Semi-Intensive Goat Farming Practice for Pasture Conservation [អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ PRISCILLA VIVIAN KYOSABA
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Okulisa embuzi
technologies_3363 - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Tusiime Edith
Kabarole District farmers association
Kabarole District Farmer Association
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Sustainable Land Management Practices of South Africa (SLM South Africa)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
17/11/2017
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Goats are stall fed during dry season and open-grazed during rain season. In a semi-intensive system, animals are kept under confinement in which they are stall–fed for some period of time (weeks to months, especially during the dry seasons) followed by another period of open grazing during the rainy seasons.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
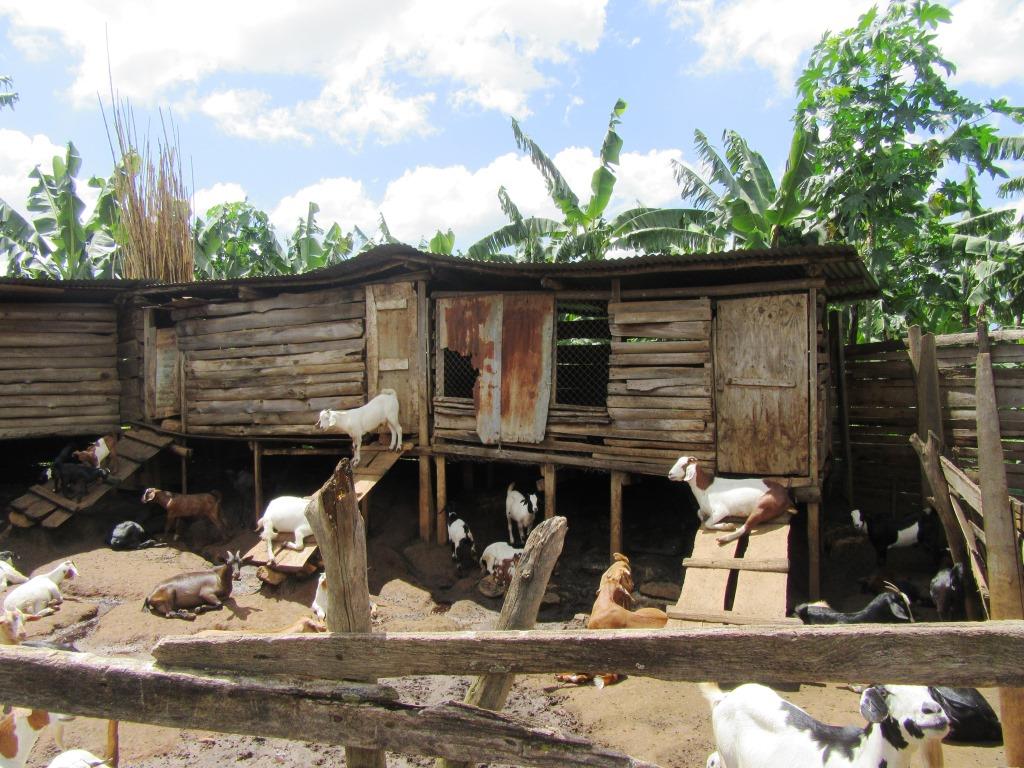
The semi-intensive goat rearing practice is a compromise between extensive and intensive grazing systems limited by shortage of pasture during dry seasons with high chances of spreading diseases requiring for stall feeding goats in an semi-intensive system. The goats are kept under confinement for some period of time (weeks to months, especially during the dry seasons). During dry season, the animals are fed on maize bran; iodized salt; peelings from banana, cassava, and sweet potatoes; and improved grasses (Napier) and forages planted at the boundaries of the banana plantation, which are harvested during the period of need.
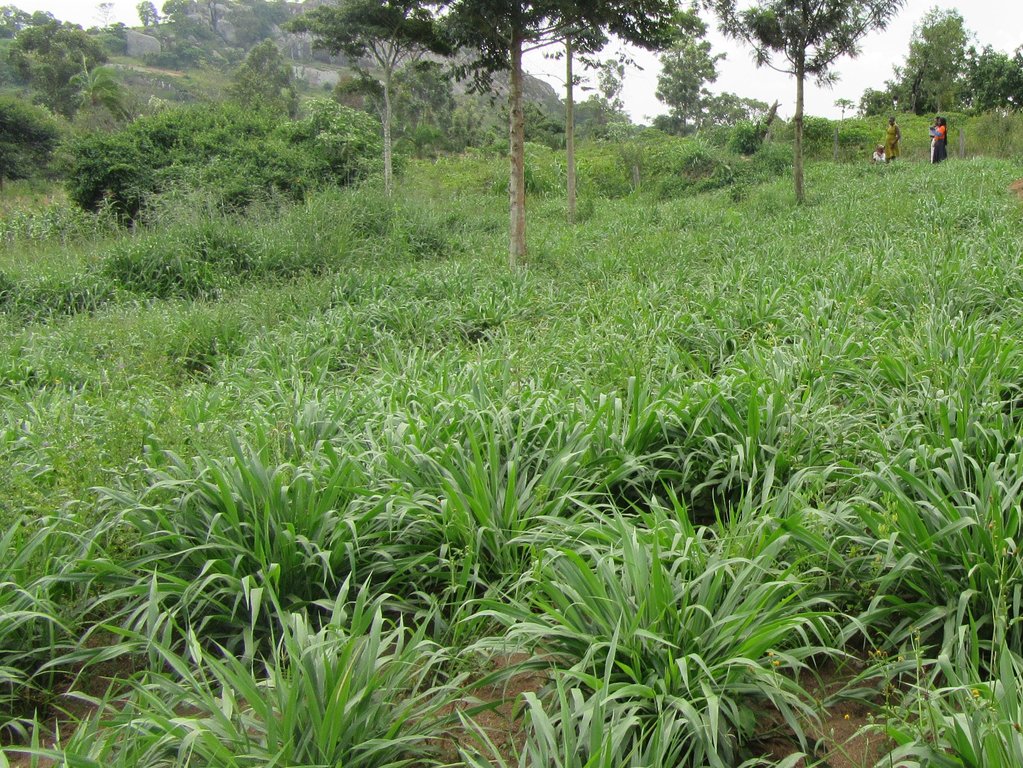
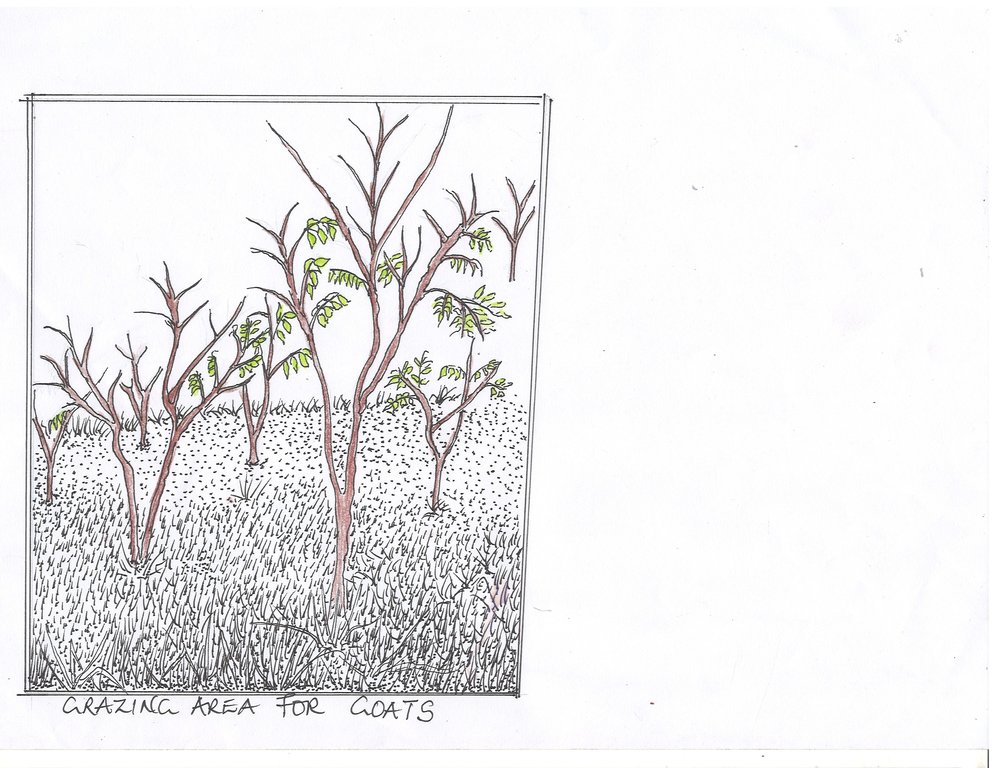
The farmer has got 2 ha of banana plantation. She grows a fodder hybrid called Napier (pennisetum perpureum) around the plantation to be used as fodder for the goats during dry season. Napier grass is a perennial grass fodder commonly called elephant Grass due to its tallness and vigorous vegetative growth. She got the Napier root cuttings from the neighbor practicing the same technology. This is grown around the banana plantation, at a spacing of 60×60cm. It produces more tillers with soft and juicy stem, free from pest and diseases and non-lodging. It can be cultivated throughout the year. Napier grasses contain 6-8% protein. Its optimum cutting interval is about 6 to 8 weeks at grass range of 60 to 90 cm, if sufficient only the tops can be cut and fed. The grass is cut into 5 to 10 cm to reduce loses.
The extensive system is practiced during rainy season where the farmer grows a mixture of fodder species including Sesbania and Napier grass grown on land size of 0.5 ha. Sesbania is a fast-growing tree with regular and rounded leaves. The flowers are white and red in color according to its species but the ones at the farm are yellow. The leaves of Sesbania trees are highly palatable and mostly liked by goats. The protein content in this is about 25%. 1kg of seed was planted at a spacing of 100 cm x 100 cm. In this field Napier grass is planted in rows at a spacing of 60×60cm. The seeds for Sesbania were supplied to the farmer by the Kabarole District Production Office.
Farmers in Kabarole District use the Semi-intensive system for rearing both local and improved breeds of goats. As dry spells are increasingly becoming common, this technology helps farmers to go through the dry season with enough feed for the goats. Farmers prefer rearing goats because they don’t have complicated feeding and medical requirements. As the human population grows and land fragmentation increases, farmers in this area are now moving towards intensive feedings systems.
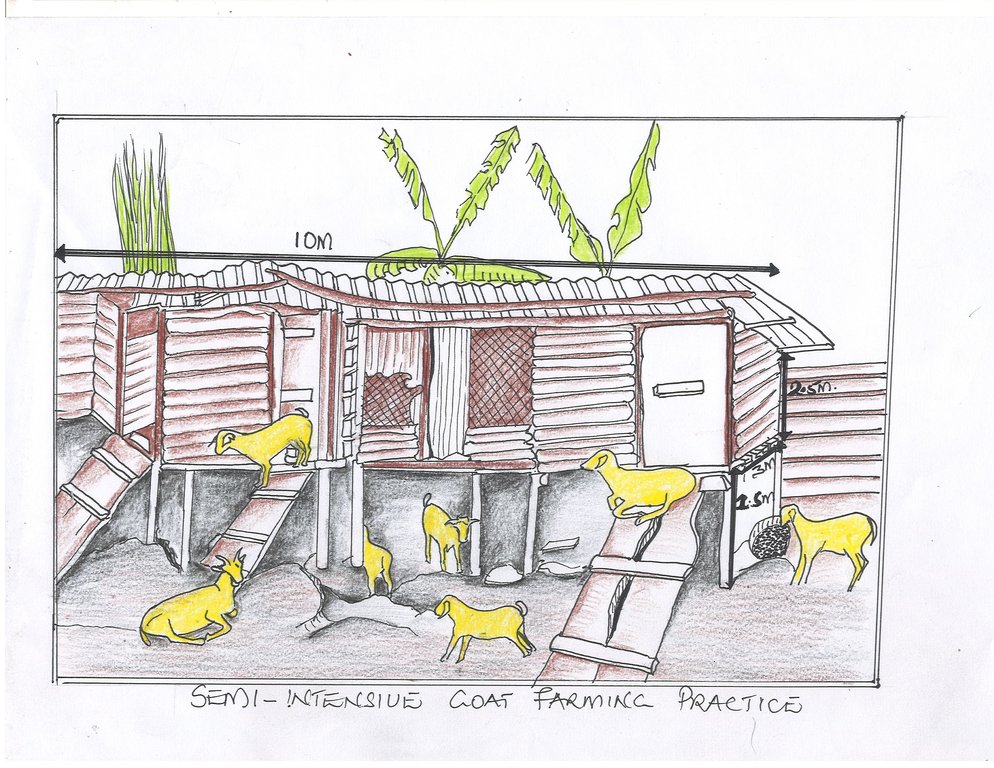
Throughout seasons of abundant forage, farmers harvest the forage together with grasses and make hay to feed the goats during the dry season when pastures are scarce. The cost of harvesting the hay is comparable to the cost of paying a herdsman in open grazing systems. Besides, the establishment of the shelter for goats is not cumbersome compared to those of other animals. The constructed structure occupies an area of about 12 ×12 meters squared with length of 10 meters and width is 3 meters. It is lifted ground to floor 1.5 meters and floor to roof by 2.5 meters. Further partitioned in 4 units and each unit measurement is 3 meters with a slope angle of 20 degrees. The Capacity of each unit is 18,17,17 and 18 goats respectively.
The shelter for the goats is made from relatively cheap materials that are readily available to the farmers. The farmer rears 70 goats on 1-acre piece of land using this technology. By planting improved forages in the grazing areas, the farmer receives increased amount of forage harvested as well as the quality of grass available to the goats during the open grazing periods and income after sale.One challenge of this technology is the dependence on family labor that is not always sufficient for all the tasks involved in the technology both at establishment and maintenance in addition to complications with of rural-urban migration of youth, thereby leaving the workload to the elderly.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
A video Showing Semi intensive goat farming practice in Kabarole District, Western Uganda
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
15/11/2017
ទីតាំង:
Kabarole District,
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Aine Amon
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Western Region
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
1960
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- Prevention of diseases
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅតូចៗ/ ផលិតកម្មចំណី:
- កាត់ និងជញ្ជូន/ គ្មានវាលស្មៅសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- បង្កើនវាលស្មៅ
ប្រភេទសត្វ និងផលិតផលចម្បងៗ:
It is a mixture of cross and local breed and the main product aimed for is meat
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
The farmer has got 70 goats, the number of animals per each constructed unit is variable. She constructed 1 unit, partitioned into 4 sections measuring to 3×3 meters each accommodating 15 goats.
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការបង្កាត់ពូជរុក្ខជាតិ/ សត្វ
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S9: រោងដំណាំ និងរោងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
It is an elevated floor housing unit with 10 X 3 meters squared with a height of 2.5m.
From ground it is elevated 1.5 m. The structure is partitioned into 4 units
The Capacity of each unit is 18,17,17 and 18 goats respectively.
Construction materials are timber peelings, iron sheets, nails.
Animal species are both crosses and local breeds.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
Per shelter as described
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
shillings
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
3650,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
25,000
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Constructing animal shelter | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once |
| 2. | Buying kids | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Once |
មតិយោបល់:
These were the activities mentioned by farmer required to establish the technology
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Animal housing Structure construction labor | Man days | 2,0 | 25000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Buying kids | Kids | 20,0 | 20000,0 | 400000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Poles | 35,0 | 7000,0 | 245000,0 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Iron sheets | 50,0 | 21000,0 | 1050000,0 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Nails | Kilograms | 30,0 | 3000,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Ropes | 20,0 | 1000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Unit doors | 5,0 | 25000,0 | 125000,0 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 1980000,0 | |||||
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Acquiring animal feeds | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Everyday |
| 2. | Animal water | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Everyday |
| 3. | De_worming the animals | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | After 2 months |
| 4. | Buying iodine salt to mix in animal feed | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | When needed |
| 5. | Repairing damaged patches of the animal shelter | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | When needed |
| 6. | Cleaning the animal housing | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Daily |
| 7. | Giving feeds to the goats | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Daily |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Animal Vaccine | Bottles | 2,0 | 25000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Iodine salt | Kilograms | 360,0 | 800,0 | 288000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labor | 100,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Stocking animal feeds | Bundles | 1300,0 | 500,0 | 650000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 988000,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Maintenance cost as reported by farmer are on yearly basis. As for labor, cost is at zero because its family labor used all through.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The organisaton and purchase of feedstuff
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
2000,00
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីផត
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កុមារ
- មនុស្សចាស់
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
An elderly widow who carries out this goat farming project to raise income to pay her children and grand children's school fees plus also taking care of her personal need.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reason given is that a farmer can now comfortably pay children school fees plus take-care of the family necessities
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Cut and carry method requires much labor
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Manure collected from the goats shelter is piled and later applied in the garden hence increasing crop yields
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Goats confined.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មធ្យម | |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | មធ្យម |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មធ្យម | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការមានបញ្ហាសត្វល្អិត/ដង្កូវ | មធ្យម |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Improved standards of living because of the incomes generated. |
| Animal manure acquired and then applied in the farmers banana plantation |
| Serves as employment opportunity for the youths in the home. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Easy access for feeding and watering |
| Nutrient requirement are met both from grazing and stall feeding. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Relatively expensive to maintain | |
| Vaccinating every after two months a bit tiresome | |
| In dry season they usually face a problem of water scarcity |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Stall feeding relatively increases the feeding cost | Supplementing stall feeding with grazing and pasture growing |
| Management and knowledge of forage storage is needed | Through training on forage management |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
2 people the elderly lady owning the farm plus her son helping in the smooth running of the farm activities
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Commercial Goat Farming in India: An Emerging Agri-Business Opportunity
វេបសាយ:
http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/47443/2/7-Shelanderkumar.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Expert System for sheep and goat
វេបសាយ:
http://agritech.tnau.ac.in/expert_system/sheepgoat/Housing%20of%20sheep%20and%20goats.html
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល