Drinking water quality improvement through conservation measures [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Madhav Dhakal
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Samrakshan bidhi dwara piune pani ko gunastar sudhar - Nepali
technologies_1496 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Dongol Bhawani
Непал
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Community efforts for improving drinking water quality [Непал]
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
- Эмхэтгэгч: Madhav Dhakal
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Structural and vegetative measures to improve the quality of drinking water contaminated due to poor sanitation and seepage
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
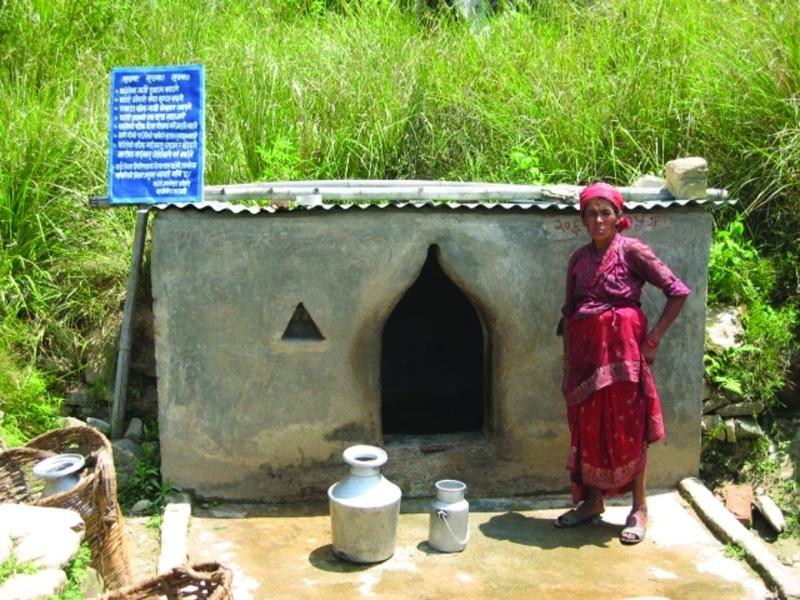
This technology combines structural and vegetative measures to improve the quality of drinking water in an open spring. The quality of water was deteriorating due to poor sanitation and seepage around the spring. The spring was located near to Dhotra village at Barbot sub-settlement, Kabhrepalanchok district. About five households depended on the spring for their drinking water supplies with a further 10 using it regularly and 10-15 using it occasionally during the dry season.
The main purpose of implementing the technology was to improve the quality of drinking water in the spring by preventing it from being contaminated by surface runoff during the rainy season. This technology has long been implemented across Nepal’s midhills. In this case a development project (PARDYP) mobilised the users and provided them with technical and material support to make the improvements.
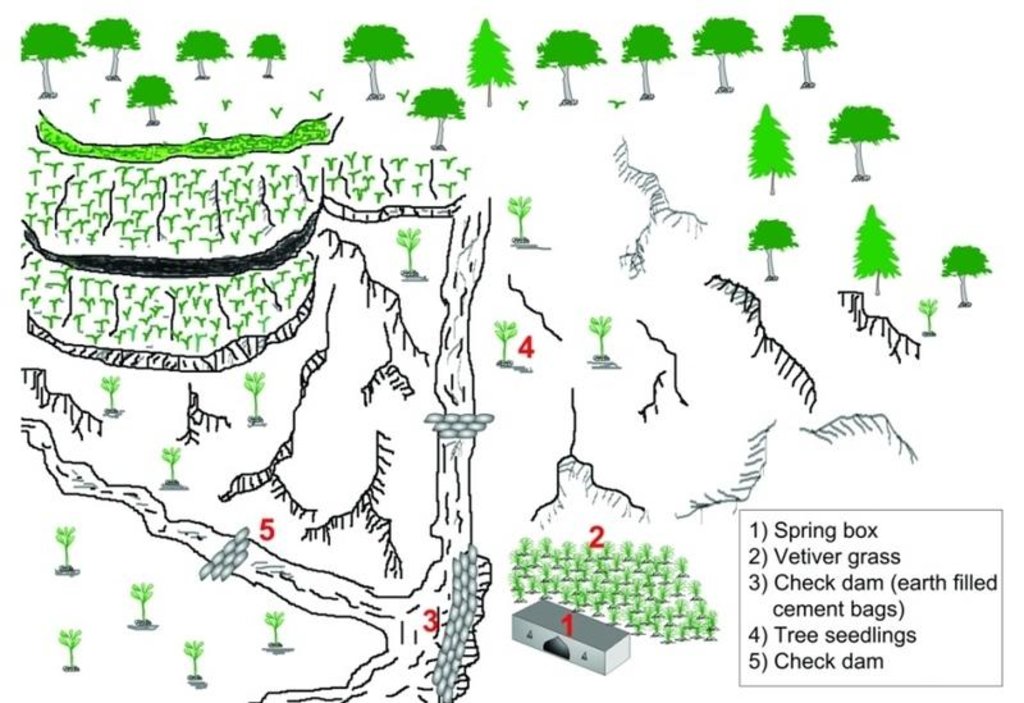
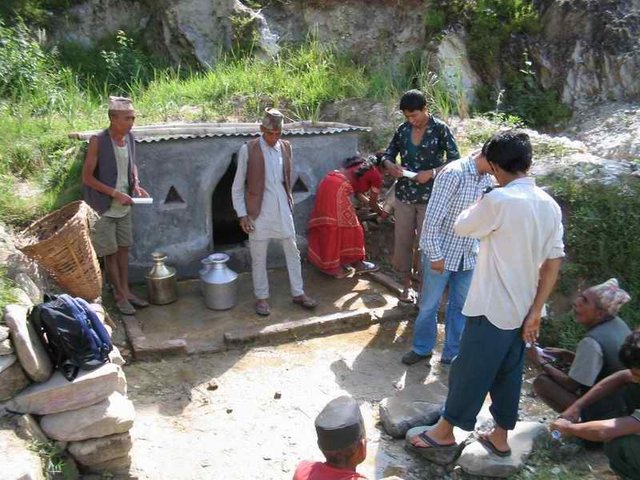
A spring user group was formed. With project help, it built a walled structure (a spring box) over the spring and check dams around the spring, and planted grasses around the spring box and trees in the catchment. These measures prevented the direct flow of surface water into the spring thus reducing contamination and turbidity. Users built a 1.8m long, 1m wide and 1.5m high spring box with a zinc sheeted roof. Check dams were built across the surrounding gullies and rills. A main 2.5m long, 0.5m wide, and 1m high check dam was constructed near the source to prevent surface runoff from entering the spring. A drainage channel was made to drain off wastewater. Vetiver grass seedlings were planted around the spring box and trees were planted in the adjoining catchment. These activities were carried out at the beginning of the rainy season.
This technology is simple and durable and the only maintenance needed is to keep the surroundings clean and to repair any damage.
The case study area receives about 1200 mm of annual precipitation of which about 80% occurs during the monsoon season (June to September). The area mostly has red soils which are highly weathered and, if not managed properly, are very susceptible to erosive processes.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kavrepalanchowk district/ Jhikhu Khola watershed
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- < 0.1 км2 (10 га)
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Local community, with the contribution from individual community members or from external support have been implementing since generations. In this particular case project mobilized the spring users community and assisted them by providing technical and material support during programme implementing period.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- Improve water quality
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар

Бусад
Тодорхойлно уу:
Private land-abondent by village elite, communal land-open grazing
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High pressure on limited land resources due to overuse of crop, forest, and grazing lands; increased inputs of agrochemicals which will lead to the deterioration of drinking water quantity and quality
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water quality deterioration resulting from poor sanitation
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: private land-abondent by village elite, communal land-open grazing
Number of growing seasons per year: 3
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- гадаргын усны менежмент (булаг, гол, нуур, тэнгис гэх мэт)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S5: Далан, усан сан, цөөрөм
Тайлбар:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (uncontrolled access to grazing land), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (concentrated runoff during rainy season), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge - water quality treatment)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (uncontrolled access to forest land), poverty / wealth (lack of captial - conservation activities)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Structural and vegetative measures applied to improvewater quality of spring
Location: Barbot Dhotra. Kabhrepalanchowk district
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Michelia champaca
Grass species: Vetiveria lawsoni
Structural measure: spring box wall
Material: concrete
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.02
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.89
Structural measure: check dams
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Structural measure: cut-off drain
Material: Stone
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Construction material (stone): locally available
Construction material (concrete): cement, sand, brick
Зохиогч:
Madhav Dhakal, A. K.Thaku
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
Spring box and plants
Нэгжийн хэмжих нэгж (тохирох бол):
1.8m long, 1m wide and 1.5m high with a zinc sheeted roof
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
1.60
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting vetiver grass around the spring box | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Planting tree species in the catchment | beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Building of check dams to divert stream and gully runoff water | start of the rainy season |
| 4. | Buildingof the spring box | start of the rainy season |
| 5. | Construction of concrete floor in front of spring box | start of the rainy season |
| 6. | Construction of drainage channel | start of the rainy season |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Building spring box and planting trees | Persons/day | 69.0 | 1.6 | 110.4 | 80.0 |
| таримал материал | Grass seedlings | unit | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Cement | unit | 1.0 | 44.0 | 44.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Gravel / sand | unit | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Bricks | unit | 1.0 | 188.0 | 188.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Empty sacks | unit | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Tinc sheet | unit | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Steel wire | unit | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Transportation | unit | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 433.4 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 433.4 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
PARDYP and District Development Committee
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | replacement/ gap filling with new tree seedings | /as required |
| 2. | maintaining height of the planted grass | /as required |
| 3. | Cleaning spring box surroundings | as per need |
| 4. | Maintenance of wall/ floor against damage | as per need |
| 5. | Maintenance of check dam against damage | as per need |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintaining springbox | Persons/day | 2.0 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 3.2 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 3.2 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: hoe,spade, shovel, nails, hammer, pliers, trowel, steel pan bucket, and jug
The cost is only for unit technology, it can not be extrapolated to hector basis, as in 2006.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Material cost was comparatively high followed by labor cost. For this technology several actors contributed. The land users contributed 61 percent, District Development Committee contributed 26 percent and PARDYP contributed 13 percent, and the department of forest and PARDYP regional coordinator contributed by providing planting materials( vetiver).
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
1200.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altitudinal zone: 900 m a.s.l.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth on average: Variable
Soil texture: Red soils with high clay content
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Water quality (untreated): More contamination during monsoon season (June- September), source: mainly natural springs
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
15% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land.
85% of the land users are poor and own 65% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Орлого, зарлага
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
decreased women's workload for collecting water, since water is available near to the households
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
water quality improvement
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
formation of user group; less conflicts for drinking water
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
group discussion, awareness
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
conflicts due to insufficient water quantity. Especially during dry and pre- monsoon months
livelihood and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Better health due to clean water.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
due to drainage trench and check dams
Хөрс
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
due to planted grasses and trees
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
due to check dams
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | муу |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
Clean water is available immediately after only a little investment. Government and PARDYP support meant that the short-term benefit was positive. Without this support the short-term costs would equal the benefits.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- > 50%
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
15 households in an area of 10 ha
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
15 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Local people with inadequate access to drinking water or whose source is contaminated are
likely to adopt the technology after raising the funds themselves.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Increased availability of drinking water has reduced women’s workload during the dry season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the technology by building a closed storage tank. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Water turbidity decreased from 23 nephelometric turbidity units (NTU) in August 2004 to 7 NTU in August 2005. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage spring users to plant more multiple grasses and tree species around the catchment area |
|
Faecal contamination decreased from 500 coliform formation units (CFU)/100 ml in August 2004 to 200 CFU/100 ml in August 2005. Similarly, the levels of ammonia (NH3) and nitrate (NO3 in the spring water have decreased (NH3 from 0.5 to 0 mg/l; and NO3 from 0.7 to 0.5 mg/l). Total hardness of spring water remained the same at 30 mg/l. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance, especially cleaning the surrounding area is needed; also need a clean pot for extracting the water. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Coliform bacteria are still a problem | Treat the water using SODIS, boiling, fi lters, chlorination or other methods before drinking. |
| The water available during the pre-monsoon season is insufficient for the15 households, leading to conflicts; the water source can be contaminated from unclean water fetching pots. |
The water in the spring box should be siphoned into a storage tank fi tted with an overfl ow mechanism,cleaning outlet, lockable cover, and taps. This would protect the water source from contamination from open access and improve the quality and availability of water. The amount available could be increased by tapping other spring sources. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management: Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
ICIMOD
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Community efforts for improving drinking water quality [Непал]
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
- Эмхэтгэгч: Madhav Dhakal
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна