfico: caminos, rieles
Comentarios:
Despite the lack of public infrastructure and services and being exposed to natural hazards people tend to prefer to live in the 'Char' as it brings significant economic benefits for them: crops grow rapidly and abundantly with significantly lower input costs than on the mainland.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
Water supply for the land comprises a mix of rainfed, irrigated and post flooding sources.
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 3
Especifique:
Kharif (monsoon crop), Rabi (winter crop), and Summer/pre-monsoon crop
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
Cow, buffalo, goat, lamb and donkey are very common in the area. People rear these for cultivation, transportation and for having meat. Every household have at least a pair or more of livestock.
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- Emergency infrastructure, shelter and linked transportation infrastructure
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 1-10 km2
Comentarios:
Though emergency infrastructures are built at specific sites, their use and benefits are evenly spread over an expanded area.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S9: Refugios para plantas y animales
- S11: Otros

medidas de manejo
- M4: Cambios significativos en la programación de las actividades
Comentarios:
In addition to the structural and management measures described above, the technology involves additional elements such as flood-proof collective water supply and sanitation systems and communication infrastructure.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wr: erosión de riberas
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio
Comentarios:
N/A
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
NA
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
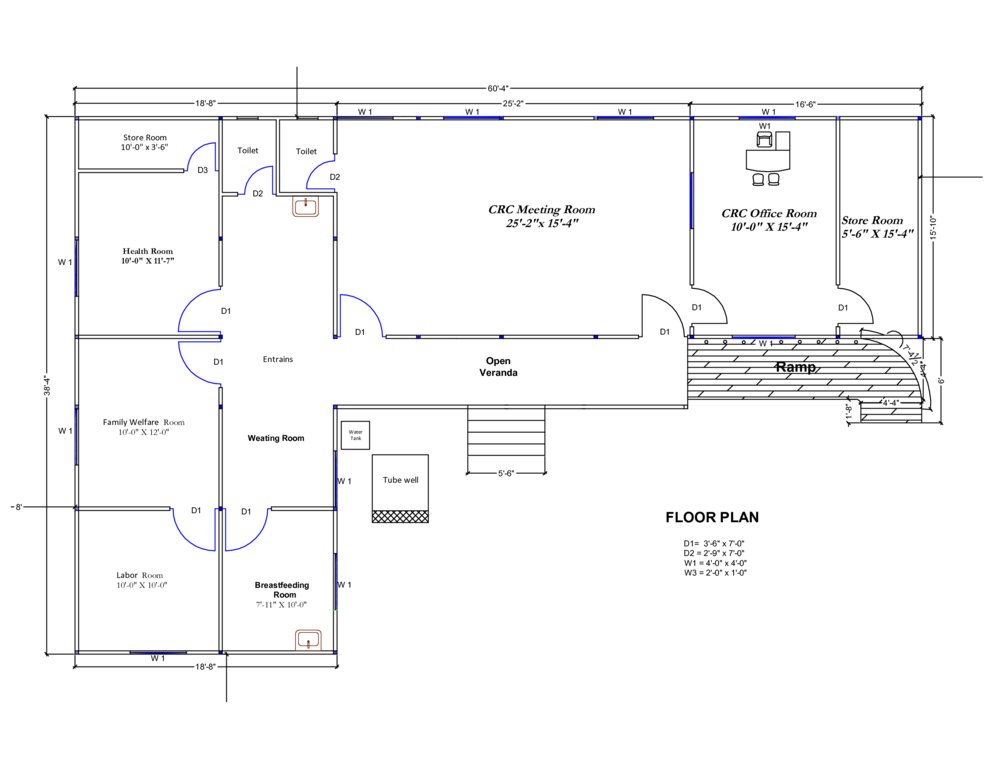
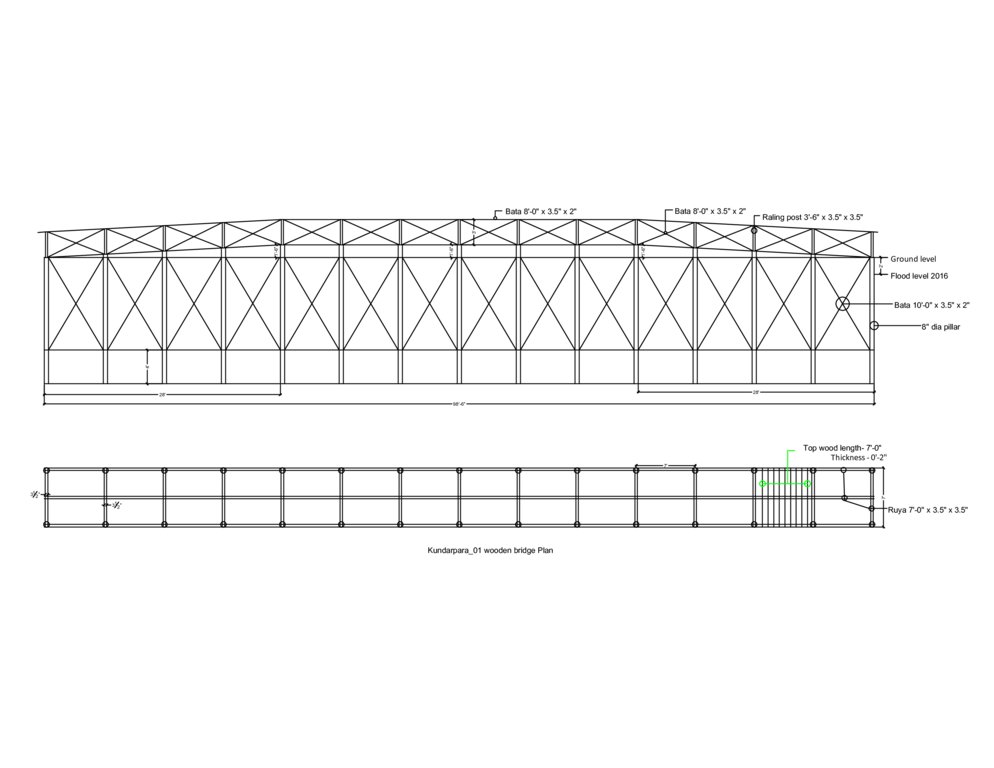
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The built structural mitigation options have following technical specification:
1. Flood shelter: Dimension: Length-220' x Width-220' x Height- 5.5', Slope: 1:1.5, Capacity: 350 families, Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass)
2. Raised school compound: Dimension: Length-112' x Width-75' x Height- 5.5', Slope: 1:1.5, Capacity: 540 person, Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass)
3. Community Resource Centre and Community Clinic (CRC-CC): Dimension: Length-60' x Width-38' x Height- 5.6', Slope: 1:1.5, Capacity: 1500 families from 5 villages, Construction material used: soil and grass plantation, bricks, sand, cement, rod, iron angel and CGI sheet.
4. Disaster resilient tube well: Dimension: Length-5' 10" x Width-5' x Height- 3', Boring: 100 feet, Capacity: 200 families, Construction material used: bricks, sand, cement, rod, tube well head, pvc pipe, cylinder, piston rod etc. Vertical intervals: 2 in each village.
5. Concrete platform for (existing) tube well: Dimension: Length-4' 10" x Width-4' x Height- 1', Capacity: 100 families, Construction material used: bricks, sand, cement, pvc pipe
6. Wooden bridge: Dimension: Length-99' x Width-7' x Height- 12', Slope: 1:1.5, Capacity: 900 families approximately, Construction material used: wood, nails, tar, soil and grass plantation
7. Road construction/repair: Dimension: Length-925' x Width-12' x Height- 3' (from existing level), Slope: 1:1.5, Capacity: 3 villages (approx:1000 families), Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass).
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
flood shelter, raised school compound, disaster resilient tube well, concrete platform for (existing) tube well, wooden bridge, road construction/repair
Especifique volumen, largo, etc. (si fuera relevante):
road: per meter
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Bangladeshi Taka (BDT)
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
79,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
350 BDT
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of Flood Shelter | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 2. | Raising school compound | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 3. | Construction of Community Resource Center (CRC) | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 4. | Installation of disaster resilient tube well | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 5. | Construction of concrete platform for (existing) tube well | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 6. | Construction of wooden bridge | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 7. | Road construction above flood level | Estructurales | During dry season |
Comentarios:
All activities are structural in nature and can be undertaken efficiently only in dry season.
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Flood shelter: earth work | m3 | 8000,0 | 64,0 | 512000,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | CRC: earth work | m3 | 53,0 | 138,0 | 7314,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | CRC: sand filling | m3 | 302,0 | 99,0 | 29898,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Raised school compound: earth work | m3 | 1790,0 | 64,0 | 114560,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Flood shelter: grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 4620,0 | 13,0 | 60060,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Flood shelter: seedlings | piece | 20,0 | 53,0 | 1060,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | CRC: grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 3890,0 | 13,0 | 50570,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | CRC: seedlings | piece | 50,0 | 53,0 | 2650,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Raised school compound: grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 1390,0 | 13,0 | 18070,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Raised school compound: seedlings | piece | 40,0 | 53,0 | 2120,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | CRC: roof truss | kg | 4375,0 | 100,0 | 437500,0 | |
| Material de construcción | CRC: grill and iron work | m2 | 88,0 | 2091,0 | 184008,0 | |
| Material de construcción | CRC: gypsum board | m2 | 478,0 | 922,0 | 440716,0 | |
| Material de construcción | CRC: RCC work | m3 | 2,9 | 19557,0 | 56715,3 | |
| Material de construcción | CRC: deformed bar | kg | 397,0 | 85,0 | 33745,0 | |
| Material de construcción | CRC: boundary fencing | m2 | 184,0 | 440,0 | 80960,0 | |
| Material de construcción | CRC: brick work | m3 | 44,0 | 5515,0 | 242660,0 | |
| Otros | CRC: electric ware and solar panel | lumpsum | 1,0 | 73000,0 | 73000,0 | |
| Otros | CRC: water supply | lumpusm | 1,0 | 66150,0 | 66150,0 | |
| Otros | CRC: transportation | lumpsum | 1,0 | 89000,0 | 89000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 2502756,3 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
10% of all construction cost (except community resource center) is borne by the user. Another 15% is provided by the local government bodies. The remaining 75% is subsidised by the project.
Comentarios:
Defining costs of establishment is bit tricky as the measures differ in size and number, costs vary from one village to another depending on the geographical location. However, average costs of the measures further to those highligted in the table are given below:
Disaster resilient tube well: labour (mason) 3'000, equipment (drilling charge) 1800, construction material (bricks, cement, sand, iron rod, PVC pipe, cylinder, GI pipe, tubewell head) 23'250, transportation 2'650, total unit costs (BDT) 30'700
Concrete platform for (existing) tube well : labour (mason) 600, construction material (bricks, cement, sand) 2'450, other (Transportation, waste water disposal) 1650, total unit costs (BDT) 4'700
Wooden bridge: labour (mason, mason assitant, painting assistant, earthwork) 30'000, plant material (grass plantation) 12'500, equipment (painting brush etc.) 1'000, construction material (timber, nails, tar, tarpin oil, paint) 260'000, Transportation 30'000, total unit costs (BDT) 333'500
Road construction/repair: labour (earthwork) 102'500, plant material (grass plantation/turfing), 12'500, total unit costs (BDT) 115'000
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of Flood Shelter | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 2. | Raising school compound | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 3. | Construction of Community Resource Center (CRC) | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 4. | Installation of disaster resilient tube well | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 5. | Construction of concrete platform ror (existing) tube well | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 6. | Construction of wooden bridge | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 7. | Road construction above flood level | Estructurales | During dry season |
Comentarios:
Due to the softness of the sandy soil and the annual inundation, every measure requires considerable maintenance. The flooding generally washes out sands and decays the foundation of the structure. If maintenance is done in regular intervals, the entire structure remains functional. Also, grass needs to be frequently replanted as it dries up during the dry season.
The users and the local government (Union Disaster Management Committee) are mainly responsible for maintenance of all built assets and structures including the Community Resource Center. The relevant operation/repair and maintenance training has been provided by the project.. Maintenance manuals and guidelines have been developed and disseminated. Also, repair and maintenance equipment has been provided to cadre of users/caretakers trained in repair/maintenance work.
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Earthwork | m3 | 80,0 | 63,0 | 5040,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Sand bag filling | piece | 50,0 | 15,0 | 750,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Pipe fitting | piece | 2,0 | 300,0 | 600,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Mason | lumpsum | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 85,0 | 13,0 | 1105,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings | piece | 15,0 | 53,0 | 795,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Plastic bag | piece | 50,0 | 10,0 | 500,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | PVC pipe | m | 15,0 | 120,0 | 1800,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Polythene pipe | kg | 5,0 | 160,0 | 800,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Ciment | bag | 0,5 | 540,0 | 270,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Sand | ft3 | 5,0 | 18,0 | 90,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Caping socket | piece | 2,0 | 35,0 | 70,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Tape etc. | lumpsum | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | 10,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 12570,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Maintenance costs are to date (2017) distributed as construction (10% by the users, 15% by the local government). A cost transfer scheme to the users and local government for maintenance is developped to be applied in the follow-up phase.
Comentarios:
Again, defining costs of maintenance is also not easy as the measures differ in size and number. Average costs of the measures, further to those for flood shelter including disaster resilient tube well as highligted in the table, are given below:
Raised school compound: labour (earth work and sand bag filling) 7'800, plant material (grass plantation) 1'000, construction material (plastic bag, rope) 500, total unit maintenance costs (BDT) 9'300
Community resource Center (CRC): labour 1'200, plant material (grass plantation, seedlings) 10'500, Transportation 1'000, total unit maintenance costs (BDT) 12'700
Concrete platform for (existing) tube well : labour (mason) 500, construction material (bricks, cement, sand) 600, total unit maintenance costs (BDT) 1'100
Wooden bridge: labour (earthwork) 2'500, plant material (grass plantation) 3'000, construction material (plastic bag, rope) 2'000, total unit maintenance costs (BDT) 7'500
Road construction/repair: labour (earthwork) 10'000, plant material (grass plantation/turfing), 1'500, construction material (plastic bag, rope) 500, total unit maintenance costs (BDT) 12'000
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Transportation of raw material from the mainland to the sites on the 'Char' Islands varies across seasons. In the dry season it is much higher compared to monsoon as the delivery of material is easier in the latter due to extended river outreach.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
2134,80
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Rainy season: April- October
Occurrence of heavy rain: June-July
Length of dry period: November-March
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
18 Gaibandha Sadar, Gaibandha
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
Tropical humid climatic zone.
Temperature: maximum 33.5°C, minimum 10.5°C
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Information on altitudinal zone collected from the website: www.getamap.net
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
N/A
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
In the dry season water crisis occurs. Open defecation and use of pesticide in farming are key pollutants of water sources.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Biodiversity can be rated as moderate or medium both in terms of species and habitat. It is stable and and often self generating.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- tracción animal
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
N/A
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
People living in Chars have small landholding which often produces enough for subsistence and, in some cases, for market purposes.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Comentarios:
Land ownership is quite complex as Chars by nature are unstable habitats. In principle land is owned by state but in most cases the politician - musclemen nexus exercises real control. This results in leasing and renting of land which is the predominant form of land ownership in Chars.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Access to mobile phone and internet:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
3600 kg/hectare (maize)
Cantidad luego de MST:
11400 kg/hectare (maize)
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop production has increased thrice due to stability of household which has led to stable use of land in the chars.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
No safe drinking water source was available
Cantidad luego de MST:
More than 40% water source are safe
Comentarios/ especifique:
Collective water supply systems have groundwater sources and thus no treatment is needed. Further, aspects of availability, easy access and sustainable availability of sufficient water of acceptable quality are well considered. Families can access 10 litres per capita per day (LPCD) during emergencies (which is in line with Sphere standards) and during normal times 40 LPCD is what families can collect from these water sources. All such water sources are within a distance of 50 metres from the settlement as per Bangladesh standards.
calidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
Reliable data not available
Cantidad luego de MST:
All households have access to safe drinking water as per govt. standard for rural areas
Comentarios/ especifique:
The collective water infrastructure built by the project ensures fulfillment of minimum standards set by the govt for safe drinking water.
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
25% families had farm income
Cantidad luego de MST:
95% families have farm income
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cattle and poultries are safe during disaster
Impactos socioculturales
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
The disaster mitigation measures has significantly improved the health situation of the target population.
instituciones comunitarias
Cantidad antes de MST:
Few credit groups in intervention villages
Cantidad luego de MST:
30 community based organisatons (i.e. village disaster management committees) and 3 Local Government Committees (Union disaster management committee)
Comentarios/ especifique:
Community based organisations and government mandated institutions have been promoted through project initiatives.
instituciones nacionales
Comentarios/ especifique:
CRC is also being used for UDMC office which is an important committee of union parishad.
mitigación de conflicto
Cantidad antes de MST:
Widespread
Cantidad luego de MST:
Rare
Comentarios/ especifique:
Conflict sensitive approach has significantly reduced the incidence of conflicts.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
Data not available
Cantidad luego de MST:
Same
Comentarios/ especifique:
The disaster resilient tube well ensures year round drinking water.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Cantidad antes de MST:
95% families were effected from flood
Cantidad luego de MST:
47% families are affected from flood
Comentarios/ especifique:
The above figures are from 2016 when Bangladesh experienced one of the worst floods in recent times.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
Comentarios acerca de la evaluación del impacto:
N/A
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | moderadamente |
| tormenta de arena/ de polvo local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de calor | bien |
| ola de frío | bien |
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
| deslizamiento | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
In some cases the appropriate answer would have been "not applicable" but since this is not there, we have selected "well".
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Comentarios:
The limited returns that have been generated by the project is highly valued by the users from a cost - benefit perspective; especially when they understand that the project is not directly linked to land management practices. Thus, the indirect benefits are perceived to have high value.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Out of a total of 8828 HHs targeted by the project, around five thousand HHs in three union have benefitted from the implementation of the technology.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Si fuera así, indique a qué condiciones cambiantes se adaptó:
- disponibilidad de mano de obra (ej. debido a migración)
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Dredging machine has been used for building some emergency infrastructure at few sites due to unavailability of labour at the time of construction.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Emergency structures are collectively owned and have a multipurpose use; in 'normal' (non-emergency) times they are used for other purpose than safety and protection which includes community meeting, workshop and training |
| Expanded opportunities of communication during flood |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Community is aware and driven to implement flood preparedness and risk reduction measures on its own |
| Appropriate measures can significantly change people's mindset and behaviour |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
|
River erosion threatens built structures |
Careful site selection for construction work through in depth discussion with community people supported by scientific analysis |
| High investment needed for building physical structures (e.g. CRC building) in the char which the local government and community find difficult to finance without external support. | Install portable semi-permanent structures in the char; Lobby for greater decentralisation of finances to local government |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
3
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
4
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
2
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Latrine and Tube well maintenance manual, SRC-BDRCS-DASCOH
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
SRC
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Early Warning Message Dissemination [Bangladesh]
An effective system for dissemination of early warning messages was established among the vulnerable communities in Chars (riverine sandy islands) of Gaibandha district, Bangladesh, in order to strengthen their coping mechanisms and reduce loss and damage caused by floods.
- Compilador: TUHIN SAMADDAR
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos