Environmentally-Friendly Community Practices [República da Moldávia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Valentin Ciubotaru
- Editores: Valentin Ciubotaru, UNCCD PRAIS
- Revisores: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Practicile comunitare prietenoase mediului
technologies_1816 - República da Moldávia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Ciubotaru Valentin
+37322 545733 / +37322 69134294
ngobios@yahoo.com / valentin.ciubotaru@yahoo.com
NGO BIOS
72/3 Columna str., office nr. 3. Chisinau- MD-2012
República da Moldávia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NGO BIOS (.) - República da Moldávia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
02/06/2014
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Community area development plans were developed taking into consideration the main problems, opportunities, necessities and wishes of the local population. All communities included afforestation of severely eroded land, re-establishing degraded forest belts and planting new forest lines, creating protection shields for aquatic areas, and an ecological education community program.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Community area development plans were developed for six communities for the period of 2008-2028, taking into consideration the main problems, opportunities, requirements and wishes of the local population. Special attention was paid to environmental impact assessment to harmonize economic and social development with environmental protection. All communities included afforestation of severely eroded land, re-establishing degraded forest belts and planting new forest lines, creating protection shields for aquatic areas, and elaborating and implementing a ecological education community program.
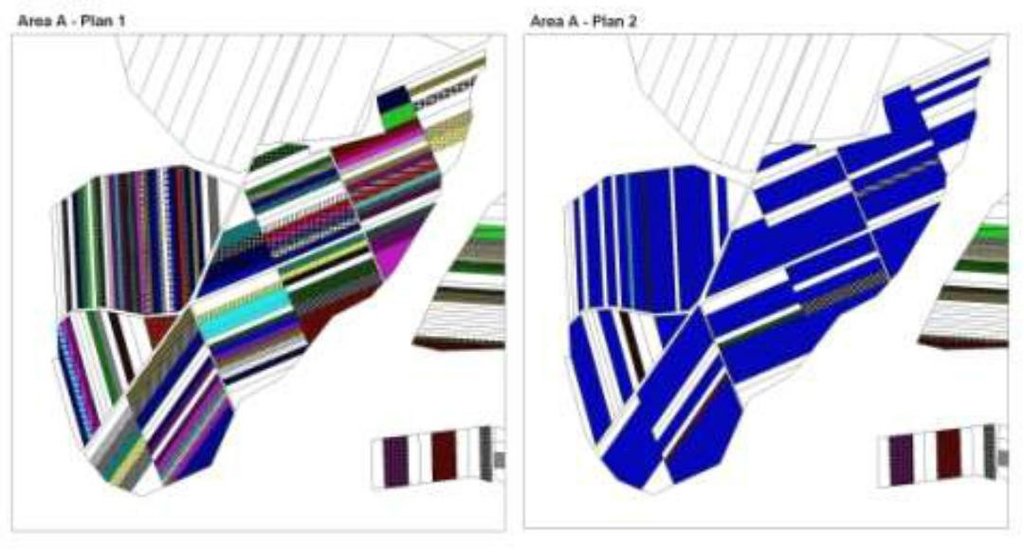
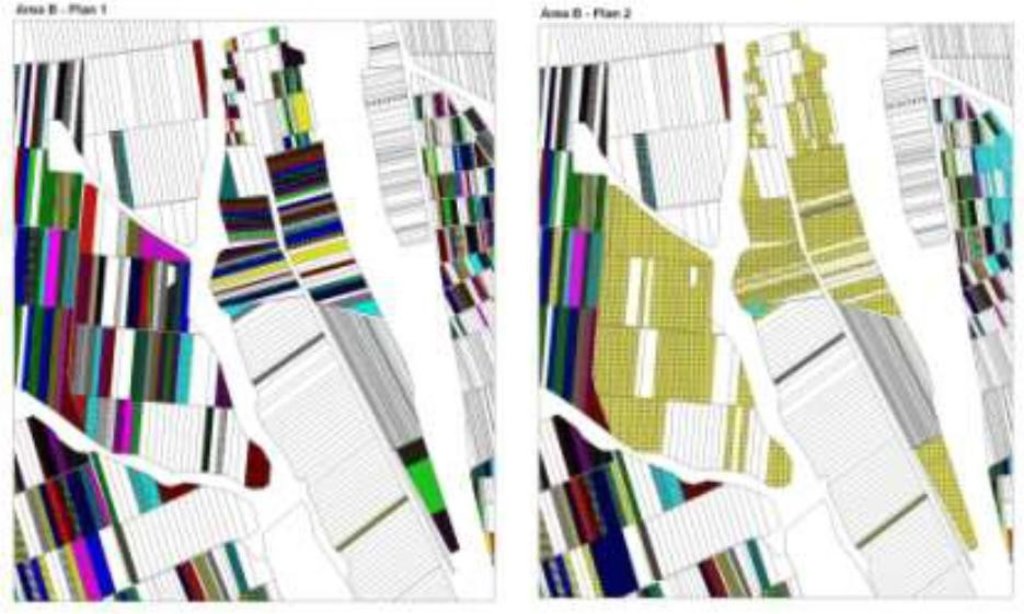
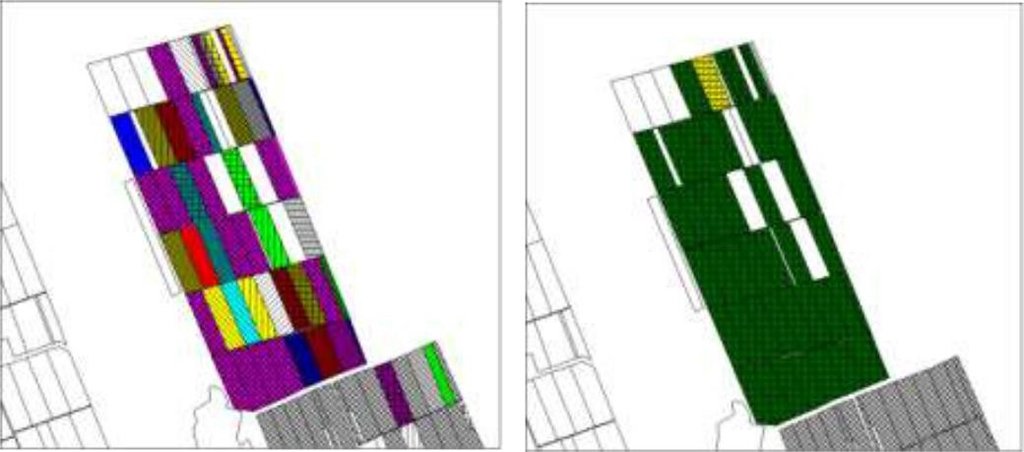
The first action implemented was agricultural land re-parcelling, based on FAO guidelines. Training programs were conducted for project staff and beneficiaries. Following land planning, discussions and individual negotiations with each land owner, the project promoted the application of the following land parcels operations: sale, exchange and long term lease. The costs incurred during land transactions were fully covered by the project. The Land Use Scheme implies changes in some categories of use and especially expanding the area of vineyards and orchards as well as using agricultural land for community development according to the needs and wishes of the population. Land re-parcelling offers farmers the possibility of rearranging agricultural land according to ecological principles and potential.
The overall goal of land re-parcelling component was to respond to the concerns of the Government and others about the fragmentation of agricultural land: it focussed on small peasant farms as its primary target group. The specific objectives of the pilot action were:
- to test the demand for and feasibility of land re-parcelling with small landowners as the primary target group;
- to facilitate development of 6 community area development plans, taking into account environmental impact assessment.
- to use the pilot experience as the basis for designing a potential national-level approach, including techniques, resource requirements and legislative framework;
- to assess the impact of re-parcelling at the local level, including on land markets, agricultural production, and equity.
The re-parcelling activities were extended to 40 villages on the proviso that the concept and the experience of the implemented re-parcelling pilots would be precisely followed. Based on this experience, the Ministry of Agriculture is in active partnership with National Agency for Rural Development and NGO BIOS, supported by the FAO-developed National Strategy for Land Consolidation.
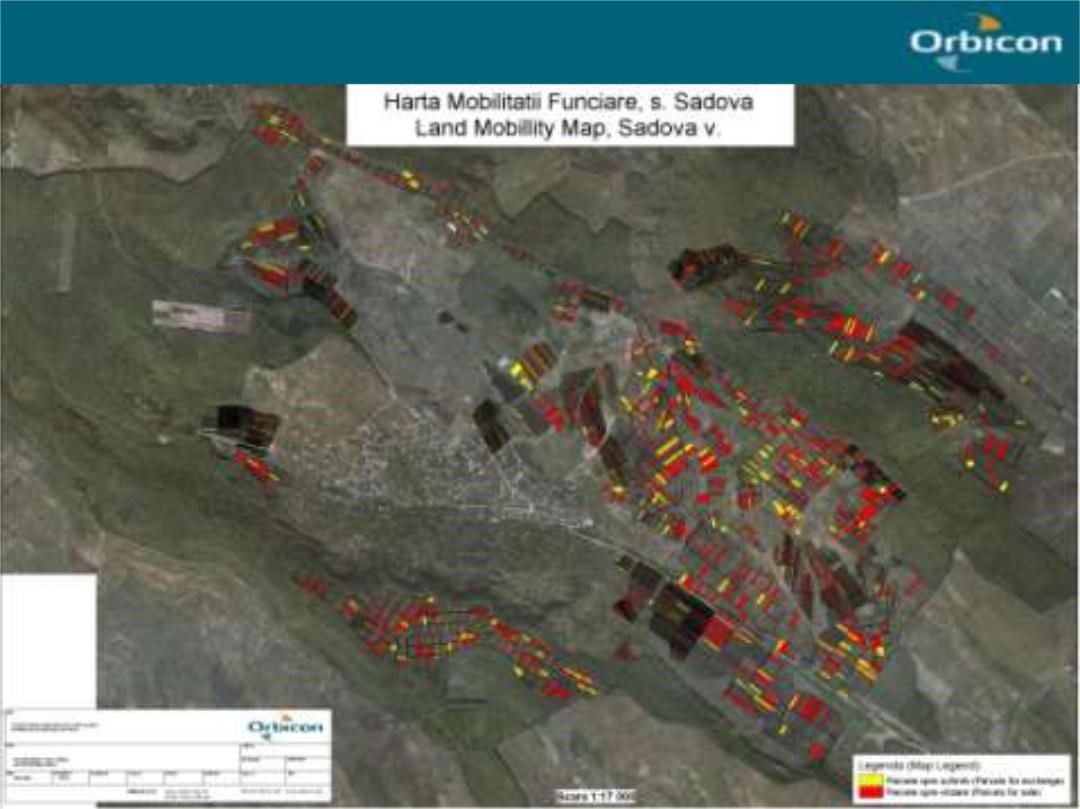
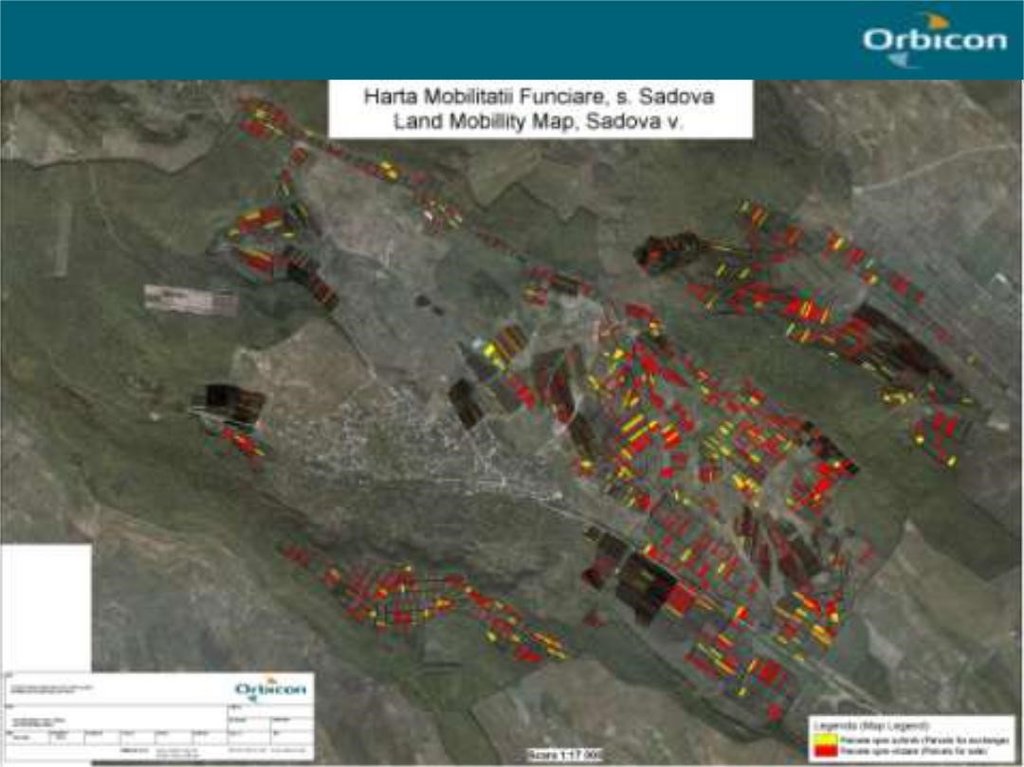
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
República da Moldávia
Especificação adicional de localização:
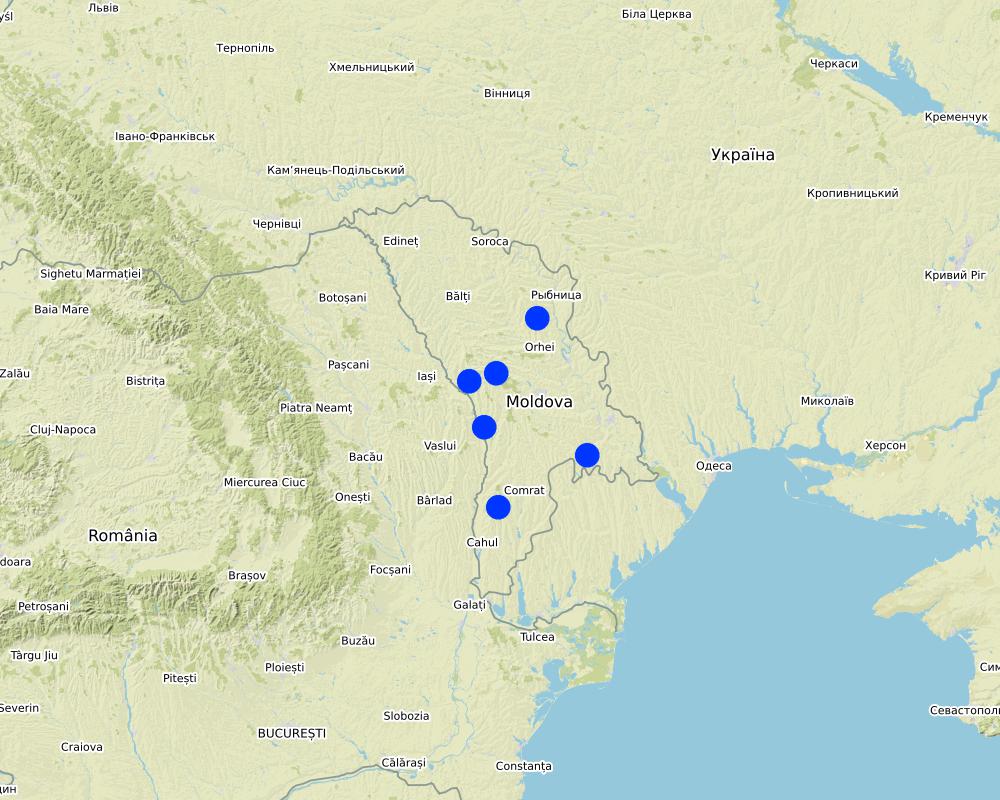
The six communes which form the pilot area, namely Basauca village Rezina district, Sadova village Calarasi district, Calmatui village Hincesti district, Bolduresti community of Cantemir district, Baimaclia community Cantemir district, Opaci village Causeni district, Republic of Moldova. The experience was replicated in 40 villages.
Comentários:
The six communes which form the pilot area, namely Basauca village Rezina district, Sadova village Calarasi district, Calmatui village Hincesti district, Bolduresti community of Cantemir district, Baimaclia community Cantemir district, Opaci village Causeni district, Republic of Moldova.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)

Outros
Especifique:
- Land fragmentation; - Environmentally unsustainable land management practices; - Illegal cutting of forests, leading to the destruction of forest belts and buffer strips; - Point and non-point sources of pollution, - Over-grazing..
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- > 10.000 km2
Comentários:
The Technology was replicated to 40 villages in South, Center and North regions of Moldova
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
- S9: Abrigo para plantas e animais

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
- Implementing activities of protection, maintenance and improving of degraded soil fertility;
- Agroforestry consisted of planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts.
- Improving the quality of pastures and implementing controlled pasturing.|
- Regeneration of degraded commune forest as well as existing forest protective belts.
- Planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts. |
Facilitate the development of farms by reducing the fragmentation and expanding the area of agricultural lands. The project provides assistance to land owners and farmers to undertake voluntarily land transactions based on market economy principles, elaborating the land ownership maps (GIS MapInfo|
The elaboration of the Community Area Development Plans was effected together with the local public administration, professors, legal persons, non-governmental organizations, and the population of communities with active involvement of Zonal Ecologic Agencies, Preventive Medicine Centers, |Agriculture and Economy Departments of district Executive Committees.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wr: erosão das margens
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
- Ed: deflação e deposição

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pu: perda da função bioprodutiva devido a outras atividades

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implementing activities of protection, maintenance and improving of degraded soil fertility | ||
| 2. | Agroforestry consisting of planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts. | ||
| 3. | Improving the quality of pastures and implementing controlled pasturing| | ||
| 4. | Regeneration of degraded commune forest as well as existing forest protective belts | ||
| 5. | Planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The Project
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Chisinau, Nisporeni, Calarasi, Cahul, Leova, Hincesti, Rezina
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Moldova's climate is moderately continental: the summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging 20 °C, and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging −4 °C. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around 600 millimeters in the north to 400 millimeters in the south, can vary greatly. The heaviest rainfall occurs in summer; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common. Because of the irregular terrain, heavy summer rains often cause erosion and river silting.|
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Most of Moldova's territory is a moderate hilly plateau cut deeply by many streams and rivers. Geologically, Moldova lies primarily on deep sedimentary rock that gives way to harder crystalline outcroppings only in the north. Moldova's hills are part of the Moldavian Plateau, which geologically originate from the Carpathian Mountains. |
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
About 75% of Moldova is covered by black earth or chernozem. In the northern hills, more clay textured soils are found; in the south, red-earth soil is predominant. The soil becomes less fertile toward the south but can still support grape and sunflower production. The hills have forest soils, while a small portion in southern Moldova is in the steppe zone, although most steppe areas today are cultivated. The lower reaches of the Prut and Dniester rivers and the southern river valleys are saline
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Sim
Especifique:
high water mineralisation
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
- idosos
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
After independence (1991), land was privatized. The average family was entitled to plots of between 1.5 and 2.5 ha. Four categories of farms emerged: (i) small individual farmers; (ii) individual commercial farmers; (iii) farmers in associations with close relatives; and (iv) farmers in groups (from less than 10 farmers to large, joint-stock companies). The small size of many farms precludes the use of agricultural machinery and advanced technology. |
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
The principal activity of local farmers is crop farming; main arable crops are maize and wheat. The cultivation of grapes and fruits is another traditional element of agriculture in this area. Vineyards and orchards take a significant share of cropped land. Income is derived from sale of agricultural produce, including milk and eggs, from forest products, but also from seasonal work at the small workshops in their own and surrounding communities.|
Income depends much on weather conditions and agricultural policies. Estimated average income per person is 50 US dollars per month for the last three years (no including this year).
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção animal
Qualidade da floresta/do bosque
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Qualidade da água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Comentários:
Expected changes include utilization of local resources, change in existing land use management, change in landscape, changes in erosion rates, etc. These in their turn are expected to lead to social and economic impacts on people.
• The main environmental indicators are largely the same. • The expected environmental impact of re-parcelling and initiated actions are significant, especially in the long run. |
People learn to live with the new approach, new land structure, alternative solutions of solving their own problems, etc. |
Implementation of the land re-parcelling project contributes to improving the structure of the agricultural land, efficient use of technology, increase the possibility of arranging the community territory with a consolidated network of roads; |
The economic levels stayed practically unchanged, while social cohesion and culture has somewhat improved from exposure to new things, common work. The expected social impact of re-parcelling and initiated actions are significant, especially in the long run.|
Expected changes include increased jobs for people, there will be favourable conditions for the young population to stay in the rural area and those who left abroad could return back and start various businesses in their village.|
Improving the community infrastructure by water and natural gas supply, etc. It offers farmers a possibility to start processing enterprises so that they can sell the final product at a higher price than the raw products.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 10-50%
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Business opportunities related to community development, etc. | Highly motivated local governments Highly motivated farmers |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
6000
7.3 Links para informação relevante que está disponível online
Título/ descrição:
Assessment Study on Land Re-parceling Pilot Project in 6 Villages in Moldova
URL:
http://www.capmu.md/wp-content/uploads/images/docs/Impact_Assessment/Final%20report%20IA%20land%20rep.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Experiences with land reform and land consolidation in Moldova
URL:
file:///C:/Users/USER/Downloads/59-357-1-PB.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos