Retention ponds [Eslovenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Gregor Kramberger
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mokri zadrževalniki vode
technologies_5933 - Eslovenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Istenič Darja
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
Especialista MST:
Škerjanec Mateja
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
Especialista MST:
Banovec Primož
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
Especialista MST:
Curk Miha
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
Especialista MST:
Cvejić Rozalija
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
usuario de la tierra:
Purgaj Donik Biserka
Fruit center Maribor (demonstrartion plantation centre), Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
Eslovenia
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - EsloveniaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
University of Ljubljana (UL) - Eslovenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
With improper implementation and intended use, it can have a negative effect on sustainability in the environment. It can be sustainable if properly anticipated/planned. The construction of the pond is usually subject to an environmental impact assessment where these matters are resolved as to whether it is sustainable or not.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Retention ponds (e.g. flood storage reservoirs, shallow impoundments) are water bodies, storing water to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. They provide storage as well as improving water quality. Retention ponds may also be used for irrigation of farmland.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
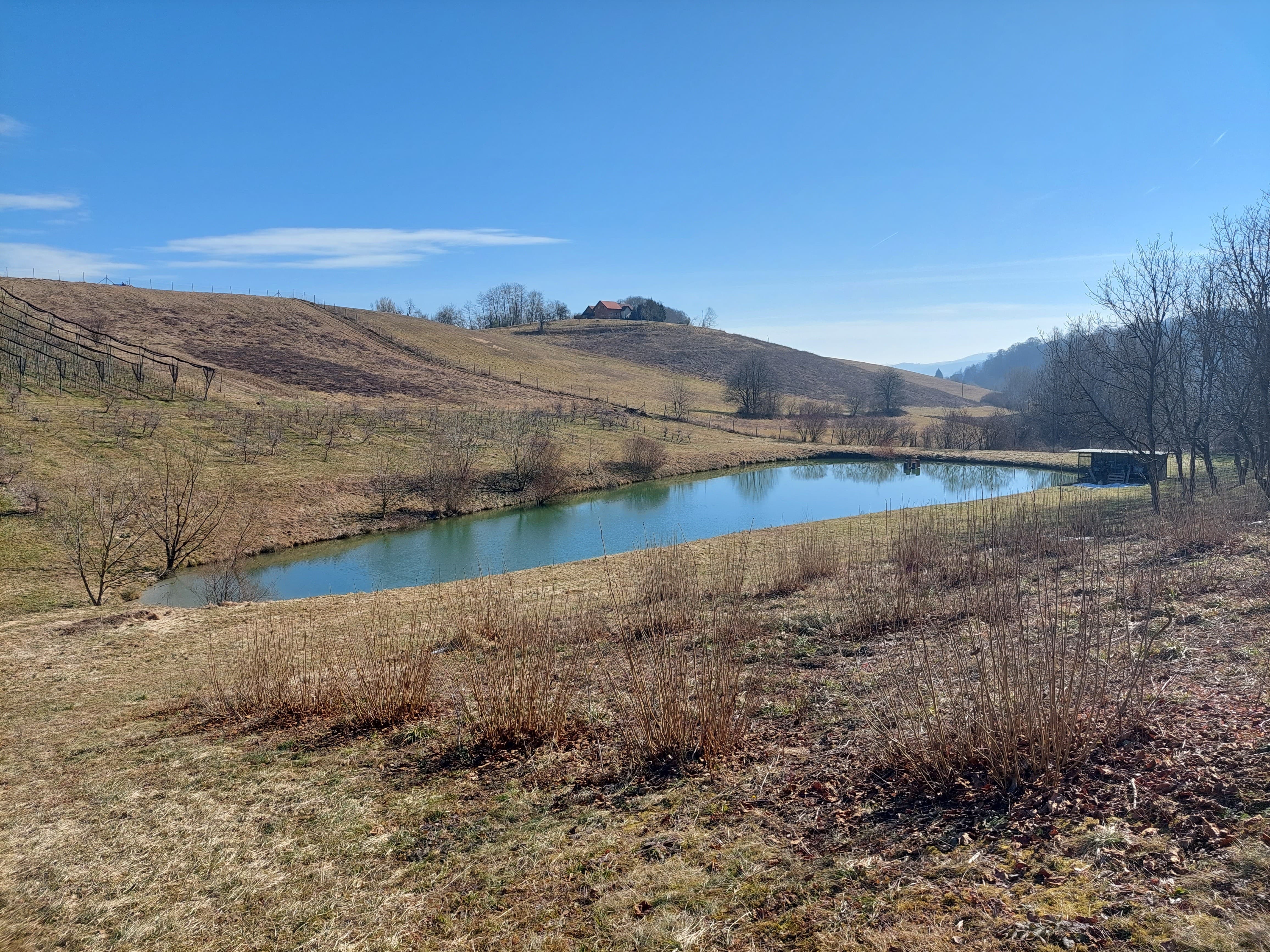
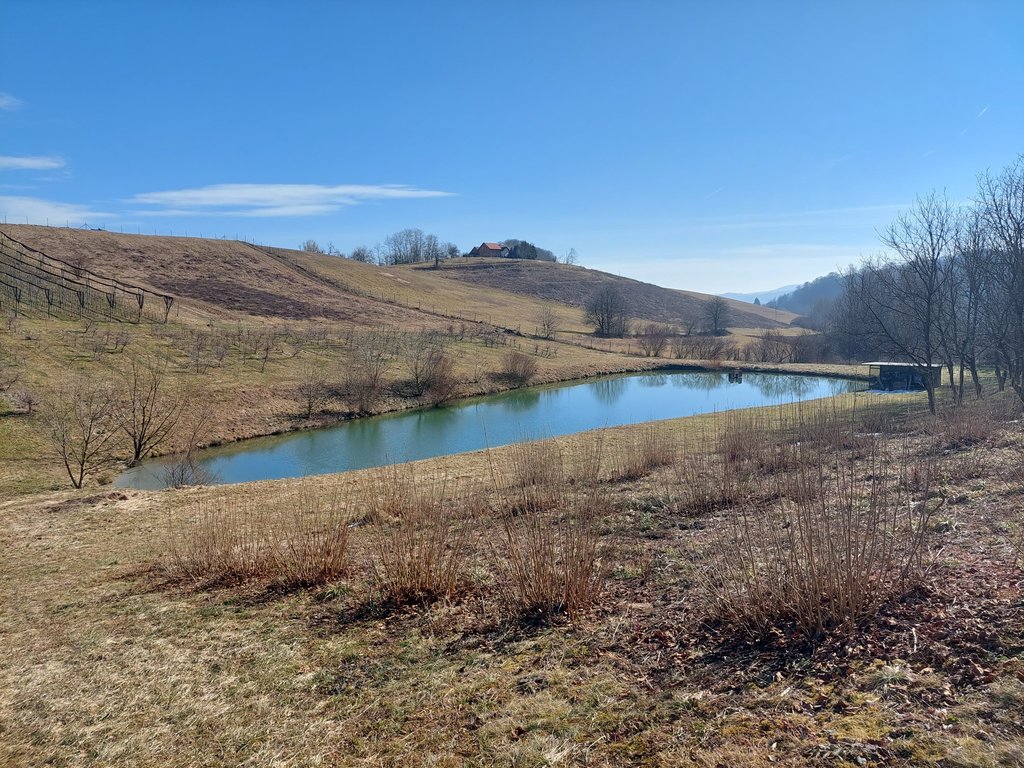
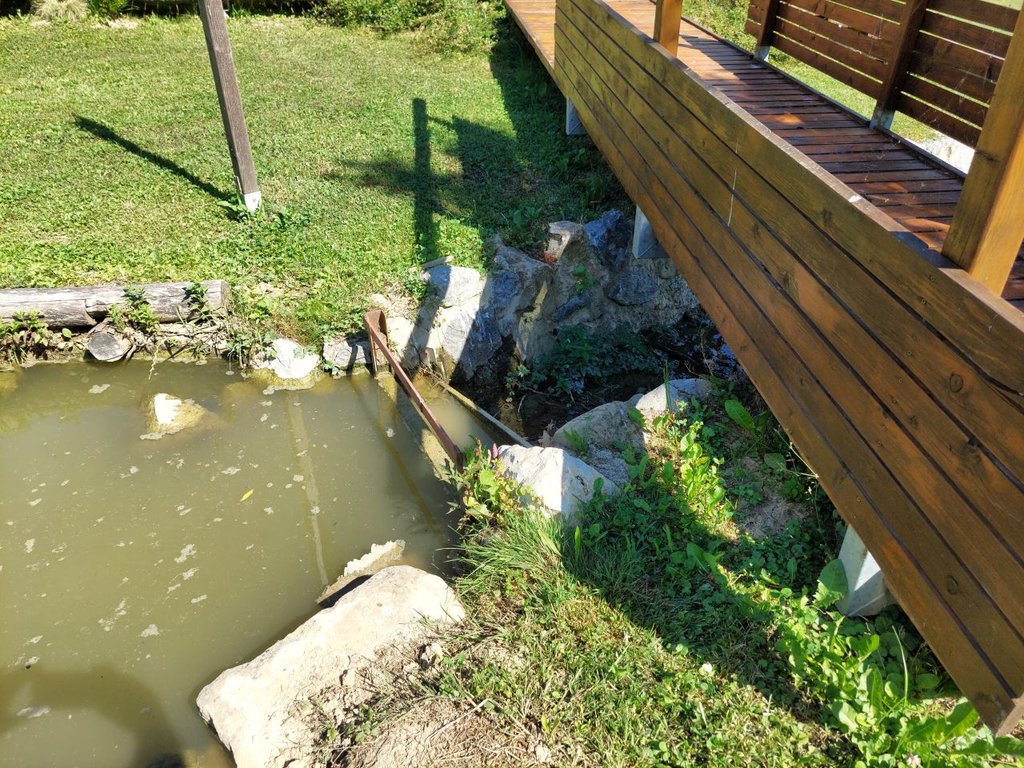
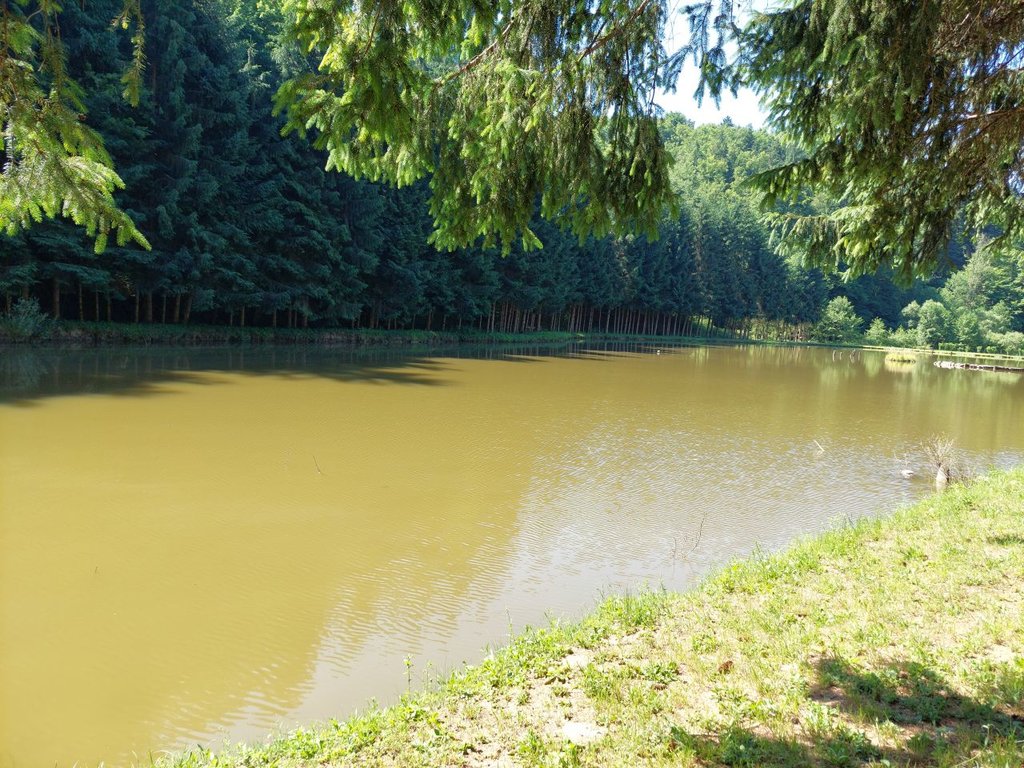
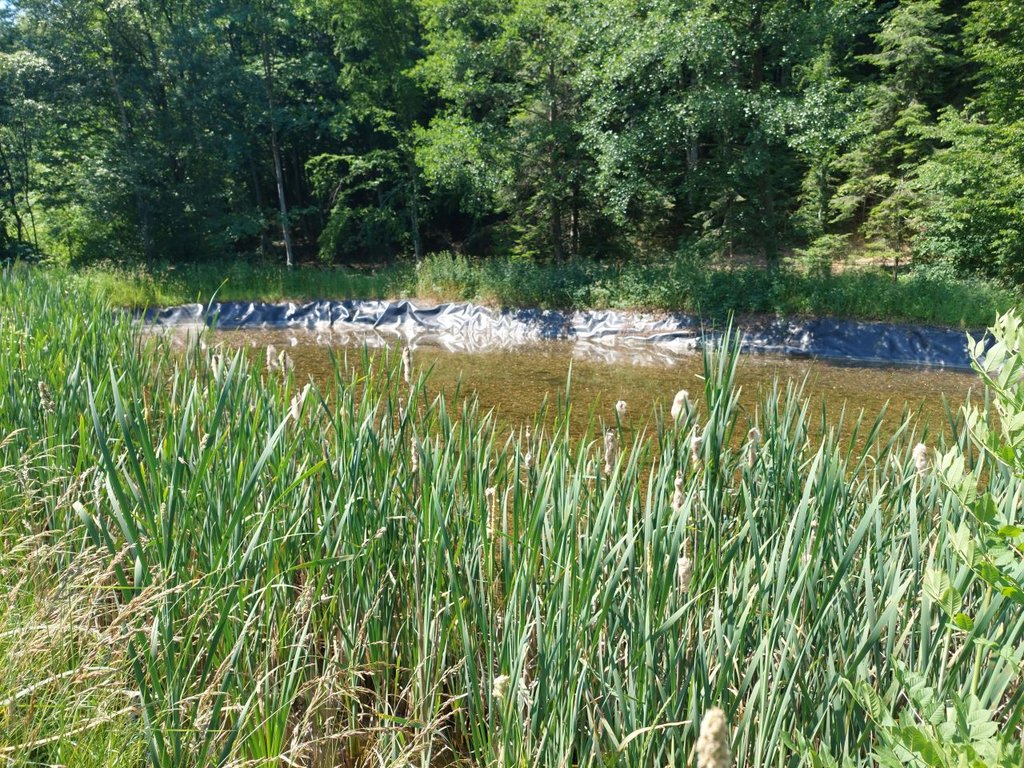
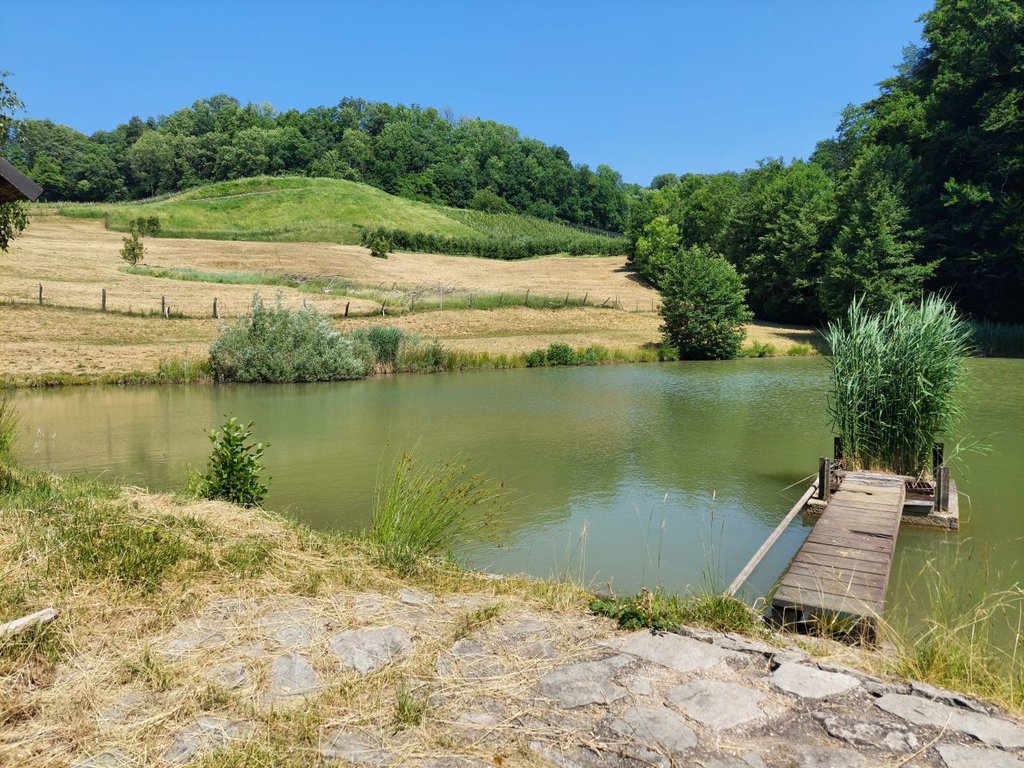
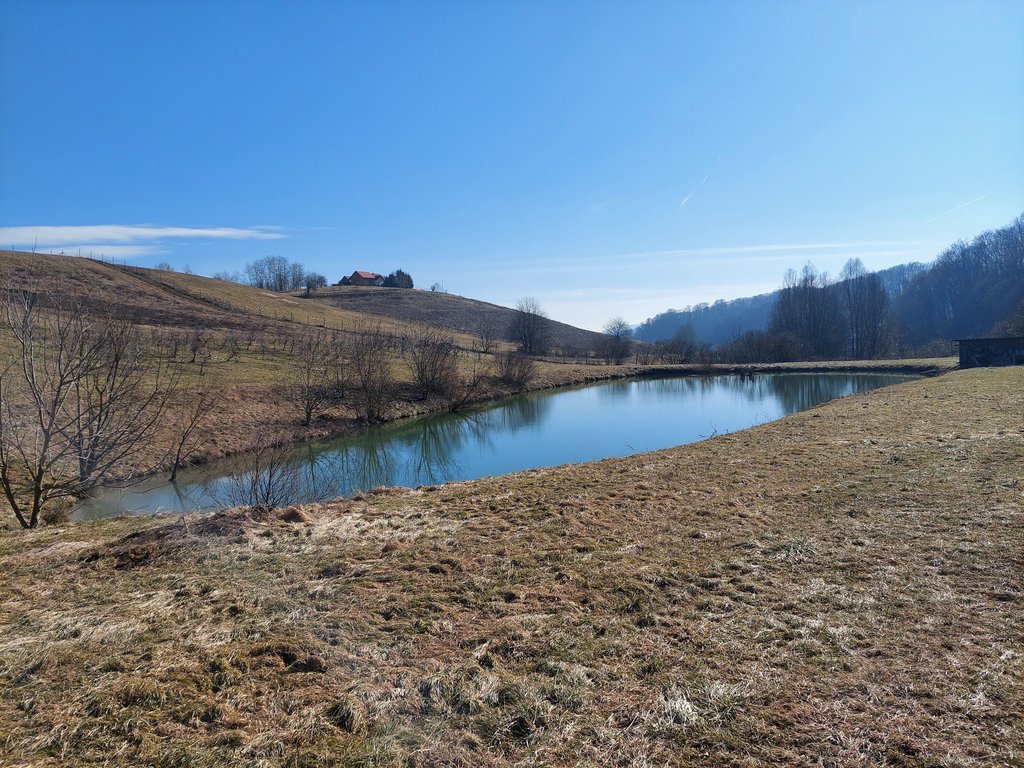
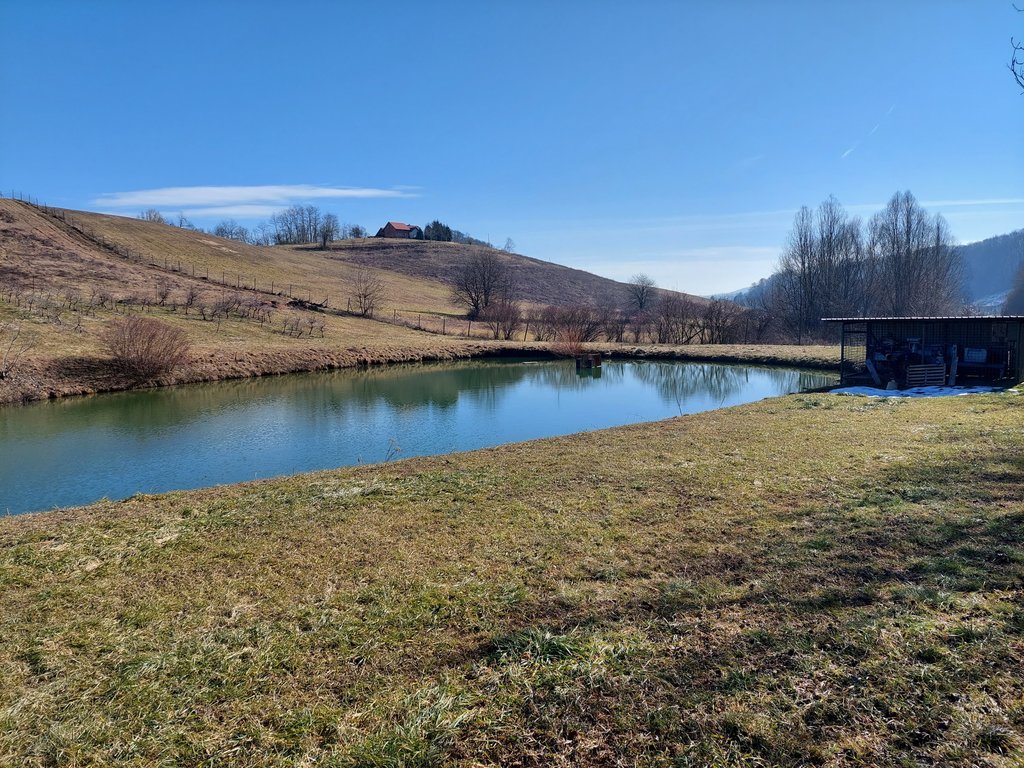
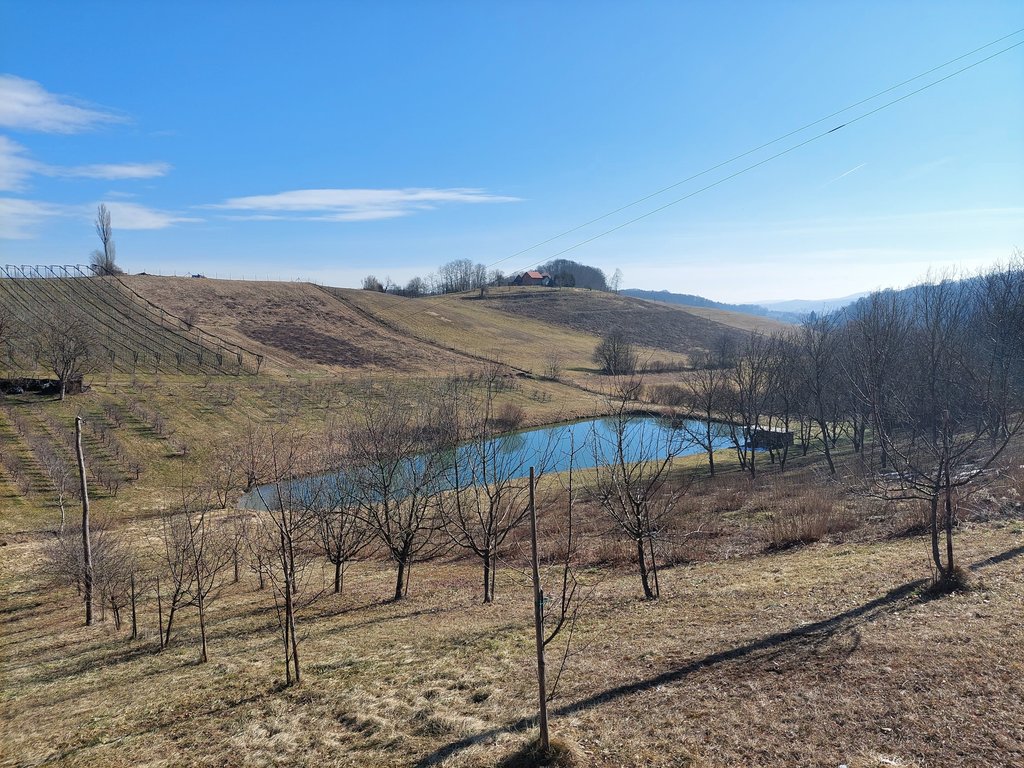
“Retention ponds” comprise both simple, small ponds (up to 2000 m3, up to 4 m deep) and larger, more complex reservoirs (greater than 2000 m3). Retention ponds are designed to provide storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. Each consists of a permanent ponded area with landscaped banks. Retention ponds achieve both storm water attenuation and water quality treatment through supplementary storage capacity of runoff. Water is then released at a controlled rate once the risk of flooding has passed. The technology can be applied in a natural or human environment. Before construction of a pond it is essential to follow legislation, which covers conditions and restrictions for the given location. Once a site is selected, technical documentation is prepared: first the conceptual design, then documentation for obtaining opinion, consent and a building permit. Later there is also project documentation for implementation. If the water is to be used for other purposes as well (e.g. for irrigation), it is necessary to plan for usage and environmental impact. Retention and still water promotes pollutant removal through sedimentation, while aquatic vegetation and biological uptake mechanisms offer additional treatment. Retention ponds are effective in removing urban pollutants and improving water quality.
They are created either by using an existing natural depression, or by excavating a new depression, or by constructing embankments. Existing natural water bodies should not be used however, due to the risk that pollution events and poorer water quality might disturb/damage the natural ecology of the system. A great benefit of retention ponds is that they hold water when there is an excess of it, which can be used later when water is not available (e.g. for irrigation). Irrigation users are farmers, so they see the advantage of using a retention system. In addition to irrigation, water has also been needed in recent years for anti-frost systems (sprinkling a consistent layer of water on the crop during an entire frost event until temperatures are back to safe levels). Disadvantages are mainly restrictions in some areas (e.g. protected areas), preparation of demanding documentation and bureaucracy, and lengthy procedures for obtaining permits.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Eslovenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Podravska region, Slovenia
Especifique más el lugar :
Pesnica
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
Setting up a measure in a protected area is limited and very difficult due to construction restrictions in such an environment.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
In the 1990s, the state financed the construction of several water reservoirs in the area.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Estanques, diques
Principales productos/ servicios:
Retention of water, collection of water. Retention ponds are ponds or basins designed with additional storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. In dry years, the water can be used for agriculture, e.g. for irrigation.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Líneas de drenaje, vías fluviales
- Pantanos, humedales
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cosecha de agua
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
- manejo de agua superficial (manantial, río, lagos, mar):
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de aguas subterráneas
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación del suelo
Comentarios:
To prevent erosion.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
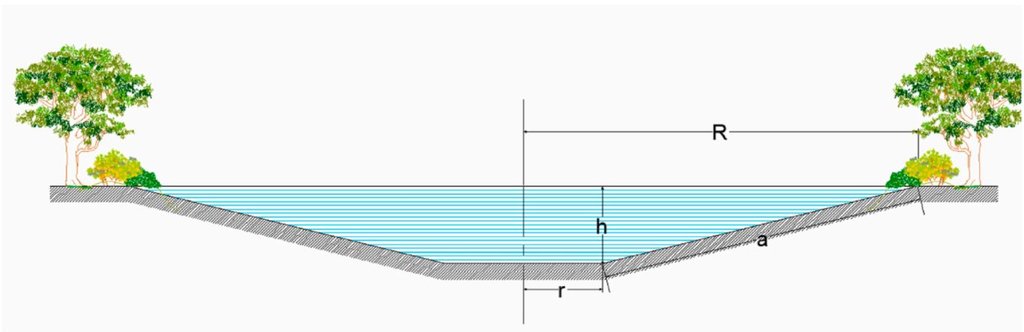
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Water retention pond – excavation scheme. R is the top radius of pond, while r is the base radius; h is the height and a refers to the bank slope. Storage volume is estimated by radius r and height h (Figure). We consider potential storage volumes of 5,000 m3 to 10,000 m3.
Prior to start of construction, detention/retention ponds should be designed by a registered design professional. Plans and specifications should be referred to by field personnel throughout the construction process. When placing a detention/retention pond in a space in the first phase it is necessary to produce a conceptual design of the intended construction of a pond, which must show the purpose and goals of the retaining wall, the size of the pond, the location, a list of plots that are encroached upon, distances from neighboring land and neighboring buildings, anticipated activities in the impoundment area, impoundment volume, barrier size data, including stability assessment, and geotechnical data (Hočuršćak 2017). When planning construction of the pond, attention should be paid primarily to the impact on the actual use of space from the point of view of water management regulations, which defines the area of use and activity restrictions, due to the possible negative impact on water and coastal lands, aquatic habitats and the ecosystem created by the construction of the reservoir. After talking with the designer, in order to obtain a water permit and consent from the authorities, it is necessary to prepare technical documentation for the installation and construction, which must also include the basis for monitoring operation and maintenance (Hočuršćak 2017). The technical documentation (dimensioning of the reservoir) may differ from the microlocation and purpose or use of the measure, e.g. if pool is intended only to contain high water, sediment or debris laoding, will it be inhabited by aquatic animals, will water be used for irrigation, drinking, etc. We also consider the shape and size of the area to identify those better suited for allocating ponds also in terms of space availability. For example, it is necessary to exclude locations with a greater slope and distance from the river considering higher slope and distance is more difficult and costly to construct. We also exclude locations where the construction of a pond is not possible because they are too narrow or too small. We should consider water retention ponds as elements of a green infrastructure network together with other natural elements (e.g. vegetated riparian zones) and protected areas (e.g. Natura, 2000 sites) with a pond design that embeds features that enhance their ecological functionality. These include mild-sloped sides with vegetated buffers along the shorelines and vegetated floating islands that facilitate the nesting of birds. We refer to excavated ponds, with no weirs or dams, since inline ponds are more costly and may have negative ecological impacts (A. Staccione et al. 2021).
Presentation of the water reservoir at the Sadjarski Center Maribor (translated: Fruit Growing Center Maribor):
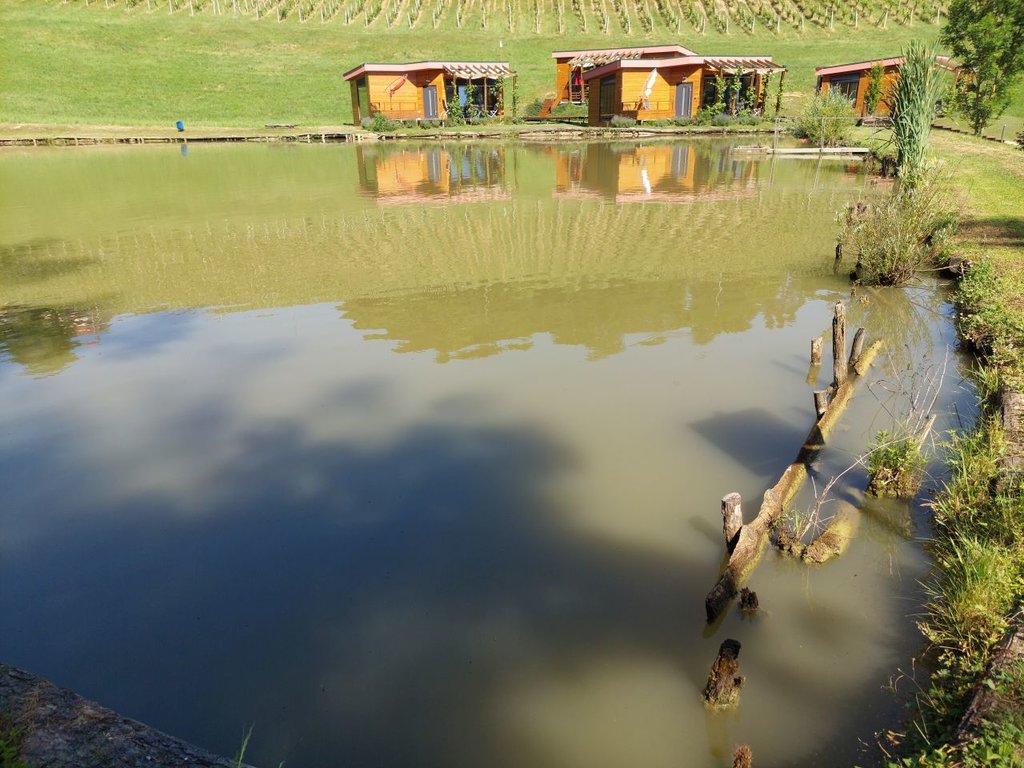
The Sadjarski Center Maribor is located on a sloping terrain, which is pedologically and configuratively quite diverse, with slopes ranging from 5-15%. The soil structure is clayey loam with a basaltic substrate. In the lower, flatter part, the soil was waterlogged, which was resolved through drainage systems. These drains are directed towards a drainage ditch, which serves as the foundation for the pond and is fed by two smaller springs. The intake point is located at the lowest point and at the southernmost part of the complex. It covers an area of 3000 m2 and has a depth of up to 3.8 m. Its capacity is 5500 m3 of water when fully filled. At its southern part, there is a concrete overflow structure (spillway) with a height of 3.8 m, which is used to drain excess water and regulate the water level. A concrete pipe, 20 m in length and 80 cm in diameter, is connected to it for the discharge of excess water. On the western side, a concrete pumping platform with a canopy and an oil trap has been constructed. It houses a 185 kW (252 HP) DAF diesel generator and a Capprari flow pump with a capacity of 300 l/min (18.0 m3/h). The pumping unit is used for filling the reservoir of the irrigation fertigation system.
Autor:
A. Staccione et al.
Fecha:
2021
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Ponds should contain the following zones (NWRM.eu, retention ponds):
- a sediment forebay or other form of upstream pre-treatment system (i.e. as part of an upstream management train of sustainable drainage components),
- a permanent pool which will remain wet throughout the year and is the main treatment zone,
- a temporary storage volume for flood attenuation, created through landscaped banks to the permanent pool,
- a shallow zone or aquatic bench which is a shallow area along the edge of the permanent pool to support wetland planting, providing ecology, amenity and safety benefits.
Additional pond design features should include an emergency spillway for safe overflow when storage capacity is exceeded, maintenance access, a safety bench, and appropriate landscaping (NWRM.eu, retention ponds).
NWRM.eu, retention ponds suggest;
- The ratio of flow path length to width in the pond should be between 3:1 and 5:1. Inlets and outlets should be placed to maximise the flow path length through the pond.
- Ponds should be wedge-shaped in plan so flow enters the pond and gradually spreads out, improving the sedimentation process and potential improvement in water quality.
- The depth of the permanent pool should be between 1.2 m and 2.0 m. Deeper pools may be subject to stratification and anoxic conditions. Shallower pools may be prone to algal blooms and high biological activity during summer months.
- Side slopes should not be steeper than 1:3 to ensure public safety and maintenance access.
- Residence time of permanent pond should be at least 20 days to allow for biological treatment of dissolved pollutants where this is required.
- Additional storage volume drained in 24-72 hours after the rainfall event depending on the intensity and duration of the storm and the design specifications of the pond
- Outfall design should be such that at least 50% of the maximum storage volume is discharged within 24 hours to allow for multiple events
- Retention ponds should ideally be combined with upstream sustainable drainage components, such as smaller detention basins and swales, which offer primary treatment and sediment management.
- Regular inspection and maintenance is important for the effective operation of ponds as designed.
Regular maintenance activities include litter and debris removal; vegetation maintenance (including cutting of bank and aquatic vegetation and removal of nuisance plants); inlet/outlet inspection and maintenance; and sediment removal from forebay (where applicable). Less frequent maintenance may include sediment removal from permanent pond; repairs; ongoing inspections and monitoring.
Appropriate signage to warn of water depth must be included for public safety.
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
pond
Especifique las dimensiones de la unidad (si fuera relevante):
5500
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
EUR
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
0,97
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
90.90
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Costs of obtaining construction, technical and project documentation | 1-2 years before before starting construction |
| 2. | Construction of a pond | 1st year |
| 3. | Costs of supervision of construction and craftsmanship | 1st year |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para establecer la Tecnología:
73600,0
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The construction of a water reservoir can be subsidized from various sources (EU, state, municipalities, etc.). The largest share of support can be obtained through the Rural Development Program, where an investment can receive support ranging from 30% to 50% of eligible project cost (establishment cost).
Comentarios:
The costs include excavation costs and bottom waterproofing costs. Determining the exact establishment costs for the entire project was challenging due to variations in location, topography, size, shape, dimensions, materials, soil permeability, and other factors. The specific establishment cost for the retention pond at the case study location is not available or relevant, as it would be significantly lower than the cost of constructing such a pond today (due to inflation). Therefore, we decided to use projected values based on the maximum eligible costs set by the Ministry of Agriculture for grant applications, which amount to 13.38 €/m3 (2016). This value represents the justified project cost for constructing the retention pond. In this scenario, the estimated establishment cost for a typical 5000 m3 pond would be 66,900.00 €.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Energy for pumping | annually |
| 2. | water fee | annually |
| 3. | Maintenance costs (vegetation management, inspections, infrastructure maintenance, mulching, invasive species removal, pumping the entire pond for cleaning and sediment removal, sludge cleaning, monitoring, bank stabilization, replacement of damaged parts, and sealing, etc.) | annually |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para mantener la Tecnología:
3000,0
Comentarios:
Obtaining precise costs for maintaining the pond and its surroundings is challenging, as it involves various factors. The costs can include anything from labor hours and manual mowing around the pond to considering professionals for inspections, infrastructure maintenance, mulching, invasive species removal, pumping the entire reservoir for cleaning and sediment removal, sludge cleaning, monitoring, bank stabilization, replacement of damaged parts, sealing, and more. The exact costs are difficult to determine due to the highly diverse infrastructure present in different locations. We have estimated the costs per square meter of the area under maintenance, which includes both the surrounding land and the water surface. If it's only about cleaning the surroundings of the reservoir, we consider only the land area. However, if it involves cleaning within the reservoir, we also take into account the water surface area. The best rough estimates we have range from 1 to 5 € per square meter.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Construction costs are affected by the shape, size, depth and microlocation of the pond layout. In addition, the cost is also influenced by the purpose of use (e.g. if pool is intended only to contain high water, sediment or debris laoding, will it be inhabited by aquatic animals, will water be used for irrigation, drinking, etc.). Geomechanically conditions are also important, because ponds and reservoirs can affect slope stability and induce landslides. The value of the investment can vary greatly depending on the design of the pond, location, water content of the area, soil structure, climate conditions,... so it is impossible to determine the exact values for pond construction, but we can only give an estimation.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1080,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are June and August, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Jareninski vrh (1981 – 2010)
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Mean annual temperature in year 2014 Jareninski vrh is 11,9°C.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
There are depressions, settlements are in the valley, concave type.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Hydro melioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
- empleado (compañía, gobierno)
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Manager of an agricultural company - fruit center - poblic demonstration plantation.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- compañía
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
Especifique:
They are based on national legal system
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Irrigation has avoided reduction in production due to drought and frost
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved fruit health (protection against drought and frost)
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Protection against drought and frost
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Change of land use (from agricultural land to water body).
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased the complexity of management.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
calidad de agua para irrigar
demanda de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Production and income stability.
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Possible diversification on farm (tourism and recreation).
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Demanding maintenance and increased complexity of management.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Lower risk of production failure, stability in business, motivation to do business in agriculture
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Possible additional activities on farm.
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
An example of good practice for the community.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
With positive effects more interest of the farmer in sustainable production.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water available in dry months.
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased in case of irrigation
pérdida de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Planting species near/around the pond.
especies invasoras extrañas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Danger in case of improper maintenance.
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
For a green reservoir, a lot of green infrastructure is placed next to it, which serves as protection for animals and plants (beneficial).
especies benéficas
diversidad de hábitats
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
impactos de sequías
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
Proximity to water.
micro-clima
Comentarios/ especifique:
It affects the microclimate, more humidity, slower temperature fluctuations
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
It is slightly increased as the ponds provide water during dry periods.
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved mainly due to water retention during wet seasons for use in dry periods.
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced due to the capacity of ponds to retain excess water during times when rivers may flood.
colmatación río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The reservoir also enables sediment retention, preventing sediment from reaching downstream watercourses.
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
Many studies indicate that ponds can trap harmful substances, causing them to settle or undergo processes (acting as natural purification systems, especially when appropriate plant species are involved). This helps maintain cleaner downstream flows in terms of pollutants.
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
The pond's ability to retain pollutants also contributes to its buffering and filtering capacity.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura estacional | verano | incrementó | bien |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | muy bien | |
| lluvia estacional | primavera | incrementó | muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de calor | no muy bien |
| sequía | muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| período extendido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The costs of establishing a retention pond are indeed very high, and it is a substantial investment. However, especially in the case of agricultural land irrigation, the benefits can be quite favorable, particularly in terms of drought protection or frost prevention. In the long run, the investment yields significant advantages, as it enables resilience to climate change. Farmers can also receive support through rural development programs, which provide 30-50% project funding. Although the maintenance costs can be considerable, they are necessary and offer substantial benefits to farmers who irrigate their crops or protect them from frost. From land users' perspective it's positive, if they have improved production results.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
It is worth noting that the availability and extent of government subsidies can vary depending on the location, specific program, and eligibility criteria. In this research area, the majority of projects received partial funding from the government.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Retention ponds are simple if space is provided. |
| They collect water for use in drought conditions. |
| Retention ponds manage storm water quantity and quality, lessening the transfer of pollutants and chemicals into nearby water bodies. |
| Improved storm water collection and flood control. |
| Retention ponds provide habitats for animals, organisms, and insects (biodiversity). |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Local farm water retention systems allow for the detainment of water captured during spring runoff as well as during precipitation events, either directly or due to transport by surface runoff. This provides water storage that can be drawn on when groundwater supplies become depleted. |
| Retention ponds are designed to hold excess storm water runoff and release it slowly to avoid flooding downstream areas. They also serve to reduce downstream peak flow and aid in retaining flood waters which reduces associated flood risks downstream. If water is released from the reservoir, they serve to replenish groundwater stores downstream. |
| Surface water retention systems have shown success in reducing nutrient and sediment loading in various locations worldwide. |
| Under drought conditions these systems enable farmers to draw water from the reservoirs to support crop irrigation. The main value of water retention ponds is related to agricultural water demand in the dry season. They are considered the only effective way to preserve agricultural productivity. The ponds can increase the monetary value of agricultural land that can cope with water needs. |
| In addition to the primary function of retaining high waters, they often also serve a multipurpose use, such as: supply of drinking water, irrigation of agricultural land, protection against erosion, aquaculture, fishing, energy source, preservation of landscape and biodiversity, tourism, recreation and others. |
| Biomass production is another benefit of multi-purpose surface water retention system – cattails bioproduction and nutrient management. |
| In the case of construction of the so-called of a "green" water reservoir, green infrastructure solutions can provide protection for various species of animals and plants, which promotes biodiversity. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Anaerobic conditions can occur without regular inflow. | Proper planning and dimensioning of the pond, location and water level are necessary. It is necessary to ensure adequate flow and depth of the pond. |
| May not be suitable for steep sites, due to requirement for high embankments. | The construction of the pond is planned at a suitable location. |
| Colonisation by invasive species could increase maintenance and pose a danger to cultivated areas. | Regular maintenance and cleaning of the pond bank is necessary. |
| Safety risk in case of slipping and falling into the pond. | It is necessary to fence and isolate the access to the pond. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Large investments in the irrigation system and access to funds for irrigation infrastructure can be difficult to attain. | The size and holding capacity of retention systems also need to be considered to maximize benefits while limiting the initial costs of building a surface water retention system. |
| The construction requires a lot of technical preparation, planning, documentation and there are many bureaucratic obstacles to comply with the spatial acts of the municipality and to fulfil the requirements of the spatial planning authorities, which also includes large initial costs. | The preparation and management of the project should be entrusted to a professional service. Check the conditions ahead of time and plan strategically several years ahead. |
| While irrigation provides an economic gain during drought years, it also increases operational costs for water supplies. | Strategies need to provide drought proofing of crops as well as limiting damages caused by floods in non-drought years to reduce risk to farmers and the region. |
| Experts identified some barriers for greener pond implementation, especially related to reduced efficiency. The higher surface required can cause loss of water stored during summer from the higher rate of evaporation. Another risk is associated with vegetation close to the pond banks which can reduce impermeabilization and increase water infiltration due to root growth in the soil. | Good technical plan with solutions and compromises for best results with natural (green) benefits. Considering the benefits brought by green systems. |
| Unregulated relations between active/potential users, both in the delimitation of water rights, especially in times of water shortage, and in cases of regulating obligations for the proper operation and maintenance. | Collective investments with a good long-term plan for operation and maintenance. Organized management of users from the organization (e.g. municipality, etc.). |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Field visit and conducted interview with the farm manager at the Fruit Growing Center Maribor. A working group was established, where we met 2 times to review and respond to the questionnaire.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Purgaj Donik Biserka is a farm manager of agriculture company "Fruit growing center Maribor" (land user).
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Matjaz Glavan, Istenič Darja, Škerjanec Mateja, Banovec Primož, Curk Miha and Cvejić Rozalija representatives from University of Ljubljana.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
As for the literature, we utilized the following documents:
- Vodnogospodarske podlage za nadzor obratovanja in vzdrževanja manjših zadrževalnikov (translated: Hydraulic basis for monitoring the operation and maintenance of small reservoirs). Miljenko Hočuršćak. Aktualni projekti s področja upravljanja z vodami in urejanje voda. 28. Mišičev vodarski dan 2017.
- Natural water retention ponds for water management in agriculture: A potential scenario in Northern Italy; Andrea Staccione, Davide Broccoli, Paolo Mazzoli, Stefano Bagli, Jaroslav Mysiak; Journal of Environmental Management 292 (2021) 112849.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
10/02/2023
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
An economic assessment of local farm multi-purpose surface water retention systems in a Canadian Prairie setting; Pamela Berry, Fuad Yassin, Kenneth Belcher, Karl-Erich Lindenschmidt, Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:4461–4478.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Web
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Natural water retention ponds for water management in agriculture: A potential scenario in Northern Italy; Andrea Staccione, Davide Broccoli, Paolo Mazzoli, Stefano Bagli, Jaroslav Mysiak; Journal of Environmental Management 292 (2021) 112849.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Web
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Natural Water Retention Measures; Report: Individual NWRM - Retention ponds.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Web
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Vodnogospodarske podlage za nadzor obratovanja in vzdrževanja manjših zadrževalnikov. Miljenko Hočuršćak. Aktualni projekti s področja upravljanja z vodami in urejanje voda. 28. Mišičev vodarski dan 2017.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Web
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos