Alliance Farming [Cameroun]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Blasius Azuhnwi
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Alliance Farming
technologies_3342 - Cameroun
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Jiedoh Duni
237 677828136
jeidohduni@gmail.com
MBOSCUDA
P.O. Box 221 Bamenda
Cameroun
Spécialiste GDT:
Sali Usmanu Mallam
237 674433655
saliusmanu@gmail.com
MBOSCUDA
P.O. Box 221 Bamenda CAMEROON
Cameroun
Spécialiste GDT:
Hammadu Bawuro Abubakar
675005574
abubawuro@gmail.com
MBOSCUDA
P.O. Box 221 Bamenda CAMEROON
Cameroun
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
In Search of Common GroundNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Mbororo Social and Cultural Development Association (MBOSCUDA) - Cameroun1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
03/12/2018
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Alliance farming refers to collaboration between crop farmers and pastoralists, who agree to use the same land and related resources (crop residues as fodder for pastoralists; dung as fertilizer for crop farmers) for their mutual benefit.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
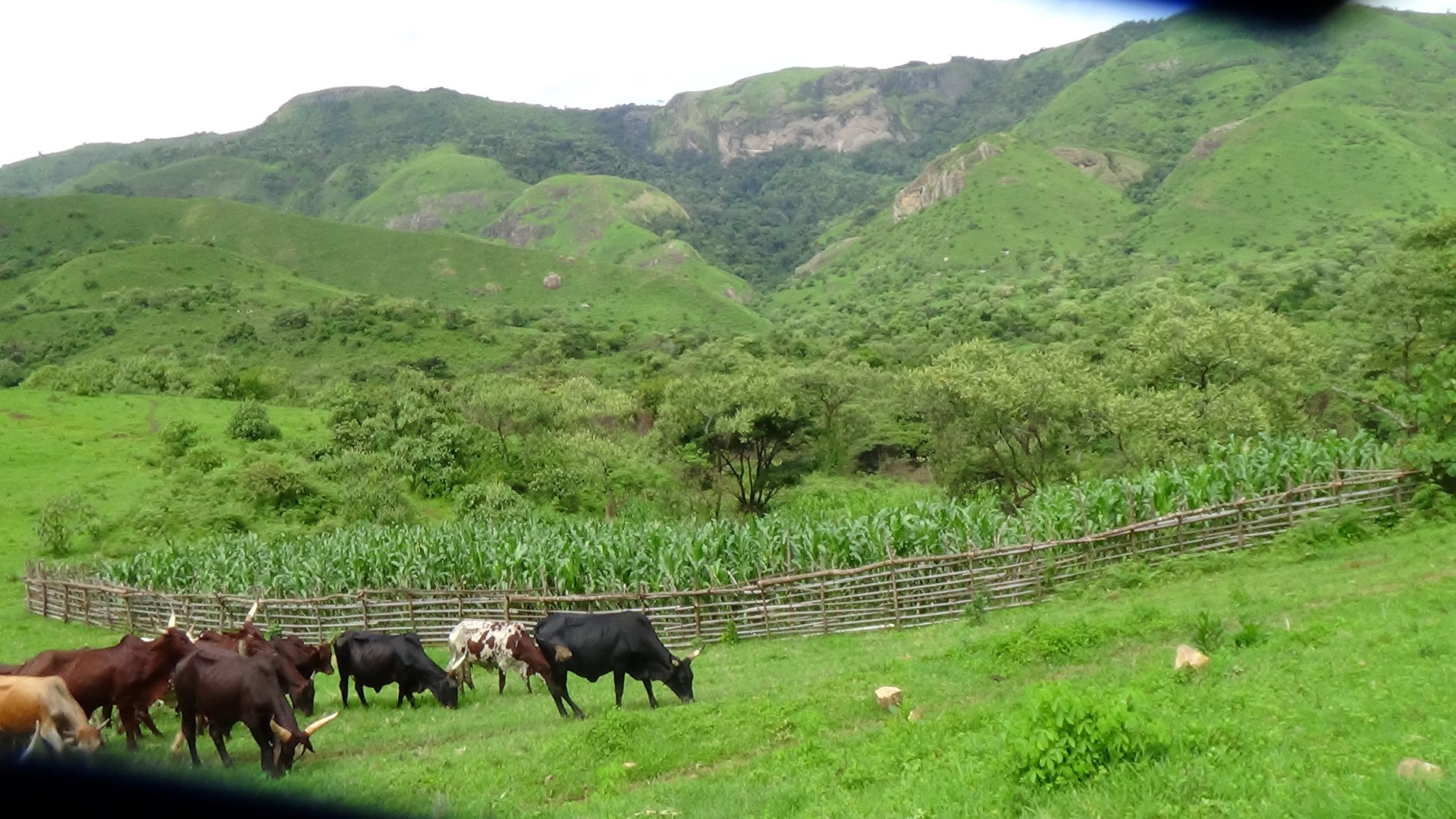
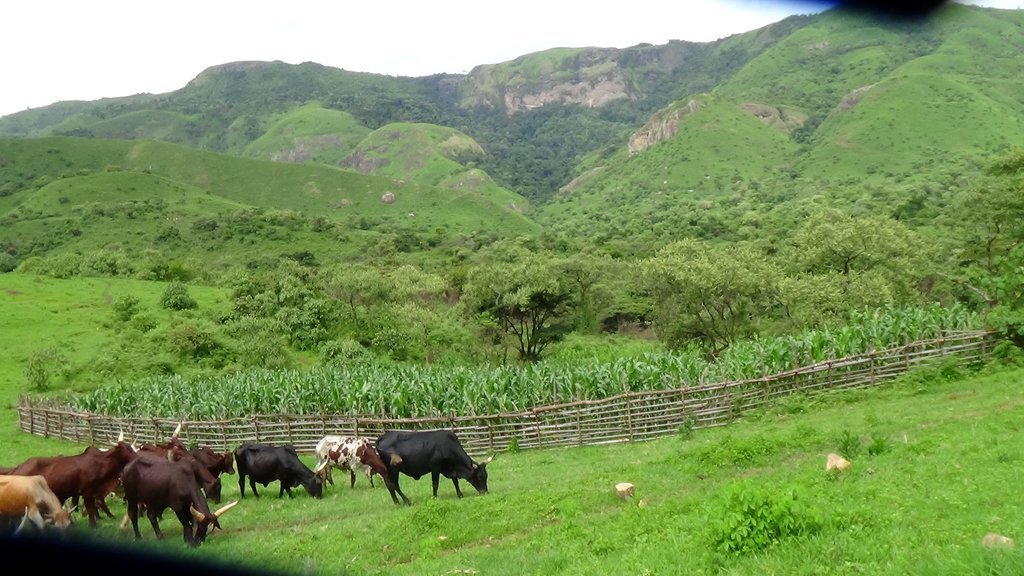
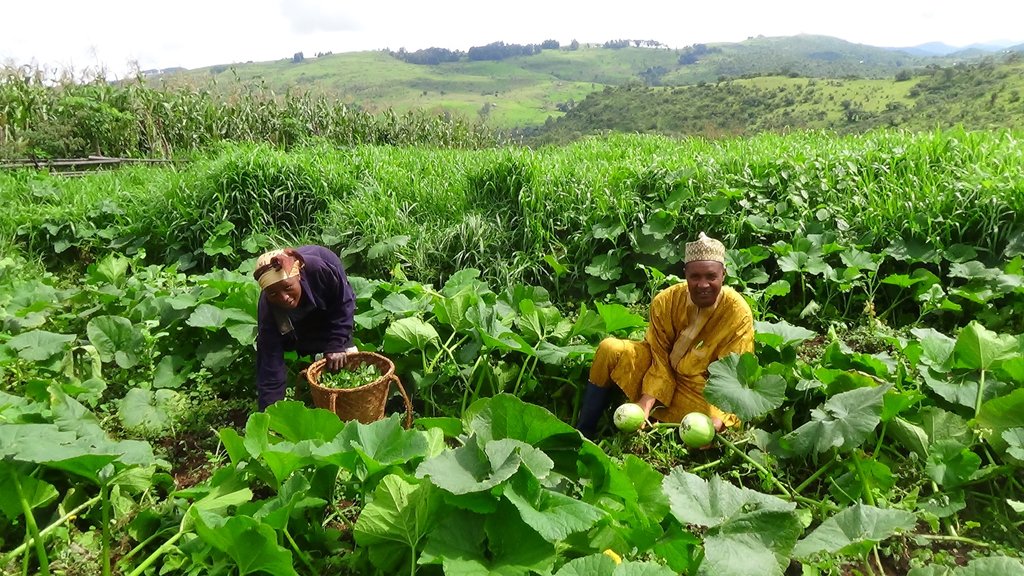
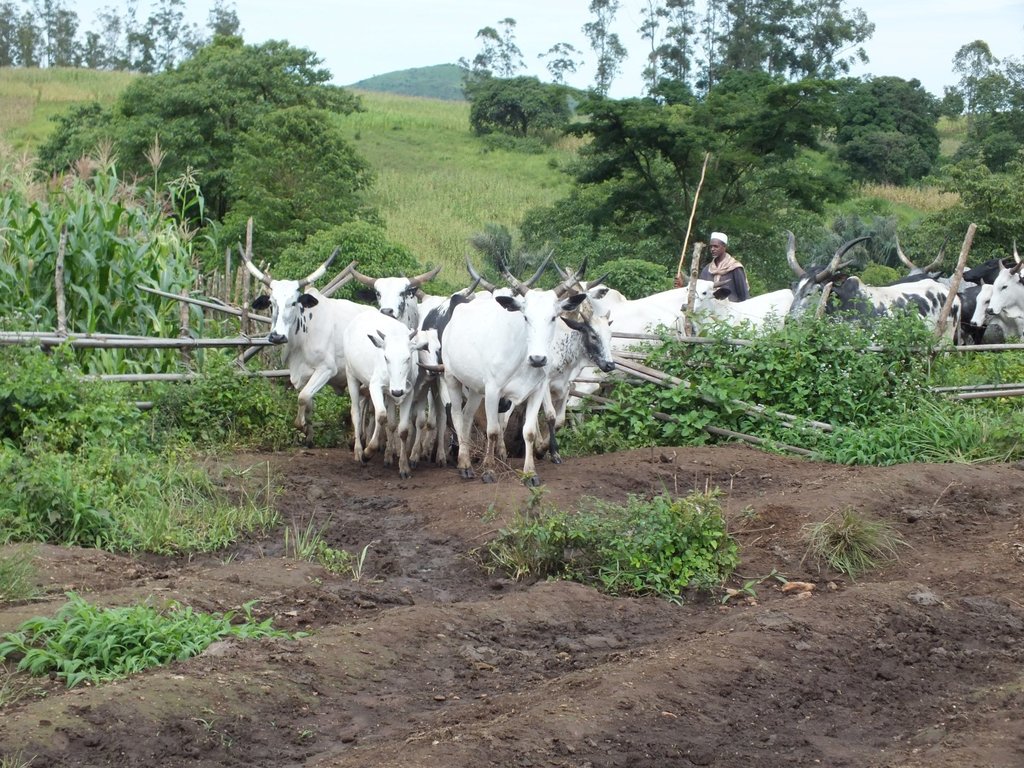
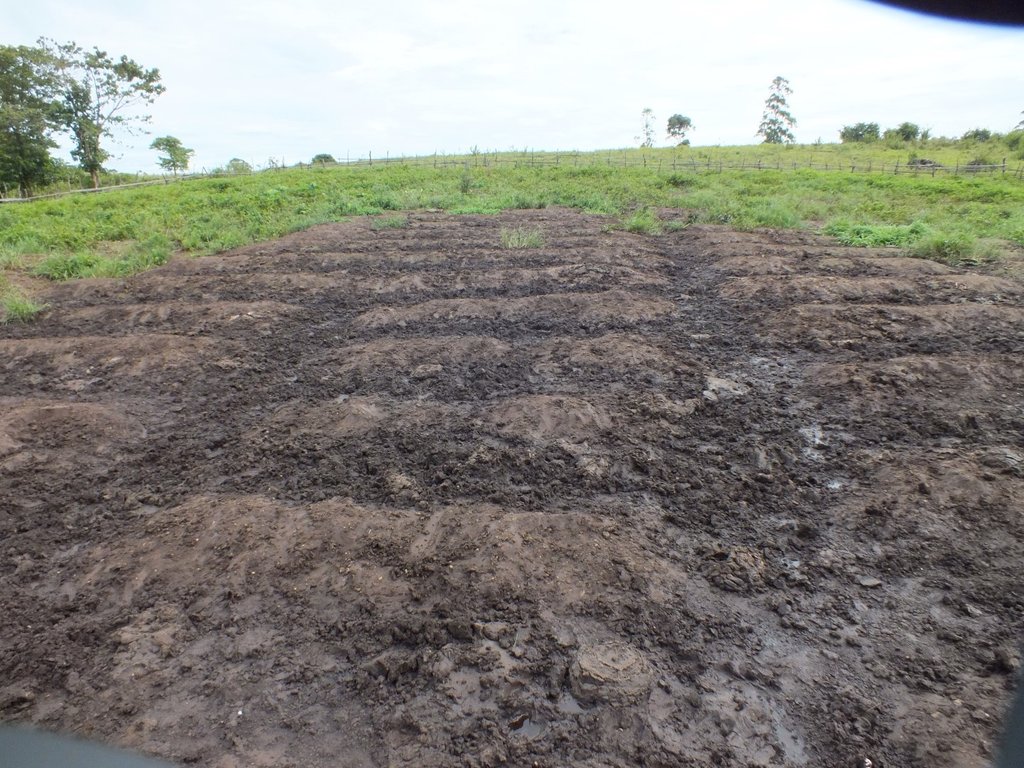
Alliance farming is partnership between pastoralists and subsistence farmers to share resources. They agree to use the same land and related resources sequentially: growing crops during the rains, and grazing cattle in the dry season. It is a further development of the conflict mediation process under which cattle are allowed to graze on cropland after harvest. The cattle consume crop residues and weeds (including some grass) on the farm and they produce dung and urine in turn, which increases nitrogen content and organic matter in the soil. This enhances its fertility and makes it more productive for the next round of crop cultivation. The crops grown are mainly annuals including maize, beans, soybeans and groundnuts. The livestock are mainly zebu cattle for beef (Bos indicus). There exists several variants (or components) of this arrangement: 1) The farmer constructs a night paddock (a corral) in farmland and invites pastoralists to kraal their animals in the paddock overnight; 2) The farmer arranges with the pastoralist to farm on areas where animals have been held overnight, in grazing land – and constructs a fence to protect the crops; 3) In communities where transhumance is common, the farmer allows a pastoralist to graze his cattle on crop residues remaining after harvest; 4) Pastoralists allow farmers to collect dung and apply it in their farms. Contracts for the most part are verbal and non-written, and each party counts on the good conscience and honesty of the other.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
4 different photos showing pastoralists and farmers who are benefiting from this technology have been provided.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
There are two videos of this technology available but each is about 125 MB and just too heavy to be uploaded on to this site.
Lieu:
n.a
Nom du vidéaste:
n.a
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Cameroun
Région/ Etat/ Province:
North West Region
Autres spécifications du lieu:
This approach has been piloted in 23 communities in the North West Region.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2011
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Some aspects of this technology were already in practise in the region over the decades but due the facilitation of Mbororo Social and Cultural Development Association (MBOSCUDA) this technology is being adopted now by many locals
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Nomadisme
- Semi-nomadisme/ pastoralisme
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Zebu cattle under extensive production which produce dung and urine.

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agro-pastoralisme
Principaux produits/ services:
Annuals such as maize, beans, soybeans and groundnuts, while livestock kept under extensive system of production produce dung and urine to enrich the soil.
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Land use is changing due to the use of this technology but this change is principally driven by the increasing demographics. Through the use of this technology, much more rangelands is being cultivated for crop production
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
This is a very low-input land use.
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Usually one growing season.
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
- gestion intégrée cultures-élevage
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
Presently common in pilot villages/communities.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol

pratiques végétales
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes
- V4: Remplacement ou suppression des espèces étrangères envahissantes

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M4: Changement majeur dans le calendrier des activités
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Some degraded land is being rehabilitated as pastoralists do invite farmers to come farm in the rangelands which have been invaded by braken fern. By tilling of the soil and removing the rhizomes in them, the spread of the invasive species is being put to check.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Auteur:
MBOSCUDA North West Region Cameroon
Date:
13/01/2018
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
• Alliance farming is an advanced outcome of the conflict mediation process whereby cattle are allowed to graze on crop lands after harvest.
• Livestock consume crop residues and weeds (including grass).
• When the land is used to paddock cattle, their manure and urine fertilize the soil making it more productive when the crop farmers return to cultivate.
• Crops are planted on the plot of land once the cattle are taken away.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
0.5 hectares
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
FCFA
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1500 FCFA
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmer harvests annual crop e.g. maize, beans | Agronomique | At the end of growing season which is usually in October |
| 2. | Farmer invites pastoralist to bring herd to graze off crop residues | Modes de gestion | After harvest of crops in Octorber |
| 3. | Cattle graze on crop residues and weeds on farm | Autres mesures | During grazing in the dry season from mid-November onwards |
| 4. | Dung and faeces passed out by animal increases N content of soil | Autres mesures | During grazing, mostly in the dry season mid-November to mid-March. |
| 5. | Pastoralist takes animals away from farm | Modes de gestion | At the beginning of the rains in mid-March. |
| 6. | Farmer then returns to till soil and plant annual crops in the field | Agronomique | At the beginning of the growing season by mid-March. |
Commentaires:
This is actually a low input technology.
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Land users bore all of the costs
Commentaires:
A low input technology.
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | n.a. |
Commentaires:
There are no maintenance costs.
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
n.a.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The only costs pertain to herding the animal to farmer's farm which is done by pastoralist or his a herder he has paid
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
It is a uni-modal in nature with rains coming in by mid March and going by mid October.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Institute of Agricultural Research for Development
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Sub-humid climate with mainly sudan savana characterized by undulating hills and short grass species interspersed with shrubs.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
- Semi-nomade
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The land users are predominantly resource poor livestock and crop farmers.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved soil fertility from dung and urine leads to increase crop production.
qualité des cultures
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved crop quality as little or no pesticides are used.
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increase fodder production from crop residues such as maize stover, legume haulms and sweet potato vines.
qualité des fourrages
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers do not use chemicals on the crops so quality of resulting crop residues is also good.
production animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The greater access that the livestock have to crop residues has led to increased animal production.
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The risk of production failure has decreased since farmers have increased the effective sizes of their farm holdings.
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production area has also increased as farmers have increase land area under cultivation mostly when they are invited to come farm in rangelands in order to till the soil and break the cycle of spread of invasive species
gestion des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better land management now with the same land put to multiple uses and more productive than previously i.e. when the two land uses were separated.
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farm income has increased from improved production and productivity of crops and animals.
diversité des sources de revenus
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Income sources have been diversified. With increased income from farms, farmers most especially are going for other off- farm enterprises such as petty trading.
disparités économiques
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Economic disparities are being bridged because of the increased income from either livestock production or crop farming.
charge de travail
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Workload is also being eased as farmers and pastoralists are witnessing improved crop and livestock productivity. Farmers, especially, do not have to bring much more new land under cultivation.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Food self-sufficiency of alliance farming practising families has improved from the increase in production.
situation sanitaire
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From the improved income as a result of increased production and productivity, alliance practitioners have more disposal income to take care of medical bills.
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land use rights especially of pastoralists has improved since farmers now acknowledge that pastoralists do own land. Pastoralists, due to their late arrival in the region, are looked upon as 'strangers' by their farming neighbours. However this perception is changing because of the positive engagement between the these two main land users.
opportunités culturelles
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase cross-cultural dialogue within the community: pastoralists are predominantly Moslems while crop farmers are mainly Christians.
institutions communautaires
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Community institutions like the Dialogue Platforms have been strengthened, as they have grown in recognition among community members as a low- stake solution to resource use conflicts.
institutions nationales
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agro-Pastoral Commissions, which are the statutory bodies adjudicating conflicts between farmers and pastoralists, have come to see effectiveness of the Dialogue Platforms and are incorporating the Alternative Conflict Management practices in their modus operandi.
apaisement des conflits
Quantité avant la GDT:
-2
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There has been a great decrease in the number, frequency and intensity of the conflicts as the two sets of land users have seen good reason to collaborate instead of antagonize each other.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The self-esteem of the Mbororos who make up the majority of pastoralists community has been improved through this positive engagement with farmers.
Impacts écologiques
Sols
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Nutrient cycling has improved as dung and urine are returned to improve soil fertility and help subsequent crops.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Soil organic matter has also being improved from the increase crop residues which animals do not eat all.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase soil fertility has meant increase crop cover
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase crop yields also mean increase crop biomass
diversité végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Plant diversity has been somewhat increased due to fertile soils make it possible for different plant species to grow
espèces étrangères envahissantes
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The spread of alien species such as bracken fern on rangelands is being controlled since farmers are being invited by pastoralists to come and cultivate crops on rangelands. The tilling of the soil is a good mechanical method of controlling the spread of these invasive species.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Commentaires concernant l'évaluation des impacts:
n.a.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | pas bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | décroît | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| averse de grêle locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| canicule | pas bien |
| sécheresse | pas bien |
| feu de végétation | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Catastrophes biologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| infestation par des insectes/ vers | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Growth of the crops most especially will be affected by climate change events such as droughts or too much rainfall. The crops are C4 crops and so will get very little benefits predicted rise in temperatures associated with climate change.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
More than 800 alliance farming pairs have been facilitated by this process.
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
Farmers have not received any incentives from project in order to adopt this.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Technology leads to increased crop yields because of the improved soil fertility. |
| Technology leads to improved crop quality because of the use of organic manure and less chemicals fertilizers. The use of chemical fertilizers can lead to leaching of inorganic nutrients into ground water, and also eutrophication of water bodies. |
| It has led to stronger social relationships between farmers and pastoralists. |
| Invasive species such as Pteridium aquilinium (bracken fern) that has invaded rangelands is being controlled. Tilling of the farms is a mechanical method of stopping its growth and spread. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
More productive use of land than when two land uses were separate. |
| More environmentally friendly since organic manure is being used. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The ratio of pastoralists to farmers is really low (about 1:6) meaning that there are not many pastoralists to form Alliance Farming pairs with willing farmers. | Increasing herd sizes to ensure more production of manure could alleviate this problem. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Agreements are verbal. | Formalizing the contracts. |
| Some variants of the technology, for example that in which pastoralists allow farmers to collect dung to go to farm in another area may lead to nutrient export. The dung does not contribute to improve the fertility of the soil where it was collected but does so at a different site where farming will take place. There is no net loss of nutrients out of the whole system though. | Transportation of dung to different sites should be discouraged. Farming should take place as much as possible on the farm that supplied crop residues to feed the animals. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
4 field visits were done.
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
About 30 people were contacted during focus group discussions and key informant interviews.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
4 SLM specialists were contacted.
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Secondary data sources were consulted.
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
MBOSCUDA Searchlight Magazine Vols 1, 2,3. 2014, 2015, 2016
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Free copies
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Blasius Azuhnwi and Fiona Flintan (2017)- Making Rangelands Secure, Issue Paper 8, Rangelands Series
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
From ILC Rome for free
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
n.a.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé