Establishment of intensive grazing areas on low productive slopes [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch
Βοσκότοπος
technologies_2900 - ប្រទេសក្រិក
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - ប្រទេសក្រិក1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
14/09/2016
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
This technology favors soil erosion and land degradation for a short period (about one month) after sowing the plants.
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
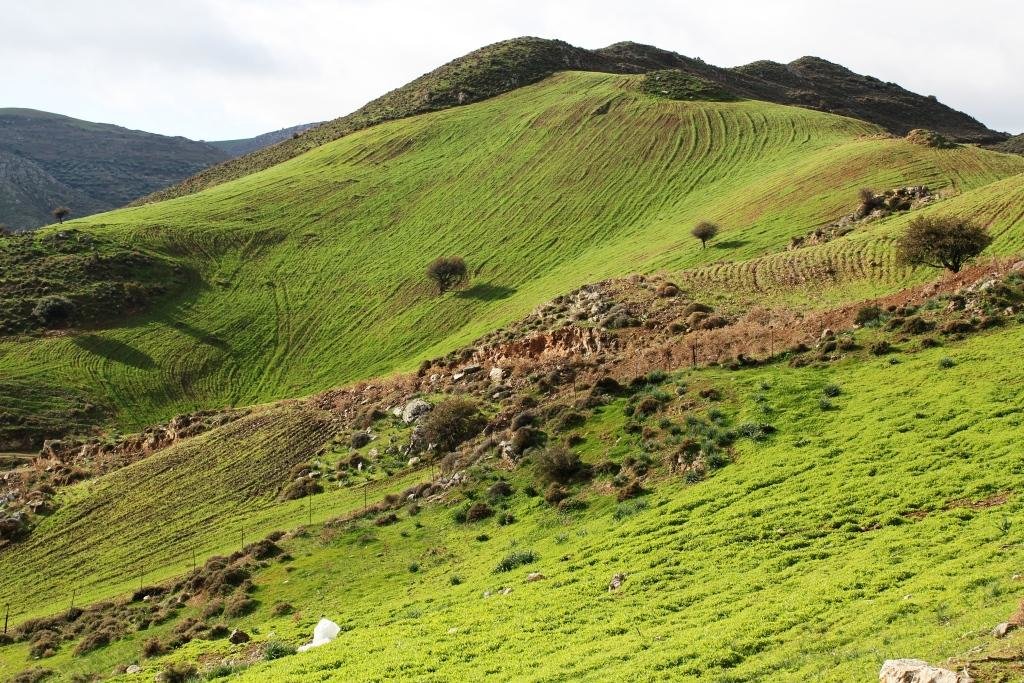
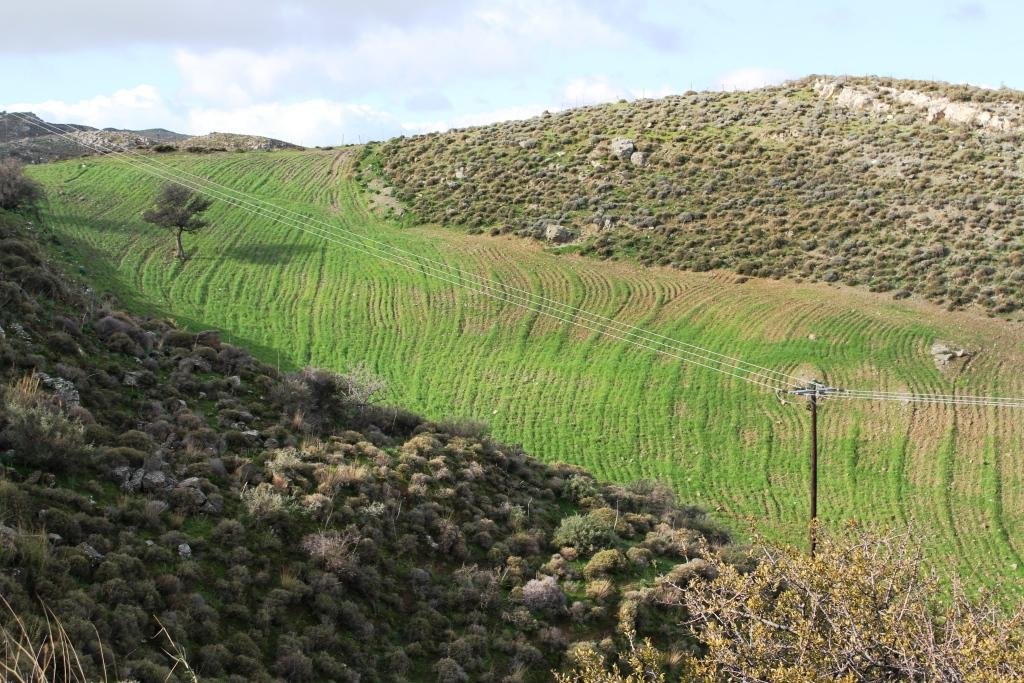
This technology consists of (a) ploughing the soil, (b) sowing the plants usually vetch or oat or in combination in November and (c) grazing the growing plants during spring. The main purpose of this technology is to increase the produced palatable biomass in a grazing land in which the biomass production is very low under natural conditions.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
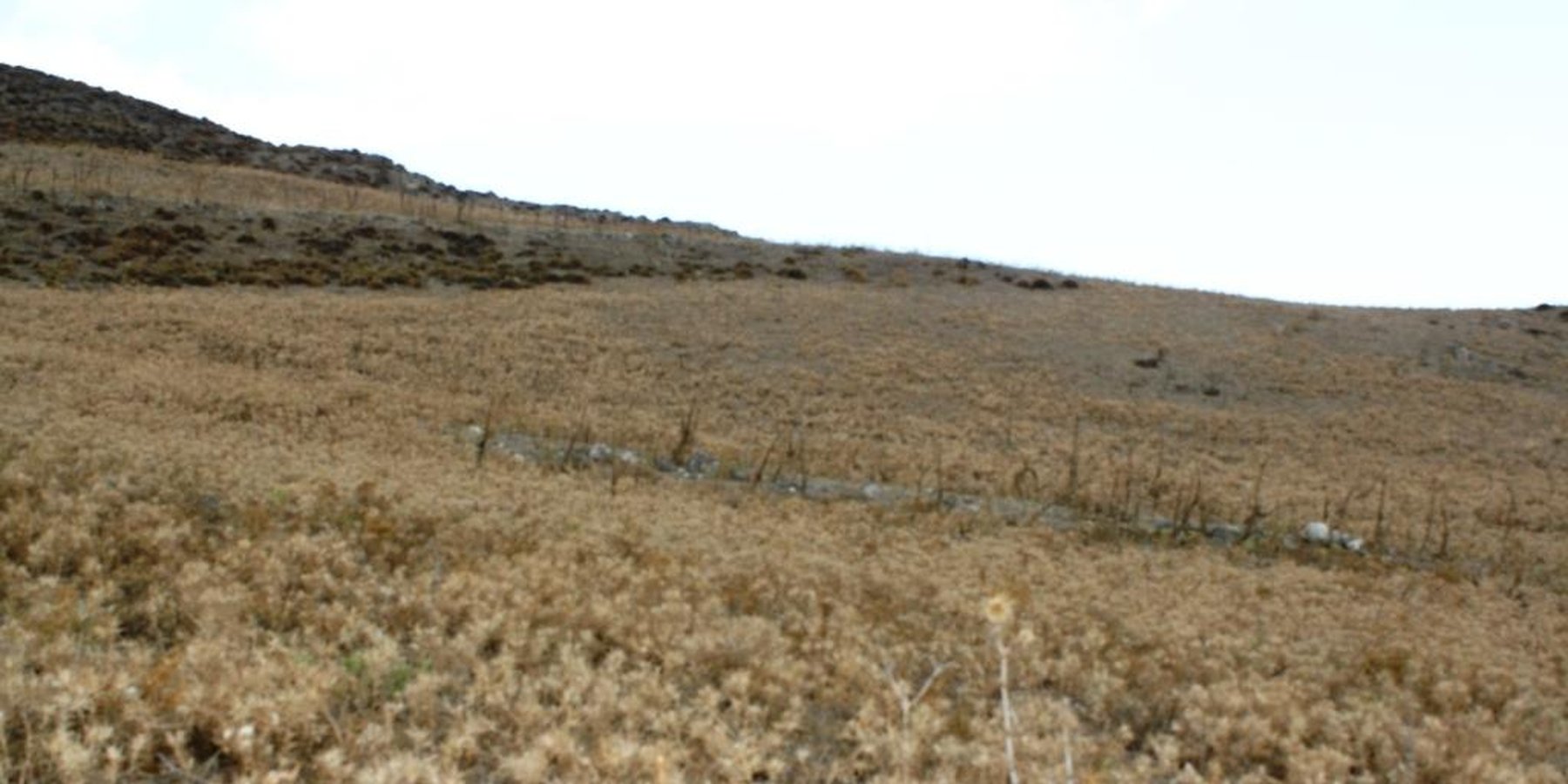
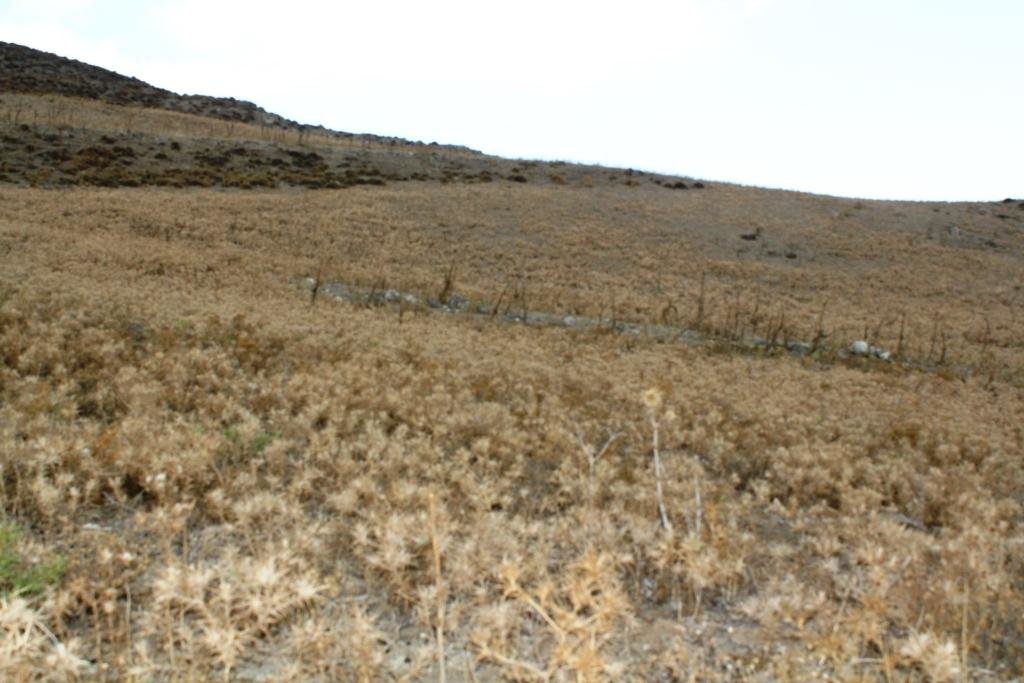
The technology is applied on semi-arid areas of Asteroussia Mountains of Crete used as grazing land with an annual rainfall between 501-750 mm. These areas are usually highly degraded, characterized by steep mountainous slopes (31-60%). This technology was mainly found in shallow (depth: 21-50 cm), moderately fine textured soils which moderate concentrations of soil organic matter (1-3%). The stock breeders in the region use a special regime for transferring livestock grazing rights from the communities to individuals. Nowadays the off farm income of breeders is between 10-50% of their total income.
Looking back, in the early 1950s to the 1980s the Asteroussia Mountains were a livestock-specialized area. Livestock production was based on controlled summer grazing in the mountains and overwintering in the lowlands. After the early 1960s, the area increasingly felt the impact of agricultural mechanization and - by consequence - excessive under-occupied rural labor force, which led to disproportionate out-migration from the area. In areas where limited natural capital was already fully utilized, such as in Asteroussia Mountains, further growth through increasing flocks was only possible by importing fodder. In a parallel, increasing intensification of agriculture in the nearby Messara plain limited the opportunities for the tradition of transhumance. Throughout the mid-1980s–2010s the economy remained livestock-dominated but the population decline continued. However, the presence of foreign migrants offering cheap labor from the early 1990s onwards contributed to keep many farms active.
Coming back to the technology, it consists of: (a) clearing natural vegetation, usually perennial shrubs accompanied with annual plants including mainly grasses, (b) sowing of high value palatable plant species for animals such as oat, vetch, etc. during winter, (c) allowing plants to grow adequately, and (d) grazing by the animals mainly during spring for a period of about one month, and (e) keeping the land bare until next wet cultivation period starts. The purpose is to increase the available biomass for the grazing animals in areas of low productivity of natural vegetation suitable for them. The major activities consists of clearing the land, plowing usually by a bulldoze type tractor, sowing the seeds and adding appropriate fertilizers. However, the establishment of this technology may face problems in clearing natural vegetation, if the existing Greek institutional framework does not allow doing it. Land degradation and desertification are very frequent processes in semi-arid areas and both processes have been enhanced in the last decades by climatic variations and human activities. The EU-funded research project DESIRE in Eastern and Western Europe, Latin America, Africa and Asia have identified soil erosion, forest fires, and overgrazing among the most important causes of land degradation. The main benefit of this technology therefore is the increase in the amount of high quality palatable biomass for the grazing animals in degraded lands. Land users like this technology, if the number of animals is high, as without the technology they face problems of feeding them. However, such an action increases the cost of animal production such as milk. In addition, soil erosion problems are expected since land remains bare for some period of the year especially after sowing the plants.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
Down-slope ploughing is more secure for the farmer and less energy consumption for the machine used.
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសក្រិក
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Crete, Heraklion province
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Asteroussia Mountain, Paranimfi
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The technology continues to be applied since farmers are trying to produce more palatable biomass for the grazing animals as the productivity of the land with the natural vegetation is low.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
ដីវាលស្មៅតូចៗ/ ផលិតកម្មចំណី:
- បង្កើនវាលស្មៅ
ប្រភេទសត្វ និងផលិតផលចម្បងៗ:
Sheep and goats for meat and milk production
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Natural vegetation consisting mainly of shruby vegetation.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
20-25 animals/ha
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
មតិយោបល់:
Isolated fields with relatively deep soils and low slope gradient
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
The technical specifications of the technology are known to almost all the people working on animal feeding. It requires a field of at least one hectare with the following soil characteristics: (a) soil depth of at least 30 cm, (b) soil texture medium to fine, (c) slope gradient less than 25%. In addition, the annual rainfall must be greater than 350 mm with an annual air temperature higher than 12° C.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
one hectare
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារអាមេរិក
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
40
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing the field by mouldboard plough. | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | November |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Clearing the field | person - days | 2,0 | 40,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Tractor equiped with a mouldboard | 1 | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 140,0 | |||||
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | once per year |
| 2. | Fertilization | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | once per year |
| 3. | Sowing | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | once per year |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Ploughing | person-days | 0,2 | 40,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Sowing | person-days | 0,2 | 40,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Fertilizing | person-days | 0,2 | 400,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Tractor equiped with a mouldboard | 1 | 0,5 | 60,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seed | Kg/ha | 250,0 | 0,2 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Fertilization | Kg/ha | 350,0 | 0,4 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 316,0 | |||||
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Fertilizers and seeds
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
670,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Low-elevation areas receive an annual rainfall ranging between 500-750 mm, while the upper mountainous area (highest elevation: 1231 m at the sea level) receives up to 1250 mm of rain.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Hellenic National Meteorological Service, station of Gortina
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
The majority of the area is characterized by an average air temperature ranging between 15°C and 18°C. Rainfall is falling from late fall to middle spring. The ETo (Potential Evapotranspiration) is high receiving values up to 1650 mm.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Hilly areas of various slopes and landforms. The Technology is only suitable for slope gradients less than 25%.
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
These soils are characterized by a surface A-horizon usually 12-18 cm thick and an underlying cambic B-horizon. Leptosols or Cambisols are the dominant soil units in the area. Soils are mainly moderately fine-textured. The 15-30 cm soil depth class is dominant throughout the area. Relatively deep soils (class 30-60 cm) have been mapped in patches. Some of these areas are used as cropland and grazing land. Slope gradient ranges between 2% and 60%. The slope class 35-60% is the dominant class covering the 49% of the total land. The minimum soil depth necessary for the Technology is 30 cm.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
The most important land cover types are schlerophyllous vegetation, transitional woodland-shrubs and sparsely vegetated areas covering the 88% of the total area. The rest of the area is covered by agricultural crops, mainly olive trees and cereals. The dominant woody plant species in the area include Olea sylvestris, Olea Europa, Salix alba (along watercourses), Pyrus amygdaliformis, Prunus webbii, Thymus capitatus, Salvia triloba, Flomis lanata, Flomis fruticosa, Sarcopoterium spinosum, Calicotome vilosa, Scilla maritime, Asfodelus aestivus, Euphorbia characias. Overgrazing coupled with frequent fires shaped the vegetation pattern in the area determining the predominance of the less palatable fire-tolerant plant species. The above-mentioned state of biodiversity existed before clearing the land even in degraded areas.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
Nowadays in Crete livestock grazing is allowed due to a special regime for transferring grazing rights from the communities to individuals (Papanastasis, 1993).
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase in biomass production for feeding the animals
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In consequence of increased fodder production
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
There are not available data on surface runoff for the area.
ដី
សំណើមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
-1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase in soil erosion due to removal of natural vegetation
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Because the natural vegetation is cleared.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The soil sediments are transported in the low land of Messara valley or into the sea.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- ច្រើនជាង 50%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 90-100%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The advantage of the technology is the increase of biomass production for feeding the animals in areas of low natural grass production. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The advantage of the technology is the increase of biomass production for feeding the animals in areas of low natural grass production. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Decline of biodiversity | |
| Create some problems of soil erosion during installation |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Decline of biodiversity | |
| Soil erosion at the initial stage of ploughing the land | From the increase in soil plant cover |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
Mapping the whole area in a scale 1:30,000
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Land users have complete questionnaires during the execution of the EU research project LEDDRA
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Costas Kosmas, Vassilis Detsis, Mina Karamesouti, Kate Kounalaki, Penny Vassiliou and Luca Salvati. 2015. Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece Land 4:541-559 doi:10.3390/land4030541.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
URL: http://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/4/3/541/htm
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Papanastasis, V., 1993. Legal status of land tenure and use and its implication for open landscapes of western Crete. Landscape and Urban Planning, 24, 273-277.
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
European framework EC-DG RTD, 7th Framework Research Programme (sub-priority ENV-2009-2.1.3.2), Research on Desertification Process and Land Degradation, project LEDDRA (243857): Land and Ecosystem Degradation and Desertification: Assessing the Fit of Responses.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល