Fodder Crops Production [Turquie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2425 - Turquie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Personne(s) ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Tolay Inci
Turquie
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT
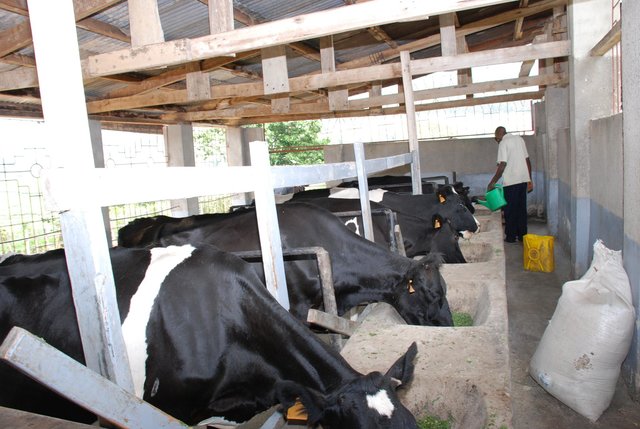

Complémentation des vaches laitières [Ouganda]
De l’herbe à éléphant (Pennisteum purpureum) et du calliandra (Calliandra calothyrsus) sont récoltés et hachés avec une hacheuse pour produire du fourrage pour des vaches laitières. Le hachis est ensuite mélangé avec du tourteau de graines de coton, de la mélasse et du son de maïs pour en améliorer l’appétence …
- Compilateur : Aine Amon
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
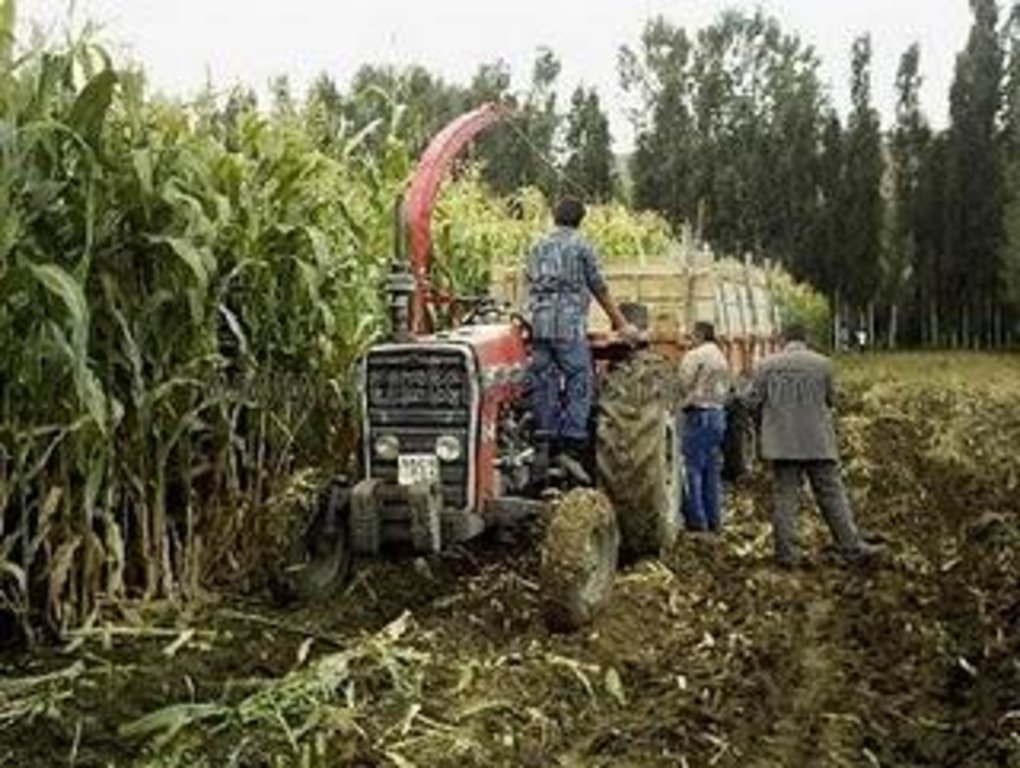
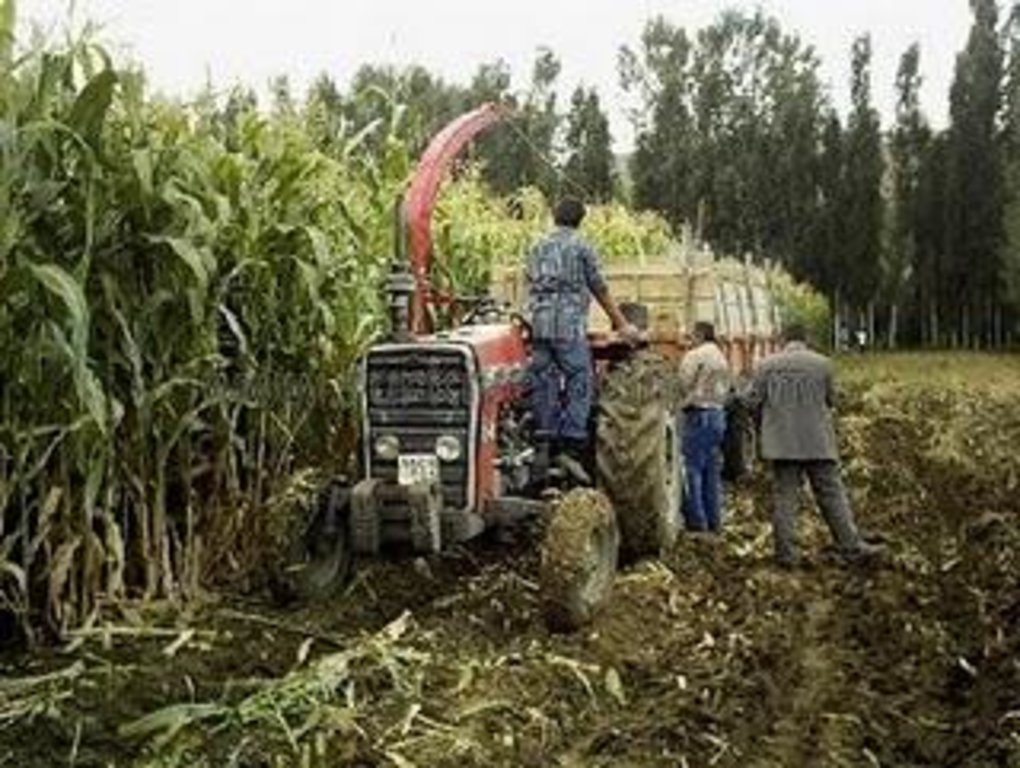
To grow different fodder crop species (leguminous and graminous) for feeding livestock
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Aims / objectives: It is aimed to grow livestocks feed for reduce costs of inputs in farms. Ease of feeding by this way is another motivation. Fodder crops especially leguminous ones are also very useful for improving and protecting soil fertility. Therefore farmers who produce both crops and livestock prefer to grow fodder crops.
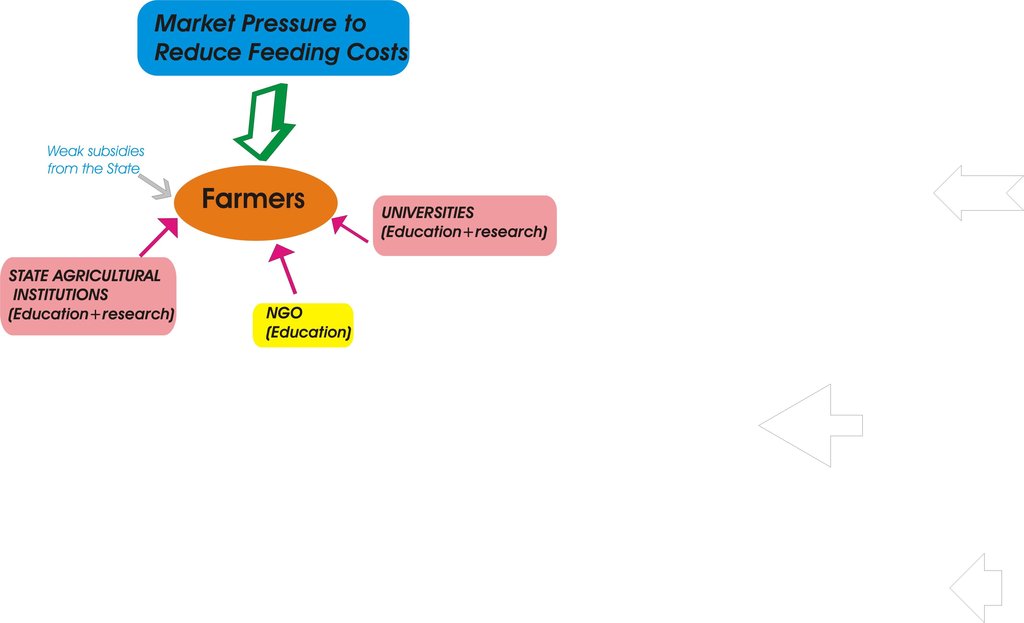
Methods: Leguminous (alfaalfa, soinfoin, vetch) and graminous (corn for silage, barley, wheat, oat, triticale, rye) fodder species are grown in different growing seasons. Graminous fodder species are grown annually, among the leguminous species. Alfaalfa, sainfain are perennial and vetch is an annual species. The fodder species can be grown under dry conditions except corn. Leguminous species can not grow well if there is not enough rainfall; therefore they need irrigation. Application of the approach is mostly forced by market conditions where meat incomes were gradually decreasing in the last years due to macroeconomic policies. Training of the farmers is achieved by state institutions, universities and NGO's in a rather discontinous and sporadic way.
Stages of implementation: Soil tillage, fertilizing the soil, sowing the seeds, irrigation, harvest (1 for graminous species several times for leguminous species). Starting the approach by individual farmers is done by traditional communication and sometimes by training activities.
Role of stakeholders: All stages of the technology application are performed by participants. Technology is applied by farmers who have all the facilities needed for technology. They get some subsidizes from the state because of promoting the fodder crop production. State organisations, universities and NGO's provide irregular training courses and demonstrations. Rare scientific studies in terms of advantages of approcah are conducted by universities and state research institutes.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Turquie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Turkey
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Keskin watershed, EskiÅŸehir
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
10
2.7 Type d'Approche
- initiative/ innovation récente locale
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused on SLM only
To reduce fodder input expenses by livestock producers.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The problems to be addressed by the approach mainly arise from drought which increases recently. Because fodder crops production mainly relies on natural rainfall in the region. Also, lack of technical knowledge is another problem. Governmental unstability for subsiding fodder crops is also one of the problem for maintaining the approach.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Education level of farmers is low and woman do not participate in performing approach.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: no solution yet.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Input casts are high.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Government partly subsidizes crop production.
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- entrave
Some of land use rights are belong to a foundation, because of that some of farmers can not got subsidizes given by government.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: No solution yet.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Some growing techniques are not known well.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Farmers get some help from governmental institutions. But most of them are aware of this.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Because of cultural, educational and social reasons there are differences between the genders. Women are not well educated and much more interested in house works and children.
Both small and large scale farmers apply technology for its benefit.
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | auto-mobilisation | |
| planification | auto-mobilisation | |
| mise en œuvre | auto-mobilisation | |
| suivi/ évaluation | aucun | |
| Research | aucun |
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- les exploitants des terres seuls (auto-initiative)
Expliquez:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, un peu
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Précisez le type de soutien:
- financier
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by government, land users through measurements; indicators: amount of yield
area treated aspects were regular monitored by government through observations; indicators: for the subsidies
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Monitoring and evaluation activities have indirect and weak effect upon the approach since applicability of the approach is determined mostly by the demand of market.
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Monitoring activities are mostly aimed to determine the subsidy payment but not to assess the efficacity of the technology. But the results of research projects is supposed to have a small impact upon the application of technology.
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 10 000-100 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (as subsidies): 20.0%; local community / land user(s): 80.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- intrants agricoles
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| semences | en partie financé | |
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Land users apply crop rotation when they use the approach. Leguminous fodder species provide nitrogen to the soil. It improves soil fertility so help sustainable land management.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les questions foncières et des droits d'utilisation qui entravent la mise en œuvre des Technologies?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
It moderately changed life quality by its ease in animal feeding and increase farm income.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
Using fodder crops allow farmers to feed their animals better and hence rise the quality of feeding.
- augmenter la rentabilité/ bénéfice, rapport coûts-bénéfices
approach basically diminish the cost of feeding and allow use of domestic (own) resources.
- paiements/ subventions
Central government gives significant subsidies.
- conscience environnementale
Farmers know that the fodder crops enrich the texture and chemistry of soil.
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- incertain
Si non ou incertain, spécifiez et commentez:
Governmental supports (subsidies) help to continue the approach. If subsidies are not given, land users can not afford easily the approach. Additionally, if the pressure of market is higher they might totaly abandon animal feeding.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| It guarantees feeding their livestock. They are not affected from fluctuation in the price and presence of fodders in the market. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By technical help.) |
| It reduces input costs. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By financial support of government.) |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| It improves soil fertility. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: informing farmers to use certain fodder crops such as leguminous fodders.) |
| It helps farmers to reduce inputs costs. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By continuous governmental support.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Livestock production is stricted by municipality due to internal regulations. | By loosing legal constrains. |
| Farmers are getting avoid to produce livestocks. | By governmal regulations. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Drought greately effects yield | By increasing irrigation facilities, and hence state help. |
| It needs governmental support. | By stabilizing subsidies |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Complémentation des vaches laitières [Ouganda]
De l’herbe à éléphant (Pennisteum purpureum) et du calliandra (Calliandra calothyrsus) sont récoltés et hachés avec une hacheuse pour produire du fourrage pour des vaches laitières. Le hachis est ensuite mélangé avec du tourteau de graines de coton, de la mélasse et du son de maïs pour en améliorer l’appétence …
- Compilateur : Aine Amon
Modules
Aucun module trouvé