Community fodder bank for sustaining supplies [Afghanistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm
- Rédacteurs : MIAJAN MAROOFI, Hekmatullah Sharifzai, Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aslam Qadamov
- Examinateur : William Critchley
Kahdon; Somonkhona
technologies_674 - Afghanistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Committee (NRMC)
Sari Joy village, Rustaq District
Afghanistan
Spécialiste GDT:
Researcher:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
17/10/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
SLM practices documented in the framework of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [Afghanistan]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
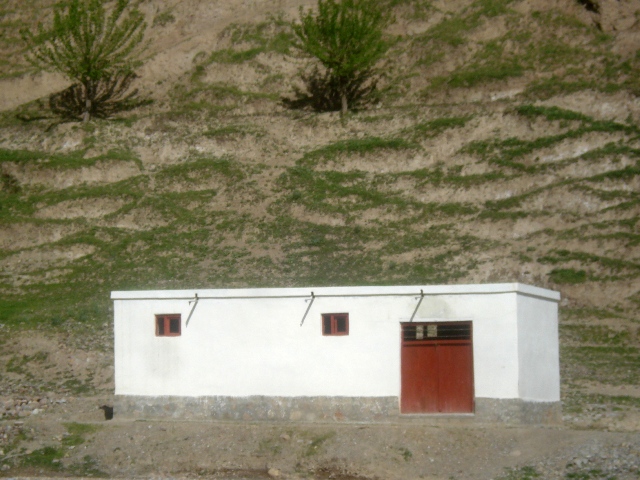
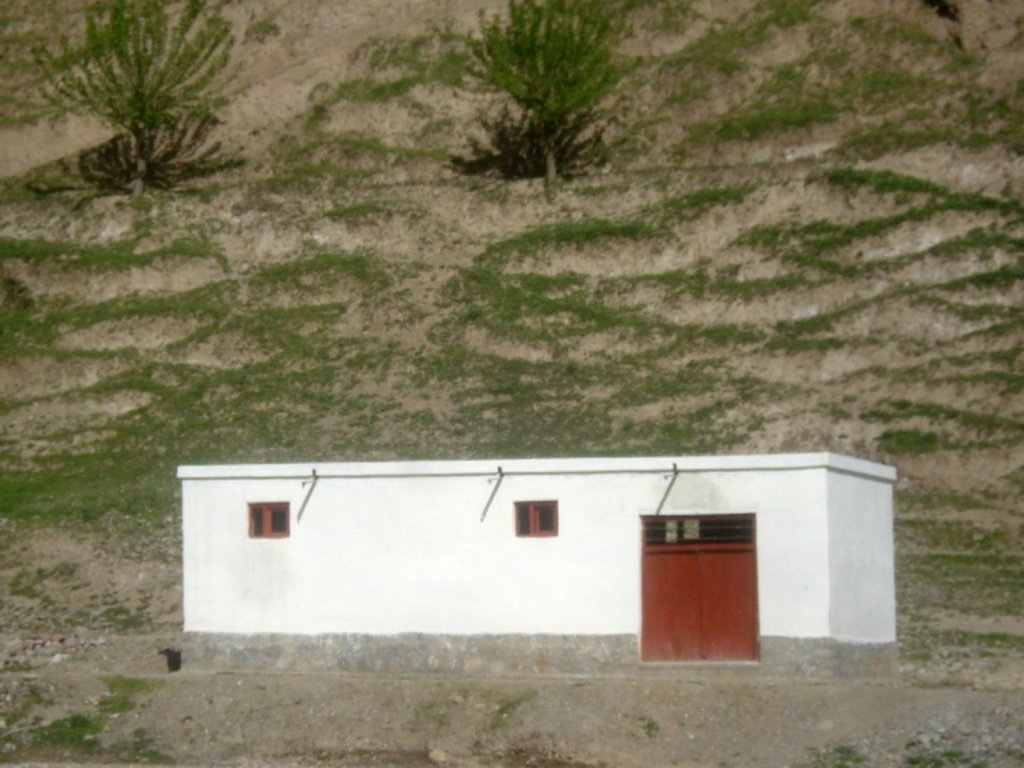
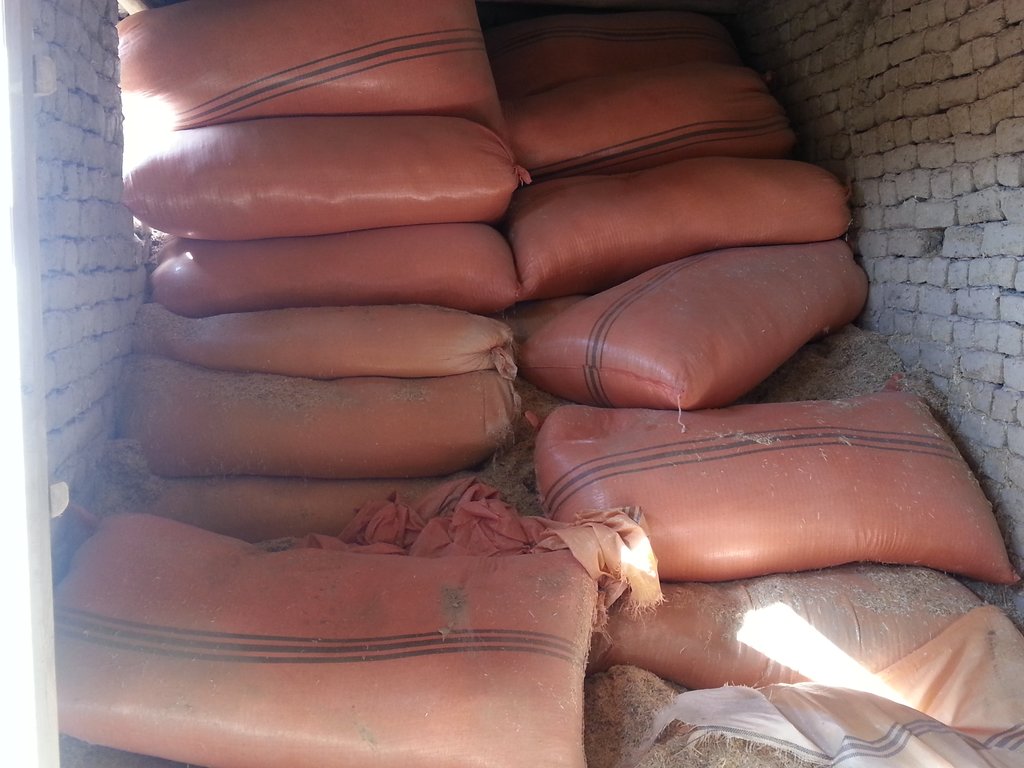
Community fodder banks have been established in villages for the purpose of ensuring supplies of livestock fodder during winter, to prevent loss of livestock and to prevent over-grazing early in spring.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Livestock keeping is one of the key livelihood strategies in rural Rustaq, in addition to cultivation of agricultural crops. Families rely on their livestock not only for consumption of meat and dairy products, but also as means of transportation (donkeys), labour force in agriculture (oxen, donkeys) and a source of cash income. When crops fail to produce enough, families sell their livestock to survive until the next season. Naturally, every family strives to increase their household’s livestock as much as they can, which increases pressure on the local pastures, leading to extensive overgrazing.
The pastures in Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai and Sari Joy are characterized by poor vegetation cover, low carrying capacity and severe erosion - with deep rills clearly visible. The quantity and quality of fodder is insufficient for all the livestock, leading to poor animal health. Starting from early spring to late autumn livestock keepers graze their animals on the open grazing lands. During winter months, the animals are kept inside and fed with the fodder conserved during summer. Very often, and especially during droughts, the fodder stocks can be extremely low and inadequate for the animals to make it through to spring - and then farmers lose livestock.
For the purpose of tackling fodder shortages during winter months and preventing livestock loss, the Livelihood Improvement Project in Takhar (LIPT) supported the Natural Resources Management Committees in Sari Joy, Dashti Mirzai and Jawaz Khana to establish community fodder banks. The fodder bank is also meant to compensate for the closure of rehabilitated pastures during the exclusion period of 1-3 years.
The NRMC mobilized the community to construct the fodder bank building. The building is composed of a large single space of 3.5 m x 10 m x 4 m. Generally the location for the fodder bank is chosen in the middle of the village near the mosque or NRMC building. On average, the fodder bank has a capacity of 250 bags of straw and 50 bundles of hay. Durable construction materials, namely stone and cement are used for the walls. The walls are painted for protection from mould. Proper windows and entrance door are installed to ensure insulation and protection from weather events. The construction materials and labour costs are fully covered by the LIPT project. The maintenance works for the building consists of repairing the roof every autumn with a clay layer.
The fodder bank serves as a reserve for the village community. After each harvest the farmers deliver a certain amount of fodder to the fodder bank, and in return they can take out fodder for their livestock needs. The established regulations require that each farmer is obliged to reimburse the fodder bank for the fodder he has taken as a loan. The NRMC appoints persons in charge of accepting, and releasing, fodder from the fodder bank. The persons in charge record the incoming and outgoing fodder in the log book for fodder. The log book registers the name of the farmer and the amount of fodder he has delivered, or taken, from the fodder bank.
The fodder banks have been functioning for only couple of years. The community has been using the fodder bank to feed their livestock during winter mainly, but also when they have shortage of fodder in other months as well. Due to the low capacity of current pastures the farmers produce just enough to feed their livestock and not much is left to store in the fodder bank. The fodder stocks are expected to increase in future as part of the ongoing process of pasture rehabilitation through cultivation of alfalfa and rotational grazing plans.
Women and children are often involved in collecting the hay and carrying it to the fodder bank. This requires long-distance walks with heavy loads since many houses are located far from the fodder bank. Despite this heavy work, women say that they find the fodder banks useful because of the opportunity to borrow hay for their livestock when they need it.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Afghanistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Dashti Mirzai, Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana Villages
Commentaires:
Coordinates of SLM plots owned by SLM implementers who participated in the FGD derived through the Rustaq NRM study QGIS database.
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM implementers from Sari Joy (1 Fodder bank), Jawaz Khana, (1 Fodder bank), and Dashti Mirzai (1 Fodder bank).
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2014
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- Improve fodder supplies
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Implantations, infrastructures
- Habitats, buildings
Remarques:
Fodder bank to store hay and wheat straw
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
- mesures post-récoltes
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

autres mesures
Commentaires:
The measures comprise construction of a facility to host community fodder bank
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
The Technology is implemented in support of pasture rehabilitation, sustaining fodder for livestock and preventing early grazing, .
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The building is composed of a large single room of 3.5 m x 10 m x 4 m. Generally the location for the fodder bank is chosen in the middle of the village near the mosque or NRMC building. On average, the fodder bank has a capacity of 250 bags of straw and 50 bundles of hay. Durable construction materials such as stone and cement are used for the walls. The walls are covered with white paint for protection from mould. Proper windows and entrance door are installed to ensure insulation and protection from weather events. The construction materials and labour costs are fully covered by the LIPT project. The maintenance works consists of repairing the roof every autumn with a clay layer.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Building
Spécifiez le volume, la longueur, etc. (si pertinent):
Measurements: 3.5 m x10 m x 4 m
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
67,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the site for building the fodder bank | Modes de gestion | Spring |
| 2. | Preparatory works and excavation of the site | Structurel | Summer |
| 3. | Construction of walls | Structurel | Summer |
| 4. | Other construction works and installations | Structurel | Summer |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Preparatory works and excavation of the site | person-day | 2,0 | 5,3 | 10,6 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of wall of the facility | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Other construction works and installations | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | |
| Equipements | Hummer | piece | 2,0 | 3,7 | 7,4 | |
| Equipements | Weel barrow | piece | 1,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | |
| Equipements | Pickaxe | piece | 2,0 | 3,7 | 7,4 | |
| Equipements | Big hammer | piece | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Equipements | Saw | piece | 1,0 | 2,8 | 2,8 | |
| Equipements | Shovel | piece | 4,0 | 3,7 | 14,8 | |
| Equipements | Gloves | set | 10,0 | 1,5 | 15,0 | |
| Equipements | Other tools | piece | 10,0 | 3,2 | 32,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone for construction | cubic meter | 12,0 | 16,0 | 192,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Cement | Bag | 71,0 | 3,7 | 262,7 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Lime | kg | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Gravel | cubic meter | 4,0 | 16,0 | 64,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Oil paint | kg | 10,0 | 1,7 | 17,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Door | piece | 1,0 | 162,0 | 162,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Window | piece | 4,0 | 17,0 | 68,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Plastic color 50% and 100% | kg | 48,0 | 2,45 | 117,6 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1196,3 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair works of the roof with clay and hay mixture | Structurel | Autumn |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Repair of the roof | person day | 2,0 | 5,3 | 10,6 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 10,6 | |||||
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
580,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimum in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximum in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Reference meteorological station considered: Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Derived from the publicly available data set on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the three study villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, and Dashti Mirzai. Sari Joy has sources and good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a lower-down stream. Dashti Mirzai has good water availability - also from an irrigation channel.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Semi-nomade
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq.
Although the men are generally the main land users, however, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within the Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While, it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of great importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however, very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land users learned about the SLM practice through involvement in the process.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Commentaires concernant l'évaluation des impacts:
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits from the Technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
- Similarly for the "ecological impacts" and on "off-site impacts": Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all Technology implementers are reflected here.
- Socio-cultural impacts: This section is answered by the scientists, based on information collected during focus group discussions, and interviews conducted with persons from the 3 villages where the LIPT project implemented the Technology.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Commentaires:
SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly , well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrices compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: During the FGD with SLM implementers, a multi-criteria matrix was elaborated, and different SLM practices were rated. In the framework of this exercise, SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) returns. As the SLM technology was only implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technology. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Commentaires:
One fodder bank is established in each village to be used by the whole community for storing their hay.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Fodder reserves are available during winter and early spring. |
| Livestock keepers can borrow fodder from the fodder bank when they need it. |
| The fodder is stored in a dry place and is protected from rain and snow. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The community learns how to regulate the use of fodder |
| By providing fodder reserves, the rehabilitated pastures are protected from early grazing in spring. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Poor awareness and community participation in storing their fodder in the fodder banks | More community awareness and mobilization |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized to collect information from SLM implementers in the villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Information provided in the reports of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Groups Discussions
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [Afghanistan]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm
Modules
Aucun module trouvé