Cut-off drain [Thaïlande]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Rong rabai nam (Thai)
technologies_1405 - Thaïlande
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Tiparat Sutep
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center
P.O. Box 36, P.O. Huay Khrai, Chiang Rai 57220
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Outarasak Vorachai
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center
P.O. Box 36, P.O. Huay Khrai, Chiang Rai 57220
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Suksom Prasong
Highland Flower Growing Promotion Project
P.O. Box 36, P.O. Huay Khrai, Chiang Rai 57220
Thaïlande
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center - ThaïlandeNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Highland Flower Growing Promotion Project - Thaïlande1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
30/11/1997
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Cut-off drain [Thaïlande]
This approach is the 'way' or 'how' the cut-off drain has been implemented on steepland in northern Thailand.
- Compilateur : Samran Sombatpanit
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
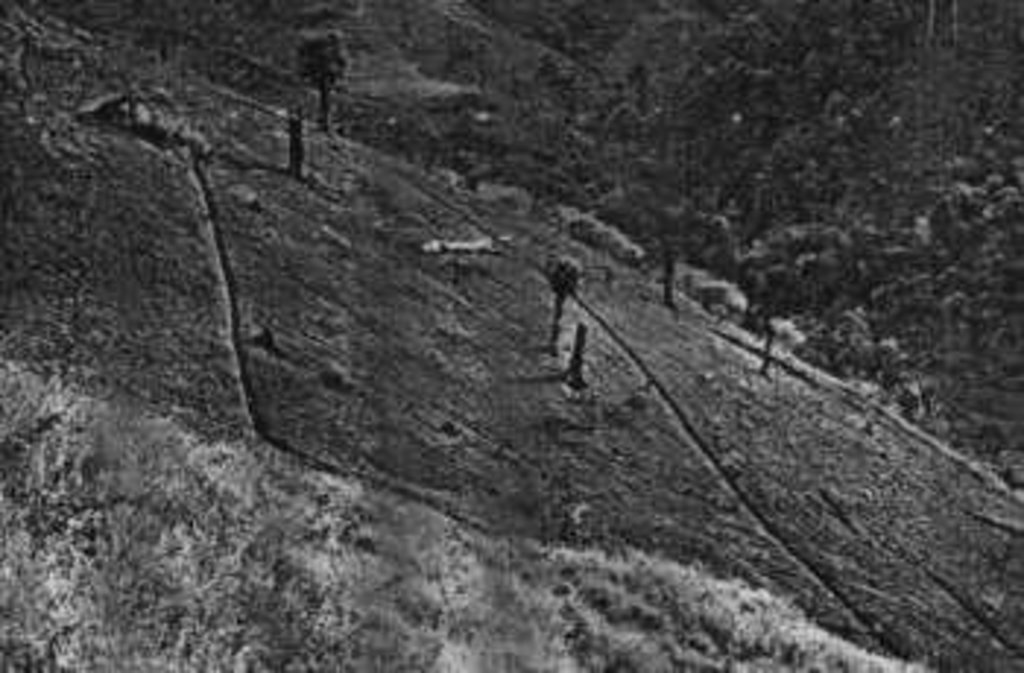
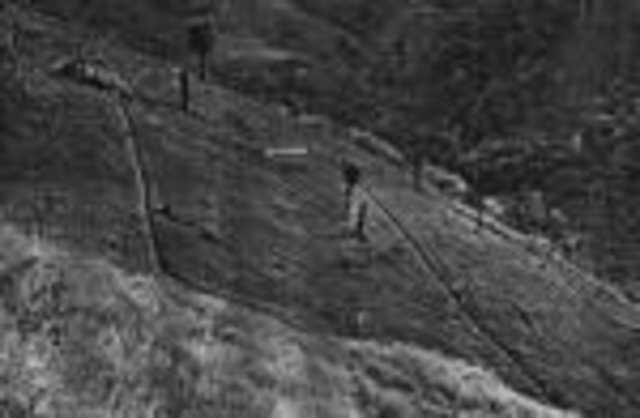
Cut-off drain is a drainage ditch dug to quickly drain water out of sloping agricultural land.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
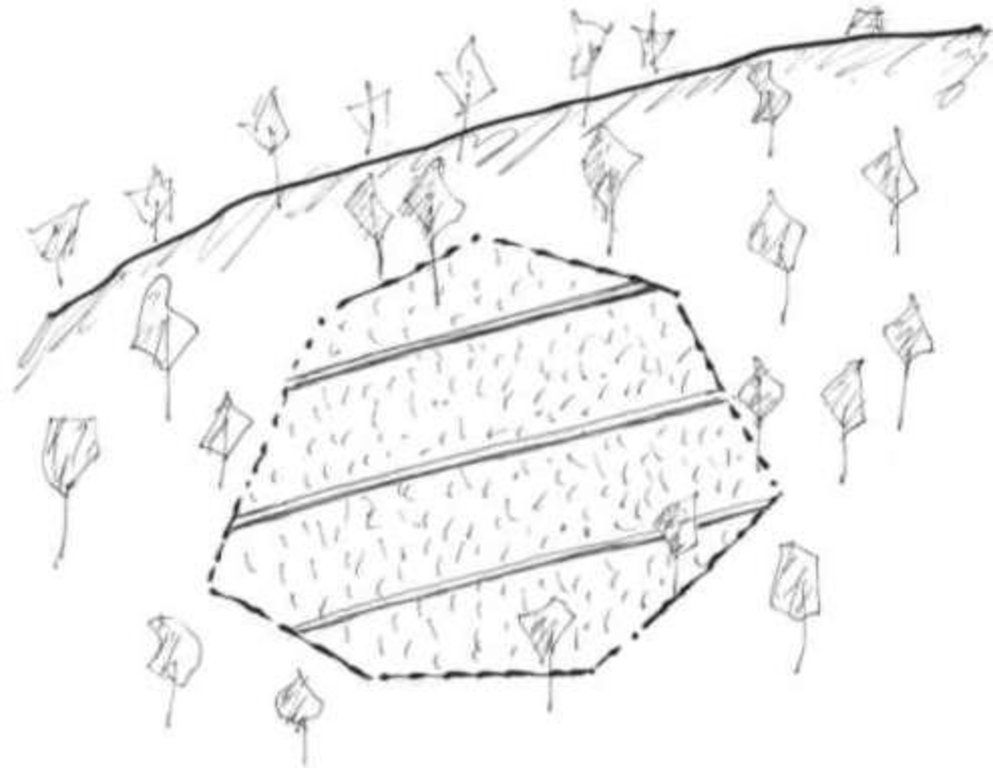
Description:
The cut-off drain is the same thing described as 'diversion' or 'diversion ditch'. It is dug by hand-hoe, only one hoe wide in the first year and may expand wider in the second and third year. It is dug with gradient from 15-50% to facilitate drainaing of runoff, not to scour the soil. Note: 1. The width of one hoe is approx. 21 cm , 2. The dimension of the ditch may become 30-40 cm wide and deep after 3 years.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Thaïlande
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Chiang Rai
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Amphur Mae Fa Luang
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
It is an original idea. No one knows how/when it was originated.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Maize
Major food crop annual cropping: Upland rice
Major cash crop mixed system: Maize
Major food crop mixed system: Upland rice
Major other crop mixed system: Fruit trees

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Nomadisme
- Semi-nomadisme/ pastoralisme
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. There is soil erosion problem because of high terrain, 2. Lacking of land ownership (The whole land area is reserved forest), 3. Low price of agricultural produce,
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Lacking of land ownership, 2. Land users do not have Thai citizenship; less than 20 % have ID cards (not citizenship).
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Aug Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Nov
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 15 m2.
E-kaw, Lahu, Lisu, Mien, Khin, Thai Yai, Haw Chinese, H'mong. They have been doing this practice for a long time. The technology transfers from generation to generation.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Lack of enforcement of legislation or authority
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural activities), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
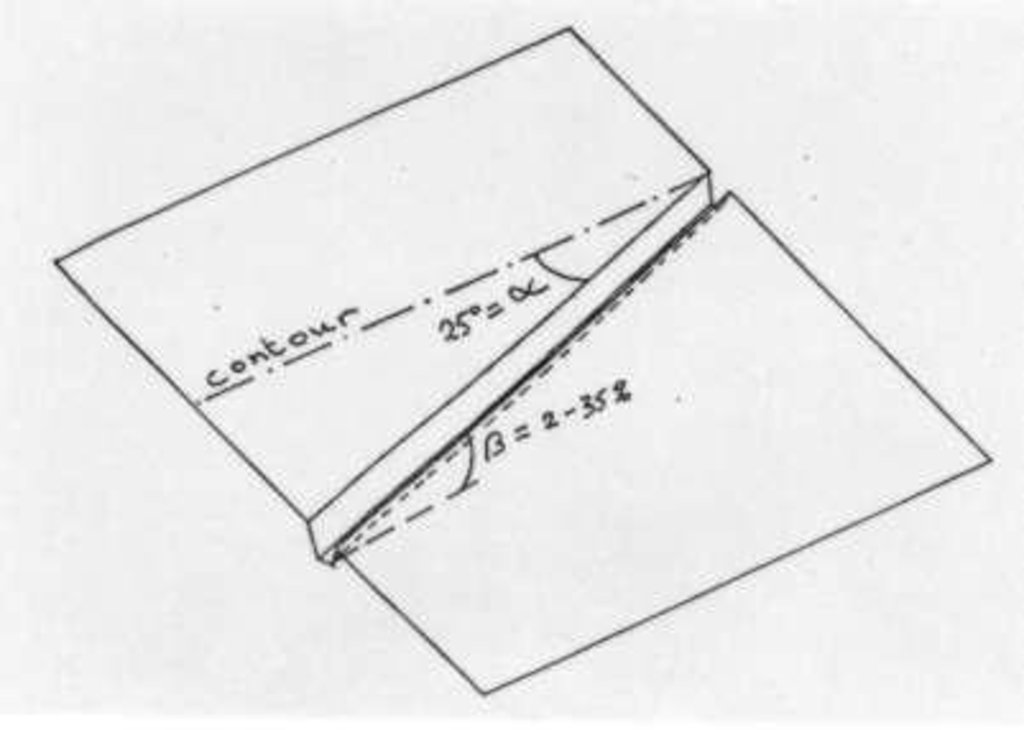
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Average slope properties of a cut-off drain.
The cut-off drain is the same as 'diversion'. It is dug by hand hoe, only one hoe wide in the firs yer and may expand wider in the second year and third year. It is dug with gradient in order to facilitate draining of runoff, not to scour the soil. The gradient may vary from 3:20 (15%) to 1:2 (50%).
Note: The land may be cropped for 3 years and left for shrubs to grow for some years. Then farmers return to clear the land to grow crop again.
Location: Average slope properties of a cut-off drain.. Chiang Rai Province
Date: 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Structural measure: Cut-off drain
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40
Construction material (earth): It is the earth dug in situ.
Lateral gradient along the structure: 20%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Baht
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
37,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.16
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the ditch after land preparation | Structurel | Before rainy season |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,32 | 4,32 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 4,32 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dredging up the earth that fell down when preparing for next crop | Structurel | Before rainy season/Annually |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,32 | 4,32 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 4,32 | |||||
Commentaires:
Cost per ha of land protected
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Steep slope will require larger number of the cut-off drains, thus affecting the cost.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average = 1600-1800 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Also shallow (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: High (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (good drainage though being clayey soil)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium and low (both ranked 1)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
6% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
24% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (Large proportion are poor).
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers spend much time doing wage earning labour jobs.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Ranked 1: 1-2 ha. Farmers may farm at 2-4 plots far apart from each other
Ranked 2: 2-5 ha
Ranked 3: 0.5-1 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production is not decreased.
qualité des fourrages
production de bois
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers don't mind
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
disparités économiques
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Drainage can function as a farm path
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Input constraints
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
20
Quantité après la GDT:
15
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
50
Quantité après la GDT:
10
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
diversité animale
diversité des habitats
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
800. 13% of the area covered
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 50-90%
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
800 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: When farmers understand the use of it they will do it.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| It can drain excess water from the field quickly, not to cause scouring of the field. |
| This T is cheap and simple to install in any field. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
It can drain excess water from the field quickly, not to cause scouring of the field. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When farmers get the idea, this T will be sustained/enhanced. |
|
This T is cheap and simple to install in any field. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cheapness and simplicity will make it sustained. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Land users do not see any disadvantages |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| This T may cause erosion of its own structure at the beginning. | Government agencies should help design the size and gradient of this T toi be properly used. |
| This T may cause erosion off-site especially when the drained water is allowed to flow directly to open land | Design and build waterway to receive the disposed water. |
| This T does not enhance soil fertility improvement | Try to use it along with other measures which improve soil fertility or change it to something else. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Pongsapich, A. Indigenous Technical Knowledge for Land Management in Asia. 152 pp.. 1998.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
IBSRAM, Bangkok
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Turkelboom, F. On-farm diagnosis of steepland erosion in Northern Thailand, PhD thesis. 309 pp.. 1999.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Laboratorium Voor Bodemvrucktbaarheid en Bodembiologie, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven,Kardinal Mercierlaan 92, B-3001 Heverlee,Belgium
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Cut-off drain [Thaïlande]
This approach is the 'way' or 'how' the cut-off drain has been implemented on steepland in northern Thailand.
- Compilateur : Samran Sombatpanit
Modules
Aucun module trouvé