Mainstreaming river water to facilitate irrigation in Barind [Bangladesh]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Udo Höggel, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Sharmongla Sech Prokolpo.
technologies_5171 - Bangladesh
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Establishing National Land Use and Land Degradation Profile toward Mainstreaming SLM Practices in Sector Policies (ENALULDEP/SLM)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Department of Environment (DoE) - Bangladesh1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
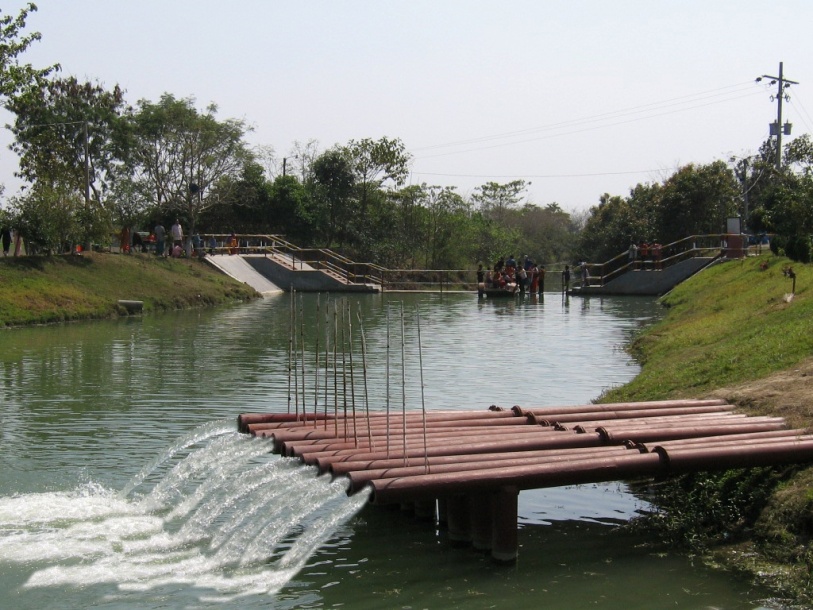
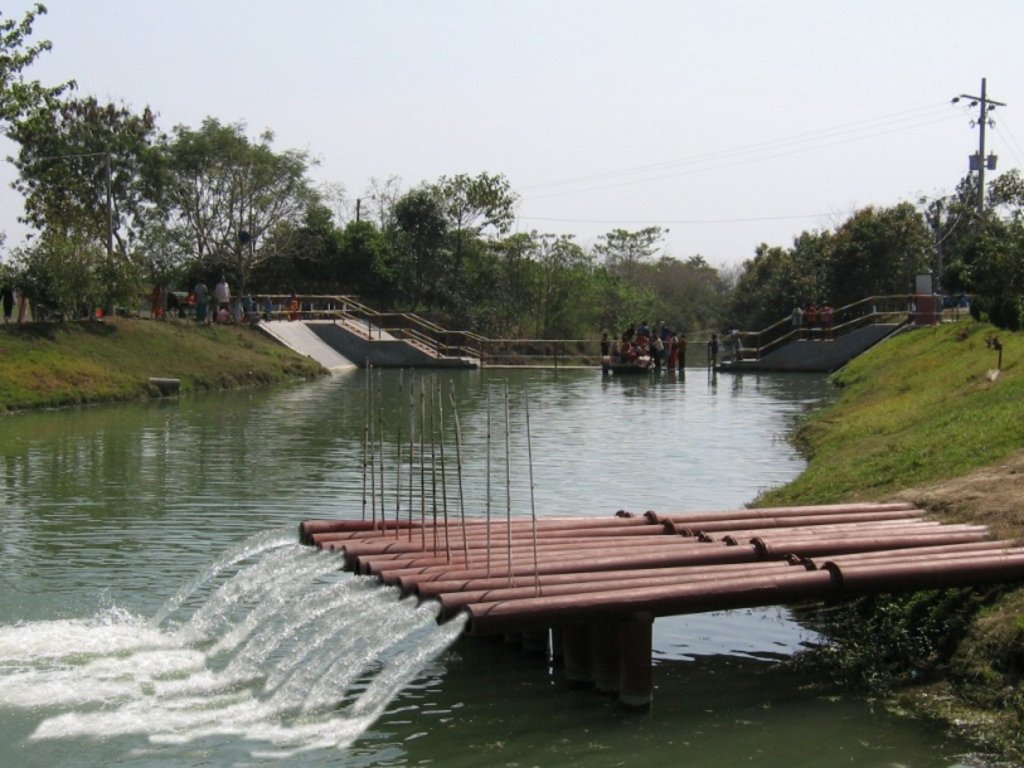
The technology promotes the lifting of river water by pump sets and conveys the water through buried pipelines to a canal. The conserved canal water is used for irrigation delivered by low lift pumps (LLP). Because water is held in the canal it revitalises the ecosystem along its length. Furthermore, using river water for irrigation avoids dangers associated with groundwater depletion.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
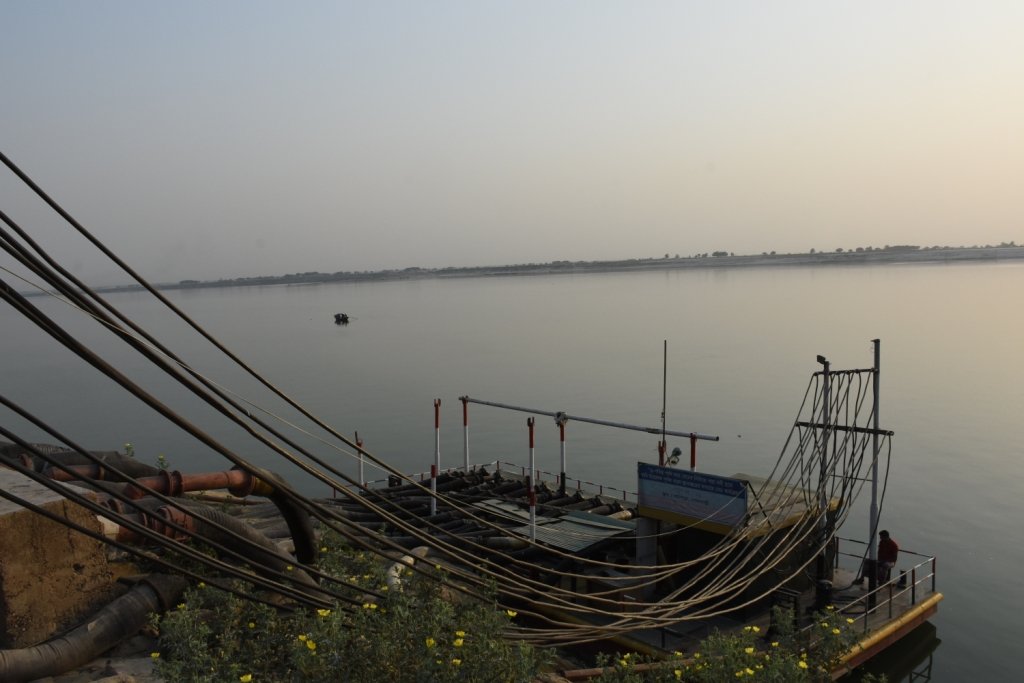
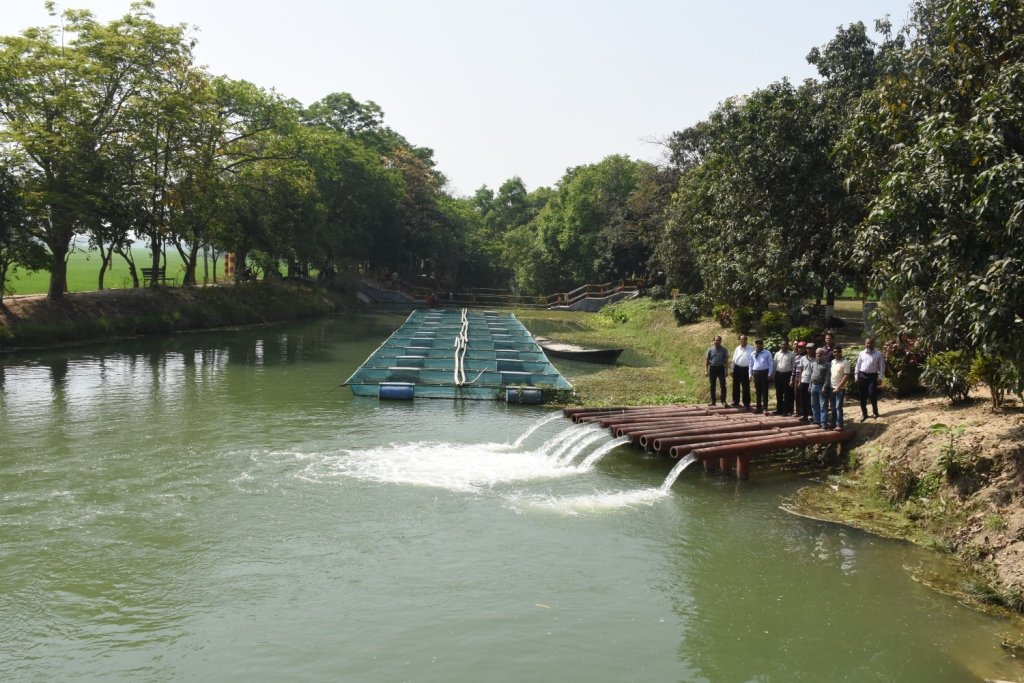
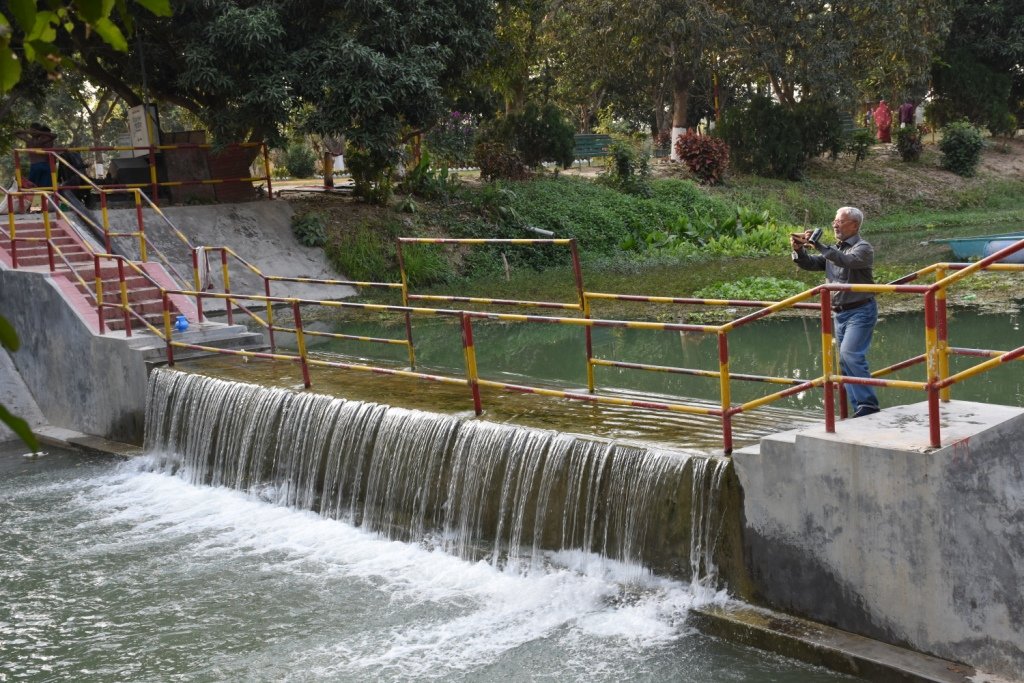
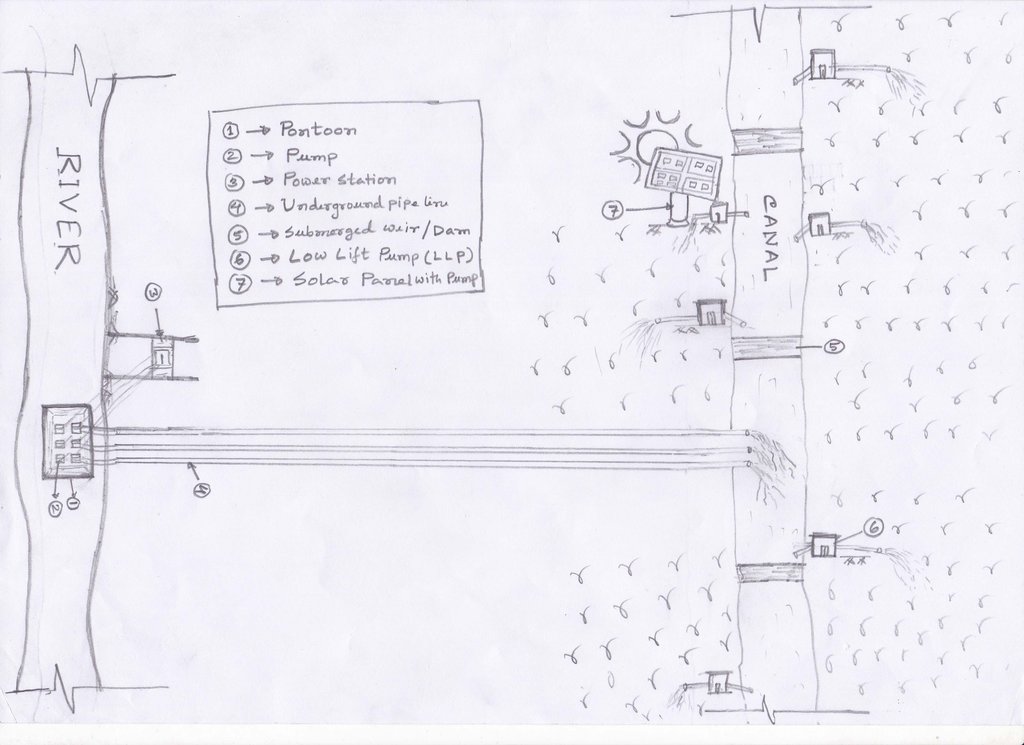
The project is sited at Sharmongla under Godagari Upazilla of Rajshahi district. The Sharmongla canal is located about 3.5 km away from the Padma river. Its total length is 29.0 km. Under this technology, water is lifted from the Padma river by pumps set on a pontoon. The lifted water is then discharged to a canal through underground pipelines. The water so discharged is lifted to the crop fields (delivery points) for irrigation. The elevation difference between the delivery points and the sourcing river is about 21 m. There are numbers of submerged weirs/dams constructed across the canal at different locations for conserving water: the water then helps regenerate the ecosystem along its banks and enriches the habitat.
Pontoon at a glance:
•Year of construction: 2004
•No. of centrifugal pumps at pontoon: 12
•Pump capacity: 50 m lifting height.
•Power of each pump: 60 HP
•Capacity of each pump: 2.5 cusec
•Total capacity of pump sets: 30 cusec
•Capacity of electric sub-station: 750 KW
•No. of discharge pipelines: 12
Sharmongla canal at a glance:
•Length of the canal: 29 km
•Average width of the canal: 15 m
•Average depth from ground level: 5 m
•No. of submerged weirs and dams within the canal: 14
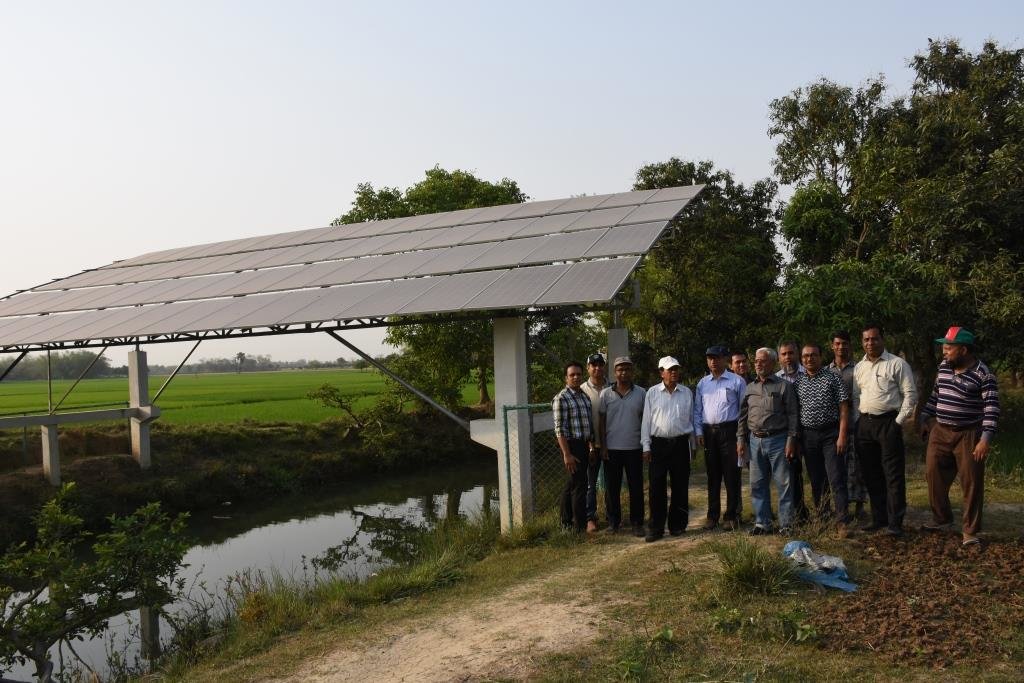
•No. of LLP (low lift pump): 27 electrified and 6 solar pumps
•Total irrigated area: 1850 ha
•Benefiting farmers: 5330
•Harvest yield of rice per year: 20,500 metric tonnes (approx.)
•Afforestation on the canal bank: 65,500 trees
Purposes/objectives of the technology:
•The main purpose of the said technology is to provide water for irrigation. This prevents abstracting of groundwater, which has adverse effects on the environment: therefore this system is environment friendly.
• Enhancing groundwater recharge thereby supports ecosystem function.
•The storing of river water in irrigation canals supports the enrichment of the habitat.
Approach for implementing the technology:
There was no irrigation facility for crop production in this drought-prone area. Government officials came to the locality, discussed with the local community, elites, as well as the farmers. Finally, the local community was convinced about the technology. Then the irrigation system could be implemented in the area. On seeing the success of the technology, the same has been replicated on approx. 9400 ha. in Barind area, benefitting approx. 32,200 farmers.
Maintenance of the technology:
In case of problems, the respective mechanic of that area informs the Assistant Engineer through the Sub-Assistant Engineer. Thus the problem is solved by their own initiative. It is also monitored by the Executive Engineer of the respective District, and finally by the Executive Director from the headquarters if needed.
Crop cultivation:
Due to the application of the technology, previously fallow land has come under cultivation/irrigation facilities, mono-cropped land has been converted into multi-cropped land. Different crops, like rice, wheat, maize, mustard, pulses, potato, tomato, spices and other vegetables are cultivated.
Farmers’ acceptance:
The technology has been well accepted by the farmers, as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation and different crops are now being cultivated year-round.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Date:
25/03/2019
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bangladesh
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The following project were providing the irrigation facilities in Barind region:
i) SEMP - Sustainable Environment Mgt. Project
ii) RWCP - Rain Water Conservation Project
iii) EIBA – Extension of Irrigation in Barind area through conservation water in canal
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
- Irrigated rice (Paddy
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 3
Précisez:
Rabi-Pre-Kharif- Kharif
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Mango with rice,
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Major crop rotation is Boro (winter rice) - Transplanted Aman, Minor crop rotations are Potato-Boro- Tasplanted Aman, Rabi crops (mainly vegetables)- Boro- Transplanted Aman
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Mango and rice
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Non
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
- S7: Collecte de l'eau/ approvisionnent en eau/ équipement d'irrigation
- S10: Mesures d'économie d'énergie

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
- M3: Disposition/plan en fonction de l'environnement naturel et humain
Commentaires:
There are two stages of harvesting water.
1 - from river water, which is not going directly to the field
2- water reserved in canals and supplied to the field
Para S10 - refers to saving conventional electricity by using solar power for distribution of water to fields
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
- Hq: baisse de la qualité des eaux souterraines
Commentaires:
Barind was driest part of Bangladesh. It was enhanced when groundwater abstraction increased to support cropping by irrigation. The reduction of the groundwater table enhanced the dry out of dug wells, which supported domestic consumption. Hence, aridification was prominent in the area. It is reported that after the application of this technology, there are indications of recharging of the groundwater. Due to the increase in vegetation, the local temperature tends to be cooler than before.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
This technology helps reducing land degradation through using river water rather than groundwater for irrigation, thereby
preventing land degradation through increasing the vegetation cover on land.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
1. Pontoon: Length 55 ft, Width: 25 ft, Height: 4.50 ft
2. Centrifugal pump (12 nos)—each pump 60 HP,capacity-2.5 cusec, pump head: 50m
3. Electric power station capacity: 750 KW
4. Underground water distribution line (12 nos): Length of each line is 3.50 km
5. Length of water storage canal (Sharmangla canal): 29.0 km (average width 15.0 m and depth 5.0 m)
6. Nos of submerged weir/dam to reserve water in the canal: 14 nos
7. Nos of LLP (electrified) to lift water from the canal to crop field through buried pipeline : 27 nos
8. Nos of solar pump to lift water from the canal to crop field through buried pipeline: 06 nos
9. Nos of Prepaid meter for collecting irrigation charges (Revenue): 33 nos
10. Irrigated area: 1850 ha
11. Construction materials:
-Pontoon: A kind of platform that float on water made of Mild steel sheet, Stainless steel etc.
- Power station: Transformer, electric pole, wire etc.
- Distribution line: mild steel and PVC pipe
- Dam/Submerged weir: steel bar, cement, sand, brick, stone etc.
Auteur:
Sayed Zillul Bari
Date:
25/03/2019
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
1 Pontoon, Pumps, Pipes, weir construction etc
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
Pontoon (Length 55 ft, Width: 25 ft, Height: 4.50 ft) is a platform build on iron sheets, that can float on river, where pumps were set. The pipes for water delivery were of PVC. Water canal in this case compiler referred to canals of Barind which were ephemeral. Now water reserve for year round use.Piping system includes PVC pipe to convey water to the field, where a valve was set to control water disposal. There is a pipe of 12 inch dia to maintain water head through out the system.
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
BDT
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
85,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
800 BDT
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 60 days |
| 2. | Pumps installation on the pontoon | 30 days |
| 3. | Construction of underground water distribution line | 70 days |
| 4. | Re-excavation of derelict canal | 120 days |
| 5. | Construction of submerged weir / dam | 180 days |
| 6. | LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 150 days |
| 7. | Solar pump installation (06 nos) | 45 days |
| 8. | Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges (33 nos) | 30 days |
| 9. | Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 120 days |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matériaux de construction | Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 1 | 1,0 | 5000000,0 | 5000000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Construction of underground water distribution line | 1 | 1,0 | 27800000,0 | 27800000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Construction of submerged weir / dam | 1 | 14,0 | 1600000,0 | 22400000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Re-excavation of derelict canal | 1 | 1,0 | 29000000,0 | 29000000,0 | |
| Autre | Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges | 1 | 33,0 | 243000,0 | 8019000,0 | |
| Autre | Solar pump installation | 1 | 6,0 | 2000000,0 | 12000000,0 | |
| Autre | LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 1 | 8,0 | 2700000,0 | 21600000,0 | |
| Autre | Pumps installation on the pontoon | 1 | 12,0 | 1833000,0 | 21996000,0 | |
| Autre | Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 1 | 1,0 | 23100000,0 | 23100000,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 170915000,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 2010764,71 | |||||
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de la mise en place de la Technologie:
1439,02
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
none
Commentaires:
Labor costs etc all included in construction, pipeline installation etc.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1/5years |
| 2. | Pump repair and maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 3. | Distribution line maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 4. | Power station repair and maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 5. | Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance | 1/5yrs |
| 6. | LLP repair and maintenance | 2/yr or as and when necessary |
| 7. | Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1/6yrs, as and when necessary |
| 8. | Prepaid meter repair | 2-3/yr |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | Prepaid meter repair | 1 | 0,2 | 100000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 0,05 | 0,05 | |
| Autre | Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 500000,0 | 500000,0 | |
| Autre | Pump repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Autre | Distribution line maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 75000,0 | 75000,0 | |
| Autre | Power station repair and maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Autre | Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1,0 | 200000,0 | 200000,0 | |
| Autre | LLP repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 915000,05 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 10764,71 | |||||
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
11,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Land users share their participation in kinds and allowing installation of pipelines and other infrastructure
Commentaires:
Land users were trained and they provided land for infrastructures. For example space for outlets and underground pipe installation. Practically they did not contribute any cash.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Pontoon construction, power supply and lining of the underground piping system.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1600,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Most of the rainfall events happen during May to October
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Agroecological region 26
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
High Barind tract, mainly dissected (Closely & Broadly) terrace, soil pH is acidic, low in Nitrogen content, low CEC
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Area is above flood level
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
Yes. The farmers of Barind are of wide range. The large farmers are basically absentee. Medium range farmers engage themselves in their land and in addition they rent land from large farmers. So there is complex ownership.
This was from field feedback.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- loué
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
qualité des cultures
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production animale
risque d'échec de la production
diversité des produits
surface de production
gestion des terres
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
qualité de l'eau potable
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
At present land users are used to grow high water demanding crops. For example Boro paddy and potato both crops require large volume of water and the irrigated area slowly increasing, that situation demand of irrigation water increasing.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The supply of agricultural inputs increased and channelized through deploying dealers etc. Hence expenses relatively decreased
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
disparités économiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Basically in this area could be grouped in to two. One group has almost no land and previously they have to migrate beyond barind area as labor and they were poor. At present they have job (agri-labor or otherwise) in their area and become more solvent then past 90's. On other hand the second group cultivate the land of their own or leased, which they could not in 90's. They also in handicap because of poor crop and no option to cultivate in two seasons. Hence apparently both groups as of their status are in well shape. The peoples those who have no land for cultivation now can engage them in many other entrepreneurship (e.g. farm product marketing, livestock/poultry raring, carpentering, grocery, etc etc) emerged.
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Along with the Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) other national institutions like Department of Agricultural Extension, Livestock, Fisheries, Bangladesh Rural Development Board (BRDB), Financial institutions- Rajshahi Agricultural Development Bank and others (NGO) are operating more effectively in the Barind in multiple dimensions. In addition students from Rajshahi University also engaged in their research on various issues. BMDA also improving its capacity and skill to develop more effective approach for Barind area.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
This comment was done comparing between conveying water by open drainage and through pipeline. Definitely there are almost no run-off from pipe line distribution. On the hand land users have to confirm their field bunds to protect run-off. Prepaid metering system also restricted land users not to allow excess water to over flow from their field. In-spite of that there may be small amount run-off, but the detachment of top soils is within tolerable limit and accumulate within field bunds.
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is reported that ground water slowly recharged, As a results shallow tube wells are also working , which were about to abandoned before.
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Vegetation coverage increased,
Sols
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased land cover-Reduced drought
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In 90's the lands were bare and in monsoon after heavy downpour a large amount of water going to downstream as run-off with detached top soil. At present land is covered, field bunds are strengthen, restrict run-off as a result soil loss decreased.
accumulation de sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Field bunds enhance soil accumulation by limiting run-off water by field bunds/dykes.
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mechanized cultivation and usage of farm machinery however enhance soil compaction.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The area is above flood level
impacts de la sécheresse
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Emission of carbon decreased as vegetation cover round the year increased.
microclimat
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced dusty wind, temperature cooler then before.
Autres impacts écologiques
The Barind was almost desert like before 90's. Its natural vegetation were almost extinct. Biodiversity both Species and habitat were low. At present it is improving spectacularly.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
In all a desert like Barind tract become green now.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Usage of surface water reduces groundwater abstraction and improves groundwater (GW) recharge
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the land cover has increased, that has a substantial impact on limiting polluted surface water to flow up to river.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | décroît | très bien | |
| températures saisonnières | été | décroît | très bien |
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | été | augmente | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
It could rather to explain as the beneficiaries of the technology. Truly a single land user or a group of land user will not able to install this type of system for multiple reasons. There are two components of this technology, one is the government institution who provided the scope of using surface water for irrigation and the second one are the land user who use the scope or facilities of irrigation system Here about 1800 farmers are involved to use surface water as their irrigation source.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
Most of the farmers of the area who has land adopted surface water for irrigation instead of ground water abstraction.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- la disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre (par ex., en raison de migrations)
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
where there are no canal for water storage , local ponds are used to reserve the surface water to irrigate land surrounding the pods and obviously where river water could not be reached.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Ensured crop production through irrigation |
| Reduced ground water irrigation and decrease ground water depletion. |
| Increased work facility at project area |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Improved socio-economic condition of beneficiaries |
| Increased ground water recharge |
| Increased fish cultivation and duck farming at the canal |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Scope of individual level implementation is very limited | Community approach will facilitate the SLM implementation etc. |
| Maintenance, distribution and regulation of water etc have no control of the beneficiaries | Capacity of the beneficiaries to be developed |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Source of lifting water points may be shifted in the long run | Efficiencies of irrigation water supply need more attention with demand and supply. |
| Weak linkage with beneficiaries | Integrated approach needed to include community and implementing agencies. |
| Crops with high water demand may not sustain in the long run | Appropriate crop and cropping patterns are to be adopted with crop zoning |
| Increasing cropping intensity leads to deficiency of soil nutrients | Monitoring of soil health essential for this region. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Three times with experts of this area
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
20
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
10
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Consulted relevant project documents
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
25/03/2019
Commentaires:
A long process was maintained from building capacity of the professionals to handle WOCAT tools, initial inventory with core experts and screening with local professionals, documentation in field and compiling data in the WOCAT format, which was again validated with large local groups of scientists, extension officials, local government, NGO, lead farmers etc.
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Project documents
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Available in BMDA
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Questionnaires on Tecnologies (QT)
URL:
www.wocat.net
Titre/ description:
Sustainable land management (SLM)
URL:
https://knowledge.unccd.int/topics/sustainable-land-management-slm
Titre/ description:
Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality at the country level
URL:
https://knowledge.unccd.int/topics/land-degradation-neutrality
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
Excellent
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé