Auto-Flowing Slurry Dam [China]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Yan ZHANG
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Falling Water Dam
technologies_1364 - China
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - China1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Falling Water Dam [China]
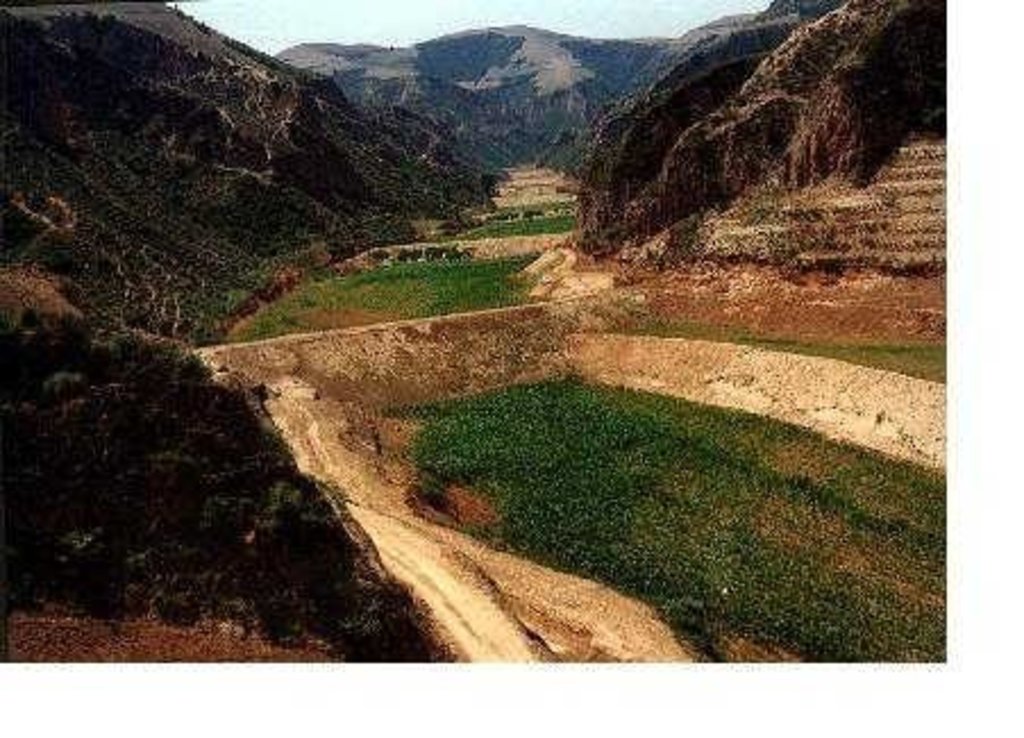
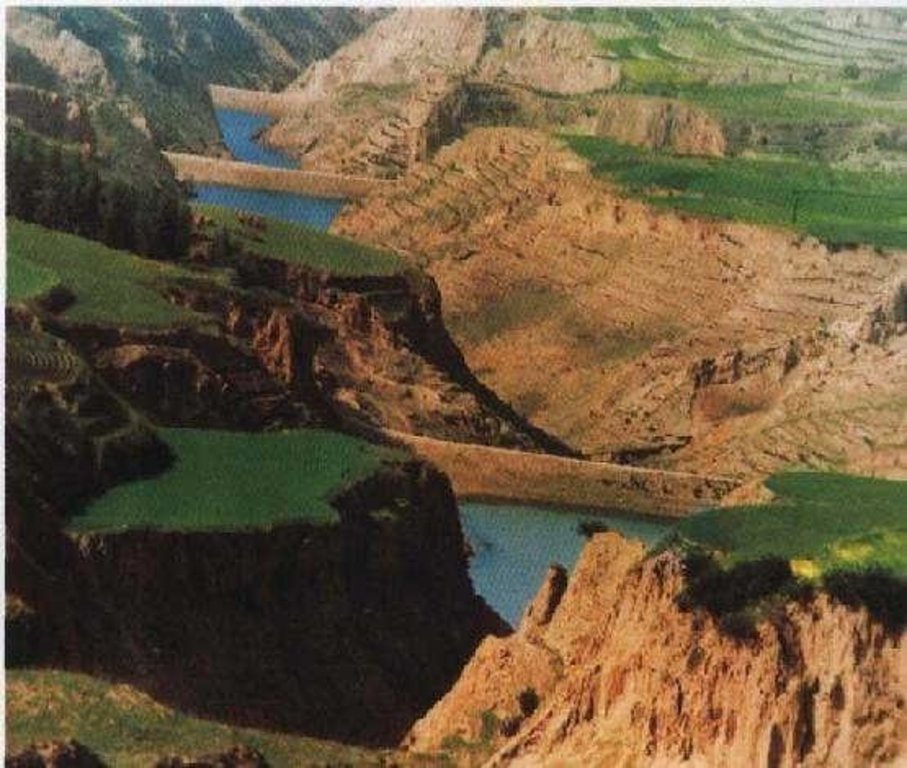
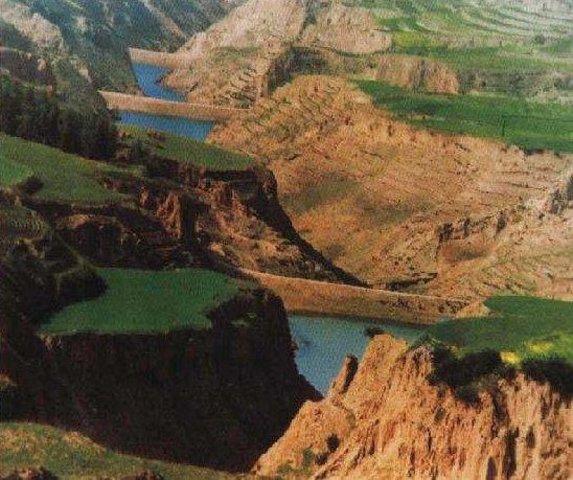
The falling water dams are widely built in the middle reach of the Yellow River, the typical dams are filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland. The approach is implemented mainly by government investment.
- Compilador: Yan ZHANG
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Auto-flowing slurry dams is filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland to maintain eroded soil particles and runoff.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Falling water filled dams distribute widely in the middle reaches of the Yellow River, they are used to store water and wrap sediment which result from soil and water loss. On the Loess Plateau, in addition to the conditions of deep gully and steep slope, earth above the top of the dams can be used to build dams. First, soil is loosed with squirt guns, exploded or manually dug. Then, water is pumped up to the loose earth so as to rush the soil down along transporting ditch, turning the soil into dense mud to dam level surrounded by tamped banks. Under the press of gravity, the mud dehydrates, consolidates and becomes uniformly dense body of the dams. Compared with dams in other areas, the water power filled dams in the Yellow River basin are characterized by much denser mud, uniform particles and body texture, smaller transect of dams body, and wide applicability to soil materials such as sand soil, loess soil and weathering residue. The types of dams have widely applied to build moderate and small reservoirs and silt arresters in the middle reaches of the Yellow River, they play an important role in increase in agricultural production and reduction of sediment into the Yellow River.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
China
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Shanxi, Shaanxi, etc.
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la Tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente a lo largo de un área, especifique el área que cubre (en km2):
13062,0
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- > 10,000 km2
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 13062 km2.
Dams filled by water power are applied mainly in the middle reach of the Yellow River, including the provinces of Shanxi, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Gansu, Qinghai, Henan, etc. The types of dams were used since 1950s, and most the dams being used were built in 1970s.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was developed by local people during the conservation practice in 1950s.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 165Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Estanques, diques
Principales productos/ servicios:
Auto-Flowing Slurry Dam
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Slope land is used as cropland
2. Too little ground cover to protect soil from erosion
3. Over grazing in wind erosion area
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Little cropland for food supply
2. The land productivity is too low
3. The benefit of returning cropland to graze land or woodland is not definite now except the compensate from government
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (Lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- no aplica
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility, improvement of soil structure
Construction material (earth): Loess earth
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 30%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 60%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
3.00
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | preparing earth | n/a |
| 2. | pumping water | n/a |
| 3. | preparing base of the dam and its perimetric banks | n/a |
| 4. | Flushing the prepared earth with water inside the banks of the dam | 0.1~1 |
| 5. | After dehydration and consolidation of the earth, repeat 3 and 4. | n/a |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 540 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Keeping the top of the dam level and free of crevice, water or rubbish | timely |
| 2. | Keeping the top of the dam level and free of crevice, water or rubbish | |
| 3. | Keeping the slope of the dam compact and free of rill or weed. | timely |
| 4. | Keeping the slope of the dam compact and free of rill or weed. | |
| 5. | Keeping the observation equipment work in order. | timely |
| 6. | Keeping the observation equipment work in order. | |
| 7. | Preventing the base the dam from destroying by white ants and other animals. | April to October/once a year |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
The volume of structure.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Since the dam construction uses local materials, the most important factors affecting the cost are labor and equipment
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
- árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landform: Also plateau/plain
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium - good
Soil water storage capacity: high - very high
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
- rico
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, poor
There are almost no people very rich in the area.
Rich people are as same as average people.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (Average people in the area where the SWC is applied should offer labor for the construction.).
Poor people can offer labor for the construction.
Very poor people are relatively rare and they are often in poor health.
Off-farm income specification: Most young male farmers often go to the city or town to earn money
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- comunitarios (organizado)
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Cantidad antes de MST:
43
Cantidad luego de MST:
35
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
80
Cantidad luego de MST:
21
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
80'000 households (3 percent of the area)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
Comentarios:
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
50000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30000 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Although the local people adopt the SWC Technology willingly, it is usually invested, designed and constructed by the land owner, the local government.
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Special Planning Of Soil And Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region , Shanxi Province. 1986-1990.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department, Beijing Normal University.
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing. 2000.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department, Beijing Normal University.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Falling Water Dam [China]
The falling water dams are widely built in the middle reach of the Yellow River, the typical dams are filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland. The approach is implemented mainly by government investment.
- Compilador: Yan ZHANG
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos