Small-scale dams [ប្រទេសម៉ាលី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Dieter Nill
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Micro-barrages (French)
technologies_1623 - ប្រទេសម៉ាលី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Abdou Sani Mamadou
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP), Niamey, Niger
ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
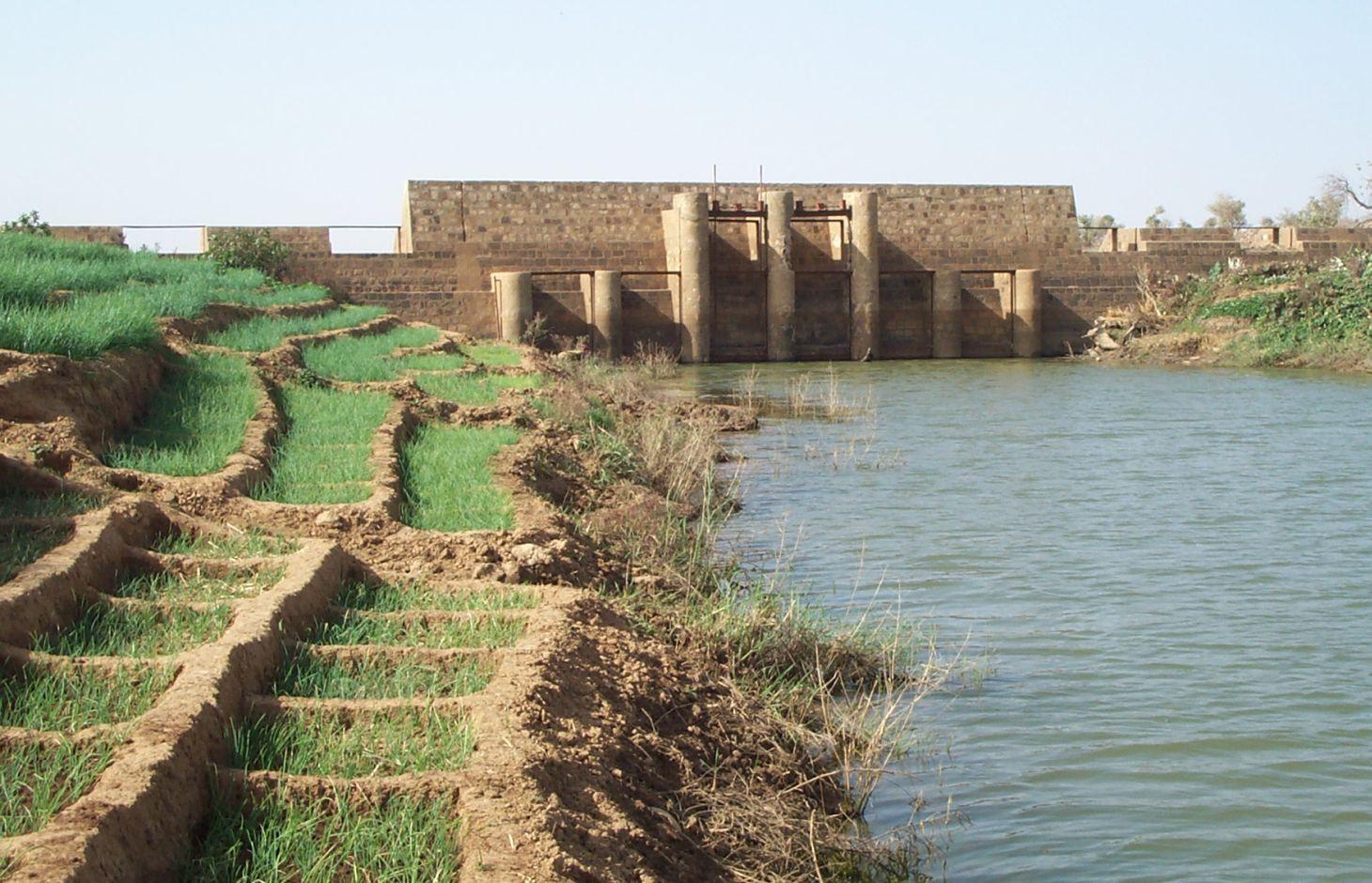
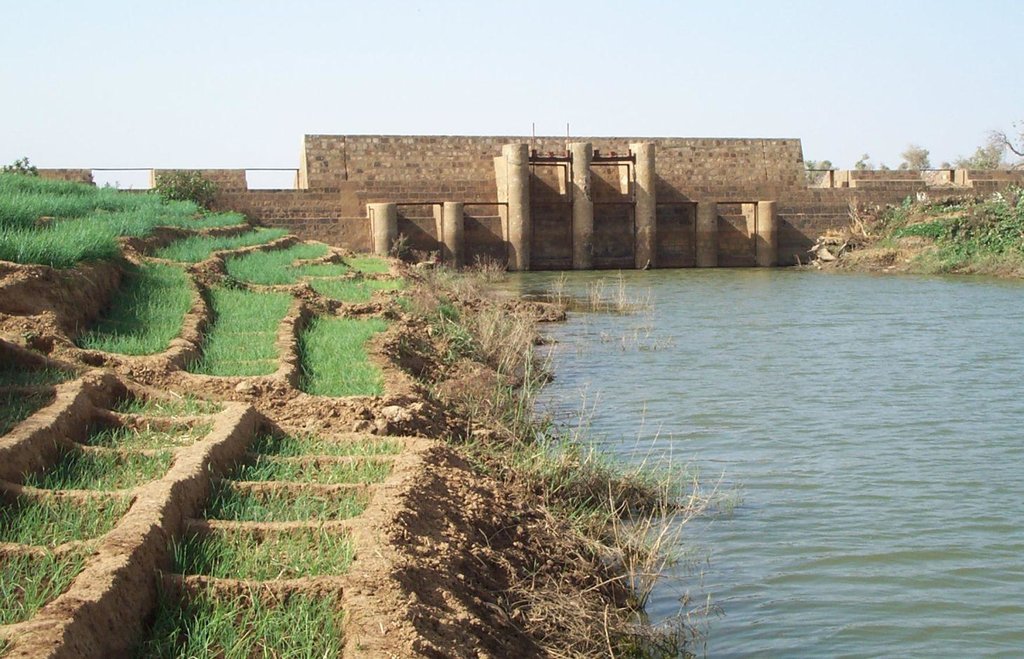
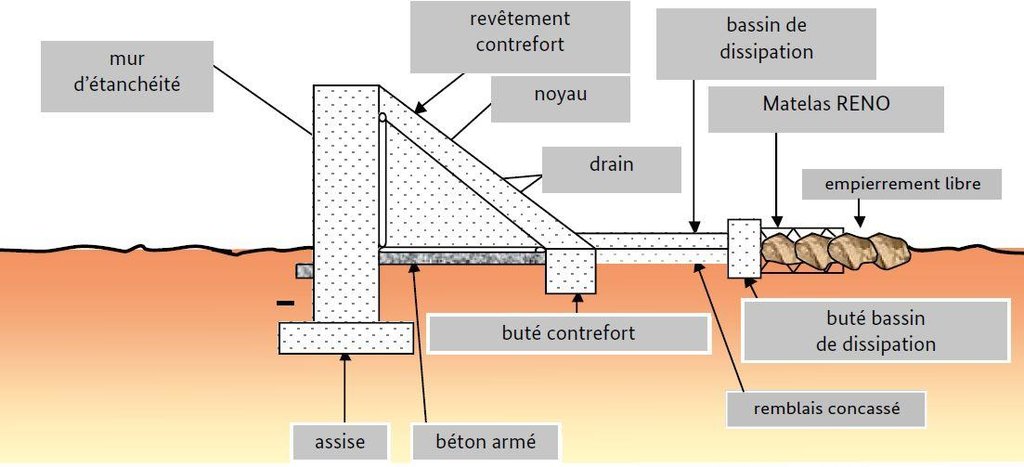
Small-scale dams are moderately-sized barriers built across valley bottoms to retain water from permanent watercourses or seasonal flows.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
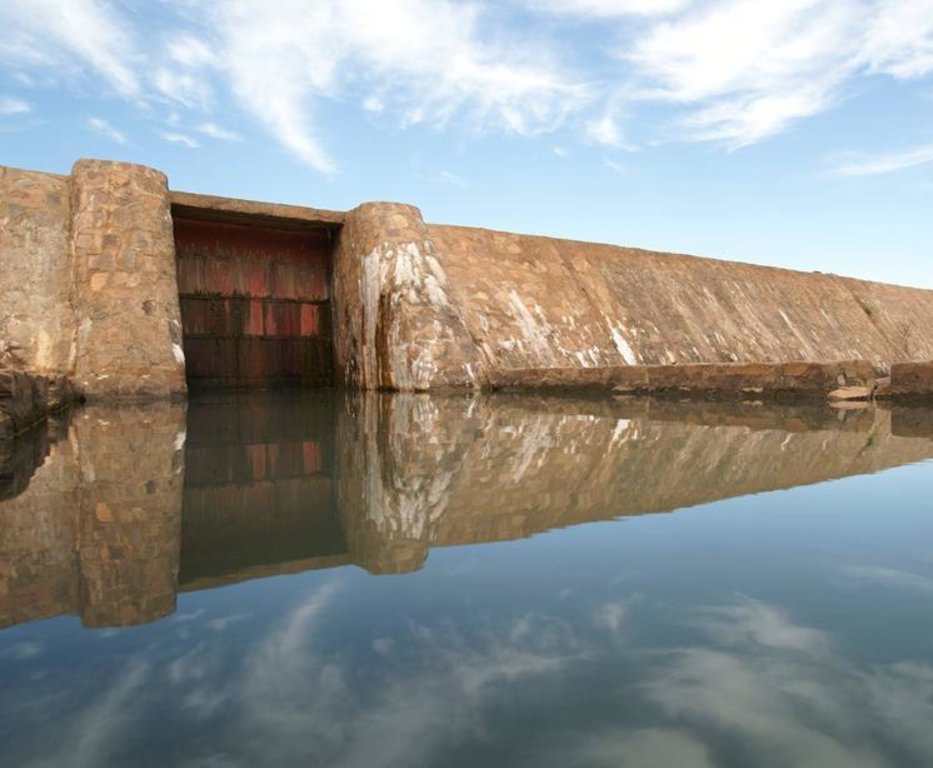
They can range in length from 100 to 200 m, and the dam wall is usually between 2 and 4 m high. Small-scale dams impound permanent or seasonal water behind them, covering areas from 5 to 15 hectares. They are built with buttresses and a stilling basin. Depending on local conditions, the dam wall can be made of quarry stone joined with mortar or concrete. The dikes are made of earth and can be reinforced with stones. Some such structures are built as bridge dams, providing a means of crossing the valley. The effect on the water table depends on the depth at which the dam is anchored. The deeper the foundation, the more groundwater is retained. Sometimes, they are fitted with geomembranes which extend down deeper to retain more groundwater.
In the rainy season, water gradually accumulates behind the dike, increasing the availability of surface water during the rainy season and groundwater in the dry season. The land is farmed upstream and downstream both in the rainy season and the dry season. During the rainy season, rice is grown, and the areas around the body of water are used for other crops (flood-recession cropping). Dams increase the area of farmable land, yields and production. The water is also used for livestock, for fish farming and sometimes for household needs. The recharged water table feeds market garden wells, enabling farmers to grow vegetables in the dry season and permitting two or three crop harvests a year which increases the availability of food, providing income for farmers and guaranteeing work all year round. This improves the stability of local communities, increases their income and raises their standard of living.
Sustainable operation and management depend directly on the participatory approach. At the planning stage, the condition of the valley upstream and downstream and all user groups must be taken into account. The question of land tenure, in particular, must be settled before construction begins. It must be determined who the owner of the bottomlands is, who will be entitled to use them once the dam has been constructed, what uses will be permitted and under what conditions. The question of project ownership and upkeep must also be clarified. Today, the role of project owner is normally assigned to the commune authorities, although management of the dam is often delegated to a management committee. In order to avoid conflicts, it is essential to take into account all the user groups, livestock keepers in particular. Watering corridors must be established to prevent animals from damaging the crops. In order to maximise the value of the investment, well-organised management committees must be set up to ensure efficient crop production and oversee maintenance work. A management committee controls the opening and closing of the gates. It organises the maintenance of the structure and the implementation of any additional measures necessary to protect the gabion structures and stone bunds. It also collects and manages funds for the maintenance of the dam and organises meetings of farmers. In dry periods, it is important to manage water resources in such a way that downstream areas have enough water. When a series of dams are built on the same watercourse, an inter-dam committee may be required to manage the distribution of water and avoid conflicts between the users of the different dams.
Well-constructed small-scale dams last at least 50 years with a certain amount of upkeep. A high standard of technical planning and construction is required for small-scale dams to avoid subsequent damage. Depending on the natural characteristics of the watershed, small-scale dams may require additional SWC/SPR measures upstream to protect them from siltation.
These small-scale dams are suitable for use in narrower valleys, as a considerable volume of water can be impounded with a relatively short structure. They are not as well suited to wide, gently sloping valleys, as very long dikes are required and this increases the cost.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសម៉ាលី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Mali
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 0.1-1 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Small-scale dams impound permanent or seasonal water behind them, covering areas from 5 to 15 hectares
2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), and the project to rehabilitate dams and tracks (PRBP) and the Mali north programme (PMN)
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

ផ្លូវទឹក ផ្ទៃទឹក ដីសើម
- ស្រះ ទំនប់
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): lack of irrigation water, surface water, soil erosion by water and wind
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
- ការបែងចែកទឹក និងប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកលើដី (ទឹកធ្លាក់ ទន្លេ បឹង សមុទ្រ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), floods, droughts, population pressure, land tenure
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
They can range in length from 100 to 200 m, and the dam wall is usually between 2 and 4 m high.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2-4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100-200
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
PIPRO-DB
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | At the planning stage, the condition of the valley upstream and downstream and all user groups must be taken into account. The question of land tenure must be settled before construction begins. The question of project ownership and upkeep must also be clarified. | |
| 2. | In order to avoid conflicts, it is essential to take into account all the user groups, livestock keepers in particular | |
| 3. | Construction of dam | |
| 4. | Watering corridors must be established to prevent animals from damaging the crops | |
| 5. | well-organised management committees must be set up to ensure efficient crop production and oversee maintenance work |
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A management committee controls the opening and closing of the gates. It organises the maintenance of the structure and the implementation of any additional measures necessary to protect the gabion structures and stone bunds. It also collects and manages funds for the maintenance of the dam and organises meetings of farmers | |
| 2. | Depending on the natural characteristics of the watershed, small-scale dams may require additional SWC/SPR measures upstream to protect them from siltation. |
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The cost of small-scale dams varies greatly depending on the physical characteristics of the site, the size of the structure and the local availability of materials. In Dogon country, in Mali, the PDRT project constructed dams with cyclopean concrete costing an average of around 20 million CFA francs and between 3 and 5 million CFA francs per hectare. The internal rate of return of the dams built averaged 17% (Nill & Kobilke, 2002). Larger dams built in the Beledougou area cost 100-140 million CFA francs. Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation reports costs of around 20 million CFA francs for areas of 10-80 hectares (PASSIP, 2012).
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អខ្លាំង
- មិនល្អ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
traditional land use rights on fields, communal land on pasture and forest land
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
contribution to human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The water impounded by small-scale dams makes it possible to farm a much larger area in the valley bottoms and ensures better yields in the rainy season and also in the off-season. The production of food staples and market garden output increases significantly. More intense production ensures employment all year round, which improves the stability of local communities, increases their income and raises their standard of living.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The small-scale dams create water reserves. When there is not enough rain or during dry spells in the rainy season, the dams retain enough water for crops throughout their growth cycle. If rain-fed crops fail, production in the valley bottoms can mitigate these losses. In wet years, the dams regulate the flow of water, preventing heavy floodwaters from causing damage to land downstream. |
| The water impounded by small-scale dams makes it possible to farm a much larger area in the valley bottoms and ensures better yields in the rainy season and also in the off-season. The production of food staples and market garden output increases significantly. More intense production ensures employment all year round, which improves the stability of local communities, increases their income and raises their standard of living. |
| In the dry season, the recharged water table makes a second and even third crop harvest possible, increasing the availability of food, providing income for farmers and guaranteeing work all year round. |
| Replenished water tables not only improve crop output, they also reduce the time and effort that women devote to fetching water and make it easier to water livestock. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| A high standard of technical planning and construction is required for small-scale dams to avoid subsequent damage. | In order to maximise the value of the investment, well-organised management committees must be set up to ensure efficient crop production and oversee maintenance work. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
01/07/2012
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល