Rotational grazing to restore degraded pastures [Афганистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Bettina Wolfgramm
- Хянан тохиолдуулагчид: MIAJAN MAROOFI, Hekmatullah Sharifzai, Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aslam Qadamov
- Хянагч: William Critchley
Ploni ba navbat charonidani mol ba khotiri behbudi charogoh
technologies_671 - Афганистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Researcher:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Швейцар1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
17/10/2016
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [Афганистан]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- Эмхэтгэгч: Bettina Wolfgramm
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
A plan for rotational grazing has been developed to control pasture use and prevent overgrazing of rehabilitated pastures.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Livestock keeping is one of the key livelihood strategies in rural Rustaq, in addition to cultivation of cereals. Families rely on their livestock not only for consumption of meat from cattle, goats and sheep, and dairy products such as milk and sour milk, but also as means of transportation (donkeys), labour in agriculture (oxen, donkeys) and as a source of income through sales. Naturally, every family strives to increase their household’s livestock as much as they can, which increases the pressure on the local pastures - leading to extensive overgrazing. The pastures in Jawaz Khana and Sari Joy are characterized by poor vegetation cover, low carrying capacity and severe erosion with deep rills clearly visible. Heavy rains in spring and autumn wash off the topsoil on pastures, resulting in heavy erosion, landslides and gully formation. These severely degraded pastures continue to be used though "open access" - without any management schemes or regulations in place. Some pastures that are not suitable for grazing have been converted to arable lands and tree plantations. The quantity and quality of livestock fodder is insufficient for all the livestock, and this affects animal health.
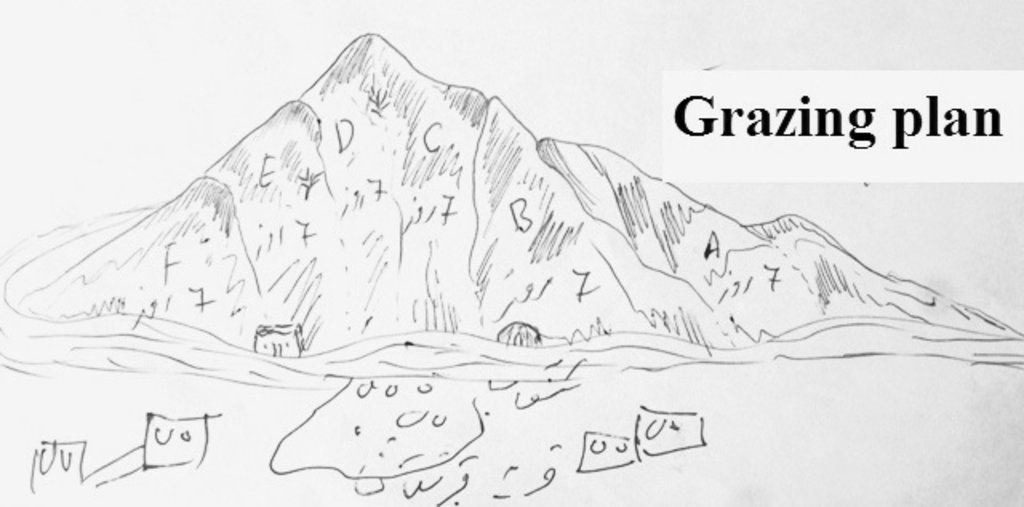
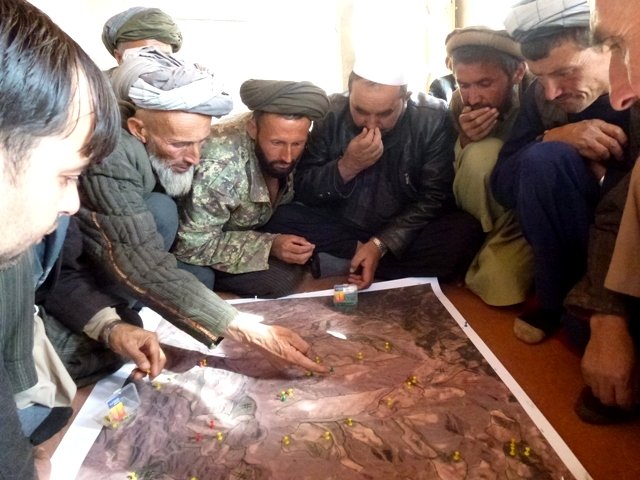
Plans for rotational grazing were prepared for the communities in Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana to organize the use of local pastures and prevent their further degradation. Rotational grazing plans regulate the frequency and intensity of livestock grazing on the pastures. The area is seeded with alfalfa to improve the fodder stock and enhance the quality of the pasture. For up to three years the seeded area is closed to grazing, during which period the community is provided with stocks of hay and straw to feed their livestock as an alternative. After the end of the closure period, the grazing area is divided into 6-7 sections (paddocks) depending on the area of the pasture. The livestock graze the first paddock for 7 days and move to the next paddock. Each paddock is grazed for the period of 7 days during April and May. From the month of May the grazing area is closed for resting. The livestock move to the summer pastures for the rest of the summer months.
The community is key in preparing the grazing plans and identifying the pastures where these plans will be applied, as well as the conditions which are part of it, such as the frequency of the grazing period. Frequent meetings need to be held with the community livestock holders to explain the purpose of the rotational grazing and how it can be beneficial in pasture improvement. The Natural Resources Management Committee and the technical staff of the Livelihood Improvement Project (LIPT) are in charge of engaging the local pasture users to meet their needs and consider their views accordingly.
The actual implementation of the rotational grazing plans is difficult to assess for the time being. The grazing area is not fully restored and the fodder stock remains low. Many land users do not fully understand the concept behind the rotational grazing plans or their purpose. In an area where there is a severe shortage of livestock fodder and very limited grazing land, accepting and following these plans will require more time and additional support in terms of awareness-raising and support feeding of the livestock during the exclusion period. The villagers have some doubts about the costs and benefits of grazing and rotation. They have no full understanding of the benefits of the rotational grazing for their household and are likely to be not ready to adhere to such schemes.
Women are part of the livestock management system, and are in charge of feeding and taking care of the livestock. However, they are not aware about the plans for rotational grazing in their village and how are these plans are applied in practice.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Афганистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana Villages
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2015
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Livelihood Improvement Project in Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуйн газар:
- Хагас нүүдлийн/ бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Сайжруулсан бэлчээр
Голлох малын төрөл ба бүтээгдэхүүн:
Cow, Sheep, Goat. Alfalfa
Хэрэв технологи нэвтрүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан бол технологи нэвтрүүлэхээс өмнө байсан газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг тодорхойлно уу:
Some areas under the Technology are former croplands, which have been completely degraded and no longer suitable for crop cultivation.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
6 ha
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрс салхиар эвдрэх
- Et: Хөрсний гадаргын зөөгдөл

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bq: биомасс буурах

бусад
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
After the end of the exclusion period the grazing area is divided into 6-7 sections (paddocks) depending on the area of the pasture. The livestock graze the first paddock for 7 days and move to the next paddock after 7 days. Each paddock is grazed for the period of 7 days during April and May. From the month of May the grazing area is closed for resting. The livestock move to the summer pastures for the rest of the summer months.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
1 ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
67.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the pasture area and awareness raising among people | Менежментийн | Fall |
| 2. | Leveling of the land | Агрономийн | Fall |
| 3. | Sowing alfalfa seed | Агрономийн | Spring |
| 4. | Site under quarantine | Менежментийн | Three years |
| 5. | Preparation of the grazing plan and community meetings | Менежментийн | Fall |
| 6. | Protection of the site during quarantine | Менежментийн | Three years |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Leveling the land with a rake | person-day | 150.0 | 5.3 | 795.0 | 71.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Sowing alfalfa | person-day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 71.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Preparation of grazing plan | person-day | 2.0 | 9.0 | 18.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Protection of the site | year | 1.0 | 447.0 | 447.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel | piece | 1.0 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Rope | Meter | 50.0 | 0.15 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Rake | piece | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Alfalfa seed | kg | 17.5 | 0.42 | 7.35 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | DAP | kg | 125.0 | 0.9 | 112.5 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Urea | kg | 125.0 | 0.45 | 56.25 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1476.9 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community agrees to leave the pasture for resting/ exclusion | Менежментийн | Three years |
| 2. | Rotational grazing | Бусад арга хэмжээ | Spring/week/grazing plot |
| 3. | Reseeding alfalfa | Ургамлын | After 5 years |
| 4. | Protection of the site | Менежментийн | Three years |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Reseeding alfalfa | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Protection during exclusion | year | 2.0 | 447.0 | 894.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Alfalfa seed | kg | 17.5 | 0.42 | 7.35 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 927.85 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimum in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximum in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the period from 1979 to 2014.
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where the technology is implemented:
- Red: shallow; texture medium, coarse; low organic matter
- Light: moderately deep; texture medium; medium, low organic matter
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
тохиолдлын
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the villages of Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana. Sari Joy has good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a stream lower down.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Хагас-нүүдэлийн
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
- ахимаг нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq.
Although the men are generally the main land users, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While, it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however, very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Тайлбар:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
малын бүтээмж
модлогийн бүтээмж
ойн дагалт баялгийн бүтээмж
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
Хөрс
хөрс алдагдах
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамалын бүрхэвч
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
Нөлөөллийн үнэлгээнд хамаарах нэмэлт тайлбар:
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits from the technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in prduct diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all terrace implementers are reflected here.
- Similarly for the "ecological impacts" and on "off-site impacts": Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all terrace implementers are reflected here.
- Socio-cultural impacts: This section is answered by the scientists, based on information collected during focus group discussions, and interviews conducted with persons from the 3 villages where the LIPT project implemented the technology.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | маш сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Тайлбар:
SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate the SLM technologies short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) return. As most of the technologies have only been implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technologies. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
6 ha
Тайлбар:
Rotational grazing plans are developed for common lands used by the whole village. There is one common grazing plan for each village.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| If implemented according to the plan and the pasture area is allowed to rest, the quality and quantity of the fodder will be enhanced. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The land users have no full knowledge about the plans for rotational grazing and how they should be applied | Increase awareness raising among the land users |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Focus group discussions were organized to collect information from SLM implementers in Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana.
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Information provided in the reports of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Groups Discussions
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [Афганистан]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- Эмхэтгэгч: Bettina Wolfgramm
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна