Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means [Намиби]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Johannes Laufs
- Редактор: –
- Хянагч: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
De-bushing
technologies_2203 - Намиби
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр хэвлэх
- Хөтөч дэх бүрэн хураангуй
- Бүрэн хураангуй (форматгүй)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 17 7-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 31 5-р сар 2019 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 02 11-р сар 2021 (public)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 21 2-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 22 8-р сар 2017 (inactive)
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - Герман1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/08/2014
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
The technology described is a means to rehabilitate degraded rangeland. Through targeted harvesting of bushes, the bush density is reduced, allowing for better growth of grass.
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
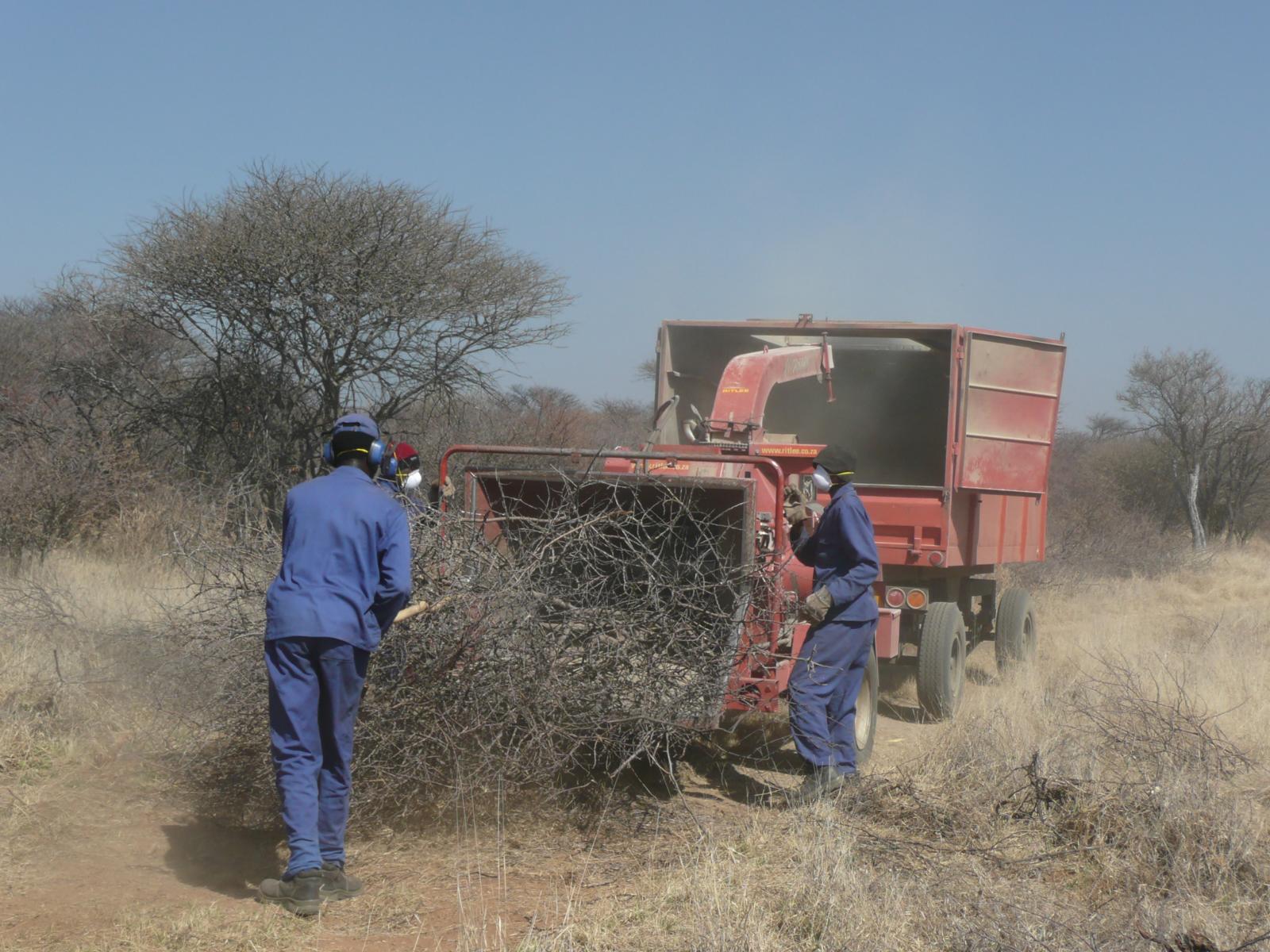
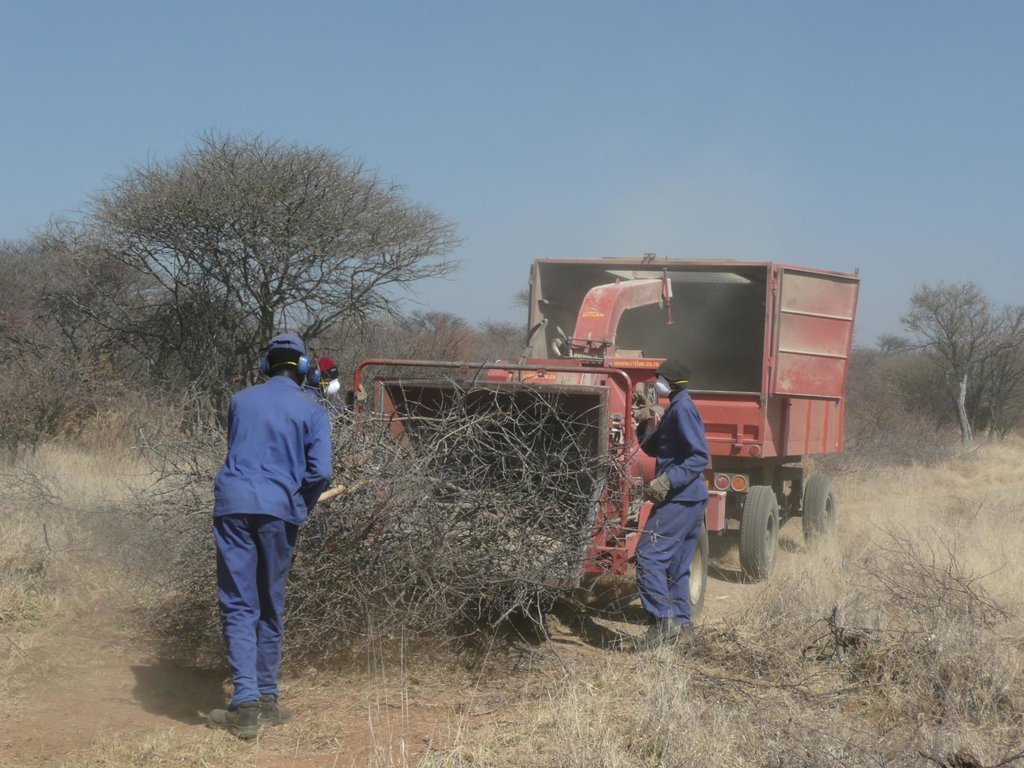
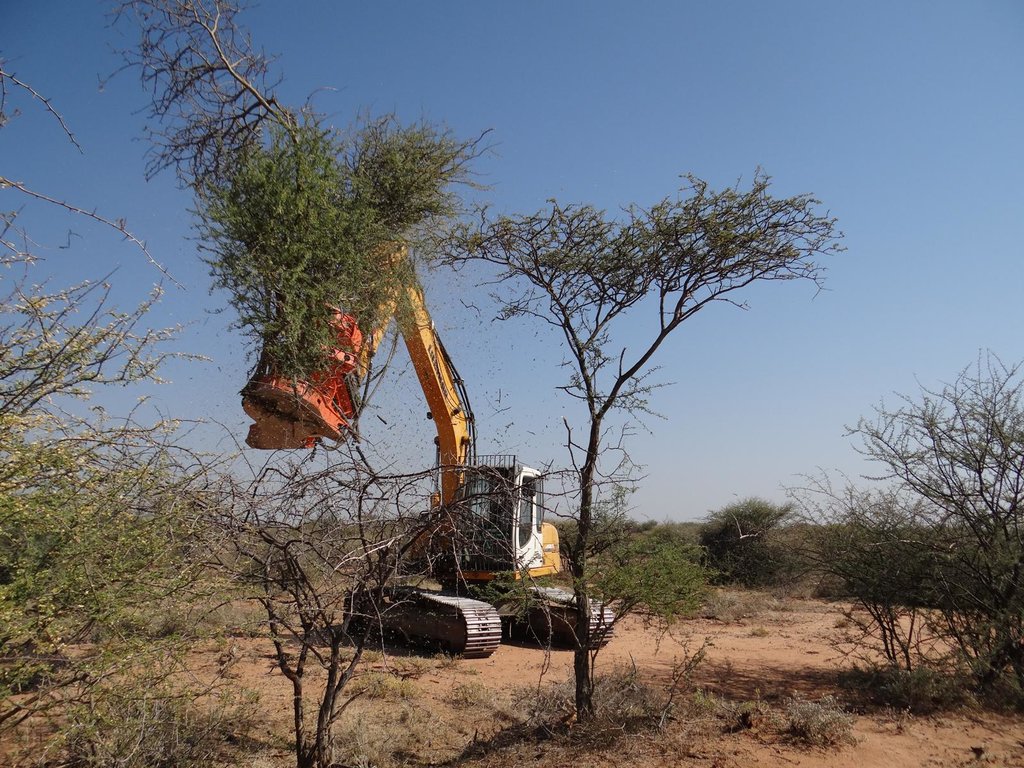
On Namibian farmland bushes are harvested in order to reduce the excessive bush densities, that stiffle the growth of other plant species, especially grasses. Bush can be harvested manually (e.g. with axes), semi-mechanised (e.g. chainsaws) or fully mechanised (e.g. customised excavators). After cutting, the bush is typically left to dry and in a second step processed into a transportable format (e.g. wood chips).
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
Bush thinning in the form of selective bush harvesting is applied on Namibian agricultural land. The main aim of the technology is the restoration of degraded rangeland, reducing bush densities, fostering the re-growth of grasses. According to the best available estimates about 45 million hectares of Namibian farmland are affected by bush encroachment. Bush encroachment negatively affects biodiversity, groundwater recharge and importantly the carrying capacity of rangeland. Bush encroachment equally hinders crop production, but this phenomenon is of less significance in Namibia due to the limited scope of crop production in the country. There is a multitude of causes for bush encroachment, among which overgrazing (i.e. overstocking with cattle or lack of rotational grazing), reduced frequency of wildfires and higher CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere feature strongly. Bush encroachment is not to be equated with the invations of alien species, since most encroacher species are indigeneous to Namibia
While it is believed that natural transitions in the ecosystems can on the long-run, under favourable climatic conditions, also lead to reductions of bush encroachment, active rehablitation measures are required in order to achieve improvements on the short-run. This is an aboslute necessity for many Namibian farmers, who experience severe economic difficulties due to the reduced productivity of their land.
Bush control comprises of responsive measures (bush thinning), follow-up measures (aftercare) as well as preventative measures (good rangeland management practices). Since vast areas of Namibian rangeland are heavily encroached by indigenous bush species, the focus is currently on responsive measures, i.e. bush thinning.
Bush thinning entails the practice of selectively harvesting a specified number of bushes, effectively reducing the number of bushes per given area. To determine the density of bush remaining after thinning, a formula based on tree equivalent (TE) and average annual rainfall is used. A tree equivalent is defined as a woody tree or bush of 1,5 metres in height. Thus, a 3 metre shrub would represent 2 TE, a 4.5 metre shrub 3 TE. As rule of thumb for estimating optimal bush density, about 30-35% of encroacher biomass should be removed. This rule is based on research that has been carried out mainly in South Africa over the past decades, measuring and comparing the re-growth experienced at various sites where bush had been harvested. Areas, in which too much bush was removed, experienced strong re-growth of bush, often resulting in even heavier bush encroachment.
Bush thinning follows strict environmental guidelines set by the Ministry of Environment and Tourism through the Environmental Management Act with regard to the equipment's used (avoiding negative side-effects such as disturbance of the soil) and the amount of bushes to be harvested (aiming at the right balance between reducing the encroachment and maintaining a healthy number of the desired bush species). The amount of bushes to be harvested must be determined by expert for each specific area and depends on various factors, e.g. soil type, topgraphy, severity of bush encroachment and intended land use type.
It is important to note, that as with most direct interventions in natural ecosystems, there is a lack of precise knowledge on the long-term effect of bush thinning and the appropriate intensity thereof. There is however no doubt that active bush control has an overall positive effect on the savanna ecosystem in Namibia.
In order to render bush thinning economically feasible, value chains have been developed. Through the processing and utilisation of the woody bush biomass, income can be generated and the cost of bush conrol balanced. Existing value chains include the production of charcoal, firewood, poles, bush based animal feed as well as heat and electricity. Value chains currently under development include composition materials, such as wood-plastic, wood-cement and bio-plastic.
Scientific observations have shown, that bush thinning cannot be implemented as a once-off activity, but requires regular follow-up to prevent the re-thickening of the bush. Follow-up measures (so-called aftercare) include the prevention of coppicing and re-growth. This can be achieved by applying aboricides selectively to the cut stems, stem fires or the introduction of browsers (e.g. goats). Research on the effectiveness and possible side effects of each of these methods is limited.
The need for bush control, and therewith bush thinning, is widely recognised among land owners and also acknowledged on the national political agenda.
A major challenge for the implementation of the technology is the limited suitability of available machines. The hardness and high mineral content of the woody biomass leads to high wear and tear on the equipment (both harvesting equipment and processing equipment, like chippers and pelletisers), often rendering operations unprofitable. Research into more suitable machinery is ongoing.
Further, the implementation of sustainable bush control must be improved through skills training and continuous monitoring of the long-term effects on rangeland.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
Гэрэл зурагтай холбоотой ерөнхий тэмдэглэл:
All photos have either been taken by the GIZ Support to De-bushing Project or were provided to the project by third parties.
2.4 Технологийн дүрс бичлэг
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=859GshR9hso&t=3s
Bush Encroachment in Namibia: Causes and Extent
An explanation of the root causes of bush encroachment and its impact on land in Namibia.
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/11/2015
Байршил :
Namibia
Зураглаачийн нэр :
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bmlzPDiqlxo&t=45s
Biomass Value Addition: Bush Based Products
An overview of existing and potential value chains based on encroacher bush.
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/11/2015
Байршил :
Namibia
Зураглаачийн нэр :
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MMSOfV2KBjA
Biomass Energy: From Bush to Electricity
Overview of the energetic applications of woody biomass from encroacher bush.
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/11/2015
Байршил :
Namibia
Зураглаачийн нэр :
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Намиби
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
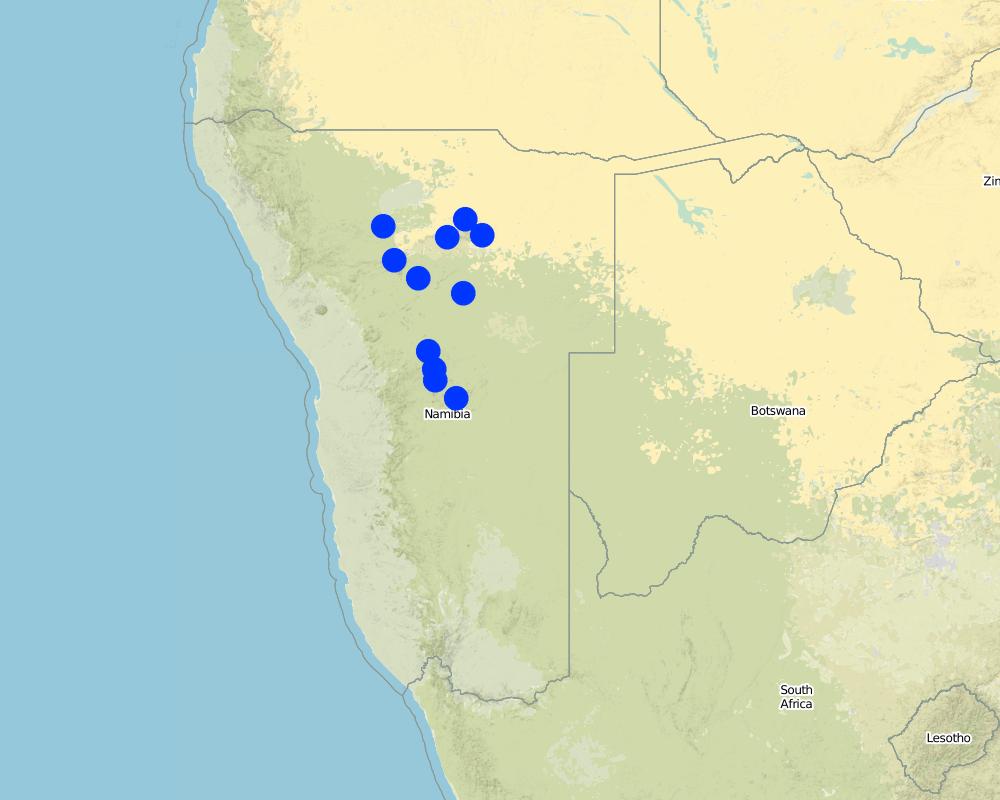
Bush control is applied across Namibia on many privately owned farms. Activities are most concentrated in the regions Khomas, Omaheke, Otjozondjupa and Oshikoto.
Тайлбар:
Pointers on the map only indicate points (e.g. urban centres) around which activities are concentrated. It is not possible to depict each site where bush control is implemented due to the high number of individual activities and projects.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2015
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Since the 1950s the phenomenon of bush encroachment has been recognised by farmers in Namibia and counter measures have been implemented over the decades. The technologies applied largely relied on the means and innovative capabilities of the respective land owner. Only as of 2014, through the introduciton of a national Support to De-bushing Project, are technologies systematically researched and tested in the field.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- Экосистемийг хамгаалах
- Биологийн төрөл зүйлийг хамгаалах / сайжруулах
- Үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуйн газар:
- Суурьшмал
Голлох амьтны төрөл ба бүтээгдэхүүн:
Cattle, goats, game
Тайлбар:
Namibia is characterised by large commercial cattle farms. Du to its aridity the land is largely unsuitable for crop farming, with exceptions in high-rainfall areas such as the Grootfontein, Tsumeb, Otavi triangle.
The Northern parts of Namibia are managed as communal land, where farmers have lease holds for their land. In these areas a combination of millet production and cattle herding is common.
Хэрэв технологи нэвтрүүлснээр газар ашиглалт өөрчлөгдсөн бол технологи нэвтрүүлэхээс өмнө байсан газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг тодорхойлно уу:
The implementation of bush thinning allows to maintain the land use (e.g. cattle ranching) and is typically applied to increase productivity in the long-term.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Малын нягт (шаардлагатай бол):
284 000 in targeted area of bush thinning (Otjozondjupa region)
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
- гадаргын/ ургамал бүрхэвч сайжрах
3.5 Технологийн тархалт
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 1,000-10,000 км2
Тайлбар:
Currently bush thinning is implemented on a total of approximately 120.000 hectares (1.200 km2) of farmland per annum. These activities are not confied to certain areas, but spread across all of Namibia, typically concentrating in the most encroached areas (e.g. Otjozondjupa, Khomas, Oshikoto and Omaheke regions).
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамалжилтын арга хэмжээ
- V4: Харийн/ түрэмгий зүйлийг солих, зайлуулах

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
- M5: Төрөл зүйлийн бүтцийн өөрчлөлт/хяналт
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Биологийн доройтол
- Bh: Амьдрах орчин доройтох
- Bq: Хэмжээ/ Биомасс буурах
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
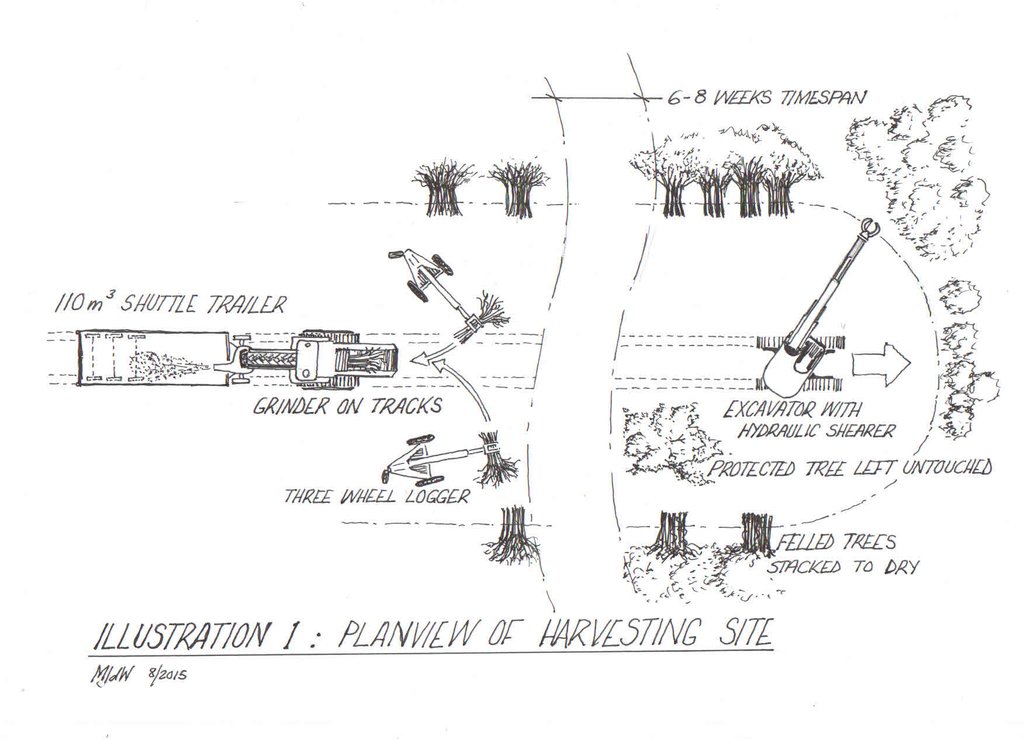
Drawing of a bush harvesting site layout. The drawing depicts fully mechanised bush harvesting and immediate processing into wood chips. This set-up is most suitable for large-scale bush thinning, e.g. for the purpose of supplying biomass in larger quantities. Such off-take includes the potential export of bush in processed form (pellets) or energetic utilisation (e.g. local biomass power plants or biomass boilers in the industry). Currently two such energy solutions exist in Namibia, one at a local brewery and one at a local cement factory.
Note that a range of bush harvesting methods exist, ranging from fully mechanised (as depicted) to manual bush harvesting (e.g. with axes). The site layout and principles are the same in all scenarios, but harvesting speed and costs differ.
The bush harvesting process:
Bushes are harvested selectively with and excavator, to which a hydraulic sheer cutter is attached. The biomass is stacked in rows and left for drying some six to eight weeks (depending on weather conditions). The biomass is then further processed with a chipper and collected with a trailer for further transport off the farm (e.g. to a biomass power plant or industrial off-taker). As a rule of thumb, one third of the standing biomass is removed, leaving two thirds standing. Harvesting starts with smaller plants and then moves to larger ones, cutting only plants with 15 centimetres of diameter or less (as per Namibian forestry regulations).
Cost of bush harvesting can be calculated per hectare (e.g. land owner's perspective) or per tonne (in fuel supply agreements with off-takers). All below stated costs are approximations, as costs vary widely depending on the local framework conditions on a given piece of land. Typically the costs to harvest bush on one hectare range from 2,000 NAD to 4,000 NAD.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Хэмжээ ба нэгж талбайг тодорхойл:
1 hectare
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Namibia Dollar (NAD)
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD = :
0.078
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
Namibia Dollar (NAD) 110
4.4 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bush harvesting/felling | Ургамалжуулалтын | Year around |
| 2. | Stacking (and drying) | Бусад арга хэмжээнүүд | Year around |
| 3. | Feeding the chipping operation | Бусад арга хэмжээнүүд | Year around |
| 4. | Transport | Бусад арга хэмжээнүүд | Year around |
Тайлбар:
The restorative measure includes bush harvesting/felling as well as aftercare measures. Additional activities include the processing (e.g. into chips) and transport of the woody material off the farm/land.
4.5 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 1 x Mechanic | person days | 0.2 | 2000.0 | 400.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 4 x Operators | person days | 0.8 | 300.0 | 240.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 1 x Operation manager chipping | person days | 0.2 | 1000.0 | 200.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 1 x Chipping operator | person days | 2.0 | 150.0 | 300.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | 1 x 12t Excavator | pieces | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | 2 x Hydraulic grab and shearing attachments | pieces | 2.0 | 60.0 | 120.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | 2 x Three wheel loggers | pieces | 2.0 | 180.0 | 360.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | 1 x Chipper | pieces | 1.0 | 840.0 | 840.0 | |
| Бусад | Management and administration overhead | lump sum | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| Бусад | 12.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 2780.0 | |||||
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Aftercare | Ургамалжуулалтын | Annually |
Тайлбар:
When land is thinned it creates a vacuum in which weeds and woody plants (sometimes more aggressive colonisers than the original encroacher species) will quickly establish themselves. Regular aftercare needs to be applied in order to prevent the excessive re-growth of bush (and therewith new degradation of the land). Various methods are in use to manage the re-growth of bush following harvesting. These include selective application of arboricides, stem burning, and intensive browsing by goats or antelopes.
The more sustainable the bush harvesting itself has taken place, importantly not completely clearing larger areas of vegetation, the less likely is agressive re-growth of bush. In all bush thinning exercises it is important to leave larger bushes and trees untouched and to start by removing the smaller, less established bushes. In addition, not only individual larger bushes must be left standing, but also islands/patches of bushes, which fulfill important ecosystem services, e.g. habitat for animals.
4.7 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
Боломжтой бол арчилгаанд зарцуулсан зардалыг дараах хүснэгтийн дагуу, орц болон түүний үнийг тусгайлан тодорхойлж задлан бичнэ үү. Хэрэв зардалыг задалж чадахгүй бол Технологийг арчилах, тордоход гарсан нийт зардлыг баримжаагаар тооцож оруулна уу.
500.0
Тайлбар:
Commonly aftercare is applied in form of manual application of herbicides to the cut stems, in order to prevent re-growth of the bushes.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
(1) Investment in machinery (if not applied manually)
(2) Maintenance of machinery (high wear and tear due to hardness of wood and high mineral content)
(3) Remoteness of farms/land from buyers/markets
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
350.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Namibia is a semi-arid country and rainfall ranges roughly from 150-550 mm per year (rough approximation due to the vastness of the area described).
Суурь болгон авсан цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Various
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас хуурай
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- шаардлагагүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Сийрэг/хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- Сийрэг/хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Муу/огт байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны давсжилт асуудал болдог уу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үер усанд автдаг уу?
Үгүй
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- Дунд нас
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын эзэмшдэг эсвэл түрээслэдэг газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Том-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Typical commercial farm size is 5.000 ha. The size increases with decreasing rainfall (towards southern Namibia).
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Хувь хүн, цол эргэм бүхий
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Bush-based animal feed production has been successfully trialed and is implemented by various farmers across Namibia.
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Carrying capacity of bush controlled land increases if regular aftercare is implemented.
Эрчим хүчний үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Bush-to-electricity value chain under development. Several industrial off-takers use woody biomass for boilers (heat), the national power utility currently develops a first biomass power plant.
Усны хүртээм ба чанар
мал услах усны хүрэлцээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Studies show a direct positive correlation between the extent of bush control and the availability of groundwater.
Орлого, зарлага
тариалангийн газрын орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Bush based value addition, e.g. charcoal production, leads to additional income for land owners and farm workers.
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Bush based value addition, e.g. charcoal production, leads to additional income for land owners and farm workers.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи С
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
түрэмгий, харь зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Alien species are completely removed where possible (e.g. Prosopis).
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж хур тундас | Бууралт | Сайн биш |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ган гачиг | Бүгд сайн биш |
Тайлбар:
Despite only limited research exists, long periods of drought that the country has recently faced, are credited to climate change. Drought intensifies the challenge for farmers, as already degraded rangeland has limited capacity to recover in the absence of rain. The technology of bush thinning itself has limited effect if no rain follows the removal of bushes.
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
Bush thinned land takes 3-5 years to fully recover its productive grass layer, thus direct economic benefits are only experienced with a delay.
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
120'000 hectares are bush thinned per year in Namibia; figures on the increase
Технологийн нэвтрүүлсэн иргэдээс хэд нь өөрийн санаачлагаар буюу өөр эх үүсвэрээс материалын болон мөнгөн дэмжлэг авалгүй нэвтрүүлсэн бэ?
- 50-90 %
Тайлбар:
Farmers largely implement bush control on their own initiative; increasingly value chains are being developed and dedicated service providers offer bush control.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Хувьсан өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд Технологид сүүлд ямар нэг шинэчлэл хийгдсэн үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар өөрчлөлтийг даван туулахад шинэчлэл хийгдсэн бэ?
- Зах зээлийн өөрчлөлт
Технологийн дасан зохицох байдлыг тодорхойл (хийц, материал, төрөл зүйл г.м.):
Increasingly bush harvesting is carried out with mechanised means, aiming at large scale production for large biomass off-takers, both in the country and internationally.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Effective measure against bush encroachment |
| Costs can be balanced with additional income through the sale of the biomass/biomass based products |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Apart from the main purpose of rehabilitating rangeland, bush control has various side benefits, such as employment creation and industrialisation. |
| Bush control and biomass utilisation can contribute to energy security in the country. |
| The available range of technologies (from manual to fully mechanised) allows to develop viable concept for all types of land/land ownership scenarios. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| High initial costs involved | Development of dedicated financial products |
| Possible negative consequences, such as more aggressive re-growth of species | Increased knowledge dissemination, skills development and mentorship programmes |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Necessity of cross-sector collaboration, e.g. agriculture, forestry, environment, industry, energy and resulting complexity | Introduction of effective steering body on national level |
| Challenges to sustain operations in communal areas/on land that is not owned by individuals | Development of concepts for community based projects and cooperation with relevant regional authorities and decision making bodies (e.g. Regional Councils, Conservancies) |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
De-bushing Advisory Service Demand Survey (2015), 361 respondents
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Various
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Baseline Assessment for De-bushing Programme in Namibia (2014)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Demand Survey for the implementation of a De-bushing Advisory Service (2015)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Value Added user-opportunities for encroacher bush (2015)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Compendium of harvesting technologies for encroacher bush (2015)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Assessment of biomass resource and potential yield in Namibia (2015)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) on bush thinning and biomass utilisation (2015)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Assesment of financial products and incentive schemes for bush harvesting and value addition (2015)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Environmental and forestry bush harvesting guidelines and generic Environmental Management Plan (2016)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Regional assessment of the economics of land degradation related to bush encroachment in Otjozondjupa, Namibia
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет дэх нээлттэй холбоосууд
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS) Namibia, Resource Section
URL:
www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG)
URL:
www.n-big.org
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Videos
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCwCICCfwf0SdVBqg2ZcAcKA
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна