Adapted management of organic soils [ເຢຍລະມັນ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Johanna Fick
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1697 - ເຢຍລະມັນ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Baum Sarah
Thünen Institute of Rural Studies
ເຢຍລະມັນ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Climate Change - Land Use Strategies (CC-LandStraD / GLUES)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Thünen Institute (Thünen Institute) - ເຢຍລະມັນ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.5 ແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ອ້າງອີງເຖີງແນວທາງ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ໄດ້ເຮັດເປັນເອກະສານທີ່ໃຊ້ WOCAT)

Open dialogue platform on sustainable land management [ເຢຍລະມັນ]
Establishing a dialogue platform on sustainable land management which is open to all stakeholders
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Johanna Fick
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
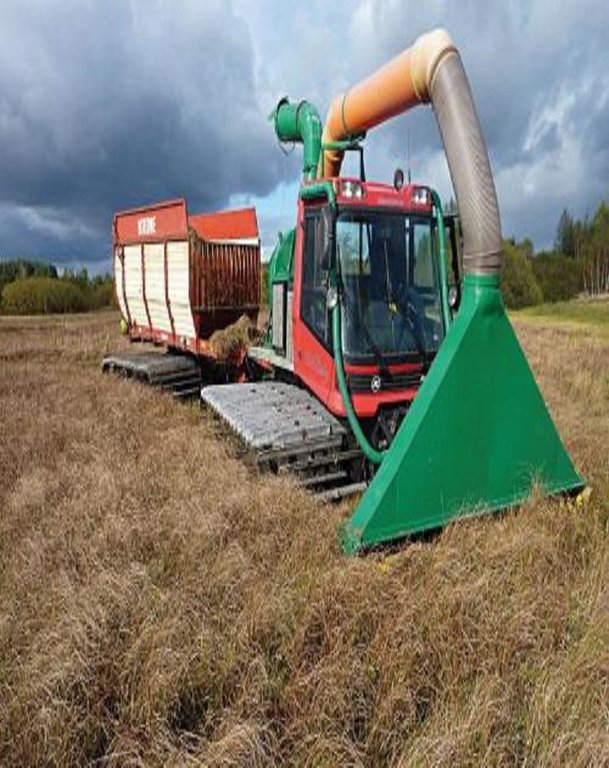
Re-wetting of organic soils and following adapted management suitable for wet conditions like extensive grazing land or paludiculture.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
In peat lands, formed over centuries, reducing the ground water level leads to min-eralization: this results in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and leaching of dis-solved organic nutrients into adjacent water bodies. Furthermore, drainage leads to the destruction of highly specialized ecosystems. Re-wetting, by removing of drain-age systems (etc.), means the restoration of a higher ground water level which can reduce GHG emissions in the long term. Re-wetting to a water-level of 10 cm below the soil surface is ideal for reducing GHG emissions and preventing peat mineraliza-tion. One prerequisite for re-wetting is that soil degradation and peat mineralization are not too advanced. An adequate water supply must be available. Re-wetting also affects adjacent areas so possible impacts such as flooding of settlements and in-frastructure must be considered.
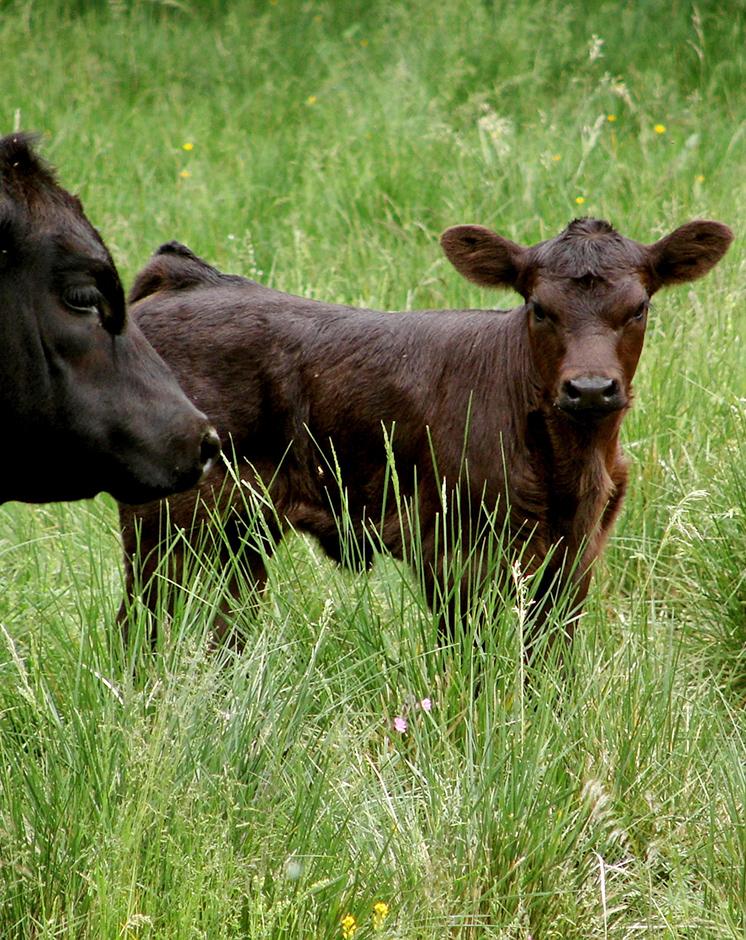
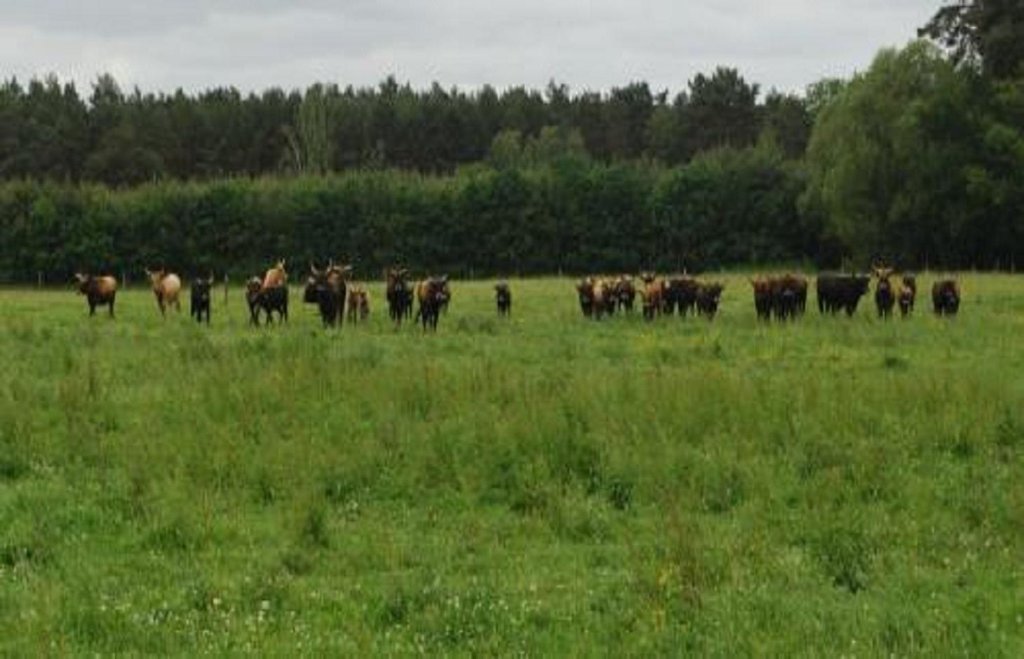
Purpose of the Technology: Land uses suitable for the soil conditions after re-wetting are extensive grazing, or paludiculture. Paludiculture is the cultivation of wet organic soils by preserving or renewing peat by planting and harvesting specific trees (e.g. alder), reeds and sedges. On fens, alder trees (for wood /biomass production) or plant species grown for their products (e.g. for thatch) or bioenergy, including the common reed, reed canary grass or cat’s-tail, can be cultivated. On peat bogs sphagnum farming as a peat substitute in horticulture, or as a medicinal plant, is possible. The first harvest of the common reed can take place four years post-establishment; thereafter annually. Alternatively, extensive livestock grazing with water buffalo or suitable breeds of cattle like Galloway or Heck has potential for re-wetted land. Year-round grazing is possible with a carrying capacity of up to 0.7 livestock units/ha.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Apart from avoiding huge amounts of GHG emissions and bringing land into alter-native production, further aims of re-wetting and adapting land use are:
-soil protection (soil structure, water content, peat protection);
-water protection (water quality, buffering / filtering water);
-protection of the landscape’s water regime and material balance (solute transport);
-biodiversity protection (retaining a sensitive ecosystem with specialized/ threatened species); and
-flood protection (organic soils can quickly absorb large amount of water).
There are many advantages for the environment while still creating a (modest) in-come for land users. Unlike most other bioenergy production chains (e.g. maize, rapeseed) which do not have these environmental co-benefits, paludiculture with the common reed can become a sustainable production system.
Natural / human environment: The Altmark region is located on the North German Plain. The region is predomi-nantly characterized by agriculture but has many forests too. Because of the high proportion of grassland, cattle are important. The use of biomass for bioenergy was increasing and many biogas plants were established in the last few years. Fens are mostly located in Altmark-County Salzwedel. Here, the average population density (42.7 inhabitants km2) is relatively low in the German context and the annual precipi-tation of 466mm is also below the overall German average.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເຢຍລະມັນ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Germany, Saxony-Anhalt
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Altmarkkreis Salzwedel and district Stendal (total area of region: 4744 km²)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 288 km2.
Potential area: 288 km2 (~ 6% of the region). The area stated is the area that is potentially usable for the technology due to available geographical data; requirements: fen (Nieder- und Anmoor), area under agricultural land use, outside of nature protection areas (national parc, nature reserve, FFH area, SPA area, Ramsar). Due to re-wetting restrictions by factors like nowadays water level in the area, settlements etc., the effective area suitable will be lower.
Boundary points of the Technology area: 52.842906; 10.760956
52.351751; 11.858462
52.541514; 12.187856
52.870405; 12.231025
53.050502; 11.633261
2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
answer refers to re-wetting
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາແບບປະສົມປະສານ (ລວມທັງ ການລ້ຽງສັດ-ປຸກຝັງ)

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 234Longest growing period from month to month: Spring-autumn

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ແບບຂັງຄອກ
ປະເພດສັດ:
- ຄວາຍ
- cattle
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main species: Water buffalo, adapted cattles (e.g. Heck cattle, Galloway)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Drainage causes mineralization, sagging and reduction of organic matter of organic soils as well as high GHG emissions, disturbed water regimes, destruction of valuable ecosystems and loss of ecosystem services.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Long term use of drained organic soils leads to soil degradation and lower productivity. Thus, more fertilizer is needed. Due to sagging of organic soils, ditches and drainages need to be renewed every 10-15 years.
Ranching: Water buffalo, adapted cattles (e.g. Heck cattle, Galloway)
Grazingland comments: extensive grassland use with mowing and/or grazing; or paludiculture (e.g. Common Reed)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
Type of grazing system comments: extensive grassland use with mowing and/or grazing; or paludiculture (e.g. Common Reed)
Livestock density: 50-100 LU /km2
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ແມ່ນ (ກະລຸນາຕື່ມໃສ່ ຄຳຖາມຂ້າງລຸ່ມນີ້ກ່ຽວກັບການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ກ່ອນການທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ)

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ແລະ ປ້ອງກັນເຂດດິນທາມ
- Re-wetting of organic soils
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
- V5: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S11: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
- M3: ອີງຕາມສະພາບແວດລ້ອມ ທາງທຳມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: paludiculture
Specification of other structural measures: removal of drainage system, dykes, etc. allowing rise in groundwater level
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
- Ps: ຊຸດຂອງດິນອົງຄະທາດ, ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານຂອງດິນ
- Pu: ການສູນເສຍ ການທໍາງານ ຂອງຊີວະພາບຜົນຜະລິດ ເນື່ອງຈາກການກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນໆ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bh: ການສູນເສຍ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊິວິດ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Ha: ສະພາບແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
- Hg: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ລະດັບນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ ຫຼື ນ້ຳບາດານ
- Hq: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
- HW: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສາມາດ ໃນການປ້ອງກັນພື້ນທີ່ດິນທາມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Ps: subsidence of organic soils, settling of soil, Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bh: loss of habitats, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Ha: aridification, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: soil management (drainage), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (drainage)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (ploughing, fertilization)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Re-wetting of a fen with adapted agricultural land use afterwards: extensive grazing with cattle and paludiculture in Common Reed production.
Date: 07/2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for planners: high (Re-wetting concerns large areas)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
In blocks
Vegetative material: G : grass, O : other
Number of plants per (ha): G: full coverage, O: 5000
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): O: 2m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): O: 1m
Grass species: Grasses for extensive grassland use
Other species: Paludicultures like Common reed, Reed Canary grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): ~0%
Gradient along the rows / strips: ~0%
Structural measure: close/chamber ditches for groundwater level rise
Change of land use type: Crop land or intensive grassland to extensive grassland or paludiculture: see 2.5.2.2
Change of land use practices / intensity level: extensification
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Closed and chambered ditches/removed drainage systems: see 2.5.3.2
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Sarah Baum, Thünen Institute of Rural Studies, Bundesallee 50, D-38116, Braunschweig, Germany
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | For fen re-wetting, removal or blocking of drainage systems like ditches, pumping stations, dykes or drainages is necessary. Extent depends strongly on local site conditions! (examples chosen from Landesumweltamt Brandenburg (2004)). | |
| 2. | Extensive grassland or paludiculture | |
| 3. | Extensive grassland: if field is not already used as grassland but as cropland: grassland sowing | July/August |
| 4. | Extensive grassland: natural spread: no input | |
| 5. | Paludiculture: planting Common Reed | Spring |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedling | ha | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Removal of drainage | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Ditch filling | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Make-ready and set-up cost | ha | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 6000.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 6000.0 | |||||
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | water level management: weir control ~once a week: efforts depends strongly on local conditions. Control is also necessary when weirs are used to ensure controlled water level. | |
| 2. | extensive grassland: mowing | 2 times per year |
| 3. | extensive grassland: grazing with water buffalo, adapted cattles (e.g. Heck cattle, Galloway) | year round |
| 4. | paludiculture (Common Reed): harvesting | Winter (ideally: frozen ground)/first harvest 4 years after establishment, thereafter annually |
| 5. | management | yearly |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Management | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1000.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 1000.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Machinery/ tools: paludiculture: harvest in winter (frozen soil): normal machinery. If soil is not frozen: special machinery: snow groomer (crawler chain) modified as harvester
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Only rough estimates on costs and income can be given due to the very new and innovative technology. The technology is still in the introductory phase at present
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Annual rainfall: 500-750 mm, 750-1000 mm, 1000-1500 mm, 1500-2000 mm
250-500mm: This only characterises the Altmark region (average 460mm); more rainfall is possible!
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: temperate. Altmark region
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (this only characterises the Altmark region), 500-1000 m a.s.l., 1000-1500 m a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ສູງ (> 3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil depth on average: shallow (21-50 cm) (refers to histic layer), moderately deep (51-80 cm), deep (81-120 cm), very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil fertility is very low-low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is very high
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ເກີນ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Seasonal fluctuations (surface water): Wet conditions throughout the year.
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ສູງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
Not high in number but in quality! Highly specified species. Depends on definition of Biodiversity
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
Market orientation of production system: nature conservation
Market orientation of cropland production system: Comercial/market (cows for dairy farming and reed sold for bioenergy and thatching)
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Comercial/market (Grazing, mowing; paludiculture )
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
- NGO
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Land owners can re-wet their land and manage it suitable for wet conditions afterwards. The state or NGO, for example, can buy land and re-wet it; normally followed by nature protection. This technology can not be done by one land user. It has major impacts off-sites and reflects normally more then one farmer.
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຕໍ່ຜົນຜະລິດ
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ຄວາມຕ້ອງການ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Thorugh extensification
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
possibly
ຄວາມແຕກຕ່າງ ທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດ
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Thorugh extensification
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ຊັ້ນນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ / ນໍ້າ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
In terms of former cropland
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Extensive usage
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
15-30
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
0.8
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Before conserv.: Ca. 15-30 tCO2eq/ha*a quantify (indicate unit) after conserv.: 0-8 tCO2equ/ha*a specify: mean reduction potential peat bogs: 15tCO2equ/ha*a; fens: 30tCO2equ/ha*a
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
Value for nature conservation/relevant species
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Perhaps
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ມົນລະພິດ ທາງນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Re-wetting is only possible on larger scales
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Depends strongly on subsidies and other incentive mechanisms as well as opportunity costs (regionally different). Further, if re-wetting is not financed by the land user the economic benefit is greater but even less as before re-wetting.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is no increasing trend to adopt the technology as it is not economically attractive for farmer. But for environment groups (NGOs), without an economical interest, this measure can be interesting.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
By re-wetting organic soil huge amounts of GHG emissions can be avoided on a relatively small area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Financial incentives for farmers are needed e.g. based on GHG-mitigation potential. Alternatively, areas can be bought by e.g. NGOs or government for re-wetting/ nature protection |
|
Paludiculture on re-wetted soils allows an adapted agricultural land use How can they be sustained / enhanced? Financial incentives (e.g. subside payments) for farmers are needed |
|
Extensive grassland cultivation on re-wetted soils allows an adapted agricultural land use (grazing/mowing) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Financial incentives (e.g. subside payments) for farmers are needed |
| The use of fertilizer and manure inputs leads to pollution of water bodies. The water quality will be enhanced by less fertilizer/manure input through this technology compared to intensive agriculture. |
| Due to the technology, higher water retention, flood prevention and biodiversity can increase compared to use of drained organic soils. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| On re-wetted soil land use options are very restricted due to wet soil conditions. | Financial incentives for farmers are needed. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| High opportunity cost for land users: income from intensive cropland on drained soils is higher than income from re-wetted soils with extensive land use. | The technology could be economically attractive if farmers get financial incentives for applying it (re-wetting and adapted extensive usage). It would become even more attractive if no incentives were paid for e.g. maize production on drained organic soils (those incentives are actually paid if the maize is used for bioenergy production). |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Bonn A, et al. (2014) Klimaschutz durch Wiedervernässung von kohlenstoffreichen Böden. In: Naturkapital und Klimapolitik-Synergien und Konflikte.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Naturkapital Deutschland TEEB DE Report. Technische Universität Berlin Helmholtz-Zentrum für Umweltforschung-UFZ, Berlin, Leipzig
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Wichtmann W, Wichmann S (2011) Environmental, Social and Economic Aspects of a Sustainable Biomass Production.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Journal of Sustainable Energy & Environment, Special Issue (2011):77-81
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
URL:
http://www.duene-greifswald.de/de/projekte.php_enim.php
URL:
http://www.naturkapital-teeb.de/publikationen/projekteigene-publikationen.html
URL:
http://daten.ktbl.de/feldarbeit/home.html
URL:
https://www.stmelf.bayern.de/idb/default.html
URL:
ttps://www.google.de/search?q=Leitfaden+zur+Renaturierung+von+Feuchtgebieten+in+Brandenburg.+&ie=utf-8&oe=utf-8&gws_rd=cr&ei=btyoVebdJcGYsAH4tpWoCA
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Open dialogue platform on sustainable land management [ເຢຍລະມັນ]
Establishing a dialogue platform on sustainable land management which is open to all stakeholders
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Johanna Fick
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ