Land Management Group [ບູຕານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Karma Dorji
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger
Phazhing Zinchung Tshogpha (Dzobgkha)
approaches_2493 - ບູຕານ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
MoA (MoA) - ບູຕານຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
National Soil Services Centre (National Soil Services Centre) - ບູຕານ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
25/03/2011
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
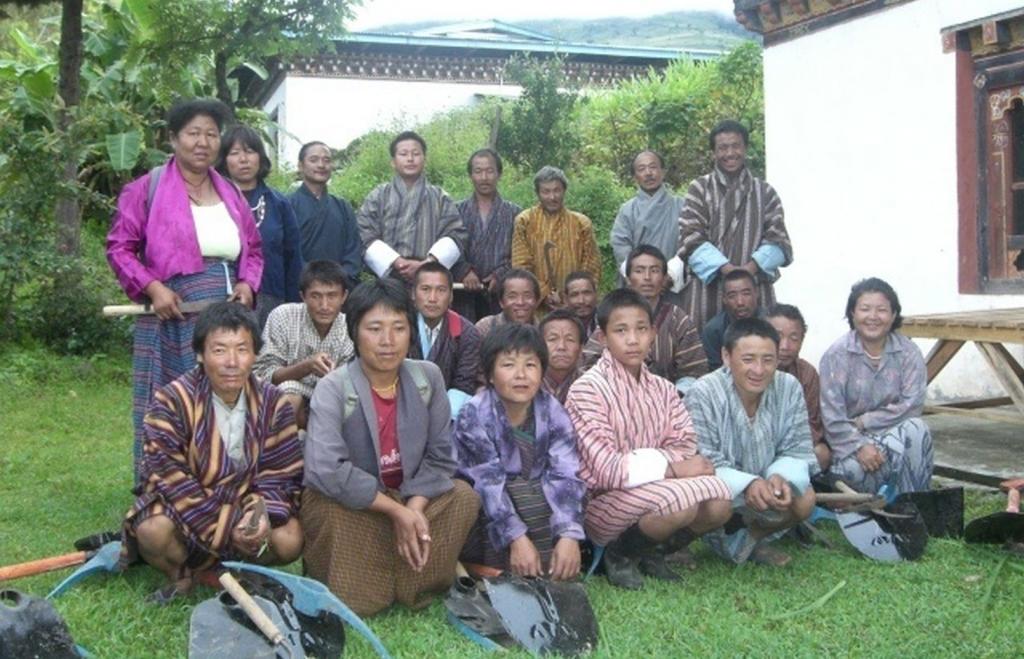
Land Management Group uniting all households in a community to plan and implement SLM and cash-generating activities
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Aims / objectives: A Land Management Group (LMG) unites all households of a village and aims to advocate, plan and implement SLM activities, based on the land-based issues of that particular community. The LMG has formal by-laws, drafted interactively with the community, and has its own group saving account, as access to credit and proper savings is still a real constraint in remote areas. A first LMG was started in 2008 in Drunggoenpa chiog in Radhi geog, Trashigang Dzongkhag, East-Bhutan. The idea for the LMG was based on pioneering work of the Renewable Natural Resource Research Centre Bajo, Wangdue Dzongkhag, in Salamji chiog, Dagana Dzongkhag.
Methods: In an effort to reinforce the social cohesion of communities and to improve the efficiency of planning for implementing SLM interventions, SLMP has initiated Land Management Groups. A LMG is considered very useful to overcome one of the main constraints of SLM implementation in Bhutan: labour-shortage. Many individual households have a growing lack of labour and therefore difficulties to implement labour-intensive SLM activities such as terracing, stone bunding or afforestation work.
Stages of implementation: LMGs are especially suitable for smaller communities, where households live relatively close to each other and have a good community bond. Instead of inter-acting with many individual households separately, the extension staff can also target their services, such as training programmes and technical guidance, to the group. The Drunggoenpa LMG was supported in their group formation process with regular meetings and took part in the annual participatory SLM action plan-ning for the chiog, identifying key land-based problems, their causes and possi-ble SLM interventions. Implementation of these SLM activities, such as grass strip establishment, stone check dam construction, group private forest establishment, vegetable production and tree and bamboo plantation, was carried out in a labour-sharing approach. Pooling labour in the group, all the land of the group members is converted or treated.
Role of stakeholders: This enables vulnerable families including single-headed households and the poorest-of-poor, to participate and get access to more labour-intensive SLM interventions. Apart from the pure SLM interventions, attention is given to cash-generating activities such as vegetable production and potato cultivation, to enhance the livelihoods of the farmers.
Other important information: Costs of forming a LMG including implementation of a series of SLM activities at the village level are limited(less than US$2,000 annually).
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ບູຕານ
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Trashigang Dzongkhag, Radhi geog, Drung Goempa Chiog
2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2008
ປີທີ່ສີ້ນສູດ (ຖ້າຢຸດບໍ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ):
2012
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (vegetable production, potato production for cash income generation)
- To overcome labour constraints of labour-intensive SLM activities by working in a group, becoming more time-efficient
- To enhance the community bond and give access to all households to SLM activities
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Severe land degradation in the village through landslides and surface erosion on very steep dryland
- Overgrazing by cattle, causing crop damage and forest degradation
- Lack of timber as result of forest degradation and deforestation
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Labour-intensive SLM activities are potentially excluding vulnerable households from access to SLM support
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Group approach enables the inclusion of all households, making use of labour-sharing
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ອໍານວຍ
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: All group members own land and this is a great help to implement SLM activities as there is a great sense of ownership.
ວຽກ, ມີກໍາລັງຄົນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Labour-intensive character of some of the SLM interventions
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Labour-sharing approach in group eases constraint, even for vulnerable and single-headed households
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
group with local by-laws
No gender bias; women are equally participating in more physically demanding activities, such as ploughing. Yes, little. All community households are participating in the land management group, including some female headed and poorest households.
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Local government (geog and chiog level)
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
ຖ້າຫາກມີຫຼາຍພາກສ່ວນທີ່ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຫຼັກ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Initial idea was developed after field visit by community members and Geog SLM Planning Team (GSPT) to Selamji Land Management group in Dagana Dzongkhag.
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Community members were inspired by visit to Salamji, a SLM focal village in Dagana Dzongkhag and advocated a similar approach in their village |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Participatory SLM action planning, annually, to discuss land based issues, causes and potential SLM interventions |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Range of SLM interventions such as grass strip establishment, stone check dam construction, group private forest plantation etc. technical guidance by local extension staff |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Participatory Monitoring & Evaluation meetings with geog extension staff and members of the municipality administration; includes regular insight in group saving account balance and status for transparency |
| Research | ບໍ່ມີ |
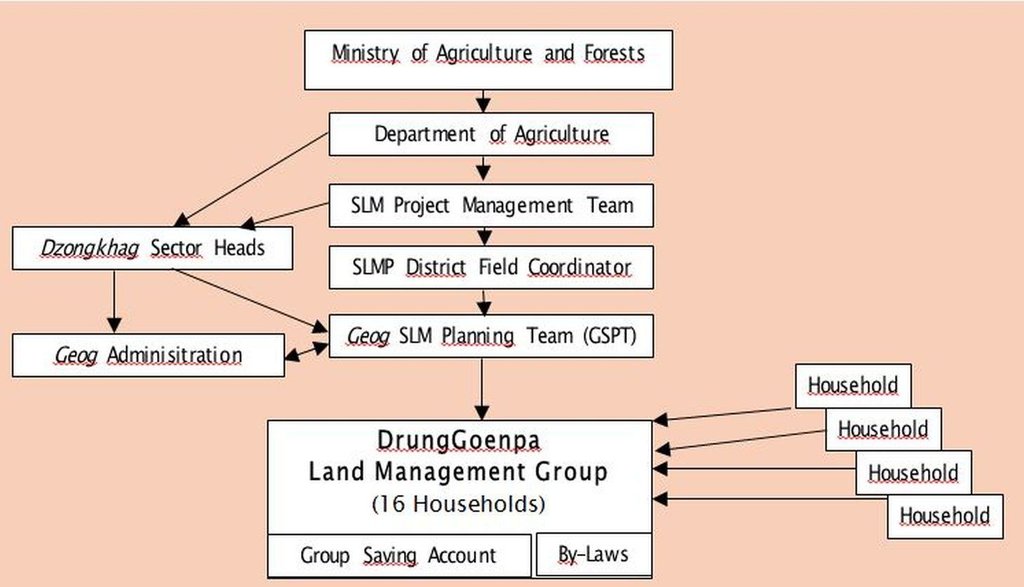
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
Organisation chart of the Land Management Group
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Hans van Noord (Schoutenkamp 43 Heteren The Netherlands)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຫຼັກ, ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໂດຍຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ອະທິບາຍ:
.Annual Participatory SLM Action Planning to discuss land-based issue, causes and interventions options and priorities.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users; consultation process in context of participatory SLM action planning and participatory monitoring and evaluation meetings.
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ການເຮັດຕົວຈິງ
- ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
- ກອງປະຊຸມ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
Training to community members on group formation and specific technical SLM interventions such as organic vegetable production, grass strip establishment, group private forestry, stone check dam construction, bamboo plantation etc. The annual participatory SLM action planning and natural resource mapping also contributed considerably in raising awareness of all villagers, developing their understanding of causal chain relations of their key land problems.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Name of method used for advisory service: SLM advisory service by extension staff; Key elements: Grass strip establishment, Group formation, Organic vegatable Production; Renewable Natural Resource Extension staff of the geog are providing on-the-job advisory service to the group members through regular visits to the community to carry out trainings, which are mainly hands-on, with a demonstration site on the land of one of the group members. At the end of the training the group members plan for a rotation schedule to carry out the SLM activity on the land of all group members.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Determination expressed by group to continue with activities post-project.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
Considerable support to the Land Management Group through group formation process guidance and concentrated effort to plan for and implement a range of SLM focused activities, combined with hands-on training events.
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations by project staff together with group members of grass strips, riser height, check dam infill and tree seedling growth
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations and measurements by project staff together with group members of grass strip area, number of check dams and plantation status (bamboo and tree seedlings)
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations by project staff together with group members on group status and feedback of group on implementation progress and issues and future activities
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations by project staff together with group on crop yield, fodder grass production along grass strips (# of loads) and animal production increase (milk in litres, butter and cheese in kilos)
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through measurements; indicators: Regular measurement by project staff and group members of area treated with grass strips and area planted with bamboo and tree seedlings
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Ad-hoc observation by group members (attendance register)
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations in participatory monitoring and evaluation meetings with group members
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: In the initial group formation process these was considerable involvement by the local extension staff, which has been reduced as the group members have taken upon themselves most of the planning and implementation as their confidence levels have risen and their technical capability enhanced by a series of training events.
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- < 2,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (GEF, World Bank): 85.0%; local community / land user(s) (Land Management Group): 15.0%
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງມື | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | |
- ກະສິກໍາ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ແນວພັນ, ແກ່ນພັນ | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | |
| Seedlings | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Labour contribution to the land management group is in principle voluntary, but for some of the specific SLM interventions SLMP pays the households a fixed amount per area converted or treated with grass strips, planted with bamboo rhizomes etc. These cash payments are an incentive to establish and start certain techniques for which considerable labour is required. All recurrent activities are carried out by the group members.
Tool sets are provided to the group, consisting of hand tools as pickaxe, crowbar and spade. Additionally, seeds and seedlings needed for SLM activities are provided free of cost by SLMP, such as bamboo rhizomes, tree seedlings, fruit tree seedlings, fencing material for the group private forest establishment and temperate grass seed mixture.
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
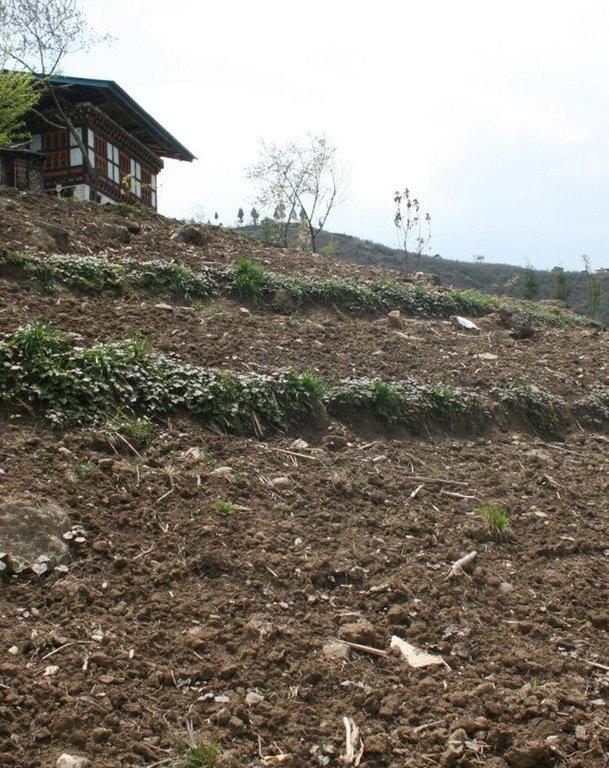
Soil and water conservation efforts have improved considerably with at least o.5 ha of land converted to/treated with SLM, such as grass strips, stone check dams and bamboo and tree plantation areas. A visible impact has been made as the area of grass strips and developing bench terraces are visible for the whole municipality.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The most vulnerable household are members of the group, representing the poorest families and female-headed households. Some of the hands-on trainings were carried out on the land of these households to give them first access and overcome their labour shortage constraint.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Approach has been rolled out to other communities in Trashigang Dzongkhag to scaling-up municipalities of SLMP, based on the experiences with the Drung Goenpa Land Management Group
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Moderate improvement of livelihoods through improved vegetable production (now self-sufficiency and cash generating), stabilization of land degradation, better workability of cropland through grass strip and bench terrace development and improved animal production through improved fodder quality and availability. Also the workload has been reduced by collecting fodder through cut-and-carry near the farm from the grass strips, instead of having to walk far to the forest for fodder collection. The group approach is able to tackle the labour constraint faced previously and includes all vulnerable households.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Considerable improvement in food self-sufficiency / security by vegetable production and increased yield on cropland treated with grass strips. Also clear improvement of animal production because of fodder improvement with the grass strips providing readily available quality fodder. Potato has now become a cash crop and some households sell vegetables, whereas they had to purchase in the recent past.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
- ກໍາໄລເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ (ຄວາມສາມາດ), ການປັບປຸງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ, ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ, ອັດຕາສ່ວນ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນພາລະວຽກ
- ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
- ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ບໍ່ແນ່ນອນ
ຖ້າ ບໍ່ ຫຼື ບໍ່ແນ່ໃຈ, ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ແລະ ຄໍາເຫັນ:
The group is expected to be able to sustain their activities independently, but a group process is always complex and there are no certainties looking forward. The improved sense of community bonding and mutual trust however is clearly expressed and essential for future sustainability of the group, supported by the existing group saving account, facilitating financial sustainability.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Are equal.... |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Enhanced community bond and mutual trust Labour-sharing approach in group eases the difficulty to implement labour-intensive SLM activities Vegetable production in group has improved food security and generates cash income Saving account of group facilitates credit need of households and serves as common bond between households (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continued support and guidance to group Continue labour-sharing in future activities Increase production area Regular bookkeeping and cash generating activities to add to savings) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Are equal... |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
|
Initially freely grazing cattle caused problems between group members with implementation of SLM activities Group expresses interest in having a simple meeting venue to facilitate group meetings |
By-laws help to overcome issues and working together in a group has improved mutual trust Seek support to construct simple meeting hall |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ