Retention ponds [สโลวีเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Gregor Kramberger
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mokri zadrževalniki vode
technologies_5933 - สโลวีเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Istenič Darja
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
สโลวีเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Škerjanec Mateja
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
สโลวีเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Banovec Primož
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
สโลวีเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Curk Miha
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
สโลวีเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Cvejić Rozalija
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
สโลวีเนีย
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Purgaj Donik Biserka
Fruit center Maribor (demonstrartion plantation centre), Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
สโลวีเนีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - สโลวีเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
University of Ljubljana (UL) - สโลวีเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
With improper implementation and intended use, it can have a negative effect on sustainability in the environment. It can be sustainable if properly anticipated/planned. The construction of the pond is usually subject to an environmental impact assessment where these matters are resolved as to whether it is sustainable or not.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Retention ponds (e.g. flood storage reservoirs, shallow impoundments) are water bodies, storing water to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. They provide storage as well as improving water quality. Retention ponds may also be used for irrigation of farmland.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
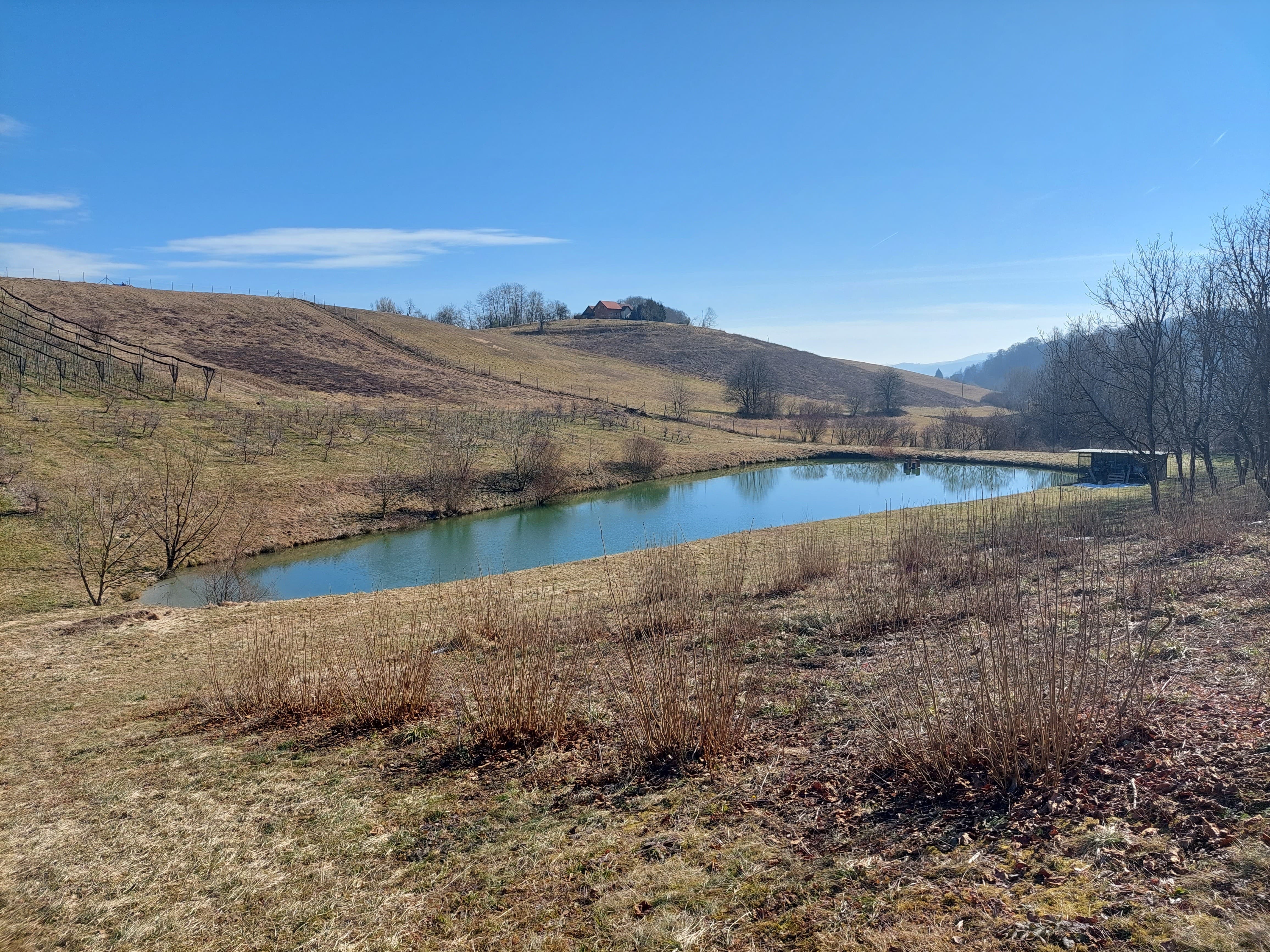
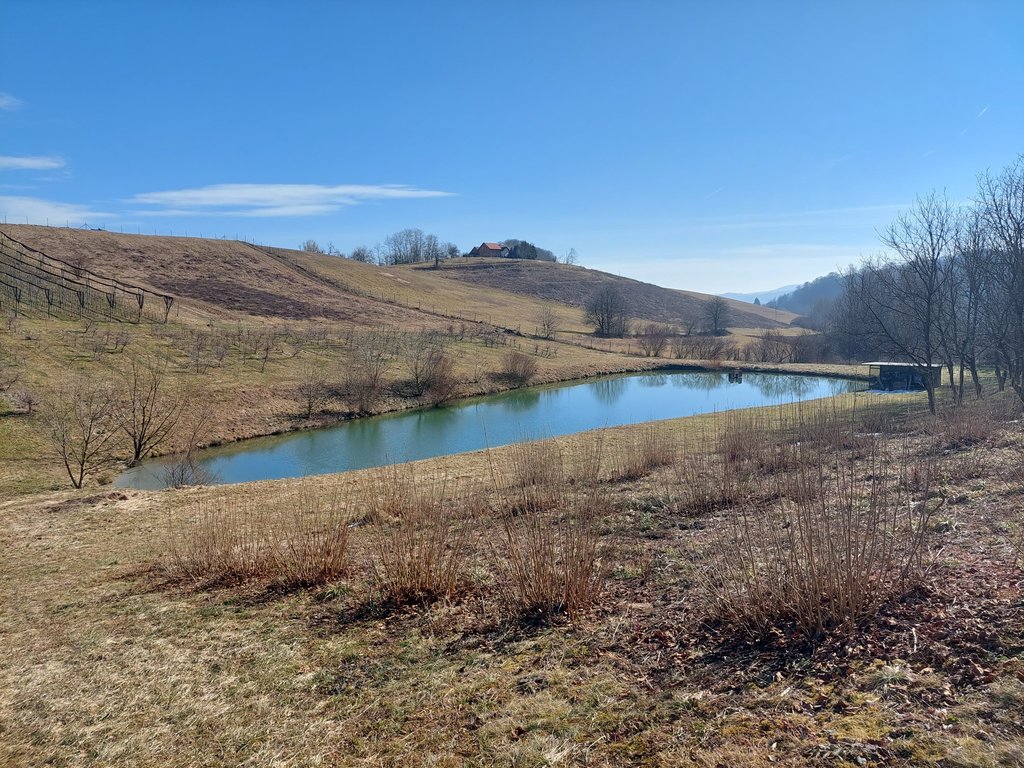
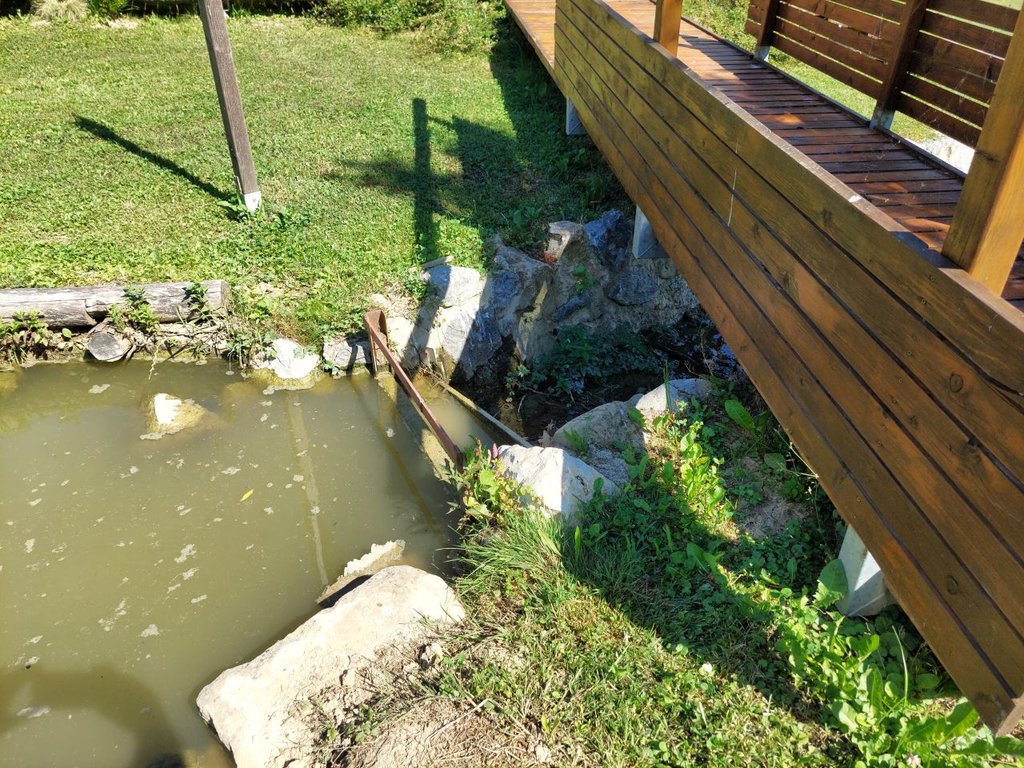
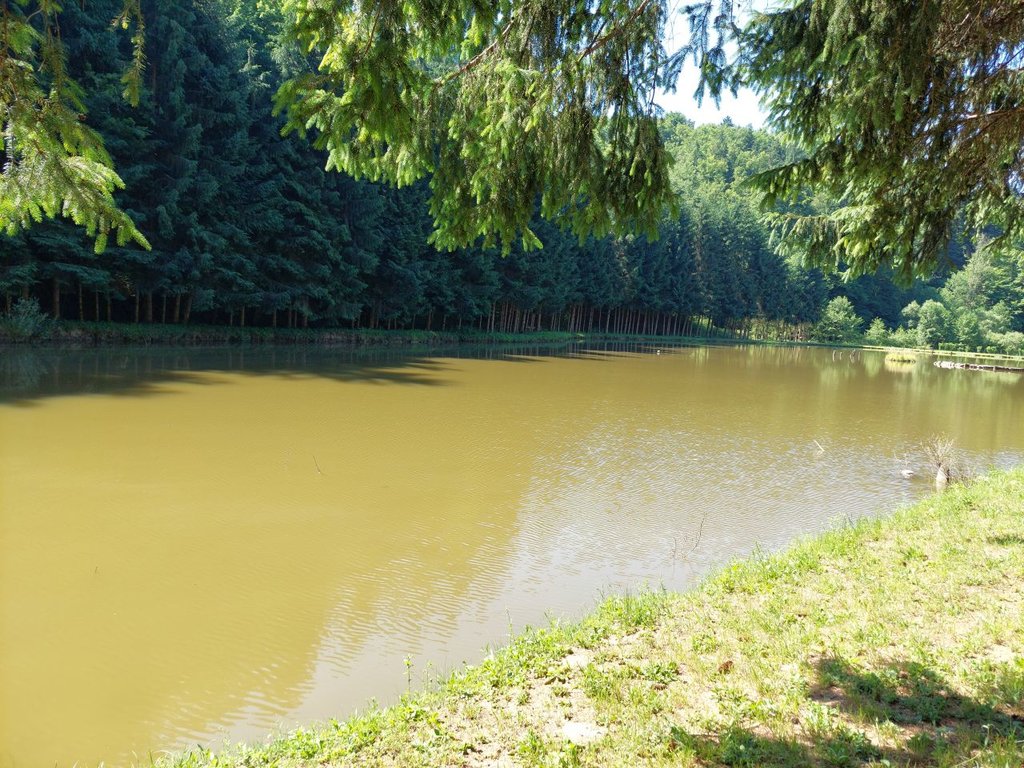
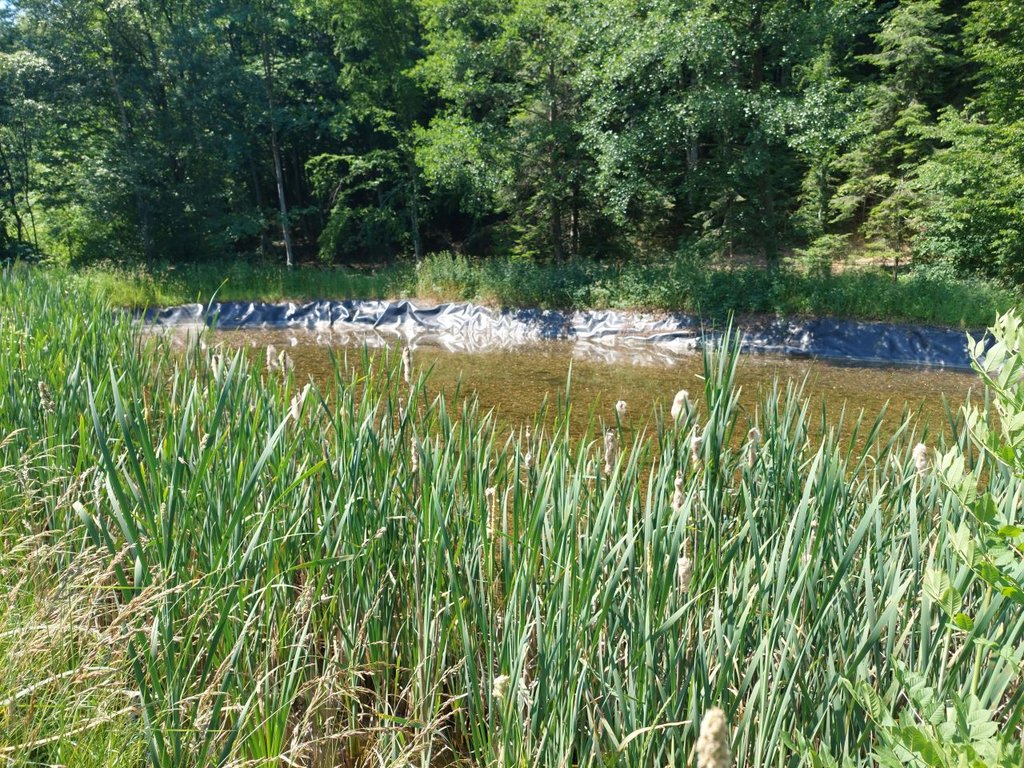
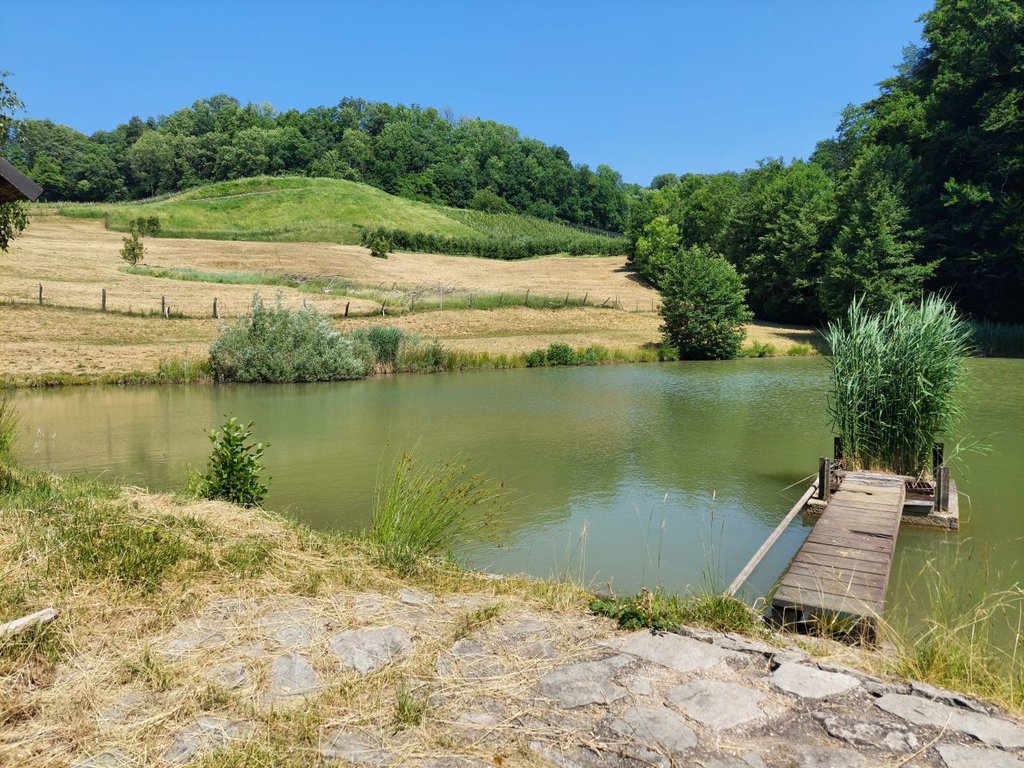
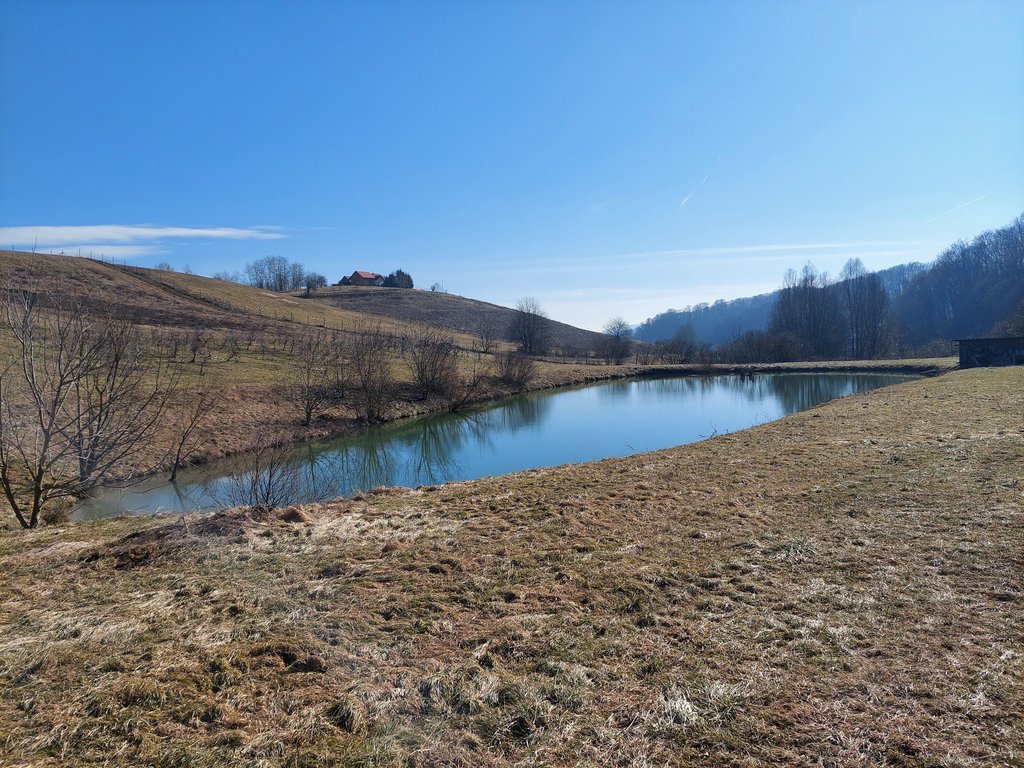
“Retention ponds” comprise both simple, small ponds (up to 2000 m3, up to 4 m deep) and larger, more complex reservoirs (greater than 2000 m3). Retention ponds are designed to provide storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. Each consists of a permanent ponded area with landscaped banks. Retention ponds achieve both storm water attenuation and water quality treatment through supplementary storage capacity of runoff. Water is then released at a controlled rate once the risk of flooding has passed. The technology can be applied in a natural or human environment. Before construction of a pond it is essential to follow legislation, which covers conditions and restrictions for the given location. Once a site is selected, technical documentation is prepared: first the conceptual design, then documentation for obtaining opinion, consent and a building permit. Later there is also project documentation for implementation. If the water is to be used for other purposes as well (e.g. for irrigation), it is necessary to plan for usage and environmental impact. Retention and still water promotes pollutant removal through sedimentation, while aquatic vegetation and biological uptake mechanisms offer additional treatment. Retention ponds are effective in removing urban pollutants and improving water quality.
They are created either by using an existing natural depression, or by excavating a new depression, or by constructing embankments. Existing natural water bodies should not be used however, due to the risk that pollution events and poorer water quality might disturb/damage the natural ecology of the system. A great benefit of retention ponds is that they hold water when there is an excess of it, which can be used later when water is not available (e.g. for irrigation). Irrigation users are farmers, so they see the advantage of using a retention system. In addition to irrigation, water has also been needed in recent years for anti-frost systems (sprinkling a consistent layer of water on the crop during an entire frost event until temperatures are back to safe levels). Disadvantages are mainly restrictions in some areas (e.g. protected areas), preparation of demanding documentation and bureaucracy, and lengthy procedures for obtaining permits.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สโลวีเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Podravska region, Slovenia
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Pesnica
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Setting up a measure in a protected area is limited and very difficult due to construction restrictions in such an environment.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In the 1990s, the state financed the construction of several water reservoirs in the area.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- บ่อน้ำ เขื่อน
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Retention of water, collection of water. Retention ponds are ponds or basins designed with additional storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. In dry years, the water can be used for agriculture, e.g. for irrigation.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- ทางระบายน้ำ ทางน้ำ
- หนองบึง พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hq (Decline of groundwater quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำบาดาล
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
To prevent erosion.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
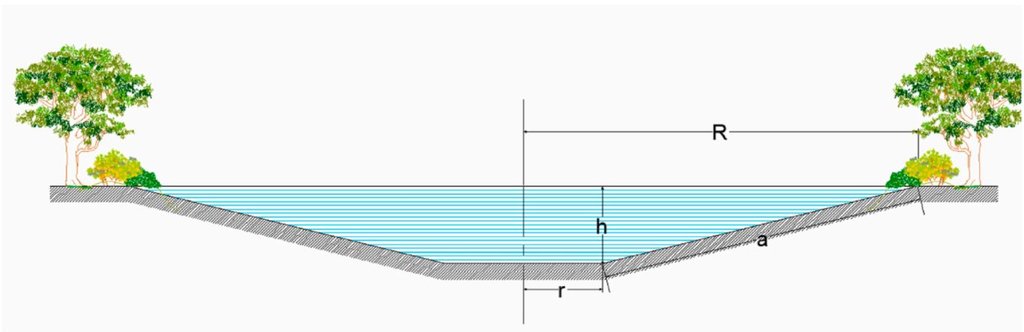
Water retention pond – excavation scheme. R is the top radius of pond, while r is the base radius; h is the height and a refers to the bank slope. Storage volume is estimated by radius r and height h (Figure). We consider potential storage volumes of 5,000 m3 to 10,000 m3.
Prior to start of construction, detention/retention ponds should be designed by a registered design professional. Plans and specifications should be referred to by field personnel throughout the construction process. When placing a detention/retention pond in a space in the first phase it is necessary to produce a conceptual design of the intended construction of a pond, which must show the purpose and goals of the retaining wall, the size of the pond, the location, a list of plots that are encroached upon, distances from neighboring land and neighboring buildings, anticipated activities in the impoundment area, impoundment volume, barrier size data, including stability assessment, and geotechnical data (Hočuršćak 2017). When planning construction of the pond, attention should be paid primarily to the impact on the actual use of space from the point of view of water management regulations, which defines the area of use and activity restrictions, due to the possible negative impact on water and coastal lands, aquatic habitats and the ecosystem created by the construction of the reservoir. After talking with the designer, in order to obtain a water permit and consent from the authorities, it is necessary to prepare technical documentation for the installation and construction, which must also include the basis for monitoring operation and maintenance (Hočuršćak 2017). The technical documentation (dimensioning of the reservoir) may differ from the microlocation and purpose or use of the measure, e.g. if pool is intended only to contain high water, sediment or debris laoding, will it be inhabited by aquatic animals, will water be used for irrigation, drinking, etc. We also consider the shape and size of the area to identify those better suited for allocating ponds also in terms of space availability. For example, it is necessary to exclude locations with a greater slope and distance from the river considering higher slope and distance is more difficult and costly to construct. We also exclude locations where the construction of a pond is not possible because they are too narrow or too small. We should consider water retention ponds as elements of a green infrastructure network together with other natural elements (e.g. vegetated riparian zones) and protected areas (e.g. Natura, 2000 sites) with a pond design that embeds features that enhance their ecological functionality. These include mild-sloped sides with vegetated buffers along the shorelines and vegetated floating islands that facilitate the nesting of birds. We refer to excavated ponds, with no weirs or dams, since inline ponds are more costly and may have negative ecological impacts (A. Staccione et al. 2021).
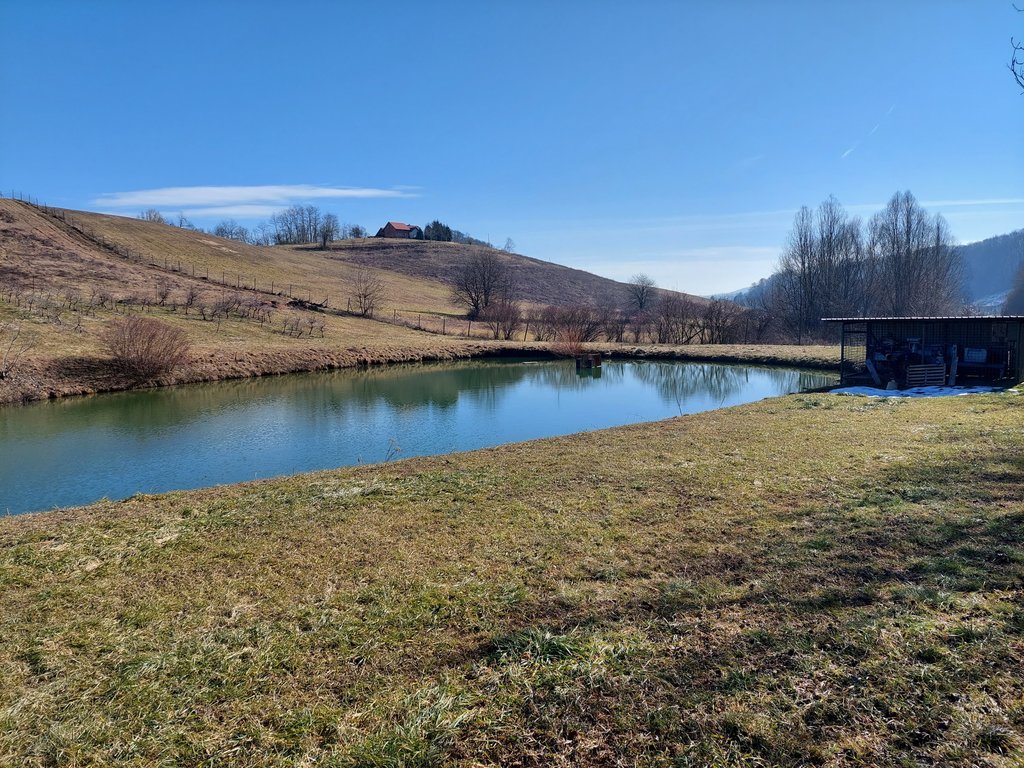
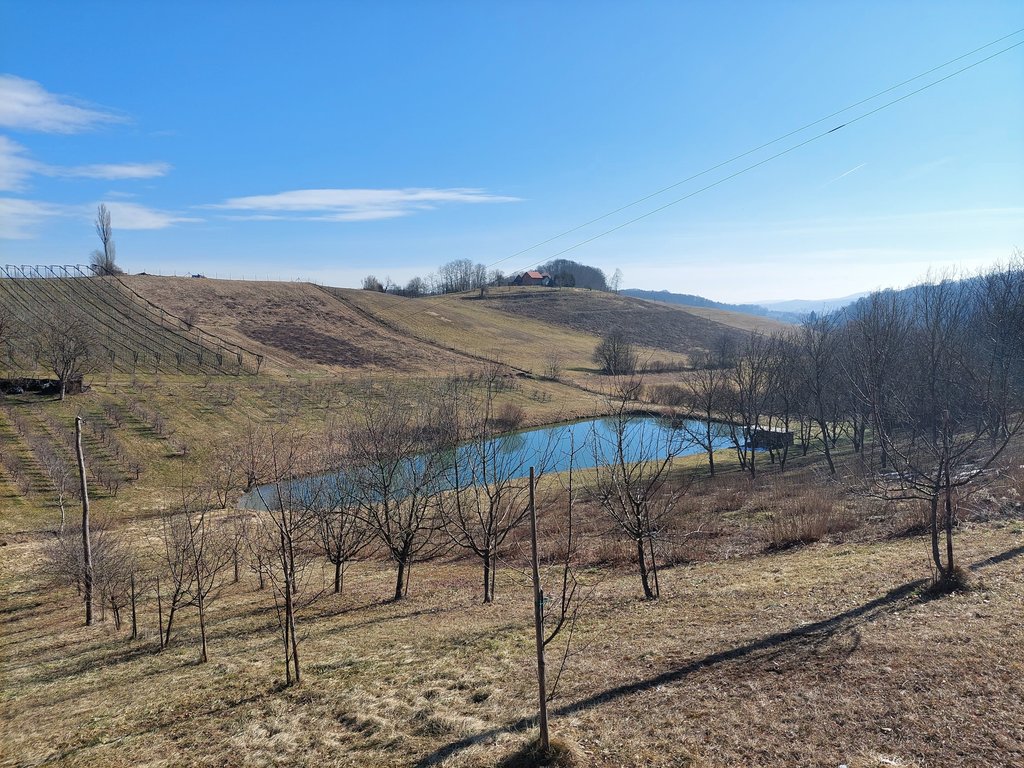
Presentation of the water reservoir at the Sadjarski Center Maribor (translated: Fruit Growing Center Maribor):
The Sadjarski Center Maribor is located on a sloping terrain, which is pedologically and configuratively quite diverse, with slopes ranging from 5-15%. The soil structure is clayey loam with a basaltic substrate. In the lower, flatter part, the soil was waterlogged, which was resolved through drainage systems. These drains are directed towards a drainage ditch, which serves as the foundation for the pond and is fed by two smaller springs. The intake point is located at the lowest point and at the southernmost part of the complex. It covers an area of 3000 m2 and has a depth of up to 3.8 m. Its capacity is 5500 m3 of water when fully filled. At its southern part, there is a concrete overflow structure (spillway) with a height of 3.8 m, which is used to drain excess water and regulate the water level. A concrete pipe, 20 m in length and 80 cm in diameter, is connected to it for the discharge of excess water. On the western side, a concrete pumping platform with a canopy and an oil trap has been constructed. It houses a 185 kW (252 HP) DAF diesel generator and a Capprari flow pump with a capacity of 300 l/min (18.0 m3/h). The pumping unit is used for filling the reservoir of the irrigation fertigation system.
ผู้เขียน:
A. Staccione et al.
วันที่:
2021
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Ponds should contain the following zones (NWRM.eu, retention ponds):
- a sediment forebay or other form of upstream pre-treatment system (i.e. as part of an upstream management train of sustainable drainage components),
- a permanent pool which will remain wet throughout the year and is the main treatment zone,
- a temporary storage volume for flood attenuation, created through landscaped banks to the permanent pool,
- a shallow zone or aquatic bench which is a shallow area along the edge of the permanent pool to support wetland planting, providing ecology, amenity and safety benefits.
Additional pond design features should include an emergency spillway for safe overflow when storage capacity is exceeded, maintenance access, a safety bench, and appropriate landscaping (NWRM.eu, retention ponds).
NWRM.eu, retention ponds suggest;
- The ratio of flow path length to width in the pond should be between 3:1 and 5:1. Inlets and outlets should be placed to maximise the flow path length through the pond.
- Ponds should be wedge-shaped in plan so flow enters the pond and gradually spreads out, improving the sedimentation process and potential improvement in water quality.
- The depth of the permanent pool should be between 1.2 m and 2.0 m. Deeper pools may be subject to stratification and anoxic conditions. Shallower pools may be prone to algal blooms and high biological activity during summer months.
- Side slopes should not be steeper than 1:3 to ensure public safety and maintenance access.
- Residence time of permanent pond should be at least 20 days to allow for biological treatment of dissolved pollutants where this is required.
- Additional storage volume drained in 24-72 hours after the rainfall event depending on the intensity and duration of the storm and the design specifications of the pond
- Outfall design should be such that at least 50% of the maximum storage volume is discharged within 24 hours to allow for multiple events
- Retention ponds should ideally be combined with upstream sustainable drainage components, such as smaller detention basins and swales, which offer primary treatment and sediment management.
- Regular inspection and maintenance is important for the effective operation of ponds as designed.
Regular maintenance activities include litter and debris removal; vegetation maintenance (including cutting of bank and aquatic vegetation and removal of nuisance plants); inlet/outlet inspection and maintenance; and sediment removal from forebay (where applicable). Less frequent maintenance may include sediment removal from permanent pond; repairs; ongoing inspections and monitoring.
Appropriate signage to warn of water depth must be included for public safety.
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
pond
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
5500
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
EUR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.97
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
90.90
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Costs of obtaining construction, technical and project documentation | 1-2 years before before starting construction |
| 2. | Construction of a pond | 1st year |
| 3. | Costs of supervision of construction and craftsmanship | 1st year |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
73600.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The construction of a water reservoir can be subsidized from various sources (EU, state, municipalities, etc.). The largest share of support can be obtained through the Rural Development Program, where an investment can receive support ranging from 30% to 50% of eligible project cost (establishment cost).
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs include excavation costs and bottom waterproofing costs. Determining the exact establishment costs for the entire project was challenging due to variations in location, topography, size, shape, dimensions, materials, soil permeability, and other factors. The specific establishment cost for the retention pond at the case study location is not available or relevant, as it would be significantly lower than the cost of constructing such a pond today (due to inflation). Therefore, we decided to use projected values based on the maximum eligible costs set by the Ministry of Agriculture for grant applications, which amount to 13.38 €/m3 (2016). This value represents the justified project cost for constructing the retention pond. In this scenario, the estimated establishment cost for a typical 5000 m3 pond would be 66,900.00 €.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Energy for pumping | annually |
| 2. | water fee | annually |
| 3. | Maintenance costs (vegetation management, inspections, infrastructure maintenance, mulching, invasive species removal, pumping the entire pond for cleaning and sediment removal, sludge cleaning, monitoring, bank stabilization, replacement of damaged parts, and sealing, etc.) | annually |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
3000.0
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Obtaining precise costs for maintaining the pond and its surroundings is challenging, as it involves various factors. The costs can include anything from labor hours and manual mowing around the pond to considering professionals for inspections, infrastructure maintenance, mulching, invasive species removal, pumping the entire reservoir for cleaning and sediment removal, sludge cleaning, monitoring, bank stabilization, replacement of damaged parts, sealing, and more. The exact costs are difficult to determine due to the highly diverse infrastructure present in different locations. We have estimated the costs per square meter of the area under maintenance, which includes both the surrounding land and the water surface. If it's only about cleaning the surroundings of the reservoir, we consider only the land area. However, if it involves cleaning within the reservoir, we also take into account the water surface area. The best rough estimates we have range from 1 to 5 € per square meter.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Construction costs are affected by the shape, size, depth and microlocation of the pond layout. In addition, the cost is also influenced by the purpose of use (e.g. if pool is intended only to contain high water, sediment or debris laoding, will it be inhabited by aquatic animals, will water be used for irrigation, drinking, etc.). Geomechanically conditions are also important, because ponds and reservoirs can affect slope stability and induce landslides. The value of the investment can vary greatly depending on the design of the pond, location, water content of the area, soil structure, climate conditions,... so it is impossible to determine the exact values for pond construction, but we can only give an estimation.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1080.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are June and August, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Jareninski vrh (1981 – 2010)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Mean annual temperature in year 2014 Jareninski vrh is 11,9°C.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
There are depressions, settlements are in the valley, concave type.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Hydro melioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Manager of an agricultural company - fruit center - poblic demonstration plantation.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- บริษัท
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
ระบุ:
They are based on national legal system
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Irrigation has avoided reduction in production due to drought and frost
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved fruit health (protection against drought and frost)
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Protection against drought and frost
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Change of land use (from agricultural land to water body).
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased the complexity of management.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Production and income stability.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Possible diversification on farm (tourism and recreation).
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Demanding maintenance and increased complexity of management.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Lower risk of production failure, stability in business, motivation to do business in agriculture
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Possible additional activities on farm.
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
An example of good practice for the community.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
With positive effects more interest of the farmer in sustainable production.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water available in dry months.
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased in case of irrigation
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Planting species near/around the pond.
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Danger in case of improper maintenance.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
For a green reservoir, a lot of green infrastructure is placed next to it, which serves as protection for animals and plants (beneficial).
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Proximity to water.
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It affects the microclimate, more humidity, slower temperature fluctuations
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It is slightly increased as the ponds provide water during dry periods.
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved mainly due to water retention during wet seasons for use in dry periods.
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced due to the capacity of ponds to retain excess water during times when rivers may flood.
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The reservoir also enables sediment retention, preventing sediment from reaching downstream watercourses.
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Many studies indicate that ponds can trap harmful substances, causing them to settle or undergo processes (acting as natural purification systems, especially when appropriate plant species are involved). This helps maintain cleaner downstream flows in terms of pollutants.
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The pond's ability to retain pollutants also contributes to its buffering and filtering capacity.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ดีมาก | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูใบไม้ผลิ | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ขยายออกไป | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs of establishing a retention pond are indeed very high, and it is a substantial investment. However, especially in the case of agricultural land irrigation, the benefits can be quite favorable, particularly in terms of drought protection or frost prevention. In the long run, the investment yields significant advantages, as it enables resilience to climate change. Farmers can also receive support through rural development programs, which provide 30-50% project funding. Although the maintenance costs can be considerable, they are necessary and offer substantial benefits to farmers who irrigate their crops or protect them from frost. From land users' perspective it's positive, if they have improved production results.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is worth noting that the availability and extent of government subsidies can vary depending on the location, specific program, and eligibility criteria. In this research area, the majority of projects received partial funding from the government.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Retention ponds are simple if space is provided. |
| They collect water for use in drought conditions. |
| Retention ponds manage storm water quantity and quality, lessening the transfer of pollutants and chemicals into nearby water bodies. |
| Improved storm water collection and flood control. |
| Retention ponds provide habitats for animals, organisms, and insects (biodiversity). |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Local farm water retention systems allow for the detainment of water captured during spring runoff as well as during precipitation events, either directly or due to transport by surface runoff. This provides water storage that can be drawn on when groundwater supplies become depleted. |
| Retention ponds are designed to hold excess storm water runoff and release it slowly to avoid flooding downstream areas. They also serve to reduce downstream peak flow and aid in retaining flood waters which reduces associated flood risks downstream. If water is released from the reservoir, they serve to replenish groundwater stores downstream. |
| Surface water retention systems have shown success in reducing nutrient and sediment loading in various locations worldwide. |
| Under drought conditions these systems enable farmers to draw water from the reservoirs to support crop irrigation. The main value of water retention ponds is related to agricultural water demand in the dry season. They are considered the only effective way to preserve agricultural productivity. The ponds can increase the monetary value of agricultural land that can cope with water needs. |
| In addition to the primary function of retaining high waters, they often also serve a multipurpose use, such as: supply of drinking water, irrigation of agricultural land, protection against erosion, aquaculture, fishing, energy source, preservation of landscape and biodiversity, tourism, recreation and others. |
| Biomass production is another benefit of multi-purpose surface water retention system – cattails bioproduction and nutrient management. |
| In the case of construction of the so-called of a "green" water reservoir, green infrastructure solutions can provide protection for various species of animals and plants, which promotes biodiversity. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Anaerobic conditions can occur without regular inflow. | Proper planning and dimensioning of the pond, location and water level are necessary. It is necessary to ensure adequate flow and depth of the pond. |
| May not be suitable for steep sites, due to requirement for high embankments. | The construction of the pond is planned at a suitable location. |
| Colonisation by invasive species could increase maintenance and pose a danger to cultivated areas. | Regular maintenance and cleaning of the pond bank is necessary. |
| Safety risk in case of slipping and falling into the pond. | It is necessary to fence and isolate the access to the pond. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Large investments in the irrigation system and access to funds for irrigation infrastructure can be difficult to attain. | The size and holding capacity of retention systems also need to be considered to maximize benefits while limiting the initial costs of building a surface water retention system. |
| The construction requires a lot of technical preparation, planning, documentation and there are many bureaucratic obstacles to comply with the spatial acts of the municipality and to fulfil the requirements of the spatial planning authorities, which also includes large initial costs. | The preparation and management of the project should be entrusted to a professional service. Check the conditions ahead of time and plan strategically several years ahead. |
| While irrigation provides an economic gain during drought years, it also increases operational costs for water supplies. | Strategies need to provide drought proofing of crops as well as limiting damages caused by floods in non-drought years to reduce risk to farmers and the region. |
| Experts identified some barriers for greener pond implementation, especially related to reduced efficiency. The higher surface required can cause loss of water stored during summer from the higher rate of evaporation. Another risk is associated with vegetation close to the pond banks which can reduce impermeabilization and increase water infiltration due to root growth in the soil. | Good technical plan with solutions and compromises for best results with natural (green) benefits. Considering the benefits brought by green systems. |
| Unregulated relations between active/potential users, both in the delimitation of water rights, especially in times of water shortage, and in cases of regulating obligations for the proper operation and maintenance. | Collective investments with a good long-term plan for operation and maintenance. Organized management of users from the organization (e.g. municipality, etc.). |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Field visit and conducted interview with the farm manager at the Fruit Growing Center Maribor. A working group was established, where we met 2 times to review and respond to the questionnaire.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Purgaj Donik Biserka is a farm manager of agriculture company "Fruit growing center Maribor" (land user).
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Matjaz Glavan, Istenič Darja, Škerjanec Mateja, Banovec Primož, Curk Miha and Cvejić Rozalija representatives from University of Ljubljana.
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
As for the literature, we utilized the following documents:
- Vodnogospodarske podlage za nadzor obratovanja in vzdrževanja manjših zadrževalnikov (translated: Hydraulic basis for monitoring the operation and maintenance of small reservoirs). Miljenko Hočuršćak. Aktualni projekti s področja upravljanja z vodami in urejanje voda. 28. Mišičev vodarski dan 2017.
- Natural water retention ponds for water management in agriculture: A potential scenario in Northern Italy; Andrea Staccione, Davide Broccoli, Paolo Mazzoli, Stefano Bagli, Jaroslav Mysiak; Journal of Environmental Management 292 (2021) 112849.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
10/02/2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
An economic assessment of local farm multi-purpose surface water retention systems in a Canadian Prairie setting; Pamela Berry, Fuad Yassin, Kenneth Belcher, Karl-Erich Lindenschmidt, Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:4461–4478.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Web
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Natural water retention ponds for water management in agriculture: A potential scenario in Northern Italy; Andrea Staccione, Davide Broccoli, Paolo Mazzoli, Stefano Bagli, Jaroslav Mysiak; Journal of Environmental Management 292 (2021) 112849.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Web
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Natural Water Retention Measures; Report: Individual NWRM - Retention ponds.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Web
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Vodnogospodarske podlage za nadzor obratovanja in vzdrževanja manjših zadrževalnikov. Miljenko Hočuršćak. Aktualni projekti s področja upravljanja z vodami in urejanje voda. 28. Mišičev vodarski dan 2017.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Web
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล