Agroforestry extension [ກອດຕາ ຣິກາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Olman Quiros Madrigal
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2391 - ກອດຕາ ຣິກາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ

Tree windbreaks within irrigated agriculture in Central Asia [ກີກັດຕັນ]
Windbreaks of poplar trees (Populus nigra pyramidalis) are a major agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture across Central Asia. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% and increase farm income by 10-15%.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Niels Thevs

Shade-grown coffee [ກອດຕາ ຣິກາ]
An agroforestry system which combines coffee with shade trees - including fruit, timber and leguminous species - in a systematic fashion.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Olman Quiros Madrigal
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
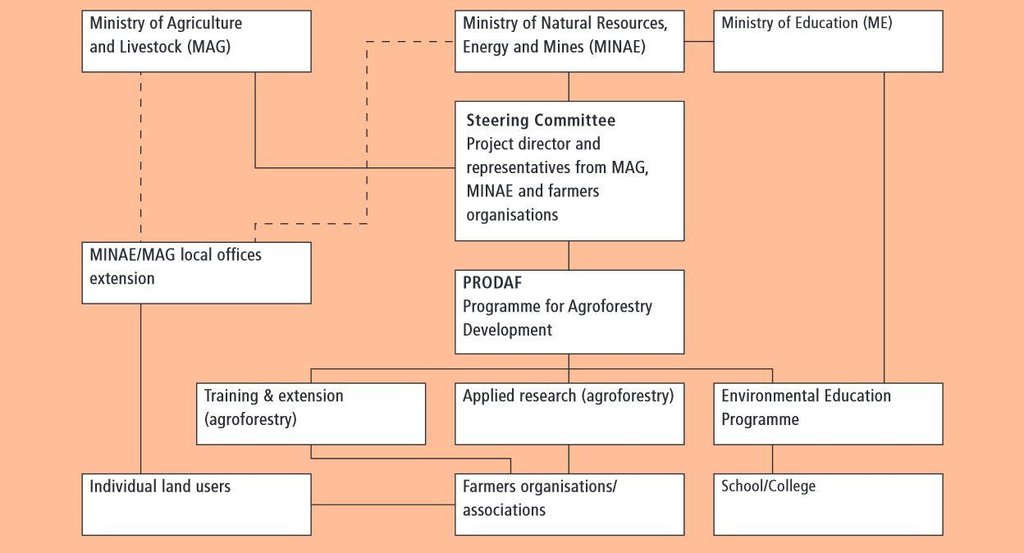
Aims / objectives: The Programme for Agroforestry Development (PRODAF) pioneered a new type of agroforestry extension in Costa Rica between 1987 and 1994. PRODAF was positioned under two national ministries (the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock - MAG and the Ministry of Natural Resources, Energy and Mines - MINAE) and was supported by GTZ (German Technical Cooperation). Agroforestry extension underpinned the following sectors: environmental education, promotion of training and technical assistance in agriculture and forestry, development of programmes for afforestation and agroforestry systems, and promotion/support of farmers' organisations. The approach was based on land users' participation at all stages. The main purpose of the agroforestry extension approach was the development and promotion of sustainable production systems, which were adapted to the local biophysical and socio-economic conditions. This was to enable environmentally friendly production on steep slopes, while at the same time generating sufficient income for small and medium scale farmers in marginal areas of the Acosta-Puriscal region. In this case study, shade-grown coffee was identified to be a system that fulfilled these conditions. Another important objective was the involvement of all family members - including the younger generation.
Role of stakeholders: In the first years PRODAF operated with a top-down development approach implementing technologies, designed by specialists, without consultation of land users. Local needs and experiences were not considered: as a result both adoption of shade-grown coffee was low, and maintenance was poor, despite initial incentives. The change to a participatory, bottom-up approach, with land users being represented in the steering committee (which during this period was absolutely innovative) increased acceptance among the majority of farmers towards shade-grown coffee. Participation of land users during planning and implementation was rewarded with provision of tools, seeds, fertilizer and biocides (fully financed or subsidised). The technology was evaluated on the test plots within existing coffee plantations together with the land users. PRODAF's legacy has been an institutional change in Government policy towards extension.
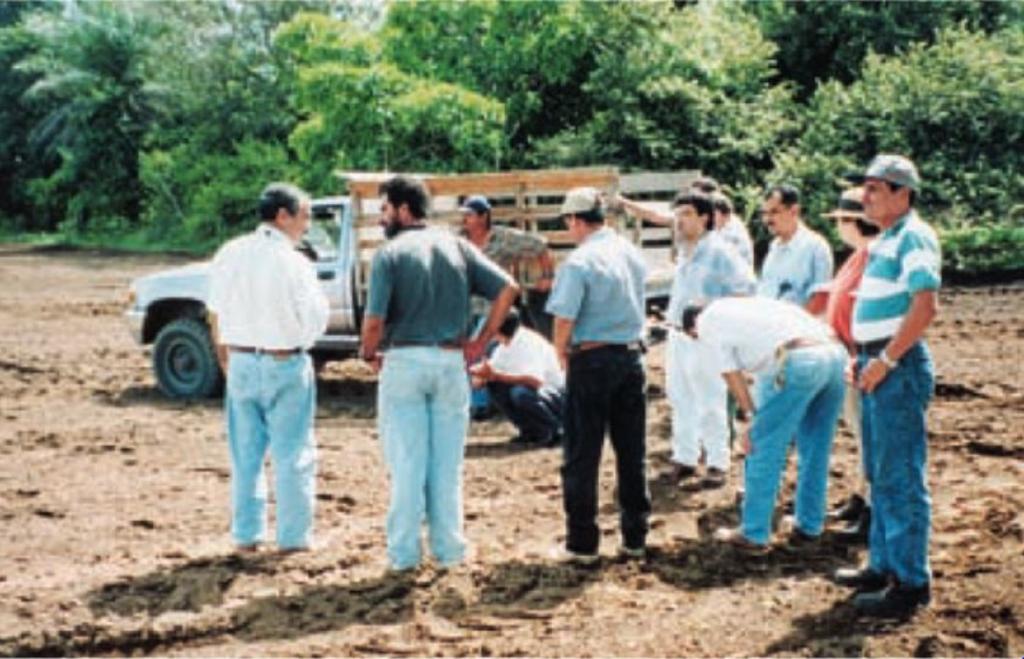
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ກອດຕາ ຣິກາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
San José/Río Parrita
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
1987
ປີທີ່ສີ້ນສູດ (ຖ້າຢຸດບໍ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ):
1994
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
Promotion of appropriate management of natural resources and adoption of the shade-grown coffee agroforestry system - café arbolado - among small and medium scale farmers.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - various different approaches of forest and agricultural technicians regarding choice and implementation of the technology, - which needed harmonising, - lack of incentives for farmers to adopt technology, - lack of participatory technology development
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Lack of credit for SWC implementation.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Credit has been made available through the 'productive re-conversion programme' and other credit systems for organic/conservation production, eg Fideicomiso (see under credit).
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Lack of collaboration and coordination between different institutions.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Innovative incorporation of land users in decision making, which in the meantime has become a common approach.
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ອໍານວຍ
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Land fragmentation leads to very small areas per household. This hinders implementation of SWC activities. Land users do not have the resources to invest in initial inputs and activities.
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Subdivision of land hinders adoption of SWC measures.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Not directly treated by the approach. Diverse incentive mechanisms have to be identified to promote SWC activities on small areas.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Lack of technical knowledge, lack of research activities/trials with SWC technologies.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Promotion of alternative production systems and SWC measures had great impact. Technology was tested on-farm. PRODAF did not focus on research activities.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Mainly men participated: women are not usually expected to carry out field activities for cultural reasons. The coffee harvest is the only activity where men and women work together in the field.
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; good participation basically through participative rural appraisal |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | workshops/seminars; incentives are provided for participating land users |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | responsibility for major steps; incentives are provided for participating land users |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | workshop/seminars, interviews/questionnaires; |
| Research | ການຮ່ວມມື | on-farm |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
- ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
- ກອງປະຊຸມ
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- trips to projects in, field days, workshops
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
The following subjects were treated: coffee agroforestry system, fruit trees and soil conservation, silvo-pastoralism, soil conservation in general. Beside knowledge transfer, awareness raising and motivation were important aims of training.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Name of method used for advisory service: Extension carried out through extension workers was the key element of the overall approach; Key elements: the adequacy of extension for continuation was very good, Different methods were used: on-farm technical assistance; farmer-tofarmer knowledge exchange; demonstration areas and workshops.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
- ອຸປະກອນ
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: yields
Socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: family size
Economic / production aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: yields and production market
No. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: land users involved in organisation
There were many changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The approach changed completely after evaluation of the first phase, from an initial top down methodology with low technology adoption by land users, to a more participative approach heeding land users' opinions and needs, and improving communication between technicians and land users. This was helped by the development of educational materials.
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
Results were rather meagre, and the effect on the approach was thus moderate. Previous to PRODAF there was a research project conducted by CATIE (Tropical Agricultural Research and Higher Education Centre) in the approach area, but results were not broadly disseminated.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - MAG, MINAE): 50.0%; international non-government (GTZ): 50.0%
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງມື | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | hand tools |
- ກະສິກໍາ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ຝຸ່ນ, ປຸ໋ຍ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | |
| seedlings | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເງື່ອນໄຂກໍານົດ (ອັດຕາດອກເບ້ຍ, ຈ່າຍຄືນ, ແລະ ອື່ນໆ) :
Repayment conditions: Credit was provided through ‘productive re-conversion programme’ to support small-scale organic production and soil conservation. After PRODAF a larger (national) credit programme to promote agroforestry systems was launched, under MAG and National Production Council. Fideicomiso is another national financing programme based on a contract between a bank and development institutions. .
Interest was lower than market rate.
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
There was substantial improvement of soil and water management through application of the agroforestry systems.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Some projects in the region as well as in other parts of the country adopted the approach. Various SWC extension programmes have adopted the extension methods promoted by PRODAF, based on the principles of land users participation. In the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock it has been taken as a basic principle in the National Programme of Agricultural Extension.
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ບໍ່ແນ່ນອນ
ຖ້າ ບໍ່ ຫຼື ບໍ່ແນ່ໃຈ, ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ແລະ ຄໍາເຫັນ:
While the approach has been institutionalised and a national credit programme set up promoting shade-grown coffee and silvo-pastoral systems, continuation of field production activities is uncertain. Farmers’ motivation to apply technologies was raised with the Environmental Education Programme, but if market prices for coffee decrease /show variability, farmers lose the motivation to maintain i
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Institutionalisation of the basic participatory extension approach within the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock. |
| Initial top-down approach replaced by participation with land users (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to spread information about the effectiveness of this change in attitude, and the need for responsiveness in projects and programmes.) |
| Training of land users (knowledge of soil degradation processes and soil and water conservation) (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Collaboration with farmers organisations, NGOs and agricultural extension services. Better dissemination of research results.) |
| Environmental education in schools (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue support through the Ministry of Education.) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| No economic security guaranteed in the long term because of price fluctuations | Provide a system of incentives, eg lower taxes for those who apply SWC technologies. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
PRODAF (1992) Informe de evaluación de las parcelas agroforestales establecidas por PRODAF, Periodo 88-91, Puriscal,Quiros O (2000) Nachhaltigkeit von landwirtschaftlichen Produktionsverfahren in bäuerlichen Familienbetrieben in Costa Rica.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Vauk-Kiel KG: series of: Sozialökonimische Schriften zur Ruralen Entwicklung, Vol. 20
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Tree windbreaks within irrigated agriculture in Central Asia [ກີກັດຕັນ]
Windbreaks of poplar trees (Populus nigra pyramidalis) are a major agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture across Central Asia. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% and increase farm income by 10-15%.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Niels Thevs

Shade-grown coffee [ກອດຕາ ຣິກາ]
An agroforestry system which combines coffee with shade trees - including fruit, timber and leguminous species - in a systematic fashion.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Olman Quiros Madrigal
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ