Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means [นามิเบีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Johannes Laufs
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
De-bushing
technologies_2203 - นามิเบีย
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 17 กรกฎาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 31 พฤษภาคม 2019 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 21 กุมภาพันธ์ 2018 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 22 สิงหาคม 2017 (inactive)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/08/2014
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology described is a means to rehabilitate degraded rangeland. Through targeted harvesting of bushes, the bush density is reduced, allowing for better growth of grass.
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
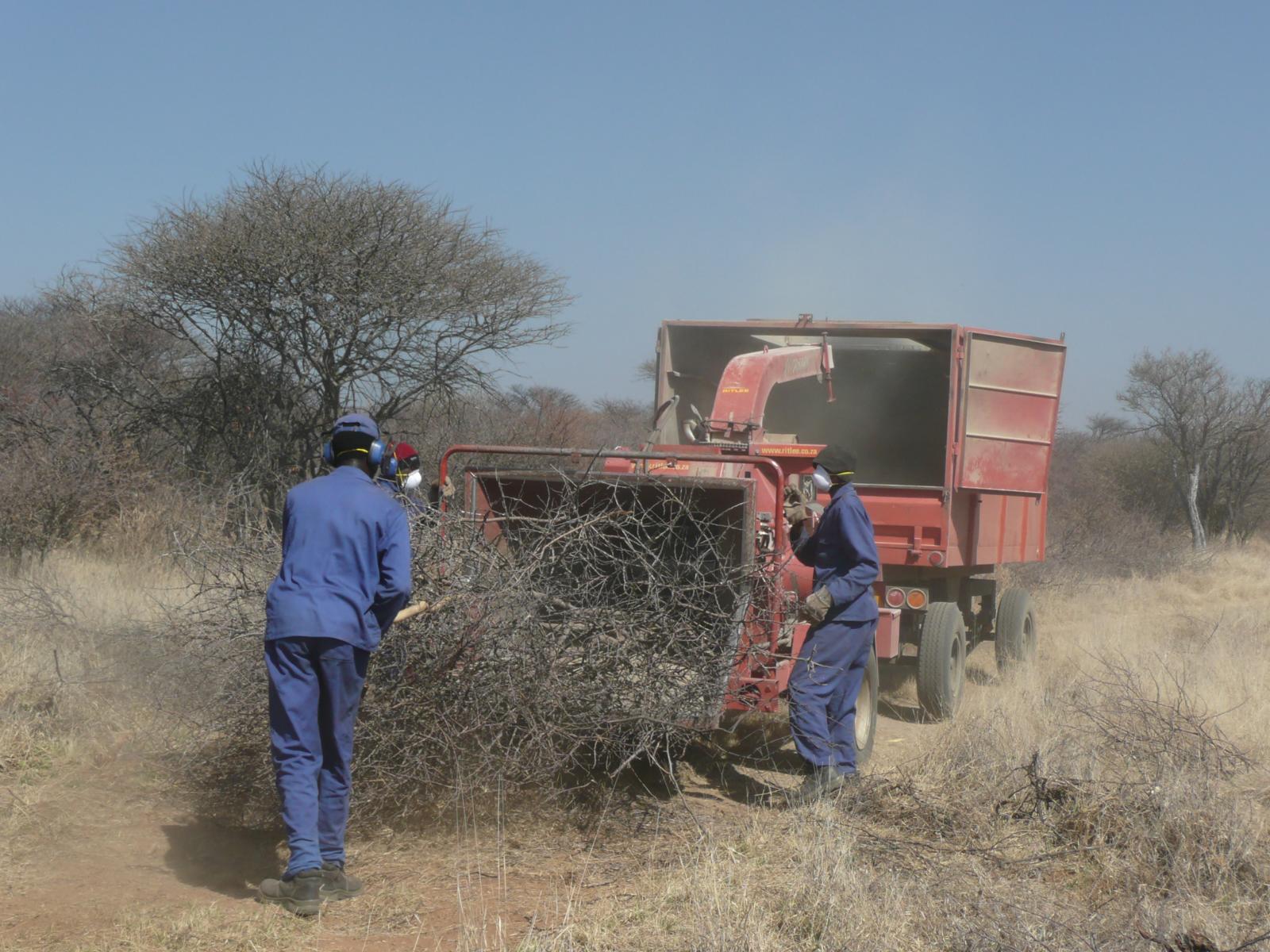
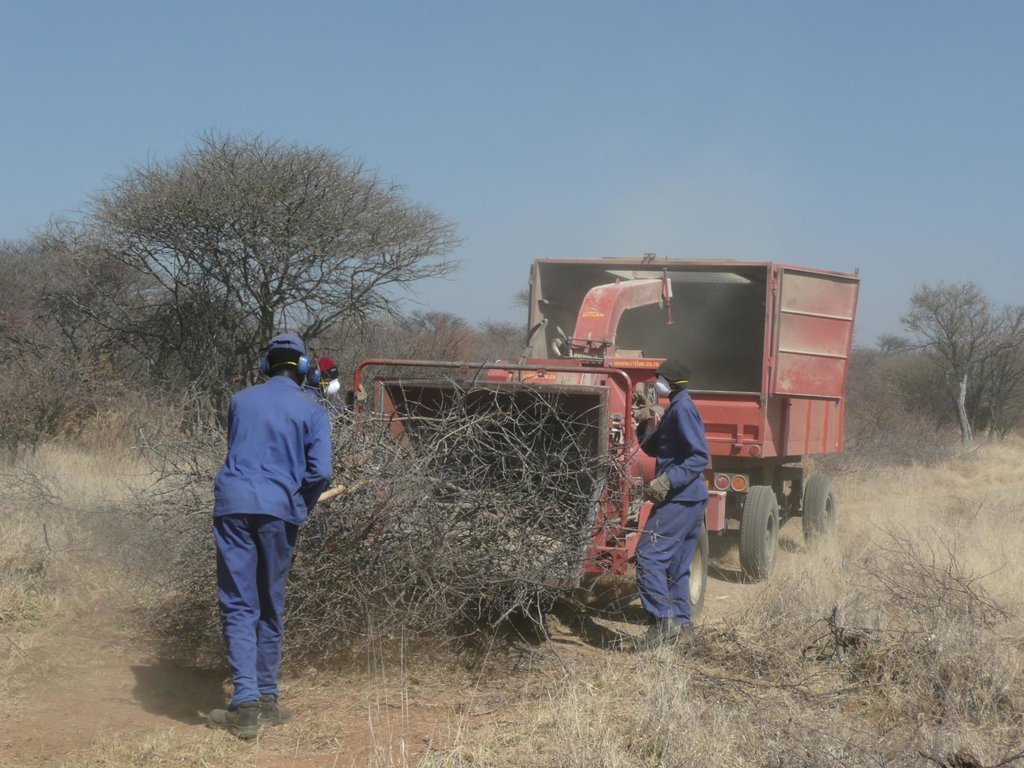
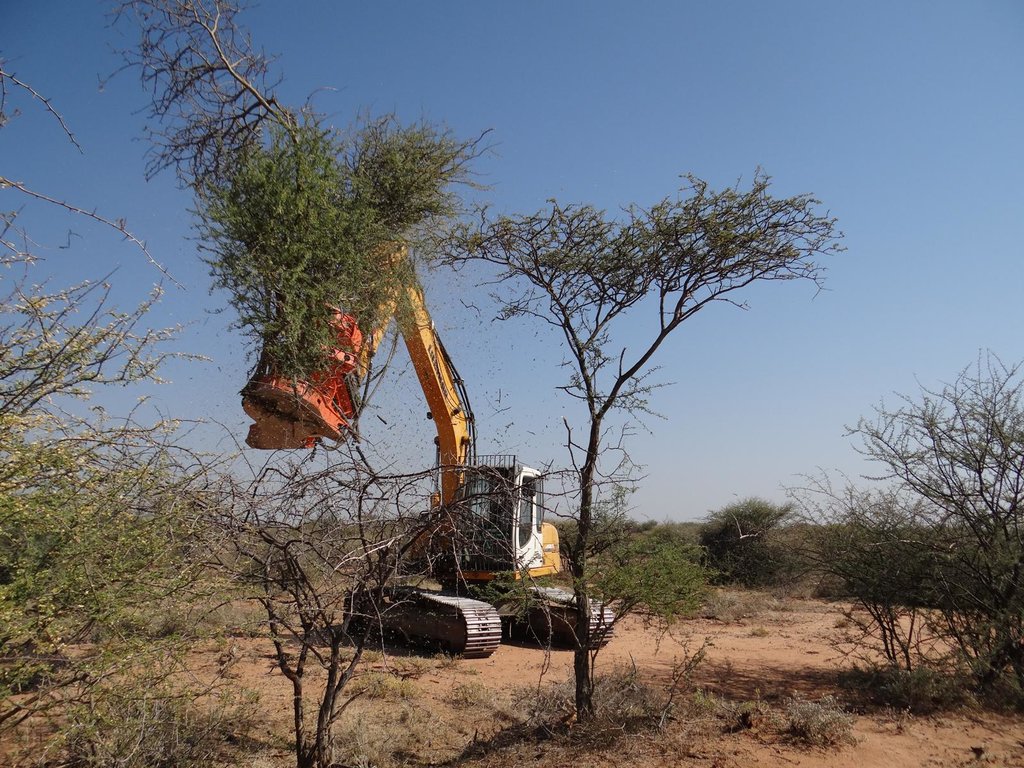
On Namibian farmland bushes are harvested in order to reduce the excessive bush densities, that stiffle the growth of other plant species, especially grasses. Bush can be harvested manually (e.g. with axes), semi-mechanised (e.g. chainsaws) or fully mechanised (e.g. customised excavators). After cutting, the bush is typically left to dry and in a second step processed into a transportable format (e.g. wood chips).
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Bush thinning in the form of selective bush harvesting is applied on Namibian agricultural land. The main aim of the technology is the restoration of degraded rangeland, reducing bush densities, fostering the re-growth of grasses. According to the best available estimates about 45 million hectares of Namibian farmland are affected by bush encroachment. Bush encroachment negatively affects biodiversity, groundwater recharge and importantly the carrying capacity of rangeland. Bush encroachment equally hinders crop production, but this phenomenon is of less significance in Namibia due to the limited scope of crop production in the country. There is a multitude of causes for bush encroachment, among which overgrazing (i.e. overstocking with cattle or lack of rotational grazing), reduced frequency of wildfires and higher CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere feature strongly. Bush encroachment is not to be equated with the invations of alien species, since most encroacher species are indigeneous to Namibia
While it is believed that natural transitions in the ecosystems can on the long-run, under favourable climatic conditions, also lead to reductions of bush encroachment, active rehablitation measures are required in order to achieve improvements on the short-run. This is an aboslute necessity for many Namibian farmers, who experience severe economic difficulties due to the reduced productivity of their land.
Bush control comprises of responsive measures (bush thinning), follow-up measures (aftercare) as well as preventative measures (good rangeland management practices). Since vast areas of Namibian rangeland are heavily encroached by indigenous bush species, the focus is currently on responsive measures, i.e. bush thinning.
Bush thinning entails the practice of selectively harvesting a specified number of bushes, effectively reducing the number of bushes per given area. To determine the density of bush remaining after thinning, a formula based on tree equivalent (TE) and average annual rainfall is used. A tree equivalent is defined as a woody tree or bush of 1,5 metres in height. Thus, a 3 metre shrub would represent 2 TE, a 4.5 metre shrub 3 TE. As rule of thumb for estimating optimal bush density, about 30-35% of encroacher biomass should be removed. This rule is based on research that has been carried out mainly in South Africa over the past decades, measuring and comparing the re-growth experienced at various sites where bush had been harvested. Areas, in which too much bush was removed, experienced strong re-growth of bush, often resulting in even heavier bush encroachment.
Bush thinning follows strict environmental guidelines set by the Ministry of Environment and Tourism through the Environmental Management Act with regard to the equipment's used (avoiding negative side-effects such as disturbance of the soil) and the amount of bushes to be harvested (aiming at the right balance between reducing the encroachment and maintaining a healthy number of the desired bush species). The amount of bushes to be harvested must be determined by expert for each specific area and depends on various factors, e.g. soil type, topgraphy, severity of bush encroachment and intended land use type.
It is important to note, that as with most direct interventions in natural ecosystems, there is a lack of precise knowledge on the long-term effect of bush thinning and the appropriate intensity thereof. There is however no doubt that active bush control has an overall positive effect on the savanna ecosystem in Namibia.
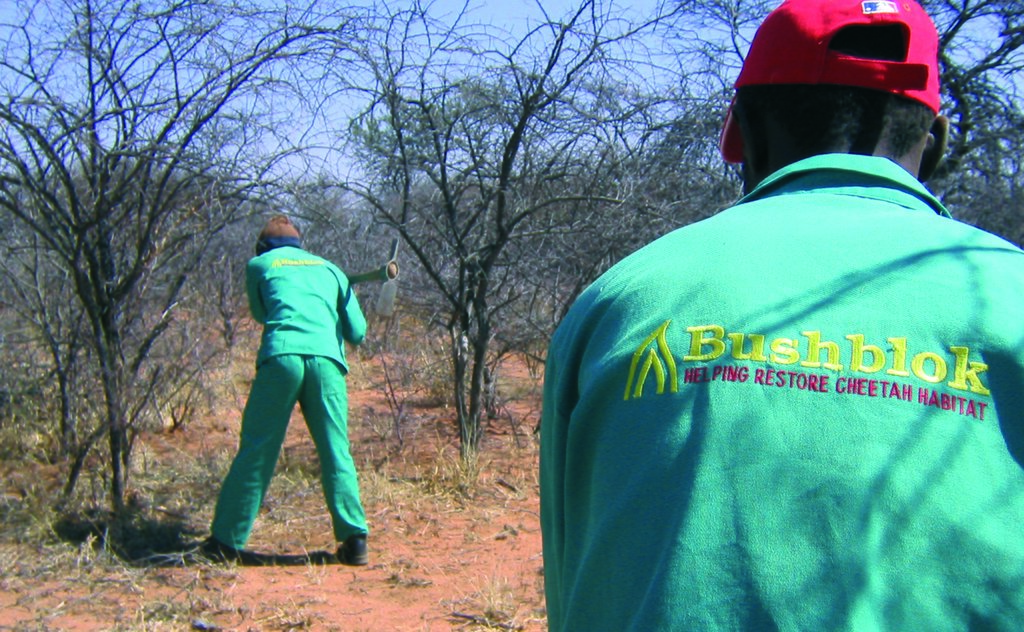
In order to render bush thinning economically feasible, value chains have been developed. Through the processing and utilisation of the woody bush biomass, income can be generated and the cost of bush conrol balanced. Existing value chains include the production of charcoal, firewood, poles, bush based animal feed as well as heat and electricity. Value chains currently under development include composition materials, such as wood-plastic, wood-cement and bio-plastic.
Scientific observations have shown, that bush thinning cannot be implemented as a once-off activity, but requires regular follow-up to prevent the re-thickening of the bush. Follow-up measures (so-called aftercare) include the prevention of coppicing and re-growth. This can be achieved by applying aboricides selectively to the cut stems, stem fires or the introduction of browsers (e.g. goats). Research on the effectiveness and possible side effects of each of these methods is limited.
The need for bush control, and therewith bush thinning, is widely recognised among land owners and also acknowledged on the national political agenda.
A major challenge for the implementation of the technology is the limited suitability of available machines. The hardness and high mineral content of the woody biomass leads to high wear and tear on the equipment (both harvesting equipment and processing equipment, like chippers and pelletisers), often rendering operations unprofitable. Research into more suitable machinery is ongoing.
Further, the implementation of sustainable bush control must be improved through skills training and continuous monitoring of the long-term effects on rangeland.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
All photos have either been taken by the GIZ Support to De-bushing Project or were provided to the project by third parties.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=859GshR9hso&t=3s
Bush Encroachment in Namibia: Causes and Extent
An explanation of the root causes of bush encroachment and its impact on land in Namibia.
วันที่:
01/11/2015
สถานที่:
Namibia
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bmlzPDiqlxo&t=45s
Biomass Value Addition: Bush Based Products
An overview of existing and potential value chains based on encroacher bush.
วันที่:
01/11/2015
สถานที่:
Namibia
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MMSOfV2KBjA
Biomass Energy: From Bush to Electricity
Overview of the energetic applications of woody biomass from encroacher bush.
วันที่:
01/11/2015
สถานที่:
Namibia
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
นามิเบีย
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
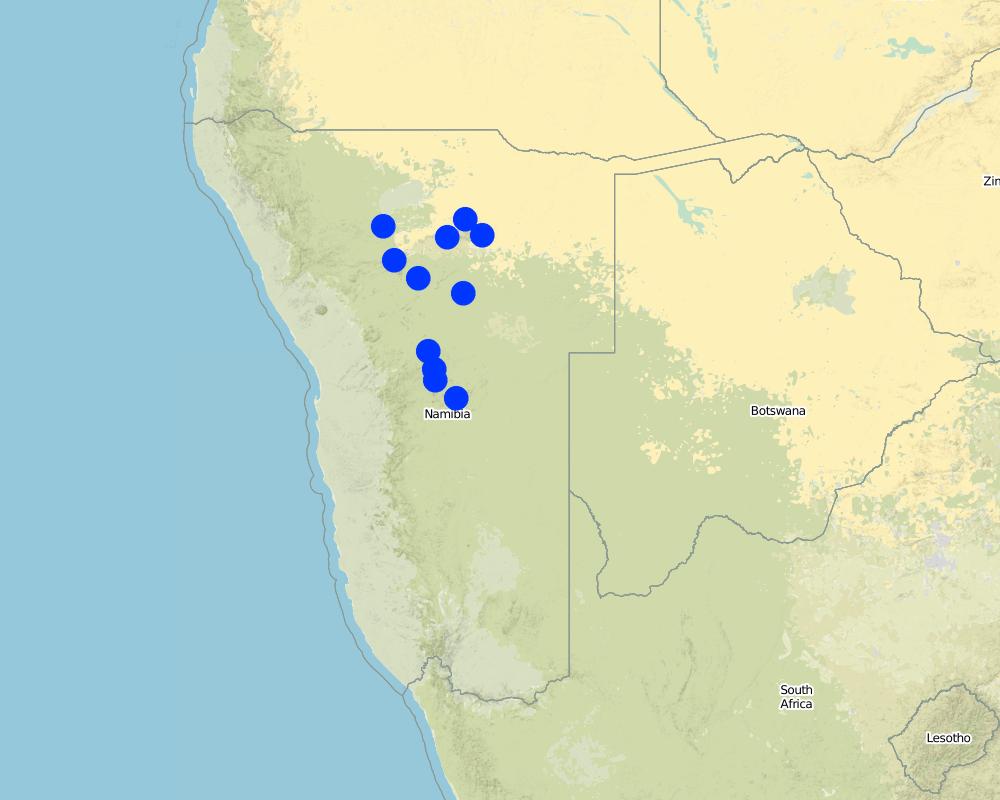
Bush control is applied across Namibia on many privately owned farms. Activities are most concentrated in the regions Khomas, Omaheke, Otjozondjupa and Oshikoto.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Pointers on the map only indicate points (e.g. urban centres) around which activities are concentrated. It is not possible to depict each site where bush control is implemented due to the high number of individual activities and projects.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2015
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Since the 1950s the phenomenon of bush encroachment has been recognised by farmers in Namibia and counter measures have been implemented over the decades. The technologies applied largely relied on the means and innovative capabilities of the respective land owner. Only as of 2014, through the introduciton of a national Support to De-bushing Project, are technologies systematically researched and tested in the field.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
Cattle, goats, game
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Namibia is characterised by large commercial cattle farms. Du to its aridity the land is largely unsuitable for crop farming, with exceptions in high-rainfall areas such as the Grootfontein, Tsumeb, Otavi triangle.
The Northern parts of Namibia are managed as communal land, where farmers have lease holds for their land. In these areas a combination of millet production and cattle herding is common.
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
The implementation of bush thinning allows to maintain the land use (e.g. cattle ranching) and is typically applied to increase productivity in the long-term.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
284 000 in targeted area of bush thinning (Otjozondjupa region)
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 1,000-10,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Currently bush thinning is implemented on a total of approximately 120.000 hectares (1.200 km2) of farmland per annum. These activities are not confied to certain areas, but spread across all of Namibia, typically concentrating in the most encroached areas (e.g. Otjozondjupa, Khomas, Oshikoto and Omaheke regions).
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V4: การแทนที่หรือการนำพันธุ์ต่างถิ่น/ที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา ออกไปจากพื้นที่

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
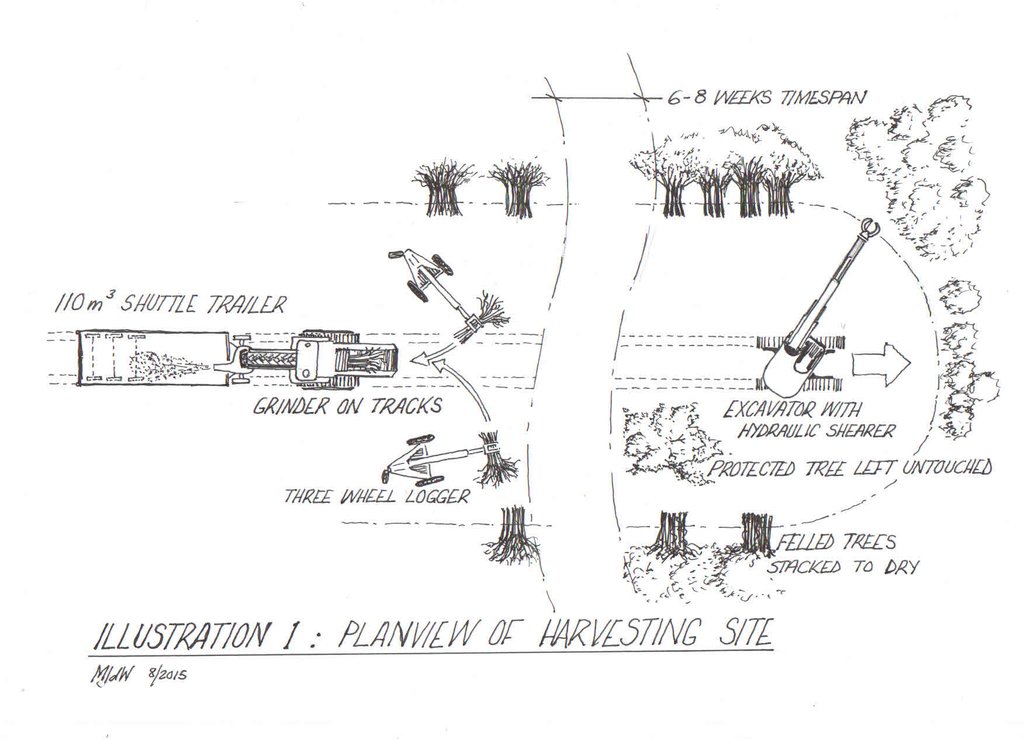
Drawing of a bush harvesting site layout. The drawing depicts fully mechanised bush harvesting and immediate processing into wood chips. This set-up is most suitable for large-scale bush thinning, e.g. for the purpose of supplying biomass in larger quantities. Such off-take includes the potential export of bush in processed form (pellets) or energetic utilisation (e.g. local biomass power plants or biomass boilers in the industry). Currently two such energy solutions exist in Namibia, one at a local brewery and one at a local cement factory.
Note that a range of bush harvesting methods exist, ranging from fully mechanised (as depicted) to manual bush harvesting (e.g. with axes). The site layout and principles are the same in all scenarios, but harvesting speed and costs differ.
The bush harvesting process:
Bushes are harvested selectively with and excavator, to which a hydraulic sheer cutter is attached. The biomass is stacked in rows and left for drying some six to eight weeks (depending on weather conditions). The biomass is then further processed with a chipper and collected with a trailer for further transport off the farm (e.g. to a biomass power plant or industrial off-taker). As a rule of thumb, one third of the standing biomass is removed, leaving two thirds standing. Harvesting starts with smaller plants and then moves to larger ones, cutting only plants with 15 centimetres of diameter or less (as per Namibian forestry regulations).
Cost of bush harvesting can be calculated per hectare (e.g. land owner's perspective) or per tonne (in fuel supply agreements with off-takers). All below stated costs are approximations, as costs vary widely depending on the local framework conditions on a given piece of land. Typically the costs to harvest bush on one hectare range from 2,000 NAD to 4,000 NAD.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 hectare
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Namibia Dollar (NAD)
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
0.078
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
Namibia Dollar (NAD) 110
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bush harvesting/felling | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Year around |
| 2. | Stacking (and drying) | มาตรการอื่น ๆ | Year around |
| 3. | Feeding the chipping operation | มาตรการอื่น ๆ | Year around |
| 4. | Transport | มาตรการอื่น ๆ | Year around |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The restorative measure includes bush harvesting/felling as well as aftercare measures. Additional activities include the processing (e.g. into chips) and transport of the woody material off the farm/land.
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | 1 x Mechanic | person days | 0.2 | 2000.0 | 400.0 | |
| แรงงาน | 4 x Operators | person days | 0.8 | 300.0 | 240.0 | |
| แรงงาน | 1 x Operation manager chipping | person days | 0.2 | 1000.0 | 200.0 | |
| แรงงาน | 1 x Chipping operator | person days | 2.0 | 150.0 | 300.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | 1 x 12t Excavator | pieces | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | 2 x Hydraulic grab and shearing attachments | pieces | 2.0 | 60.0 | 120.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | 2 x Three wheel loggers | pieces | 2.0 | 180.0 | 360.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | 1 x Chipper | pieces | 1.0 | 840.0 | 840.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Management and administration overhead | lump sum | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | 12.0 | |||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2780.0 | |||||
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Aftercare | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Annually |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
When land is thinned it creates a vacuum in which weeds and woody plants (sometimes more aggressive colonisers than the original encroacher species) will quickly establish themselves. Regular aftercare needs to be applied in order to prevent the excessive re-growth of bush (and therewith new degradation of the land). Various methods are in use to manage the re-growth of bush following harvesting. These include selective application of arboricides, stem burning, and intensive browsing by goats or antelopes.
The more sustainable the bush harvesting itself has taken place, importantly not completely clearing larger areas of vegetation, the less likely is agressive re-growth of bush. In all bush thinning exercises it is important to leave larger bushes and trees untouched and to start by removing the smaller, less established bushes. In addition, not only individual larger bushes must be left standing, but also islands/patches of bushes, which fulfill important ecosystem services, e.g. habitat for animals.
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
ถ้าเป็นไปได้ให้แจกแจงรายละเอียดต้นทุนการบำรุงรักษาตารางข้างล่างดังต่อไปนี้ ให้ชี้ระบุลงไปถึงปัจจัยการผลิตและค่าใช้จ่ายต่อปัจจัยการผลิต ถ้าคุณไม่สามารถแจกแจงรายละเอียดต้นทุนได้ ให้ทำการประมาณค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดในการบำรุงรักษา:
500.0
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Commonly aftercare is applied in form of manual application of herbicides to the cut stems, in order to prevent re-growth of the bushes.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
(1) Investment in machinery (if not applied manually)
(2) Maintenance of machinery (high wear and tear due to hardness of wood and high mineral content)
(3) Remoteness of farms/land from buyers/markets
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
350.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Namibia is a semi-arid country and rainfall ranges roughly from 150-550 mm per year (rough approximation due to the vastness of the area described).
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Various
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Typical commercial farm size is 5.000 ha. The size increases with decreasing rainfall (towards southern Namibia).
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Bush-based animal feed production has been successfully trialed and is implemented by various farmers across Namibia.
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Carrying capacity of bush controlled land increases if regular aftercare is implemented.
การผลิตพลังงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Bush-to-electricity value chain under development. Several industrial off-takers use woody biomass for boilers (heat), the national power utility currently develops a first biomass power plant.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Studies show a direct positive correlation between the extent of bush control and the availability of groundwater.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Bush based value addition, e.g. charcoal production, leads to additional income for land owners and farm workers.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Bush based value addition, e.g. charcoal production, leads to additional income for land owners and farm workers.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Alien species are completely removed where possible (e.g. Prosopis).
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Despite only limited research exists, long periods of drought that the country has recently faced, are credited to climate change. Drought intensifies the challenge for farmers, as already degraded rangeland has limited capacity to recover in the absence of rain. The technology of bush thinning itself has limited effect if no rain follows the removal of bushes.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Bush thinned land takes 3-5 years to fully recover its productive grass layer, thus direct economic benefits are only experienced with a delay.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
120'000 hectares are bush thinned per year in Namibia; figures on the increase
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 50-90%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Farmers largely implement bush control on their own initiative; increasingly value chains are being developed and dedicated service providers offer bush control.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Increasingly bush harvesting is carried out with mechanised means, aiming at large scale production for large biomass off-takers, both in the country and internationally.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Effective measure against bush encroachment |
| Costs can be balanced with additional income through the sale of the biomass/biomass based products |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Apart from the main purpose of rehabilitating rangeland, bush control has various side benefits, such as employment creation and industrialisation. |
| Bush control and biomass utilisation can contribute to energy security in the country. |
| The available range of technologies (from manual to fully mechanised) allows to develop viable concept for all types of land/land ownership scenarios. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High initial costs involved | Development of dedicated financial products |
| Possible negative consequences, such as more aggressive re-growth of species | Increased knowledge dissemination, skills development and mentorship programmes |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Necessity of cross-sector collaboration, e.g. agriculture, forestry, environment, industry, energy and resulting complexity | Introduction of effective steering body on national level |
| Challenges to sustain operations in communal areas/on land that is not owned by individuals | Development of concepts for community based projects and cooperation with relevant regional authorities and decision making bodies (e.g. Regional Councils, Conservancies) |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
De-bushing Advisory Service Demand Survey (2015), 361 respondents
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Various
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Baseline Assessment for De-bushing Programme in Namibia (2014)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Demand Survey for the implementation of a De-bushing Advisory Service (2015)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Value Added user-opportunities for encroacher bush (2015)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Compendium of harvesting technologies for encroacher bush (2015)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Assessment of biomass resource and potential yield in Namibia (2015)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) on bush thinning and biomass utilisation (2015)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Assesment of financial products and incentive schemes for bush harvesting and value addition (2015)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Environmental and forestry bush harvesting guidelines and generic Environmental Management Plan (2016)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Regional assessment of the economics of land degradation related to bush encroachment in Otjozondjupa, Namibia
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS) Namibia, Resource Section
URL:
www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG)
URL:
www.n-big.org
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Videos
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCwCICCfwf0SdVBqg2ZcAcKA
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล