Level ditches in cropland [Slovaquie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Zuzana Studvova
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Záchytné pásy na poľnohospodárskej pôde (Slovak language)
technologies_1666 - Slovaquie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Slovak University of Technology (Slovak University of Technology) - Slovaquie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river … [Slovaquie]
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
- Compilateur : Zuzana Studvova
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
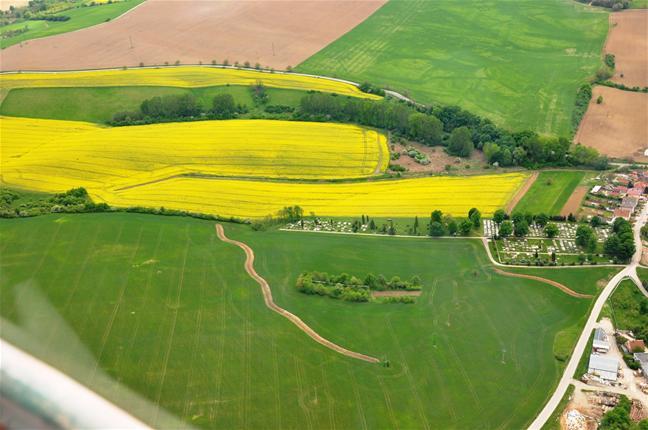
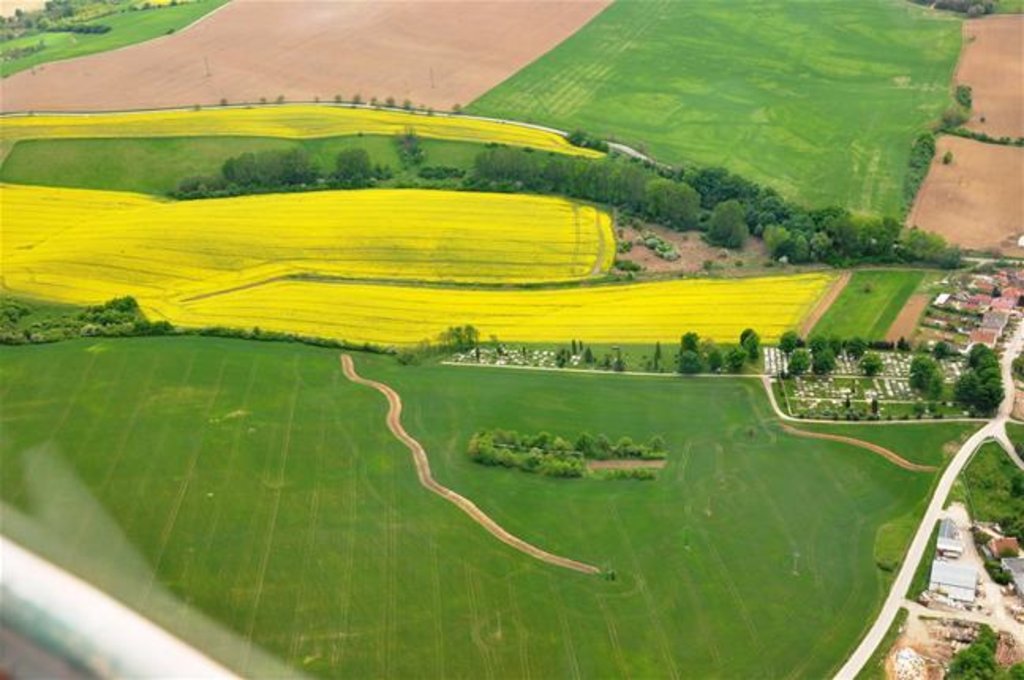
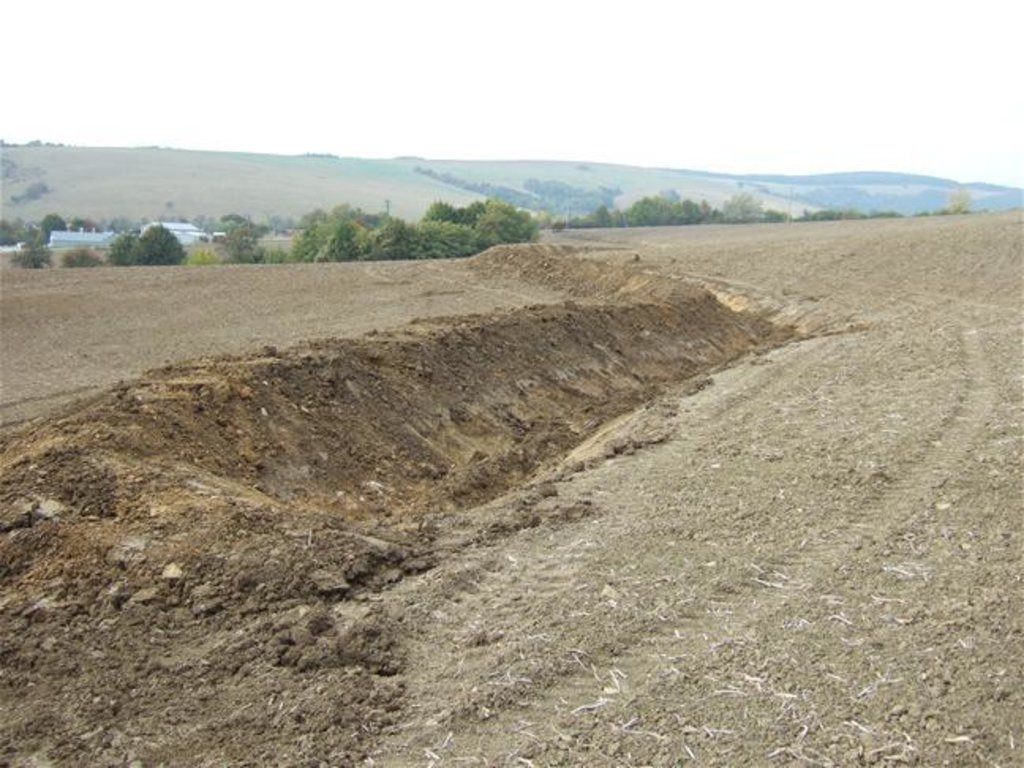
Conservation measures for eroded cropland. The technology contains level ditches of various lengths, which are digged along a contour.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The structural measures are characterized as small technical structures to control and slow down surface runoff, created after extreme rainfall. The ditch is digged across the slope (along the contour) according to the terrain. Along the four of dithes there were also vegetative strips that should protect and retain rainfall.
Purpose of the Technology: Some damage has been observed on the farmland during storm rainfalls, long-lasting rainfalls, and periods of melting snow. The aim of the conservation measures is to eliminate hazards and damage to health and the economy, to improve the accumulation and infiltration of water into the soil, and to retard the surface runoff on the farmland.
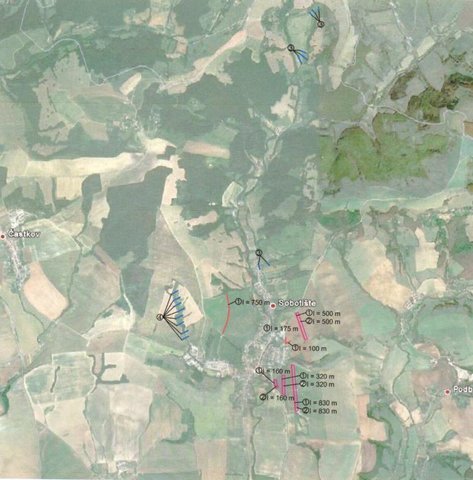
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are 7 ditches in the area (2842 m in total/ 23873 m3). In the locality of Padelky there are level ditches with lengths of 160 m + 320 m+ 830m = 1310 m; in the locality of Kubíny there are level ditches with lengths of 500 m + 100 m + 175 m = 775 m; in the locality of Šlachovec there is one ditch with the length of 750 m. The total water retention volume is 23873 m3. The ditches are in the shape of a trapezoid with a base width of 1 m, a height according to the terrain, and a slope of 1:1.5 while the digged soil is moved to the lower part of the ditch.
Natural / human environment: Sobotište is a village in the Teplica river basin; it is situated near the town of Senica in the Trnava region of western Slovakia. It is located in a valley at the foothills of the White Carpathians, which are part of the Carpathian Flysch Belt. The sedimentary flysh rocks are erodible, disintegrable, and sensitive to erosion.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Slovaquie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Slovakia
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Sobotište
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12.4 km2.
Total area of the cropland cover is 12.37 km2 and the eroded area was estimated as 40 % (4.948 km2). This technology is used in the locality of Padelky and Kubina. Together 7 ditches were built. The area of the village 32.3 km2.
Map
×3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures oléagineuses - tournesol, colza, autres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April to September
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major problem is surface runoff that is formed by extreme rainfall whereby tillage, gully,or interrill erosion is forming.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There are some soil threads connected with erosion probably due to agricultural practises and heavy mechanism that are visible e.g.: people had noticed a decrease of the hills peak that is tilled. Some problems with sediments occured after heavy rains, mud flowing directly to the city (cemetery, roads etc.) from the surrounding hills and fields.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Slope in connection with heavy rainfall results in surface runoff that causes erosion and mud floods in the part of the city and nearby roads), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (mud flows)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (tillage along the slopes, deep tillage), land tenure (Land belongs to private owners and there is often a problem to get permission to use their land for other purposes, or to built conservation measures. The process of land consolidation is too long.), governance / institutional (Legislation: The financial support from the state is mainly focused on flood protection for the main rivers.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
There are 7 ditches in the area (2842 m in total/ 23873 m3). In the locality of Padelky there are level ditches with lengths of 160 m + 320 m+ 830m = 1310 m; in the locality of Kubíny there are level ditches with lengths of 500 m + 100 m + 175 m = 775 m; in the locality of Šlachovec there is one ditch with the length of 750 m. The total water retention volume is 23873 m3. The ditches are in the shape of a trapezoid with a base width of 1 m, a height according to the terrain, and a slope of 1:1.5 while the digged soil is moved to the lower part of the ditch.
Location: Sobotište. Myjava, Slovakia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): -
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): -
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): -
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): -
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 40
Other species: Red clover, seeded along the ditch
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): various, 2842 m in total
Construction material (earth): The excavated earth is placed on the lower part and mechanically compacted to hold retained water.
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 23873m3
Catchment area: 12 ham2
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Eur
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
0,88
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the ditch for 600 mm width | |
| 2. | Adjustment of the ditch´s embankment | |
| 3. | Digging of the ditch for 600-2000 mm width | |
| 4. | Digging of the ditch for over 2000 mm width | |
| 5. | expert guarantor and planner | |
| 6. | Transfer | |
| 7. | Vegetative strips next to the ditch in 40 m width. Red clover. | spring |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Digging of the ditch for 600 mm width | m3 | 9,9 | 18,14 | 179,59 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Adjustment of the ditch´s embankment | m2 | 3861,0 | 0,82 | 3166,02 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Digging of the ditch for 600-2000 mm width | m2 | 5253,0 | 10,24 | 53790,72 | |
| Main d'œuvre | or Digging of the ditch for over 2000 mm width | m2 | 5253,0 | 1,26 | 6618,78 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds for vegetative strips next to the ditch in 40 m width. Red clover. | kg | 704,0 | 8,15 | 5737,6 | |
| Autre | expert guarantor and planner | person | 1,0 | 3062,61 | 3062,61 | |
| Autre | Transfer | t | 58,655 | 46,11 | 2704,58 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 75259,9 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 85522,61 | |||||
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Together 7 ditches were built in the study area (1240 ha of cropland). The prices and costs were available as a summary for whole project, therefore the prices correspond for all 7 ditches together. Each of the ditches were slitly different (e.g., the length). The prices are valid for the year 2011. The prices are mostly given for m3 as a unit. (The prices were calculated with the 20% VAT)
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The costs differ from project to project, it depends on the design, building company atc.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Flat (59%), gentle, (23%) and moderate (9%)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (75%), shallow (17%) and very shallow (5%)
Soil texture is coarse/light (34%), fine/heavy (12%) and medium (5%)
Soil fertiliy is medium
Top soil organic matter is unknown
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is unknown
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table is unknown
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
- commercial/ de marché
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: no.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 16%
Off-farm income specification: unknown
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
There are 485 permanently occupied dwellings (2001)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Impacts socioculturels
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology decreased risk of the mud flows that are capable of destroying homes, washing out roads, knocking down trees, and obstructing roadways.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Sols
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Autres impacts écologiques
Risk of mud flood
Hazard towards averse events
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced risk of flooding and damage of the gardens and household.
Reduced the hazards and damage of the surrounding area by heavy rainfall events.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
There were no maintanance required so far.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The implementation of the technology was founded by the state (subsidy).
Comments on adoption trend: UNknown
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The technology shows to be effective, however the rainfall events that have occured so far were not that extreme as before the implementation. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The technology is easy to realize. There is no extra knowledge required. The mechanism used to implement the technology is easy to provide. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The land users are satisfied with effectivness of the technology. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| I don´t see any disadvantage or weekness of the technology. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Project documentation, Hydrotechnológia Bratislava, s.r.o., April 2011
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
URL:
http://www.obecsobotiste.sk/Vodozadrzne-opatrenia.aspx
URL:
https://www.nku.gov.sk/documents/10157/19a2305b-d9c2-43a7-8262-743650db289b
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river … [Slovaquie]
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
- Compilateur : Zuzana Studvova
Modules
Aucun module trouvé