Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots [Тажикистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Loes Masselink
- Редактор: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
technologies_977 - Тажикистан
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр хэвлэх
- Хөтөч дэх бүрэн хураангуй
- Бүрэн хураангуй (форматгүй)
- Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots: 20 8-р сар 2019 (inactive)
- Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots: 02 11-р сар 2021 (public)
- Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots: 04 4-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots: 19 7-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots: 17 7-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Conversion of grazing land to fruit and fodder plots: 10 3-р сар 2017 (inactive)
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Soil Science Institute (Soil Science Institute) - ТажикистанТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Киргизстан1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/06/2004
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
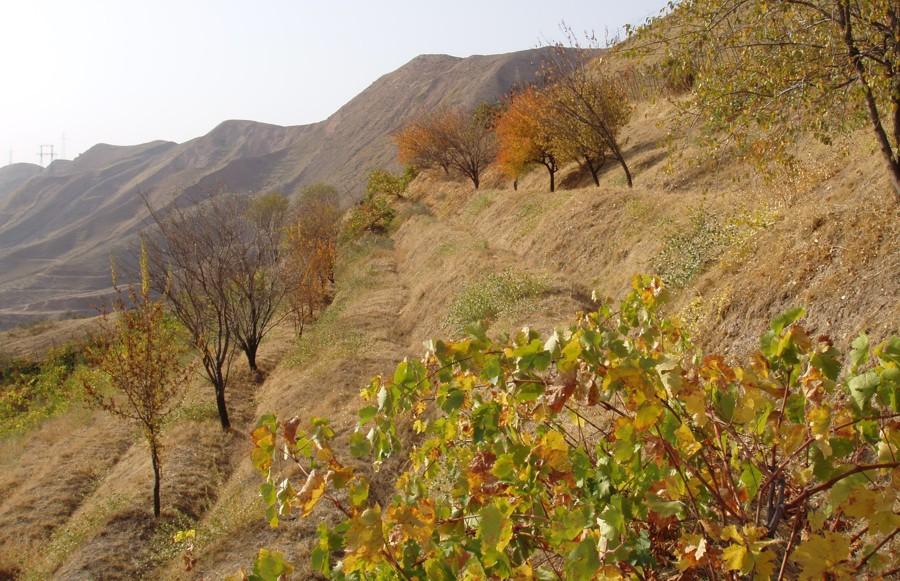
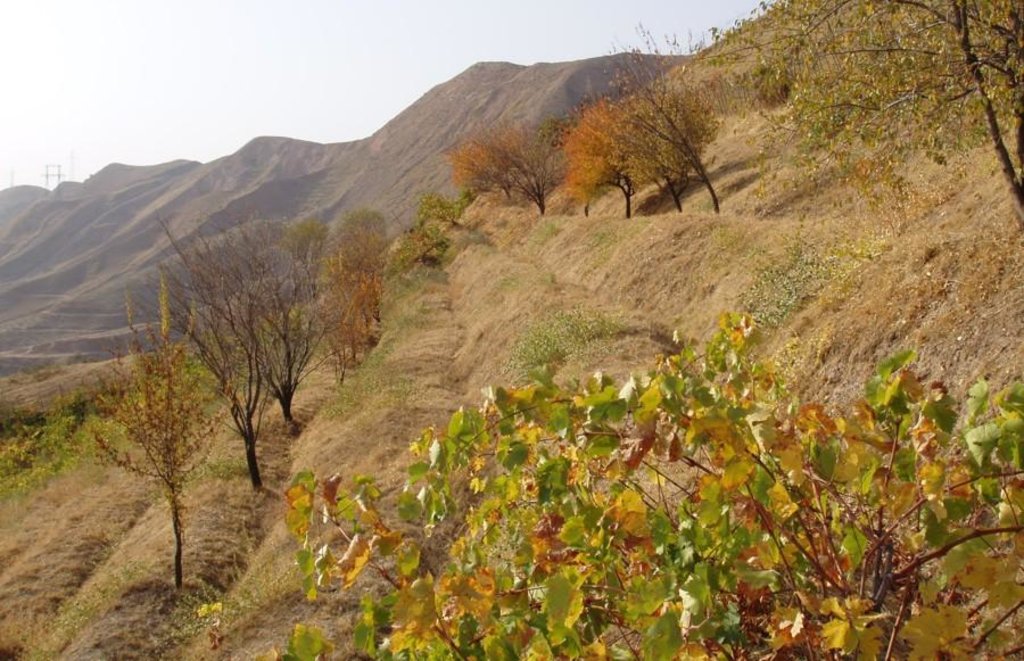
Fencing part of an overgrazed hillside, combined with terracing, manuring and supplementary irrigation for grape, fruit and grass production.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
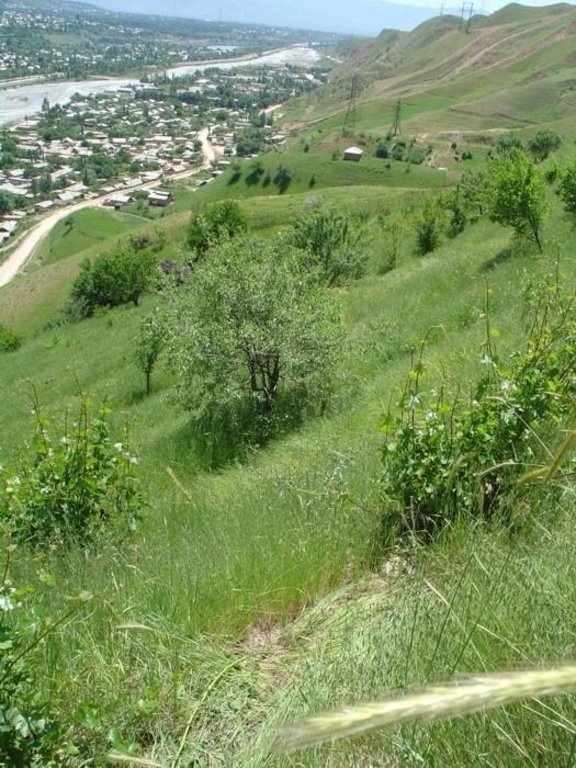
In the Varzob valley of Tajikistan, slopes of around 30% are used communally, and are heavily overgrazed. This has led to a reduction in vegetation cover, to soil compaction, and to severe sheet and rill erosion. In 1982, one innovative land user began to set up half a hectare vineyard/fruit plot with intensive grass/fodder production for cut-and-carry and also a separate section above for hay making - by his own initiative. By the application of various conservation measures, within five years an area exposed to severe water erosion was converted into an area of sustainable use. Fodder and fruits are now flourishing and the natural resources of soil and water are conserved more effectively.
Purpose of the Technology: The start of the process was fencing of the plot to keep out animals. Scrap metal and other materials from a machinery depot were used to build a 1.5 m high fence. To harvest and hold runoff water from the hillside for grapes and fruit trees, narrow backsloping terraces were constructed, each with a water retention ditch along the contour. During the initial phase, the terraces did not harvest enough water for establishment of the seedlings. So water for supplementary irrigation was carried to the plot by donkeys in old inner tubes from car tyres. Manure is applied to the plot to improve soil fertility. The manure is collected on the high pastures where the herders graze their animals during summer. The total amount of manure applied to the plot so far amounts to about 3 t/ha over 20 years.
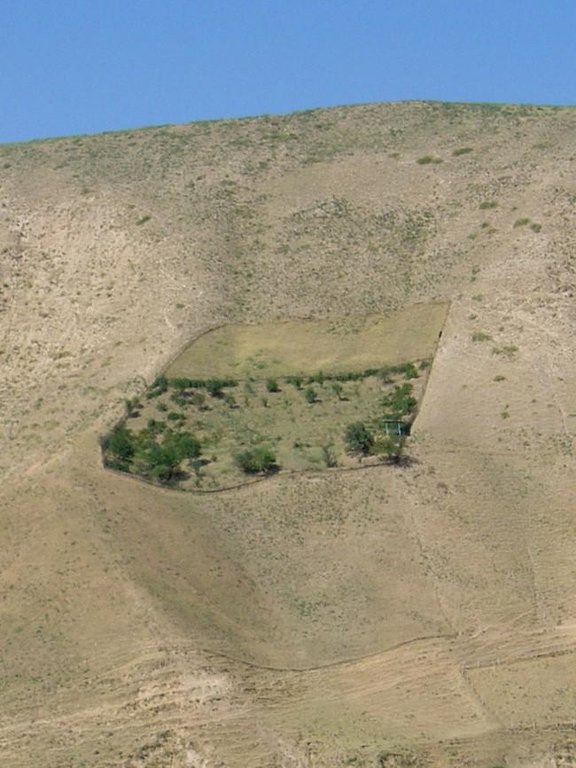
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of such a plot is very demanding in terms of manpower. However within 5-6 years the system becomes self-sustaining and the productivity of the land is improved several times over. Following this positive experience, other households in the area have adopted the technology spontaneously, and today about 15 ha of degraded grazing land in the Varzob valley have been converted into productive fruit gardens.
Natural / human environment: For the innovator, his most valuable fruits are grapes, followed by apricots, almonds and plums. He has also successfully grown mulberry, pomegranate and cherry trees. Not all the seedlings survive: the farmer considers a 40% survival rate of grape vines to be reasonable. The fruit harvest is mainly used for home consumption. However, in a good year the table grapes and apricots are sold on the market. The hay harvest, from naturally regenerated grasses and fodder plants between the fruits amounts on average to 0.2 t/ha/year. The pruned branches from the vines are collected and used as firewood.
The establishment of such a plot is very demanding in terms of manpower. However within 5-6 years the system becomes self-sustaining and the productivity of the land is improved several times over. Following this positive experience, other households in the area have adopted the technology spontaneously, and today about 15 ha of degraded grazing land in the Varzob valley have been converted into productive fruit gardens.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Тажикистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Tajikistan
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Varzob
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)

Холимог (тариалан/бэлчээр/мод), үүнд. ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Агро-сильво-пасторализм
Гол бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
major food crop: grapes, apricots,almonds, plums, mulberries
other: hay (cut-and-carry)
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - shortage of cultivable land on the gentle slopes next to the rivers
- low yield of natural pastures due to overgrazing
- heavy erosion taking place near residential areas
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): heavy erosion near the settlements
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ma: Agro-silvopastoralism
Хэрэв технологи нэвтрүүлснээр газар ашиглалт өөрчлөгдсөн бол технологи нэвтрүүлэхээс өмнө байсан газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг тодорхойлно уу:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Бүрэн усалгаатай
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March-October
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Гэрийн цэцэрлэг
3.5 Технологийн тархалт
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.15 m2.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим

Ургамалжилтын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

Хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
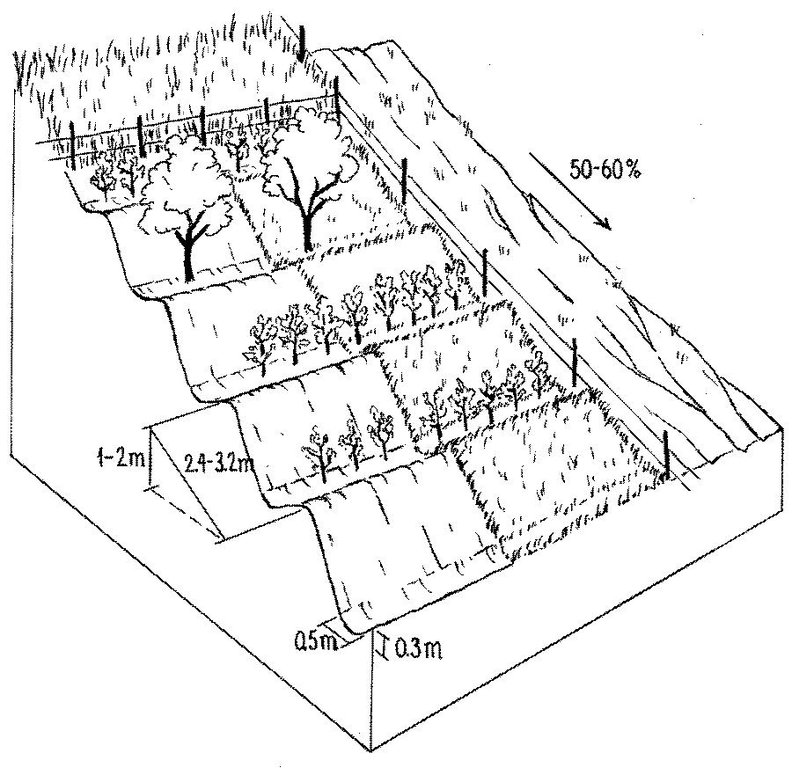
The fenced-off agroforestry system comprising fruit trees and cereals grown on a steep hillside. Terracing is crucial for water conservation. Grass cover (right) is established for fodder production and simultaneous soil conservation. Note the adjacent plot for haymaking (above) and degraded rangeland outside the protected area (right).
Location: Varzob. Varzob, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), retain/trap dispersed runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, water harvesting / increase water supply, reduction in wind speed, retain/trap concentrated runoff (prevention of gully erosion)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: manure
Remarks: 3 t per ha over 20 years
Vegetative measure: fruit trees/vines aligned
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.4-3.2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: grapes, apricot trees, almond trees, plum trees, mulberry trees, pomegranate trees, cherry trees
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 16-30%
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-2
Spacing between structures (m): 2.4-3.2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Structural measure: fence
Construction material (other): waste material, from a machinery depot
Change of land use type: from grazing land to tree crops
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк Доллар
4.4 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of vines and fruit tree seedlings (apricot, plums, almonds) | Ургамалжуулалтын | |
| 2. | 1. Fencing of an area of 0.5 ha using waste material from a machinerydepot. | Бүтцийн | |
| 3. | 2. Construction of backward sloping bench terraces. | Бүтцийн |
4.5 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Planting/Fencing/Constructing | ha | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 99.0 |
| Таримал материал | grape vines | ha | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | manure | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 2690.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 72 month(s)
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Irrigation (old inner tubes filled with water carried to the plot by donkeys). In summer: 5 litres of water per tree, per week. | Агрономийн | first 5–6 years |
| 2. | Irrigation (old inner tubes filled with water carried to the plot by donkeys). In summer: 5 litres of water per tree, per week. | Агрономийн | first 5–6 years |
| 3. | Manuring: applied at first to the newly planted vines/trees only,with restricted availability. During the second half of the establishment phase also applied elsewhere within the plot | Агрономийн | |
| 4. | Manuring: applied at first to the newly planted vines/trees only,with restricted availability. During the second half of the establishment phase also applied elsewhere within the plot | Агрономийн | |
| 5. | Irrigation of new seedlings. | Агрономийн | |
| 6. | Harvesting of fruits and fodder: transport of the yield to the house by donkey | Агрономийн | |
| 7. | Manuring, when replacing grapes or trees that had died. | Агрономийн | every year |
| 8. | Vines and trees that fail are replaced. | Ургамалжуулалтын | |
| 9. | Grapes and trees pruned | Ургамалжуулалтын | every year. |
| 10. | 1. Repairs to the fence | Бүтцийн | every year |
4.7 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Irrigation/manuring/keeping in good repair | ha | 1.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Таримал материал | Grape vines (replacment) | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | manure | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 570.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Labour cost per day is US$2. The fence constructed by the farmer was free because he utilised scrap from a machinery depot. Note that the total length of fencing is relatively less for a larger plot. In the villages, almost no money changes hands: there is a barter system between the farmers. Even salaries are often paid in terms of fruits, wood or free rent of land.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас чийглэг
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- Худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын % 10-50 хувь
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Хүнд хүчир ажил
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: 50% of the families' total income comes from three sons working in Moscow
Market orientation of production system commercial/ market: apricots sold on the market, in good years
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын эзэмшдэг эсвэл түрээслэдэг газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Төр засаг
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- Хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
модлогийн бүтээмж
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н хөрөнгө оруулалтын зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
for manure application
тариалангийн газрын орлого
хөдөлмөр хүчний хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
high labour input needed for establishment and recurrent irrigation
Бусад нийгэм-эдийн засгийн нөлөөллүүд
fruit production
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
terrace construction requires collaboration with relatives and friend
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
in the beginning conflicts due to jealousy, loss of community grazing land and fear of landslides caused by water retention on sloping loess areas
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
илүүдэл ус урсгах
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
poorly maintained terraces may lead to increased erosion (medium (20-50%))
Бусад экологийн үр нөлөө
soil fertility
biodiversity
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
flooding of the road at the bottom of the slope
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
conserved area is too small to have significant impact
risk of landslides due to water harvesting
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
5 households in an area of 15 ha
Технологийн нэвтрүүлсэн иргэдээс хэд нь өөрийн санаачлагаар буюу өөр эх үүсвэрээс материалын болон мөнгөн дэмжлэг авалгүй нэвтрүүлсэн бэ?
- 90-100 %
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Adoption was spontaneous in all cases and there are signs of further spread.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Rehabilitation of degraded areas: reduced soil erosion and increased productivity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Complement manure inputs by using other fertilisers. |
|
Production increase: good fruit yields How can they be sustained / enhanced? Introduce low input demanding crops |
|
Diversification: different kinds of fruit trees growing on the plot How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other trees (nuts for example) and annual crops such as wheat might also be suitable for this area. |
| Income generation. |
|
Where open access communal grazing leads to land degradation, individuals sometimes enclose land for productive purposes. This positive example is from Tajikistan where the initiative began during the period of the soviet regime. Similar initiatives can be seen in western Iran. However, if a significant number of land users follow suit, there will be a reduction in the amount of land available for common use. 2.6.11: Level of technical knowledge required: land user: partly moderate (construction of terraces) and partly low (simple knowledge of agronomy, manure application, harvesting etc) |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Bringing water for supplementary irrigation to the orchard is very labour intensive | An irrigation supply system could be installed (irrigation channels, water tank). But so far this is too expensive, and it is questionable whether irrigation could be installed and maintained sustainably |
| Not all tree species can grow in these dry conditions (for example apple trees will not survive without regular irrigation or watering) | irrigation water required (see above). |
| Difficulty in establishment of the young vines in the well developed grass | Remove or cut down grass and herbaceous plants around the vines at least until they have been well established. |
| Generally high manual labour input | Difficult to reduce labour inputs. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет дэх нээлттэй холбоосууд
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Loes Masselink. 2012. Monitoring SLM Practices in Tajikistan. BSc thesis, Land Degradation and Development Group, International Land and Water Management at Wageningen University. The Netherlands.
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/fileadmin/user_upload/documents/Theses/Masselink2012.pdf
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна