Relay Intercropping [ອີທິໂອເປຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: GERBA LETA
- ບັນນາທິການ: Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Kurcheta
technologies_6630 - ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Sankura Goa
Farmer
ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - ເຄັນຢາ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Intercropping is friendly to the farm. It also increases the "land equivalent ratio" of a plot of land. However, farmers note that surface compaction can be a problem under relay intercropping - because of the frequent field operations required for each of the crops at different times.
1.5 ແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ອ້າງອີງເຖີງແນວທາງ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ໄດ້ເຮັດເປັນເອກະສານທີ່ໃຊ້ WOCAT)

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [ອີທິໂອເປຍ]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: GERBA LETA
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Intercropping is the growing of two or more crops on the same piece of land at the same time or in temporal sequence. Relay intercropping usually involves planting a legume into an established cereal crop. This farming practice has multiple benefits and is a popular among smallholders in Wolaita zone of SNNPR.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
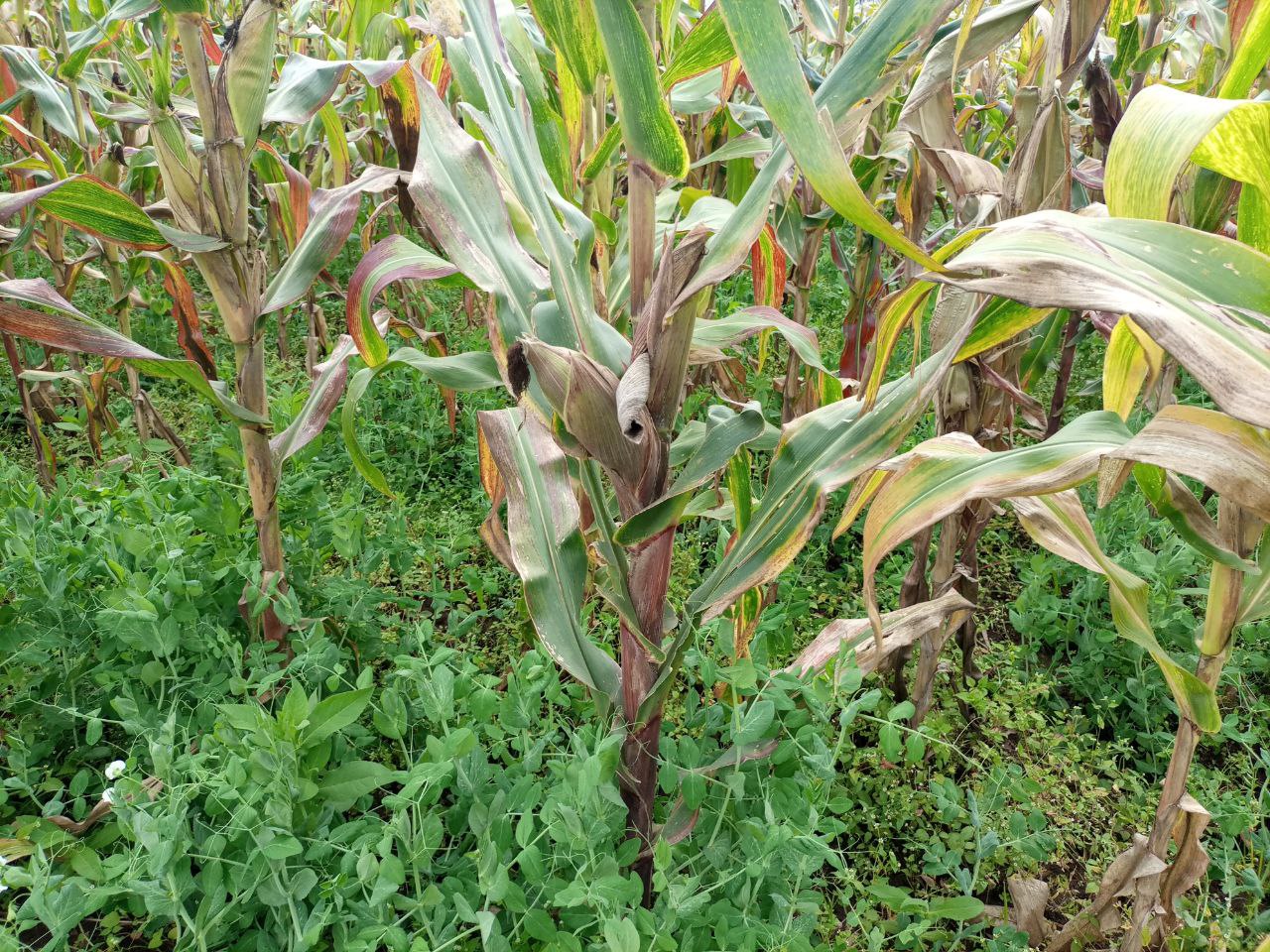
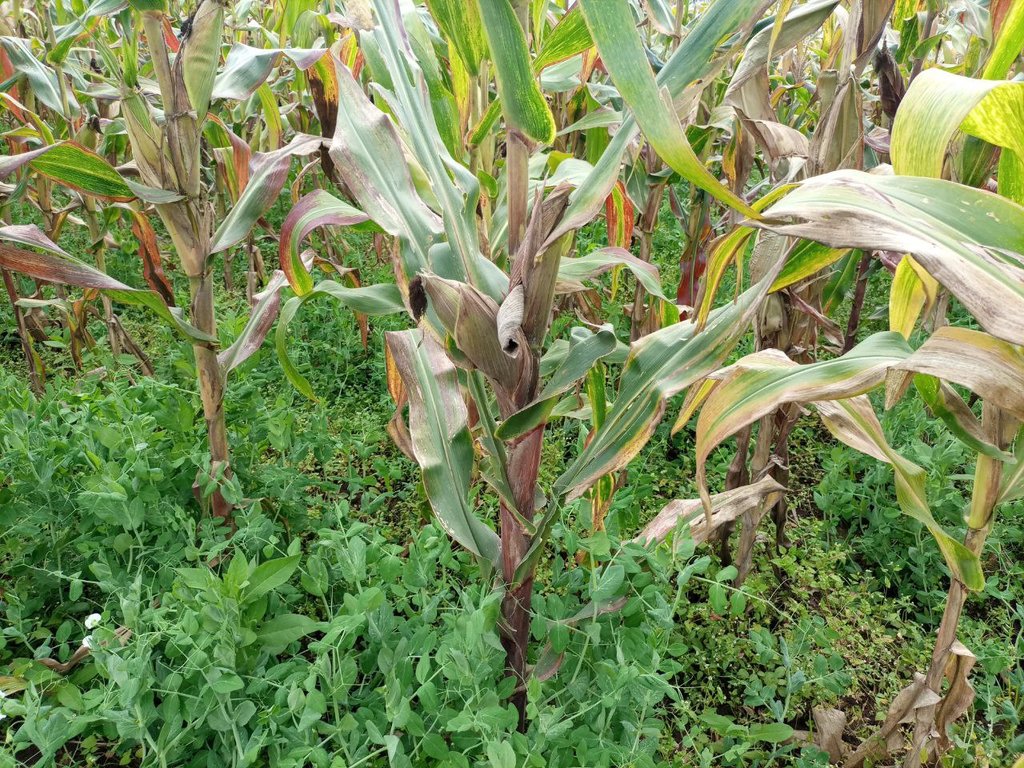
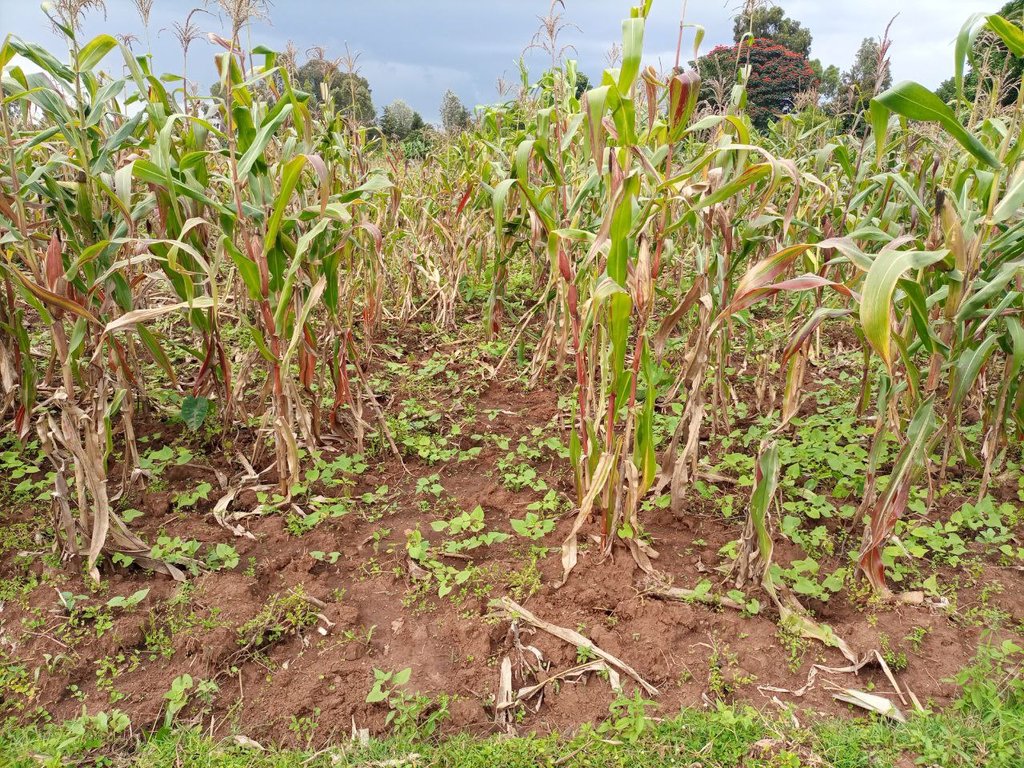
Intercropping systems in Sodo Zuria of Waraza-Lasho kebele are characterized by relay intercropping. Under relay intercropping a second crop is planted alongside a growing crop, typically when it has reached its reproductive stage of growth. The practice enables efficient use of available space. In this kebele (lower administrative unit), field peas and haricot beans are commonly intercropped within maize. The seeds of these legumes are either sown in no particular pattern, or simply broadcast, under the main crop, maize. They are planted when the maize comes close to physiological maturity. Intercropping of cereals with legumes improves soil fertility through nitrogen fixation: this system extracts fewer nutrients from the soil than do monocrops. The practice also avoid risks of crop failure, improves effective use of available land, generates additional income and ensures food and nutrition security of the family farmers. Making the right choices about crops and timing of relay planting is crucial. Furthermore, good intercropping demands improved varieties of cereals and legumes. Adequate and timely labour is required also. Conventionally, the farmers till the land up to five times before planting the main crop. In relay intercropping further more land cultivation is essential to plant the companion crop.
Various researchers have reported considerably higher yields from intercropping compared with a pure stand. This can be measured through the “land equivalent ratio” which describes the relative land area required under sole cropping to produce the same yield as under intercropping. Intercropping has been regarded by many farmers as a technique that reduces risk in crop production. It improves carbon sequestration since it enhances biomass accumulation both above and below the surface of the soil. Intercropping is also a form of climate change adaptation strategy as it spreads risks and allows opportunistic use of extra moisture. However, relay intercropping can subject the land to compaction because the companion crops demand extra field operations. These include harvesting the main crops, or sometimes stripping the leaves to reduce the shading effects for the low growing companion crops. There is also extra labour required for weeding and harvesting of the intercrop.
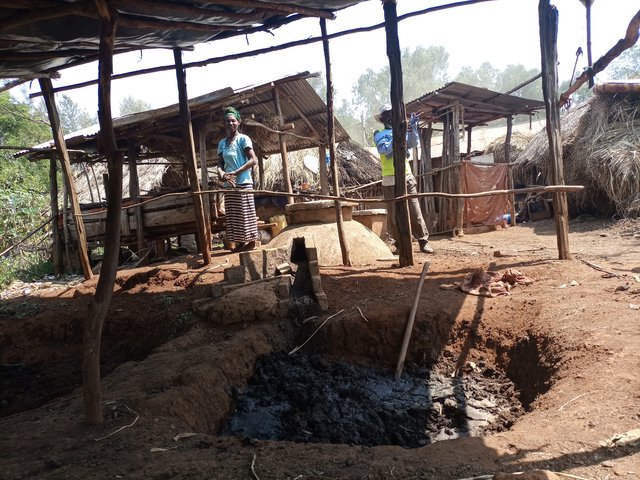
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດທົ່ວໄປທີ່ກ່ຽວກັບຮູບພາບ:
The photo portrays relay intercropping whereby beans were planted late when the main crops nearly matured. The practice has an immense contribution to the family farmer not only in terms of improving soil fertility but also improving food and nutrition security of the family farmer.
2.4 ວິດີໂອ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ, ຄໍາອະທິບາຍຫຍໍ້:
Videos of the technology is not documented.
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
SNNPR
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Sodo Zuria
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 0.1-1 ກມ 2
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
- through agricultural extension system
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Intercropping is a common practices since over 5 decades but the distribution limited to a few farmers. The agroecology project/ISFM+ intervention stimulated its pervasive implementation.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ສາລີ
- ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວປະເພດອື່ນໆ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
The area received Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain with summer maximum).
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Rotating cereal crops with root crops.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ (ຕໍ່ເໜືອງກັບ ຄຳຖາມ 3.4)
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ລະບົບການປູກພືດໝູນວຽນ (ການປູກພືດໝູນວຽນ, ປ່າເລົ່າ, ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່)
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງພືດ ແລະ ລ້ຽງສັດ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການຈັດການອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຂອງດິນປະສົມປະສານ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ
- A5: ການຈັດການ ແລະ ການປັບປຸງແກ່ນເມັດພັນ ແລະ ແນວພັນ
- A6: ການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ
A6: ລະບຸການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ:
A 6.3: ເກັບລວບຮວມແລ້ວ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M5: ການຄວບຄຸມ / ການປ່ຽນແປງຂອງອົງປະກອບຂອງຊະນິດ
- M6: ການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ (ຂີ້ເຫຍື້ອ, ນໍາໃຊ້ຄືນໃຫມ່ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ)
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
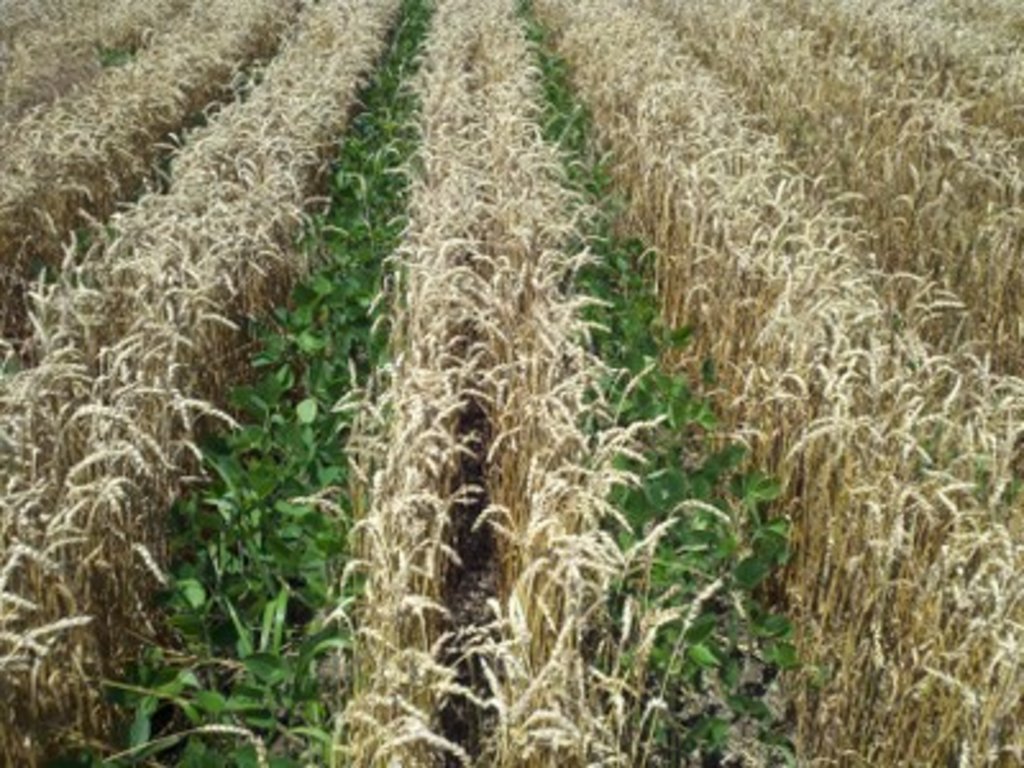
Soybean intercropped with wheat. Adopted from https://www.no-tillfarmer.com/articles/4084-lessons-learned-from-2014-modified-relay-intercropping.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Ohio State University
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
4 Timad
ຖ້ານໍາໃຊ້ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ເນື້ອທີ່ຕາມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ, ໃຫ້ປ່ຽບເປັນ 1 ເຮັກຕາ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: 1 ເຮັກຕາ = 4 ໄລ່ ): 1 ເຮັກຕາ = :
4 Timad = 1ha
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Ethiopia Birr (ETB)
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
53.6283
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
400
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
We consider documentation of maintenance costs only to put in place the companion crops.
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
As we opt to focus on the maintenance cost of the relay intercropping, establishment cost is intentionally skipped.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | Before and during planting of companion crop. |
| 2. | Planting | During the long rain for associated crop. |
| 3. | Weeding | Three weeks after emergency of companion crops seedling onwards. |
| 4. | Harvesting | At the end of harvest season. |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Land preparation | PDs | 8.0 | 400.0 | 3200.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Planting | PDs | 4.0 | 400.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Weeding | PDs | 8.0 | 100.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Harvesting | PDs | 8.0 | 100.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Haricot beans/field peas seeds | kg | 40.0 | 60.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | NSP fertilizer | kg | 50.0 | 45.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 11050.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 206.05 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Almost all labor cost, seed and other inputs are covered by land users for maintaining the technology.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Usually, the cost is influenced by the economic crisis and high inflation rate experienced in the last few years in Ethiopia. It is also related to global fuel and fertilizer prices as well as other crises which are the potential causes.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
1452.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Bimodal rainfall is intercepted in the area with a summer maximum from June to September.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Sodo Center Meteorology
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
High temperature is experienced from December to February.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
The altitude of the place is 1,940 m above sea level.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
The SLM experts describe the soil texture as clay loam.
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ສູງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ຕໍ່າ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ຮັ່ງມີ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
The farmer piloted conservation agriculture practices. Also, the land users plant woodlots around the periphery of his farmland.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Land users owns 3.5 hectares of land.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
The land is inherited from the family line but aligned with the constitution adopted by the government that guaranty usufructs to the land.
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
There is a high unemployment rate. Of course, the area is highly populated. As the site is located closer to the zonal capital they have good financial services particularly access to Bank services such as for saving.
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increases as the technology best use the available space and surplus moisture in the soil system.
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increases as the arrangement allows the relay crop to enjoy the space and available residual nutrients at disposal.
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Relay intercropping increases the number of crops harvested per unit of land in one season.
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Combining cereal with legumes improves land management by increasing biomass production and combining cereal with nitrogen-fixing legumes that contribute to land management.
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ນໍ້າດື່ມ ມີຄຸນນະພາບ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Combining two different types of crop on a farm diversify farm income.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມແຕກຕ່າງ ທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດ
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Workload increases as it demands additional labor for land preparation, planting, weeding, and harvesting two crops grown in temporal sequences.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Relay intercropping allows ensuring the food and nutrition security of family farmers.
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Soil moisture can exhaustively be used by the companion crop.
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Frequent farm operation for two different crops increases the pressure that leads to soil compaction.
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Ground cover by two different crops on a temporal basis increases the absorption and storage of carbon.
ການປ່ຽນແປງ ອາກາດ ໃນວົງແຄບ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
No actual data to forecast the potential off-site impacts.
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Land covered by crops for extended part of a season contributes to carbon sequestration and reduction of greenhouse gases.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ປານກາງ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Maintenance cost for intercropping limited largely to labor and agricultural inputs such as seed and fertilizers.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
About 6% of land users adopted the technology on their own motivation.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Improve family farmers diet from the perspective of food and nutrition security. |
| Generate income from the sale of companion legume crops. |
| Improve soil fertility and management of the land |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Improve effective resource utilization such as land, labor, and inputs. |
| Insure against total crop failure under unfavorable weather conditions, and pest outbreaks. |
| Improve and maintain soil fertility as the combination is mostly cereal with legumes. |
| Increase total biomass and crop production per unit of land. |
| Pest levels are often lowered in intercrops, as the diversity of plants hampers the movement of certain pest insects and in some cases encourages beneficial insect populations. |
| Reduce soil erosion, lower soil surface evaporation & reduce weed infestation. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Demand more labor. | Overlay planting season, and promote row intercropping to simplify the management practices. |
| Relay intercropping triggers soil compaction, | Promote row intercropping for effective utilization of space and reduction of soil compaction. |
| Shortage of best fitting varieties of legume crops for relay intercropping. | Facilitate and improve land users access to suitable companion crops from the nearby research institutes. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| It is time-consuming as it requires more attention and thus increases intensive management. | Promote row intercropping and overlay planting season to avoid giving separate management practices. |
| There is reduced efficiency in planting, weeding and harvesting which may add to the labor costs of these operations, especially if the practice is at a larger scale. | Plant the main and companion crops simultaneously and apply optimum management practices. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Five persons.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
Only the land user.
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Three experts.
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
17/01/2023
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Guidelines for Intercropping. Mohler, C. L. and Stoner, K. A. 2009.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
EBook for $24 (https://www.sare.org/publications/crop-rotation-on-organic-farms/guidelines-for-intercropping/)
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Raza, M.A. et al. 2019. Growth and development of soybean under changing light environments in relay intercropping system. DOI: 10.7717/Peerji.7262.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Free online from Research gate
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Intercropping: What it is, what it isn't and why we do it.
URL:
https://www.permaculturenews.or/2016/08/12
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Intercropping Agriculture System
URL:
https://fscluster.org/gaziantep
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Intercropping: Ergonomic and Efficient Farming
URL:
https://eos.com/blog/intercropping/
7.4 ຄຳຄິດຄຳເຫັນທົ່ວໄປ
Specifications under 3.6 such as tillage system, and reside management are not well aligned with the pdf version. So, it is difficult to make choices.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [ອີທິໂອເປຍ]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: GERBA LETA
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ