Grassing of Recharge Areas [Чехийн БНУ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Antonín Zajíček
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Zatravnění zdrojové oblasti
technologies_5934 - Чехийн БНУ
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Газар ашиглагч:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
New approaches to the revitalization of main drainage facilities in relation to drainage systems in terms of water retention in the landscape (TH02030397)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Approaches for design and realization of complex effective measures for tile drained agricultural catchments by land consolidations (QK21010341)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Research Institute for Soil and Water Conservation (VUMOP) - Чехийн БНУ1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Catchment Approach [Кени]
A focused approach to integrated land and water management, including soil and water conservation, where the active participation of the villagers - often organised through common interest groups - is central.
- Эмхэтгэгч: James Gatero Njuki
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
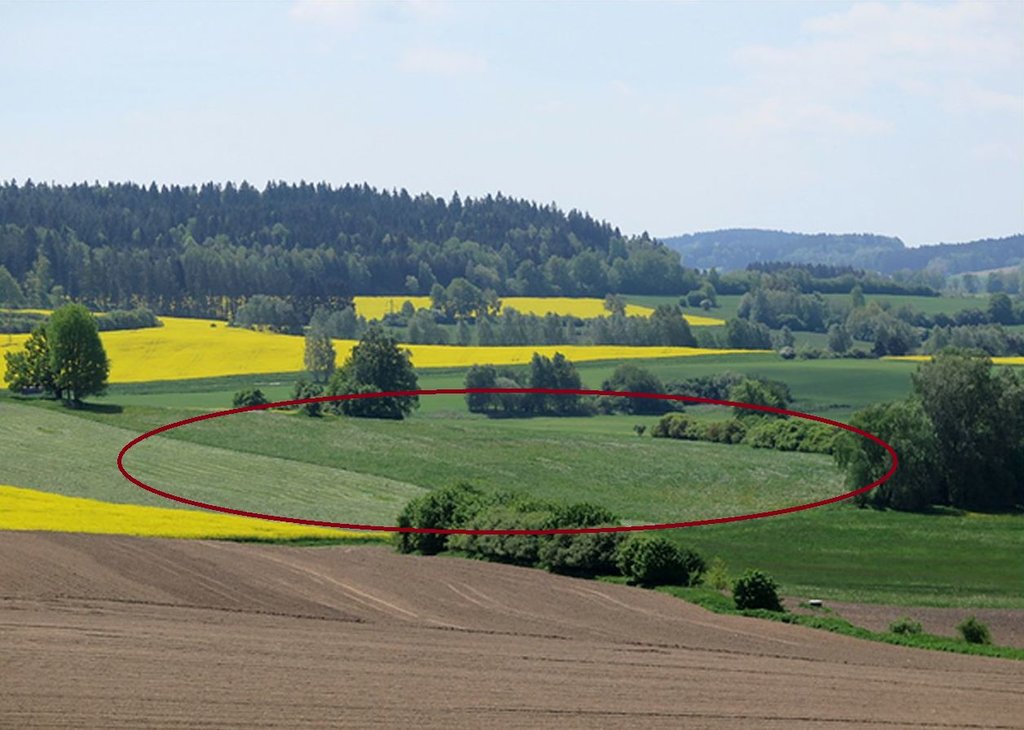
Grassing recharge zones of agricultural drainage systems significantly improves the quality of drainage water. It can be a useful, effective and relatively cheap measure for improvement of shallow groundwater quality.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Grassing of recharge zones of agricultural drainage systems significantly improves the quality of drainage water: it can be a useful, effective and relatively cheap measure. Grassing is an effective preventative strategy to prevent nitrogen pollution. Reduction of nitrate pollution by grassland occurs mainly through grassland’s ability to absorb and use large amounts of nitrogen compared with field crops, and this capacity remains effective for a longer period of the year. Permanent grasslands cover the soil year-round and have a large stock of active subsurface biomass in the root system, which can immobilize a significant amount of soil nitrogen. Moreover, grassland has a greater amount of active soil microbes than under field crops (Griffiths et al. 2008). Besides nitrogen remedial ability, grasslands offer other regulation and supporting ecosystem service (ES) benefits (Hönigová et al., 2012) – for example carbon sequestration, erosion prevention and water flow regulation. On the other hand, used too widely, grassland can be seen as a negative ES provider, in the sense that it reduces the area of crop production (Hauck et al., 2014). That is why it is recommended to limit the use of grassing so that it acts within relatively small areas focused on the catchment area. The effectiveness of grassing has been evaluated statistically, when Fučík et al. (2008) reported that an increase in grassed area of 10% can decrease the C90 (90% probability of non-exceedance) nitrate value in the waters of streams (small water courses) by 6.4 mg/l.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Чехийн БНУ
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Bohemian - Moravian Highlands
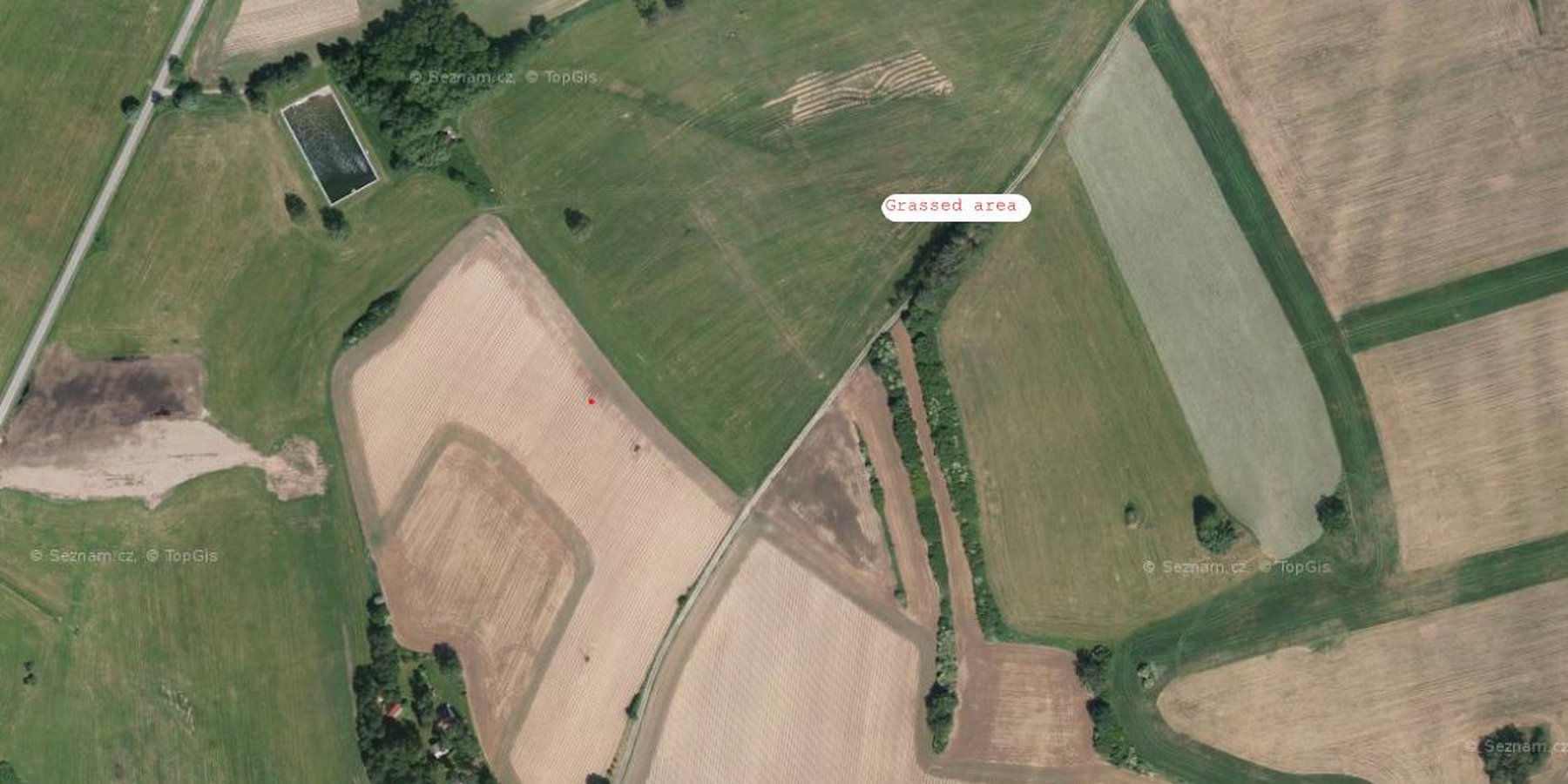
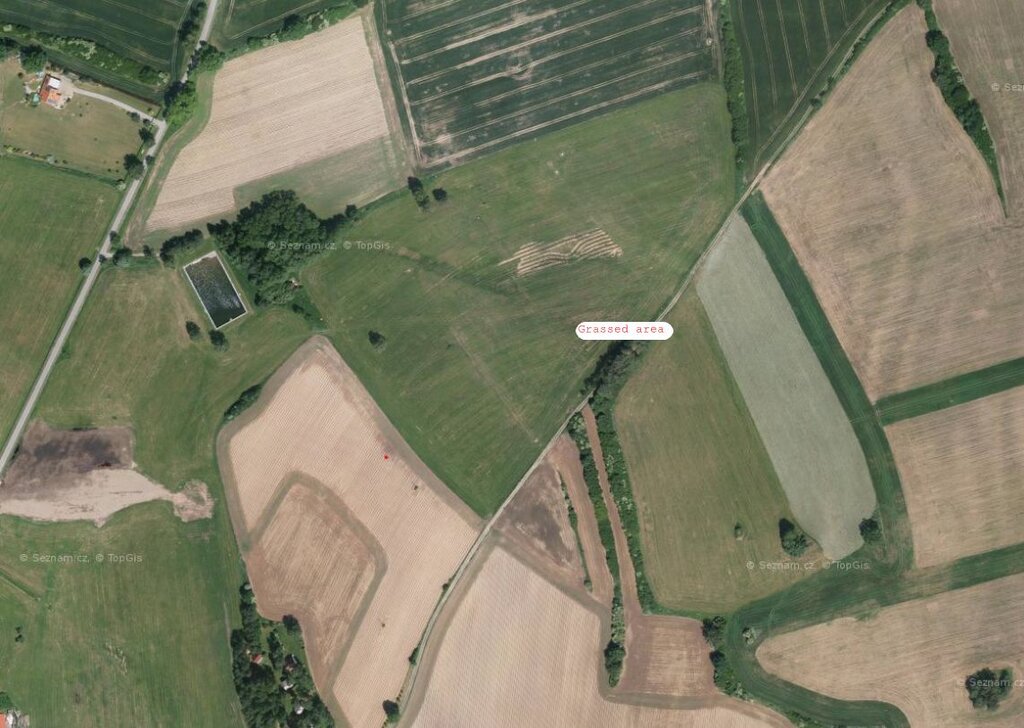
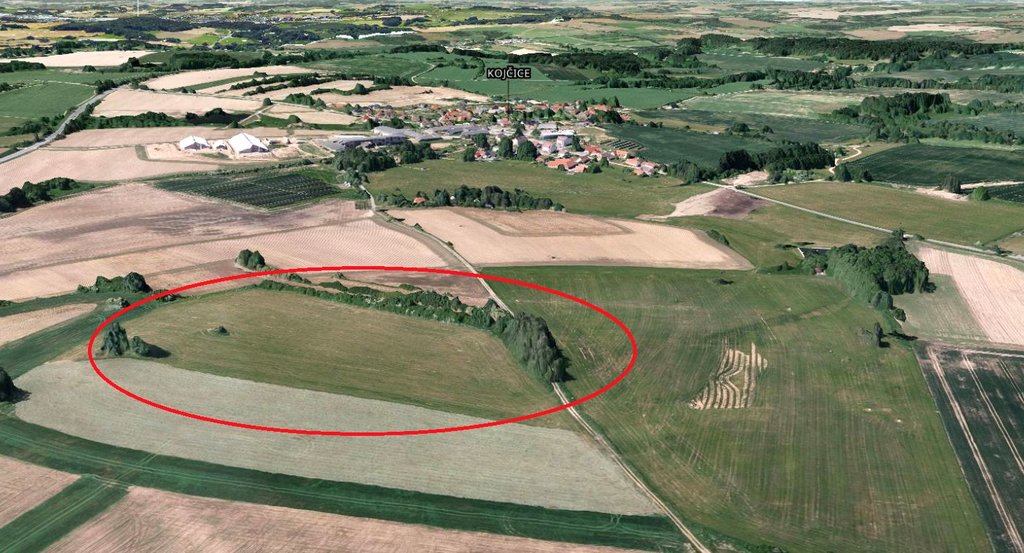
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Kojčice
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
0.05
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- < 0.1 км2 (10 га)
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2006
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Linking of the land use in the source areas to drainage water quality has been tested in several research projects since the first decade of the 21st Century. The methodology for defining source areas has been developed by the Research Institute for Soil and Water Conservation for a long time. Nowadays this measure has become part of the Czech Ministry of Agriculture subsidy and farmers can use it themselves.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- сав газрыг хамгаалах (усны эх/ голын адаг) - бусад технологитой хослуулах
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн талбай
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
Олон наст (модлог биш) тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- тэжээлийн ургамал - үетэн
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Үгүй
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Тийм
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Тийм (Технологи хэрэгжүүлэхээс өмнөх үеийн газар ашиглалтын талаархи асуулгыг бөглөнө үү)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - арвай
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- үр тариа - улаан буудай (өвлийн)
- тосны ургамал - наран цэцэг, рапс ба бусад
- үндэст/булцуут ургамал– төмс
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар таримлыг сөөлжлөн тариалдаг вэ?
In some seasons, spring cereal mix, legume-cereal mix or undersown clover is used as an intercrop
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
five-year or seven-year crop rotation with winter cereals, spring cereals, potatoes, red clover, oil seed rape and maize
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

усны доройтол
- Hp: Гадаргын усны чанар муудах
- Hq: Гүний усны чанар муудах
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
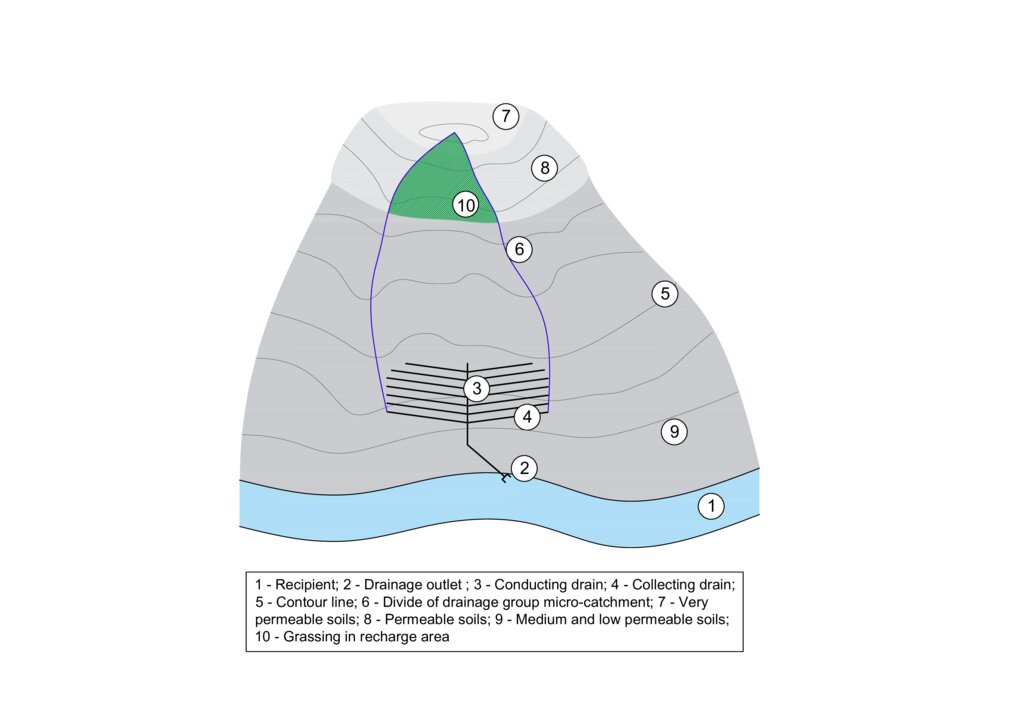
The figure shows a model example of a drainage structure built at the bottom of a slope (3, 4). In this case, a substantial portion of the drainage runoff consists of water that infiltrates in areas with shallow soils that are highly permeable to water, nutrients, and other pollutants (7 and 8). In the case of drainage constructed in this way, the entire micro-catchment of the drainage group must be taken into account in terms of runoff generation and drainage water quality (6). The area where the microwatershed of a drainage group intersects with an area of shallow permeable soils is the source area for drainage runoff and it is to these locations that the grassed area should be directed (10).
Зохиогч:
Antonín Zajíček and Tomáš Hejduk
Он, сар, өдөр:
12/10/2022
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
3.5 hectares
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
EUR
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
0.92
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
60
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Vulnerable area delimitation | one year before establishment |
| 2. | Obtaining the consent of the owners and users of the affected land | one year before establishment |
| 3. | Grass sowing | after harvest of previous crops |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Work for delimitation | person - days | 3.0 | 130.0 | 390.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Project and administration | person - days | 4.0 | 150.0 | 600.0 | 90.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Manual work on the field | ha | 5.0 | 30.0 | 150.0 | 90.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machinery - sowing machine, chopper | ha | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | 89.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Fuel | ha | 5.0 | 60.0 | 300.0 | 90.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 5.0 | 40.0 | 200.0 | 90.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Feritilizers (mostly urea and pig slurry digestate) | ha | 5.0 | 30.0 | 150.0 | 90.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Biocides (only the year of establishment) | ha | 5.0 | 60.0 | 300.0 | 90.0 |
| Бусад | Fixed costs | ha | 5.0 | 180.0 | 900.0 | 90.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 3990.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 4336.96 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
Czech Ministry of Agriculture
Тайлбар:
The amount of agricultural subsidies in the Czech Republic is currently (2024) variable depending on the size of the farm. For a farm with an average size of 1500 ha, the subsidy is approximately EUR 160. For the conversion of arable land to permanent grassland in vulnerable areas, an additional subsidy of approximately EUR 310 per hectare is available from the Ministry of Agriculture.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | re-sowing | before vegetation season if needed |
| 2. | harrowing | if needed once per season after re-sowing |
| 3. | fertilising | once or twice per season |
| 4. | harvesting | twice or three times per season |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Manual work on the field | ha | 5.0 | 25.0 | 125.0 | 85.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machinery - sowing machine, chopper, tractor | ha | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | 85.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Fuel | ha | 5.0 | 60.0 | 300.0 | 85.0 |
| таримал материал | seeds | ha | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 | 85.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Feritilizers (mostly urea and pig slurry digestate) | ha | 5.0 | 25.0 | 125.0 | 85.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Biocides (when needed) | ha | 5.0 | 30.0 | 150.0 | 85.0 |
| Бусад | Fixed costs | ha | 5.0 | 150.0 | 750.0 | 85.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 2550.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 2771.74 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
Czech Ministry of Agriculture
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Fuel prices, level of subsidies
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
666.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хамааралгүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
The substrate is formed by partially migmatized paragneiss in various degrees of degradation.
Quaternary sediments are represented by slope sands and loams reaching 1–2 m thickness. The representation of soils (according to the World Reference Base for Soil Resources
2006) is variable, with Gleyed Cambisols, Gleysols, and sporadically Histosols. In the recharge area, the soil cover is more homogenous, with prevailing Modal, Ranker and Arenic Cambisols.
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ба газрын доорхи ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Үгүй
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Water quality from agricultural drainage systems
(both tiles and ditches) has been discussed by the studies which draw attention to the reduced
quality of drainage waters caused by elevated concentrations of nutrients (N, P, C) and/or
pesticides.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- хоршоо
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
The Czech Republic is characterised by a significant size of agricultural holdings. During the socialist era (1948-1989), large agricultural cooperatives were established. Today, most agricultural land is still farmed by similar enterprises, whether in the form of cooperatives, limited liability companies or joint stock companies.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- компани
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Үгүй
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Farmers will lose land for growing commercially viable crops (cereals, potatoes, rape) and grass production (hay, haylage) will increase.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Permanent grassland in the recharge area will protect the shallow soils especially from accelerated erosion.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
This measure will reduce the intensity of surface and subsurface runoff from the catchment.
усны чанар
гадаргын урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Grassing will slowdwn the surface runoff especially during intensive rainfall-runoff events.
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reducing surface runoff will promote infiltration of rainwater into the soil profile and increase soil moisture.
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Permanent grasslands cover the soil year round.
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
This measure prevents soil loss from the accelerated erosion.
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Permanent grasslands have a big stock of active subsurface biomass in the root system, which can immobilize a significant amount of soil nitrogen. Moreover, it has bigger amount and increased activity of soil microbes supporting e.g. carbon sequestration.
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамалын бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Unlike arable land, permanent grassland provides full land cover even in the non-growing season.
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Properly managed grasslans will increase biodiversity (compared to the arable lands), especially amount of insect.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
In intensively drained catchments, drainage structures have a significant contribution to total runoff and water pollution.Grassing in recharge zone will significantly mitigate water pollution, especially nutrients and pesticides loads.
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Decrease in rapid erosive runoff will reduce the risk of sediment input to lower lying lands.
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учрах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Decrease in rapid erosive runoff will reduce the risk of sediment input into the intravilane of lower lying villages or public roads.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| улирлын хур тундас | зун | Өсөлт | сайн |
Тайлбар:
Gradual climatic has been causing changes in precipitation distribution in course of year. In winter, the period with snow cover shortens and in summer, precipitation often takes the form of rapid and intense episodes. Permanent grassland will mitigate these rainfall extremes by its ability to slow down both surface and subsurface runoff and to increase water retention in agricultural catchments.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг сөрөг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Тайлбар:
From an economic point of view, the increase in the area of grasslands will clearly reduce the turnover of the agricultural entity. The fall in costs and income will also lead to a reduction in profits, which is partly offset by higher subsidies for permanent grasslands. However, the increase in dependence on subsidies is dangerous in terms of the long-term stability of the farming entity, as the amount and focus of subsidies can change from year to year. It is also important to note that the production of grass biomass only make sense if the farmer also runs livestock production or a biogas plant, taking into account the amount of grass that the farmer is able to process.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| A relatively low-cost measure in terms of finance and agricultural management |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| grassing focused to the proper catchment area (recharge zone) can be a useful, effective and relatively cheap measure for improvement of shallow groundwater quality, or optionally the quality of local drinking water sources |
| stabilise of catchment area with shallow soils - can lead to decrease in soil erosion. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Increasing areas of grasslands would lead to decrease of landscape productive service, farm turnover and profit and the bigger dependence on subsidies. | The grassing should be applied in small, precisely defined parts of the catchment, which are real recharge (infiltration) areas. |
| Possible sudden change in the subsidy system | It is necessary to consider the non-productive functions of grasslands also as public service, taking into account the saves in water cleaning costs and the price of increased water retention |
| Excess amout of grass or hay, especially for farms without livestock production | Balanced share of grasslands and arablale lands in cultivated field blocks, support for livestock production |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| An incorrectly defined source area will lead to ineffective measures | Careful preparation |
| Unwillingness of conservative companies and farmers to adopt this measure | Properly set up subsidy policy |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
The effectiveness of this measure was tested withim the long-term survey(2006-2016) at the pilot site of Dehtáře (Bohemian-Moravian Highlands, Czech Republic). During the research, drainage water quality indicators, meteorological and hydrological characteristics of the experimental site and agricultural management were monitored.
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
The research was primarily carried out in cooperation with one agricultural cooperative; the implementation of the measures is being carried out in discussions with more than thirty agricultural enterprises, mainly in the catchment area of the Švihov reservoir on Želivka - the largest potable water reservoir in the central Europe.
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
2016
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Kvítek, T.; Zajíček, A.; Dostál, T.; Fučík, P.; Krása, J.; Bauer, M.; Jáchymová, B.; Kulhavý, Z.; Pavel, M. Slowing Down Quick Runoff—A New Approach for the Delineation and Assessment of Critical Points, Contributing Areas, and Proposals of Measures to Reduce Non-Point Water Pollution from Agricultural Land. Water 2023, 15, 1247.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061247
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Zajíček, A., Hejduk, T., Sychra, L., Vybíral, T., Fučík, P. (2022): How to Select a Location and a Design of Measures on Land Drainage – A Case Study from the Czech Republic. Journal of Ecological Engineering 2022, 23(4), 43–57. ISSN 2299–8993.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/146270
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
ZAJÍČEK, A., FUČÍK, P., DUFFKOVÁ, R., MAXOVÁ, J. 2018. How does targeted grassing of arable land influence drainage water quality and farm economic indicators? Int. J. Environ. Impacts, 1(3): 344–352.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
DOI 10.2495/EI-V1-N3-344-352
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Fučík P., Zajíček A., Kaplická M., Duffková R., Peterková J., Maxová J., Takáčová Š. 2017. Incorporating rainfall-runoff events into nitrate-nitrogen and phosphorus load assessments for small tile-drained catchments. Water, 9, 712; (ISSN Print:2575-1867 ISSN Online: 2575-1875)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
doi:10.3390/w9090712
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Janglová R., Kvítek T., Novák P. 2003. Soil infiltration capacity categorization based on geoinformatic processing of soil survey data. Soil and Water Scientific Studies, 2, 61–81.
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
ZAJÍČEK, A., SYCHRA, L., VYBÍRAL, T., HEJDUK, T., ČMELÍK, M., FUČÍK, P., KAPLICKÁ, M. 2021: Design of the Revitalization measures on the Main drainage facilities and hydrologically related Detailed drainage facilities (In Czech)
URL:
DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.34421.50403
7.4 Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Grassing focused on the catchment area (recharge zone) can be a useful, effective and relatively cheap measure for improvement of shallow groundwater quality, or optionally the quality of local drinking water sources.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Catchment Approach [Кени]
A focused approach to integrated land and water management, including soil and water conservation, where the active participation of the villagers - often organised through common interest groups - is central.
- Эмхэтгэгч: James Gatero Njuki
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна