Reduced tillage [Estônia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Endla Reintam
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
minimeeritud harimine
technologies_3120 - Estônia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Aruksaar Ahti
Viljameister OÜ
Estônia
researcher:
researcher:
Lauringson Enn
Estonian University of Life Sciences
Estônia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
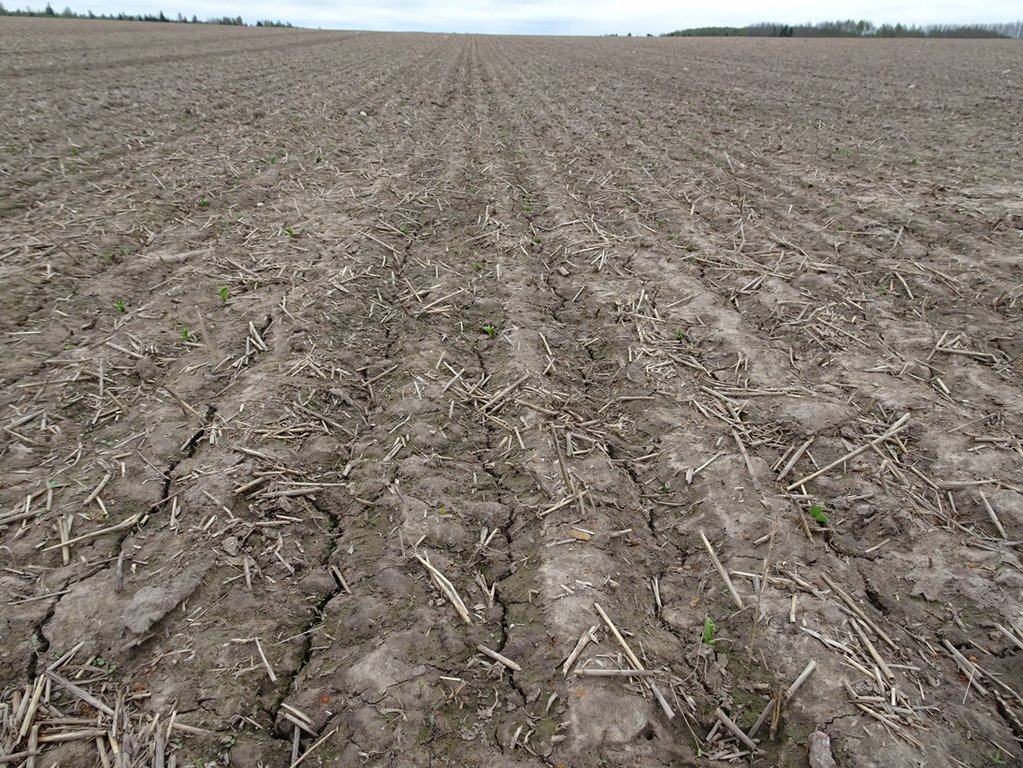
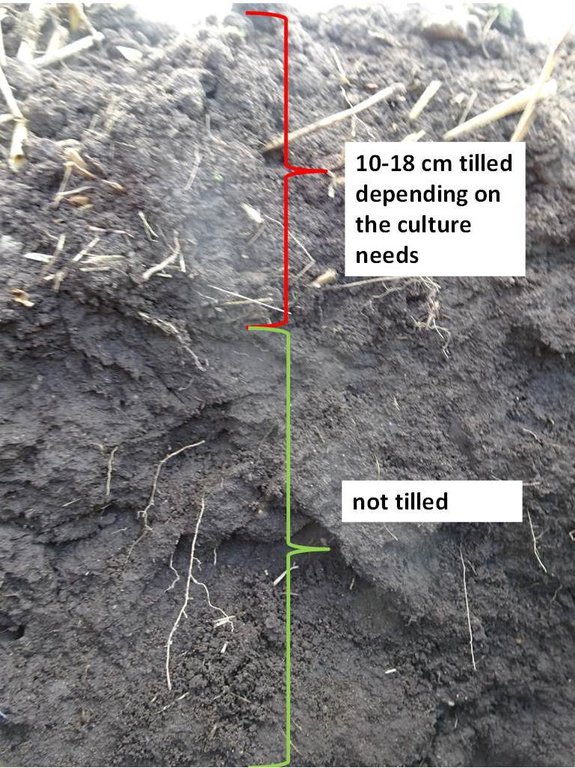
Reduced (minimum) tillage is a tillage method that does not turn the soil over. Usually only the upper 10-18 cm of the soil surface is tilled.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat, the southern part is hilly with slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) in the north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. In the agricultural area the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) to high (>5%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater is near the surface in wet soils and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity varies from high to low depending on soil and landscape. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income is less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users, but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 100 ha).
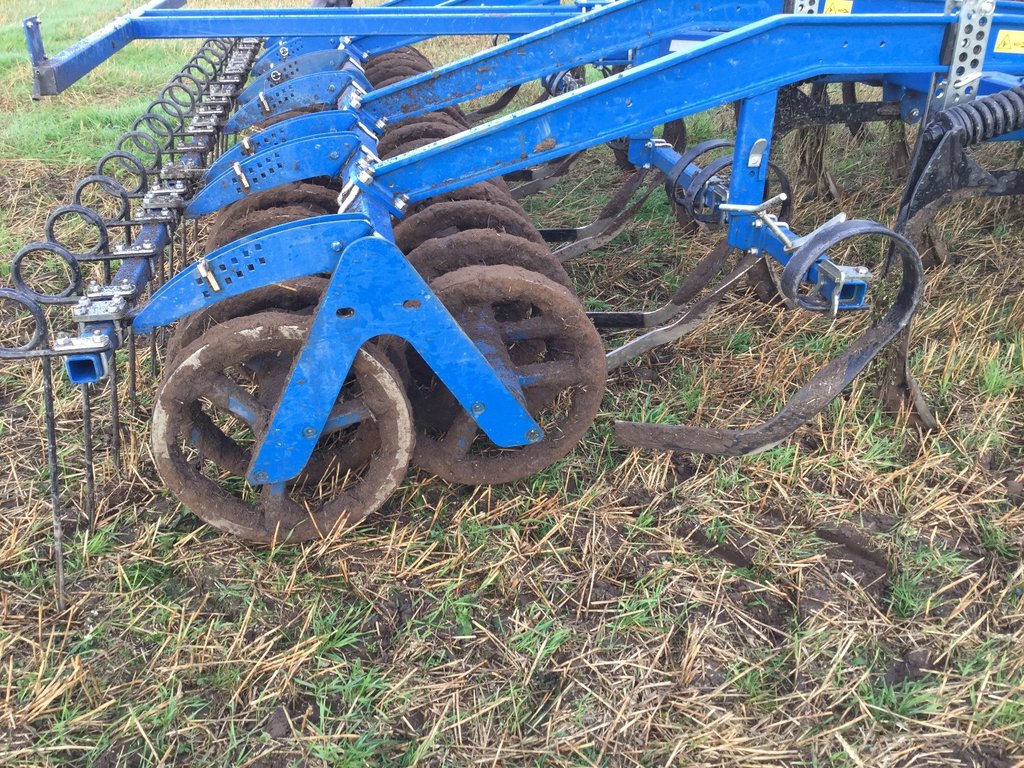
Reduced tillage is the tillage method used in agriculture to prepare the seedbed. Usually only the upper 10-18 cm of the soil surface is tilled. There is no use of ploughing and thus it is the method that does not turn the soil over. This may involve the use of a chisel plough, field cultivators, or other implements. Depth of the soil preparation depends on the culture in the rotation - before cereals 10-12 cm, before oilseed rape 15-18 cm. The main equipments to prepare the seedbed are the disc cultivator and the tine cultivator or a combined cultivator. The work can be ordered from contractors as well. Usually farms own the equipment.
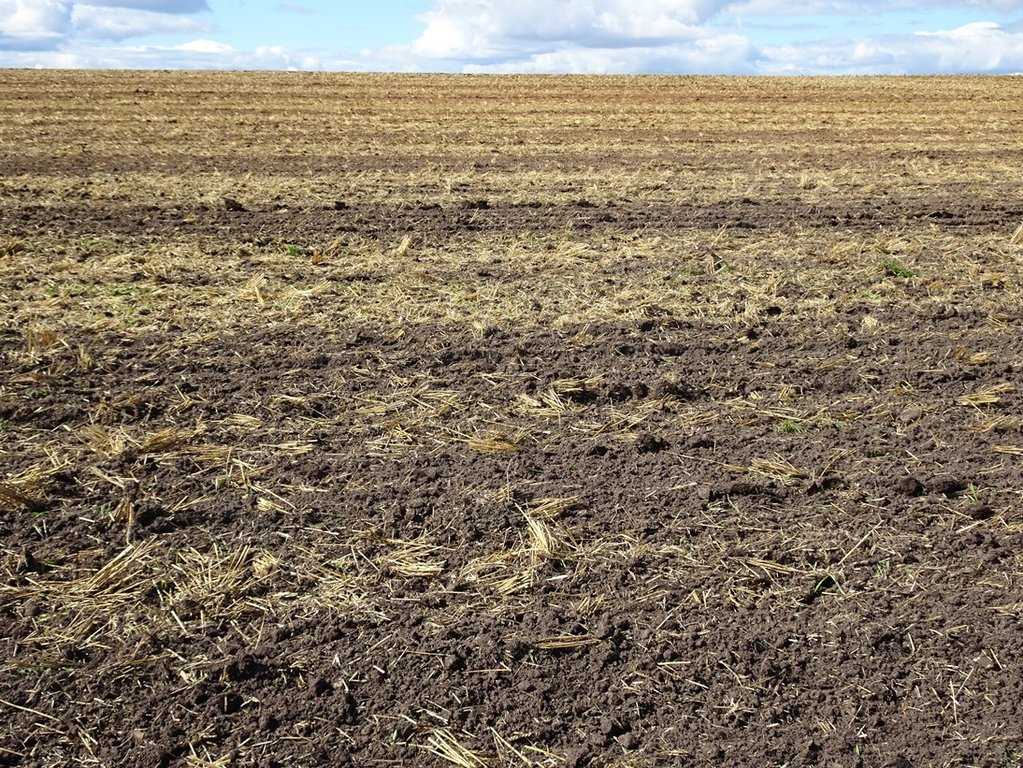
The main goal is to maintain soil structure, to improve water infiltration, to reduce compaction, and to reduce fuel and labour costs. As there will remain 30% more residues on the soil surface it will promote the activity of soil organisms. Less disturbance in deeper layers increases number of earthworms and increases species diversity. The greatest benefits for the land users are the reduced fuel and labour costs. The reduced tillage is more suitable for crop rotations without root crops. For example, rotation can be as follow: winter oilseed rape - winter wheat - pea (or bean) - winter wheat - spring barley undersown with red clover - red clover. However, the soil compaction and weediness can drastically increase during the first years of the implementation without using a proper crop rotation or management plan. The soil conditions (compaction and weediness) can get worser inside the first 4 years and start to improve after that. It is not suitable for fields which are heavily affected by perennial weeds, as noninversional tillage can spread the weed roots and higher doses of herbicides are needed.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Estônia
Região/Estado/Província:
Tartu county
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kobilu
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
2/3 of cereals is cultivated by minimum tillage technology in Estonia.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - milho
- cereais - aveia
- cereais - outros
- cereais - centeio
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
- legumes e leguminosas - ervilhas
- culturas oleaginosas - girassol, colza, outros
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
One harvest of cereals per year.
Comentários:
Main crops: winter and spring wheat, winter and spring barley, oat, rye, pea, bean, oilseed rape, corn for silage, buckwheat
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Comentários:
Before the use of reduced tillage conventional tillage (with ploughing) has been used.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
To till the soil chisel ploughing or disc cultivator is used without turning the soil over. For cereals the suitable depth is 10-12 cm, for oilseed rape 15-18 cm. Ca 30% from straw will remain on the soil surface. To loosen the soil of deeper layers the deep chiseling down to 25 cm is used.
Autor:
Endla Reintam
Data:
14/08/2017
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
hectar
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
EUR
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
1,18
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of cultivator (disc or combination cultivator) |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Disc cultivator | piece | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 15000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 12711,86 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedbed preparation (tillage before drilling) | before drilling (spring crops in spring (April), winter crops in autumn (August)) |
| 2. | Fertilization, drilling | in spring or in autumn, drilling and fertlization at the same time |
| 3. | Plant protection | up to 3 times during growth period depending of weediness, infections and insects |
| 4. | Fertilization during growth period | For winter crops in spring after snowmelt in the beginning of growth, for spring crops in the beginning of intensive growth |
| 5. | Harvest and grain transport | in the end of season (end of July to beginning of September depending of the crop) |
| 6. | Drying of grain and soil tillage | after harvest |
Comentários:
The example is based on the assumption that the yield will be around 6 t/ha and we grow cereals (winter or spring wheat)
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Seedbed preparation, fertilization, sowing | times | 1,0 | 131,9 | 131,9 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Plant protection | times | 3,0 | 11,2 | 33,6 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Fertilization during growth period | times | 1,0 | 16,2 | 16,2 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Harvest and grain transport | times | 1,0 | 118,5 | 118,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Drying and after harvest activities | times | 1,0 | 132,1 | 132,1 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seeds | kg | 200,0 | 0,28 | 56,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Ammonium nitrate (2x per season) 147 kg/ha N (200 kg fertilizer per ha) | kg | 147,0 | 0,84 | 123,48 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Complex fertilizer (27 kg N, 40 kg P and 112 kg K per ha) (450 kg of fertilizer per ha) | kg | 179,0 | 0,74 | 132,46 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Herbicides (1 time) | times | 1,0 | 27,0 | 27,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fungicides (1 time) | times | 1,0 | 33,2 | 33,2 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Insecticides (1 time) | times | 1,0 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Retartants | times | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 822,04 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 696,64 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
Agricultural producers can have governmental support per unit 83.71 EUR/ha and the greening support 38.81 EUR/ha.
Comentários:
The labour costs are included to the machinery work costs. An average the labour cost for a driver is 15-18 EUR/ha. The average machinery work costs to produce 4.5 t of winter wheat were 388 EUR/ha, 355 EUR/ha and 322 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively in 2016. Cost of production in this case was 159 EUR/t, 152 EUR/t and 147 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively.
To produce the same amount of spring barley, the cost of machinery was 365 EUR/ha, 345 EUR/ha and 300 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively. Cost of production in this case was 142 EUR/t, 139 EUR/t and 129 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively.
The machinery cost for minimum tillage is 33 EUR and 20 EUR less than for conventional plough based tillage for winter wheat and spring barley, respectively.
By minimum tillage the use of fuel is ca 38% less than by ploughing.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Fuel costs, labour cost
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
696,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Tartu Tõravere
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
On the main investigated area it is sandy loan Stagnic Luvisol, in some parts Calcaric Luvisol. pH in water 6.9-7.3
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
- Cooperativa
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
The total area of one investigated farm is 1036 ha (all covered by minimum tillage), another farm size is 2320 ha and under minimum tillage it is 1231.5 ha.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Empresa
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
6.3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
6.75
Comentários/especificar:
The example is based on winter wheat. For spring barley 4.56 and 4.52, for spring oilseed rape 2.24 and 2.15 t/ha with ploughing and with minimum tillage, respectively.
Different studies have shown that the yield can be higher and also lower compared to the conventional tillage. It depends also on the weather conditions and intensity of mangement (fertilization, pesticides).
Qualidade da safra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
37.7
Quantidade posterior à GST:
38.1
Comentários/especificar:
The weight of thousand grain of winter wheat can be higher under minimum tillage than under conventional tillage in some years. As an average of different years, there is no differences and under conventional tillage the weight of 1000 grains can be slightly higher.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
As there is no conventional ploughing, the management is simplified. However, bigger attention should be paid on weed management and crop rotation, which may hinders the land management. There is need to include weed suppressing species, such red clover (or similar) into the rotation.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10.1
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5.2
Comentários/especificar:
Fuel cost by ploughing and with minimum tillage as EUR/ha. The fuel demand for tillage will decrease from ca 14 l/ha to 7.2 l/ha
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Production costs for producing 1 ton of winter wheat are 5 EUR less by minimum tillage than by ploughing at high yield level (6 t/ha). In some calculations they show 1.7-1.8 times less costs for tillage by minimum tillage compared to ploughing.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Field operations takes less time, decreasing labour costs.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Decreasing production costs allows to sell the food with lower price.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers turning to the minimum tillage have to clarify for themselves the behaviour of their soils, crop rotations etc. to prevent excess compaction, weed infestation.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
30% remaining residues on the soil surface helps to catch more snow during the winter.
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Higher amount of residues on the soil surface allows water to infiltrate quicker into the soil, as raindrops can not damaging the soil structure as much as after ploughing.
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Better soil structure allows water to infiltrate quicker into the soil. Without ploughpan and with intact pore system water drains quicker to the deeper soil.
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
30% plant residues do not allow water to evaporate in the same speed as by ploughing.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Slight differences in deeper soil (20-25 cm) ca. 4% more moisture in minimum than conventional tillage.
Cobertura do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
30%
Comentários/especificar:
30% more plant residues remain on the soil surface after minimum tillage compared to the ploughing.
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Extra residues on the soil surface and better soil structure compared to ploughing reduces soil loss by wind and water.
Acumulação de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of soil organic carbon by 0.1-0.2% compared to ploughing.
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Stronger soil structure because the increasing organic carbon level improves the resistance to raindrop impact and by this it reduces soil crusting.
Compactação do solo
Comentários/especificar:
In the layer 10-20 cm the increase can be over 0.2 g/cm3 compared to ploughed soils. However, after 4-5 years the conditions starts to improve and there will be less compaction in mentioned layer and deeper (plough pan starts to disappear).
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Less intensive decomposition of organic matter leaves more nutrients in the soil.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Slight increase of organic carbon by 0.1-0.2%. Depends more on crop rotation than tillage method.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the need to suppress weeds more winter crops or cover crops are included into the rotation. However, this effect can only be stated if the rotation and management plan will be changed.
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the need of changes in crop rotation, more diverse rotations instead of monoculture to suppress weeds. Weeds diversity might increase due to the reduced tillage intensity.
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
More spiders, beetles, ants compared to ploughed soils.
Espécies benéficas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2 species of earthworms
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3-4 species of earthworms
Comentários/especificar:
More earthworm species and higher abundance compared to ploughed soils.
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the decreased tillage intensity more attention should be paid on weed, pests and disease control by crop rotation and pesticies. As the residues remain on the soil surface there are also better conditions for pests and disease spreading.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the decreased decomposition intensity, less CO2 emission from soil organic matter (increase of soil organic matter 0.1-0.2% compared to ploughing). As the fuel consumption is ca 40% less than by ploughing, less emission is coming from agriculture.
Risco de incêndio
Comentários/especificar:
As there will remain 30% of residues on the soil surface, there is an increased risk of fires in spring.
Microclima
Comentários/especificar:
Residues regulate soil evapotranspiration and temperature. The fluctuations are not so high as by ploughing.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
As the soil organic carbon content increases, also the water holding and the nutrient holding capacity increase.
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
Less sediments due to the lower tillge intensity and more residues on the soil surface
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
Less sediments from the field to the neighbours fields. Effect on water erosion depends on the slope.
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the reduced water erosion, less soil will be transported to the diches and roads (depends on slope).
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the decreased decomposition intensity, less CO2 emission from soil organic matter (increase of soil organic matter 0.1-0.2% compared to ploughing). As the fuel consumption is ca 40% less than by ploughing, less emission comes from agriculture.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido | |
| Temperatura sazonal | inverno | aumento | não conhecido |
| Temperatura sazonal | primavera | aumento | não conhecido |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | não conhecido | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | inverno | aumento | não conhecido |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | outono | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Trovoada local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de granizo local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de neve local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de frio | não conhecido |
| Condições de inverno extremo | não conhecido |
| Queimada | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
85 371 ha
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Decrease of work load, time and labour costs. |
| Decrease of fuel consumption, increase of income. |
| Increase of soil biological activity, soil organic matter content, better structure and infiltration. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Decrease of soil organic carbon decomposition. |
| Decrease of soil erosion. |
| Increase of soil biological activity. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Increase of weed abundance and soil compaction | Proper crop rotation and timing |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Higher use of pesticides and risk to soil and water pollution. | Changes in crop rotation, use of cover crops |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
5 during the iSQAPER project, more than 20 in total with other projects
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
5, more than 40 in total with other projects
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
7
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
18/05/2017
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut. ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1:
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.:
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
Título/ descrição:
Erinevate viljelusmeetodite ( sh. otsekülv) rakendusteaduslik kompleksuuring. Riikliku programmi “Põllumajanduslikud rakendusuuringud ja
URL:
http://www.pikk.ee/upload/les/Erinevad_viljelusviisid_pikk_aruanne.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut.:
URL:
http://taim.etki.ee/taim/public/pdf/Trukised/Otseklv-minimeeritudmullaharimine.
Título/ descrição:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi meetmete ja 3. prioriteedi loomade heaolu meetme püsihindamisaruanne 2015. aasta kohta ja
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/avaleht/
Título/ descrição:
Projekti ”Erinevate mullaharimise ja külvitehnoloogiate mõ-ju uuring tera- ja kaunviljade saagikusele viljavahelduslikus ja monokultuurses külvikorras” lõpparuanne
URL:
http://www.pikk.ee/upload/files/Teadusinfo/Lopparuanne_111_2002_2006.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos