Taungya systems for forest management [ប្រទេសតង់សានី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Philip Ileta
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kilimo cha miti na mazao ya msimu (Swahili), Intercropping trees with annual crops
technologies_1156 - ប្រទេសតង់សានី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Mugishagwe Wilson
Ngara District Council
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Waluce Michael
Ngara District Council
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Sangatati Joesephat
Ngara District Council
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Waziri Zawadi
Ngara District Council
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - ប្រទេសតង់សានី1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
A forest management system whereby trees are inter-cropped with annual crops until when the crops below can no longer flourish due to the dense canopy of trees.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The overall purpose is to establish and manage forest in a sustainable manner. Land preparation is done during the dry season. Prepared seedling is planted at the beginning of the rainy season at recommended spacing. The area between trees is intercropped with selected annual crops. The crops can continue to be grown until the tree canopy covers the ground (3 to 4 years period). At this stage the system does not support intercropping and the trees are left to grow on their own. The Taungya technology is applied on degraded forest or a new established forest. Recomended supportive technologies are contours for erosion control and manure application for soil quality improvement.
Purpose of the Technology: A well established and managed forest/woodlot ensured in the degraded forest by:
-Intercropping with selected annual crops to improve soil cover, water infiltration, soil organic matter, reduce soil erosion and water evaporation.
-To conduct multiple tending operations for the tree plots and crops (weeding,firebreaks,pruning and thinning)thus minimizing the costs and maximizing returns
-Increased productivity and production through diversification strategies.
-Enhance food security and income.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: -Land preparation during dry season (June to Sept).
-(Allignment,marking and pitting for tree seedlings (Oct-Nov)
-Planting of trees(Nov-Dec)
-Planting of crops (Oct-Nov)
-Weeding
-Harvesting crops
Natural / human environment: Fire threats during dry season, Termite attacks to trees, High costs for labour to perform tending activities in large forest plots
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kagera
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Ngara
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 0.1-1 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is <0.1 km2.
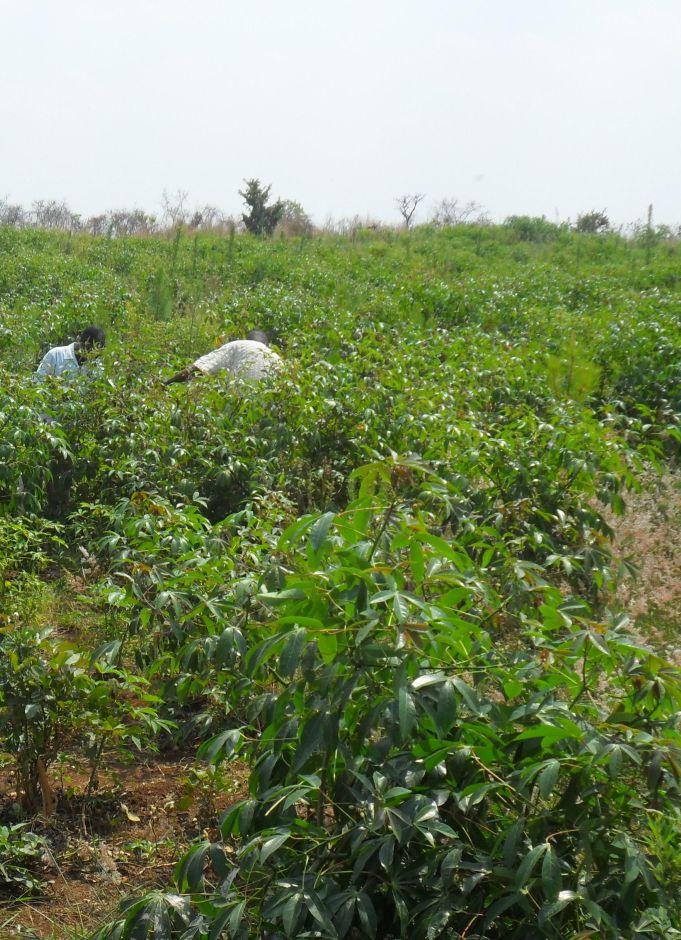
The plantation is planted mainly with Pinus caribaea and few compartments Maesopsis eminii of 3 years and intercropped with cassava,gnuts and beans,well weeded and firebreaks established. The plantation covers 32 hectares.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Various projects of afforestation have been active in the area before and during the Refugee influx from Rwanda and Burundi 1994-2007
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកបារាំង
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងមី
- gnuts
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct to Dec; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំដើមឈើឡើងវិញ៖ បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទក្នុងតំបន់ និងប្រភេទលុប:
- ពូជបញ្ចូលគ្នា
- timber trees
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ឈើហ៊ុប
- អុស
- វាលស្មៅ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High fire incidences during dry seasons, Red clay loam soils harden and dry easily during dry spells, Forest are usually long term investments,thus high costs of inputs before harvests
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): High fire incidences during dry seasons, High costs for weeding and slashing
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Softwood plantation
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងព្រៃធម្មជាតិ និងព្រៃពាក់កណ្តាលធម្មជាតិ
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V3: ការកាប់ឆ្ការរុក្ខជាតិ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
- Pi: ការគ្របផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), change in temperature (Fires become more aggresive in hot dry season)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (To enhance infiltration of water to hard subsoil), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Acute shortage of fuelwood in the area)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
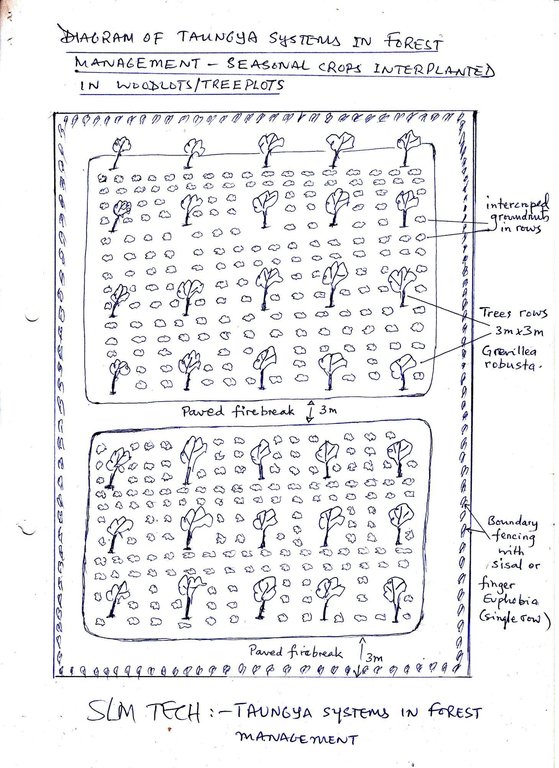
Diagram of Taungya system in forest management -seasonal crop inter planted in woodlots/tree plots.
Location: Rusumo village. Ngara District Council/Kagera/ Tanzania
Date: 15 May 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Experience in agroforestry extension is usually enough to assist farmers)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (A number of manuals provide guidance on afforestation projects)
Main technical functions: reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), control of fires
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: cassava cuttings
Quantity/ density: 500/ha
Remarks: between tree rows
Cover cropping
Material/ species: beans
Remarks: between tree rows
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Plant tree seedlings
Quantity/ density: 1700/ha
Remarks: Line planting 2.5mx2.5m
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues in repeated seasond
Remarks: remain to decay in tree plots
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: thorough land cultivation using hand hoes
Remarks: during initial land preparation
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: continuous cultivation and weeding -hoes
Remarks: enhance water infiltration
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 1700
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Pinus caribaea
Perennial crops species: cassava
Gradient along the rows / strips: 8%
Change of land use type: convertion of rweya(uncultivated grassland) to woodlot/forest plantation
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Perform agronomy practices for crops,sivicultural practices for trees
Layout change according to natural and human environment: increseased soil cover due to many planted trees and agricultural crops
Major change in timing of activities: plant trees at the start of long rains to maximise survival rates
Control / change of species composition: indigineous trees highly deforested, replaced with planted forest of high cormecial value
Other type of management: Establishing firelines/roads each year enables easy prevention/controll of wild fires.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Ileta Philip, P.O BOX 30 Ngara
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Tanzania shilling
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1600,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1.25
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Allign and screef 3m wide roads around tree plot and between compartments | before dry season |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Allign and screef 3m wide roads around tree plot | persons/day/ha | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 400000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hoes, machetes and axes | pieces | 10,0 | 6000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Tree seedlings | pieces | 1700,0 | 200,0 | 340000,0 | 50,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Cassava cuttings | pieces | 5000,0 | 20,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Beans | kg | 25,0 | 500,0 | 12500,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 912500,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 570,31 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | routine twice sesonally |
| 2. | Slashing and screefing firebreaks | once yearly |
| 3. | Prunning excess tree branches | every 3 yrs |
| 4. | Slashing short grass and screef firebreak roads | once yearly |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Weeding | persons/day/ha | 100,0 | 2000,0 | 200000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Slashing and screefing firebreaks | persons/day/ha | 50,0 | 2000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Prunning excess tree branches | persons/day/ha | 5,0 | 4000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Slashing short grass and screef firebreak roads | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 2000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 340000,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 212,5 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: hoes, matchets, axes, slashers, handsaws, per hectare year (2012)
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
high labour especially during establishment and repeated tending of crops and trees
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is medium - high
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table: The plot is on top of the plateau/ridge
Availability of surface water: Is good when further away, because the permanent rivers Kagera and Ruvuvu are 2km below the plateau.
Water quality (untreated): Good because a gravity scheme supplies water to nearby areas 2kms, but for agriculture only because seasonal agriculture in the dry season in wetlands along the rivers.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: labour works performed well by both men and women
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The land user is a businessman and have good number of cattle,however there are many other tree plots in the village owned by other farmers
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
0.5-1 ha: Farmers in the village have many eucalyptus tree plots for firewood and poles,but now opening new land for planting pines Agroforestry practices widespread in banana cropping system in the village
15-50 ha for cropland
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់:
water free for agricultural use,minimum payments for domestic use
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Harvesting of crops
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
At rotation age 15-20 yrs
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Multiple tending operations (crops and trees)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
liv
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
livelihood and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increased income from agriculture crop sales improve food security availability of forest products decreased workload mainly for women-branches of trees and thinnings for firewood
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
ដីប្រេះ
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As windbreaks
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
The control of fires can be improved by boundary planting of fire tolerant plant species e.g sisal(Agaves sisalana),euphobia spp etc
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
Benefits from timber harvest from18 yrs and above,but can harvest for pulp at 8yrs,short term benefits from trees include thinnings for firewood short term from crop sales, decreased input costs due to multiple tending
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- > 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
24 households covering 100 percent of stated area
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 51-90%
មតិយោបល់:
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The planting of pine and intercropping with cassava,gnuts and beans has been adopted by many farmers due to the anticipation of carbon trading in future and expansion of cormecial forestry
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Large ares of land in Rusumo are still uncultivated/no settlements and many farmers have opted to establish woodlots of pines-as highly paying project in future with posibilities for accessing bank loans
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Increased incomes |
| Diversified food crops |
| Fire outbreak prevention/control |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Production of timber and firewood |
| Enhanced food security |
| Prevention of fire to damage trees/crops |
| Reduce soil erosion-improved soil cover |
| Improved carbon sequestration |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High labour costs | grow food crops for 3-4 yrs |
| Shading increases and can no longer support crops | seek advise from agriculture/forestry depts prunnings, thinning on time |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High labour costs | in places with shortage of lands renting farm plots |
| Difficult to use machines in tending,weeding etc | Timely prunning and thinning regimes |
| Shading increses and can no longer support crops | Keep dogs and seek support from Game control department |
| Can be hiding place for vermin |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
12/12/2011
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល