Indigenous Management of Tapia Woodlands [Мадагаскар]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Unknown User
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1359 - Мадагаскар
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Kull Christian
School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University
Австрали
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University - Австрали1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
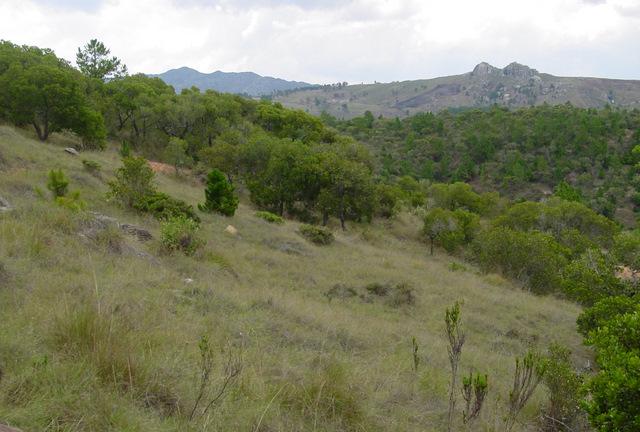
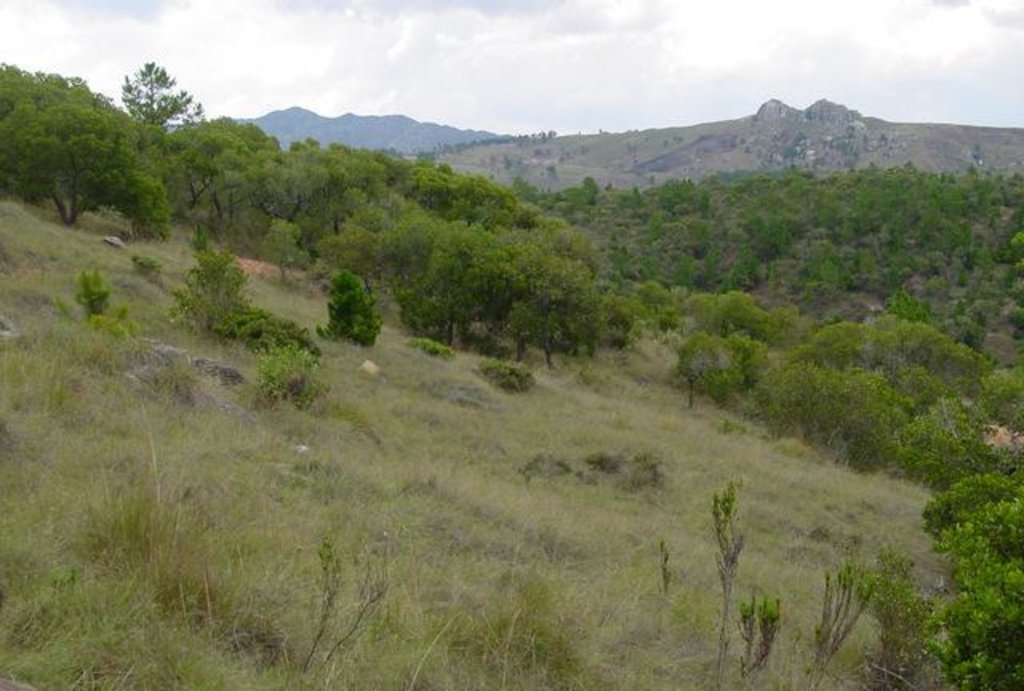
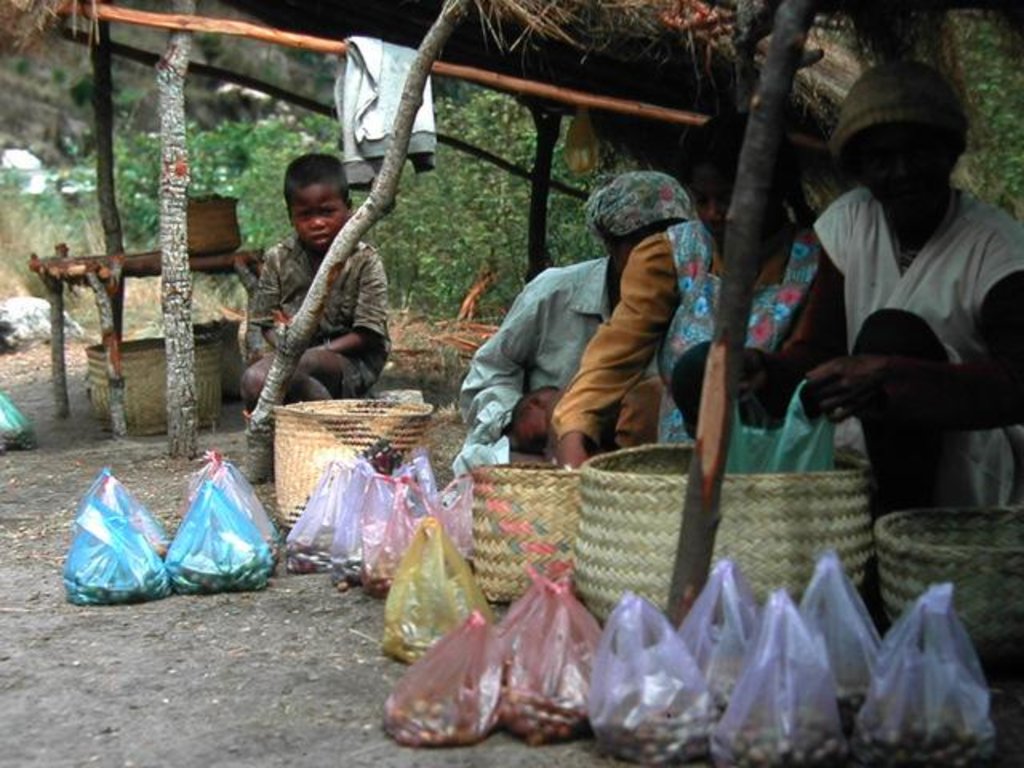
For centuries, the population of the highlands of central and south-western Madagascar has sustainably managed and conserved the local tapia woodlands.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
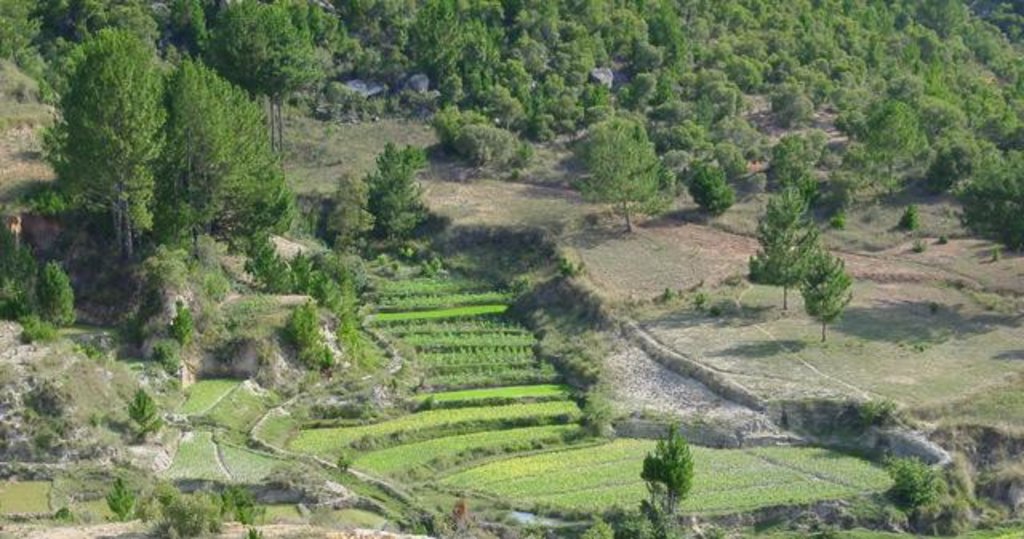
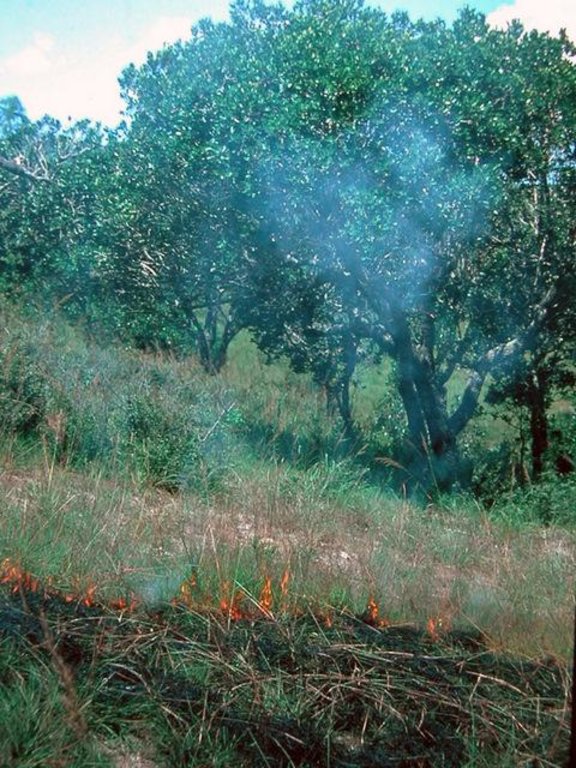
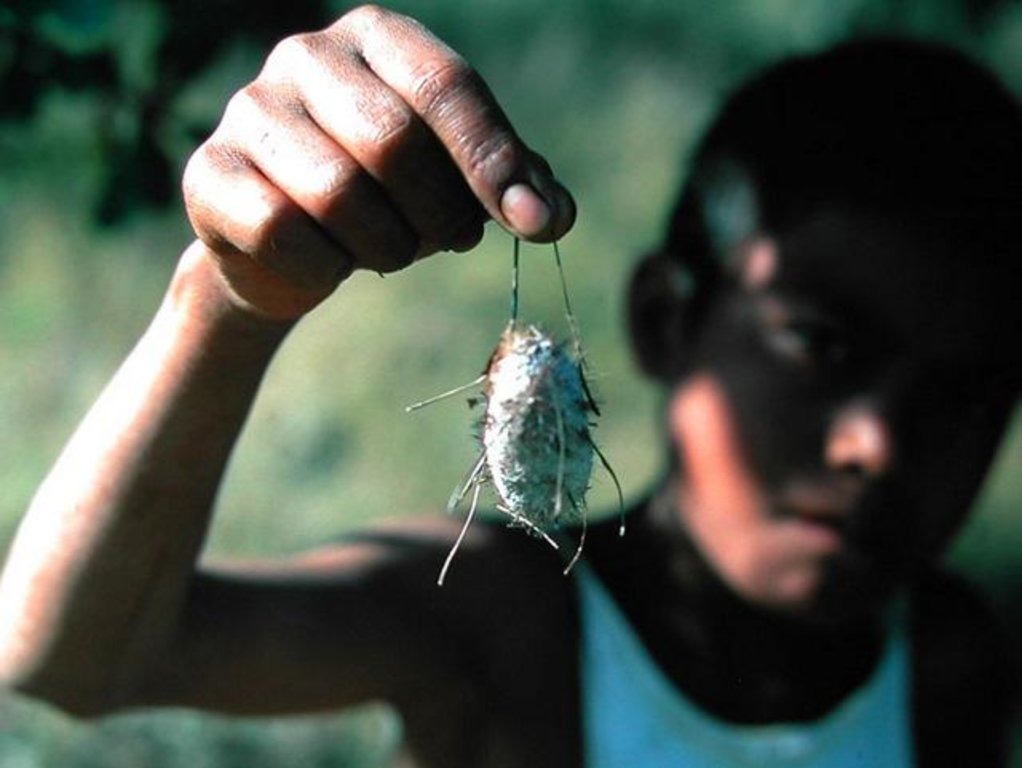
These woodlands play an important economic role as a source of non-timber forest products (NTFP) such as wild silk, fruit, mushrooms, edible insects, and herbal medicines. Tapia trees (Uapaca bojeri) comprise up to 90% of all trees in these woodlands, bear an edible fruit, and their leaves nourish an endemic silkworm (landibe). Landibe silk is used to produce ritual burial shrouds throughout the highlands. Trading silk products and tapia fruits is a crucial source of cash income for the local communities. The tapia woodlands are maintained by the local villagers through burning and selective cutting. Burning favours the dominance of pyrophytic (fire-tolerant) tapia trees and protects silkworms from parasites. Selective cutting of non-tapia species and pruning of dead branches also favours tapia dominance and perhaps growth. Other common species include the endemic Sarcolaena eriophora and the invasive Pinus patula/khasya. The Tapia woodland is clearly an anthropogenically shaped forest. However, the creation and maintenance of the woodlands should be seen as positive transformation rather than a form of degradation.
Local and state-imposed regulations protect the woodlands from overexploitation. The Forest Service has placed restrictions on forest cutting and burning while allowing for traditional use rights. The collection of forest products is regulated through a type of common-property regime. For example, fuelwood collection is limited to dead trees or fallen branches. It is forbidden to break off large branches to access cocoons. Thanks to these protective regulations, forest boundaries are mostly stable, and woodland density has increased in several cases.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Мадагаскар
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Col des Tapia
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Antsirabe and Ambositra
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
2600.0
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2600 km2.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Экосистемийг хамгаалах
- Үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Сильво-пасторализм

Бэлчээрийн газар

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
- (Сайжруулсан) байгалийн ой/мод бүхий газар
- Sustainable forest management
(Хагас)байгалийн ой/тармаг ойд: Менежментийн төрлийг тодорхойлно уу:
- Сонголттой огтлол
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Түлшний мод
- Жимс, самар
- Бусал ойн дагалт бүтээгдэхүүн
- Бэлчээрийн талбай/Хариулгатай бэлчээрлэлт
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduction of vegetation cover; Quantity biomass decline
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Other type of forest: sustainable forest management
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Байгалийн ба хагас-байгалийн ойн менежмент
- зөгийн аж ахуй, засагны аж ахуй, тахиа үржүүлэг, туулай үржүүлэг, торгоны хүүхэлдэйн аж ахуй г.м.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bq: Хэмжээ/ Биомасс буурах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: (traditional practice)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (children often harvest fruit; silk cocoon harvest is easy)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The tapia woodlands are maintained by the local villagers through burning and selective cutting
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | N |
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective cutting of non-tapia species, especially invasive pines | |
| 2. | Pruning of dead branches | |
| 3. | Controlled burning mainly through understory fires after the rainy season | Jan-May |
| 4. | Collection of non-wood forest products such as fruits, medicinal plants, mushrooms, berries, insects, and hunting of mammals etc | Sept.-Dec |
| 5. | Collection of landibe silkworm twice a year. The cocoons are cooked, spun and woven into silk fabric | Nov-Dec and May-June |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 20.0 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 20.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Traditional method; no establishment phase and costs.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
The estimation of costs is difficult - fruit are gathered over a two month period by school children going out for an hour in the early morning each day; the silkworms are collected by individuals (usually experienced collectors) on free days. In some areas, projects exist that run silkworm nurseries, establish firebreaks in the woodlands, grow and plant tapia seedlings, and finance the purchase of silk looms. These projects obviously require much larger budgets.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
7 months of dry season
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Гадаргын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Slopes on average: hilly (16-30%), steep (31-60%), very steep (>60%)
Altitudinal zones: 500-2000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Сийрэг/хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil texture is coarse/light (sandy) (silica-rich soils compared to the main lateritic soils of highland Madagascar)
Soil fertility is low ( mostly nutrient-poor or rocky soils )
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Population density: 20-40 persons/ km2 in the central highlands and 10-20 in the western highlands
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Төр засаг
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Тайлбар:
Woodlands are officially state-owned, but in practice managed by neighbouring communities (either unofficially, or increasingly through community-based management contracts
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
модлогийн бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Stable supply of fuelwood
Орлого, зарлага
тариалангийн газрын орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Through selling silk-fabrics and other NTFP
Бусад нийгэм-эдийн засгийн нөлөөллүүд
Production of NTFP as important dietary supplements
Provision of medicinal plants
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийгөө хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Thorugh the forest products
Соёлын боломжууд
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Sacred forest
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи С
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Endemic biodiversity
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Тайлбар:
Silk and fruit harvests vary from season to season but drivers are poorly understood (could include precipitation and temperature)
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Тайлбар:
The larger rainy season silk harvest provides crucial cash income during the meagre months before the rice harvest. In 1998 the price of 200 cocoons was between US$ 0.10-0.15. For a basket of Tapia fruits villagers earned between 0.02-0.06 US$/ kg. During
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Тайлбар:
Comments on adoption trend: see Annex 3
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Thanks to these protective regulations, forest boundaries are mostly stable, and woodland density has increased in several cases |
| La vente des produits en soie et des fruits de Tapia est une source de revenus capitale pour les communautés locales |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Partly individual indiscriminate cutting and/or strong use of fires leads to overuse of the forest resources | needs clear regulations, guidelines and observation of the rules by the local authorities as well as awareness raising about the multiple benefits of the forests. As long as the communities continue to be interested in the forests and its products, they will protect it from destructive cutting. |
| Invasion of exotic tree species such as pine and eucalyptus from private and village woodlots | the forest service has rightly been encouraging communities to cut these trees from the tapia forests without the need for complicated permits. |
| Insecure land use rights | in 1996 a new legislation opened the way to officially decentralize management of state-owned renewable natural resources to adjacent communities, which would aid woodland protection by increasing stakeholder involvement. |
| In some areas, silkworm populations have been very low for decades | recent projects seek to establish silk nurseries and reintroduce the worm |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Kull CA (2002): The ‘Degraded’ Tapia Woodlands of Highland Madagascar: Rural Economy, Fire Ecology, and Forest Conservation. Journal of Cultural Geography Spring/ Summer 2002.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна