Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources [Chade]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Bonnet Bernard
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Donia Mühlematter, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Simone Verzandvoort, Joana Eichenberger
Projet Almy Al Afia
technologies_3356 - Chade
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 12 de Março de 2019 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 9 de Maio de 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 28 de Maio de 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 13 de Maio de 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 9 de Maio de 2018 (inactive)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Bernard BONNET
IRAM
França
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Degradation of natural resources is taken into account in the management of water resources for pastoral land, and in the social approach prior to the development of the technology. For example, the locations of new sites for water supply structures should correspond to the capacity of the grazing land in terms of the period of access, the quantity of available resources and the integration of the area into a larger coherent landscape (especially the complementary relationship between the agropastoral zones in the south and the pastoral zones in the north). Several impact assessments and preliminary analyses have been carried out, including diagnoses of the pastoralist system with regard to the logistics of the movements of the herds, the social organisation related to the management of the areas, diagnoses of the grasslands, geophysical analyses, etc.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Securing the mobility of pastoralism through access to water sources (open wells and ponds in pastoral areas) and marking the livestock routes for transhumance: the case of the project Almy Al Afia in Chad and its consultative approach.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
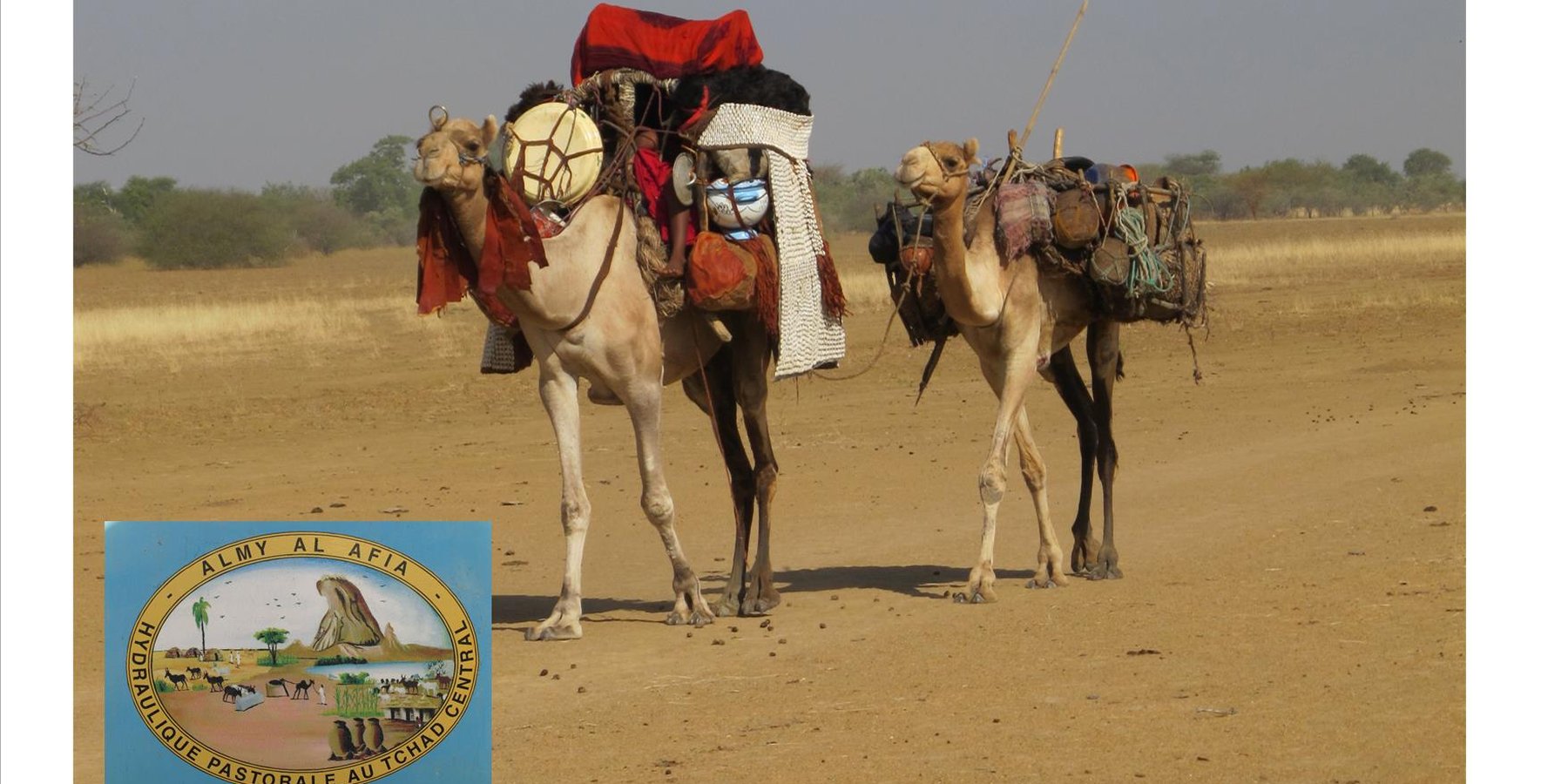
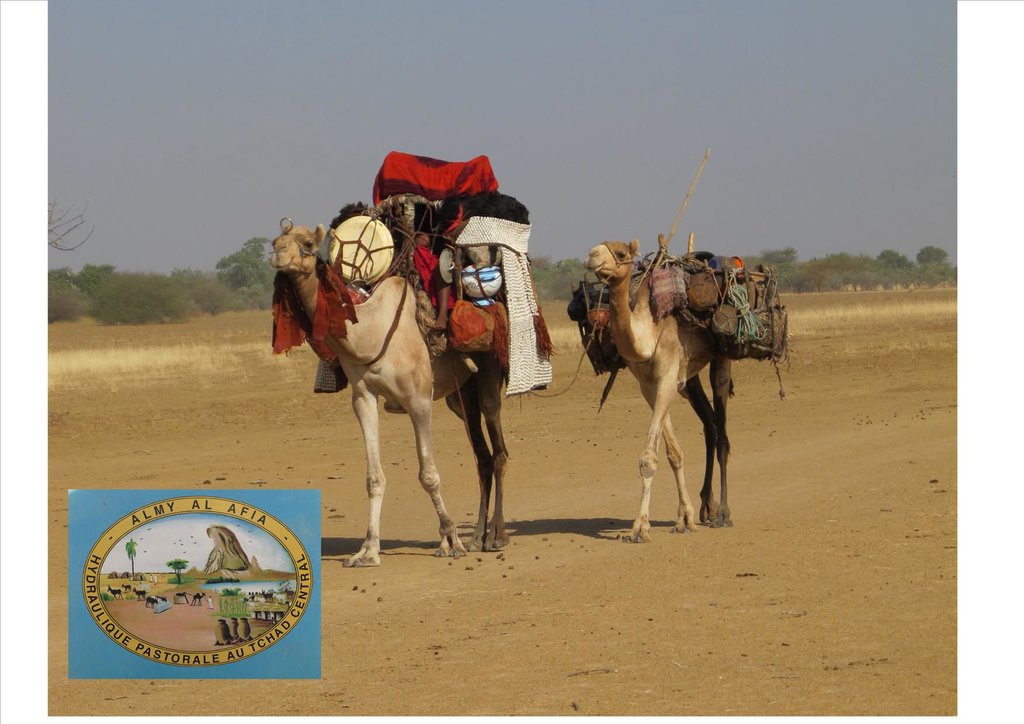
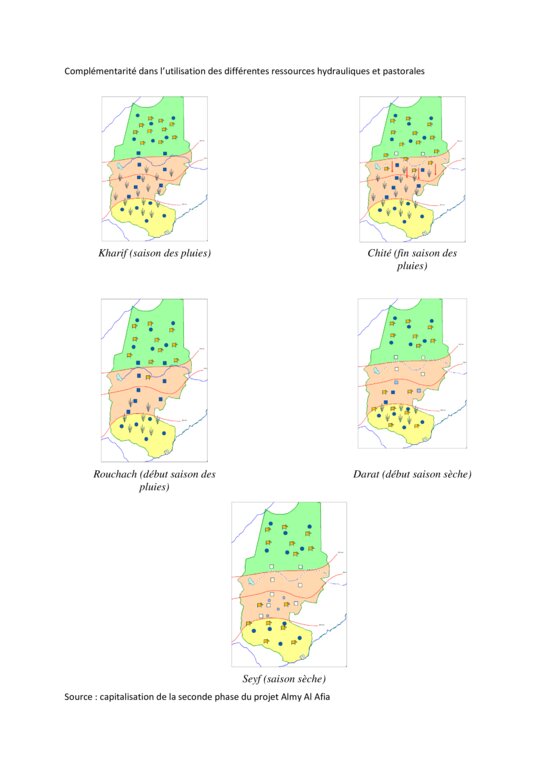
Livestock keeping is one of the main economic resources in Chad (in support of 40% of the population and 18% of the GDP, Ministry of Livestock, General census). Pastoralism in the country is based on the mobility of herds in a context of irregular precipitation and variable forage resources in time and space, and benefits from complementary relationships between the different ecological zones. In Chad, herds are taken in regular movements with the seasons between the Sahelian and the Sudanese grazing areas. The former are nutritious but limited in quantity, while the latter are more abundant but of lower quality, and not accessible until the fields are cleared after the harvest (meta-evaluation of projects on pastoral water sources, IIED, 2013). Thus, pastoral livestock keeping is founded on mobility and rangeland management, and on building complementary relationships and trade around farming systems and cultivated areas. The pastoralist systems are economically competitive (limited use of food inputs), and occur in marginal land which is characterized by conflicts, riots and a high level of insecurity (Conference of N'Djamena: 'Pastoral livestock keeping: a sustainable contribution to development and security in Saharan and Sahelian regions'). In the pastoral zone of Chad, where access to water is limited, the management and control of water sources by a social group in practice also leads to the monitoring and control of the use of grazing land which becomes available when water is present.
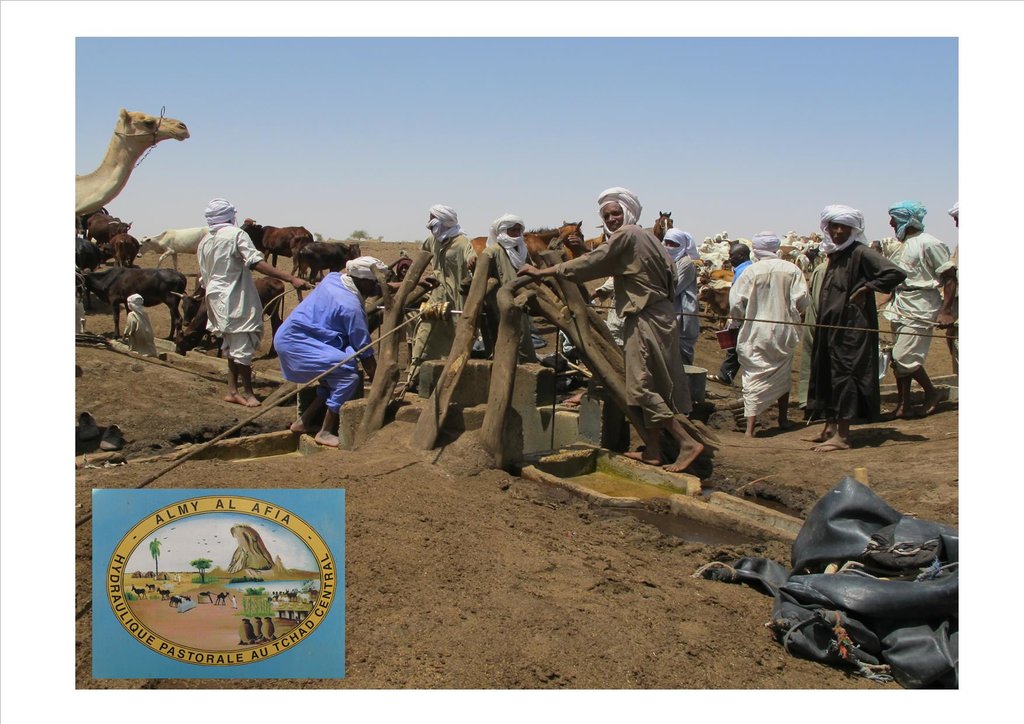
The project Almy Al Afia (2004-2016), developed by a partnership between the AFD and the Ministry of Water of Chad, operated in two regions of central Chad. The project Almy Al Afia was based on an entry 'development', concurrently with a process to consult and involve joint agencies. The project has improved approaches of preceding initiatives: concerted action and identification of water sources derived from the dialogue between users and authorities, and development of the local management of infrastructures and rangeland. The latter counteracts an exclusively private management or, instead, an ineffective public management which promotes free access to water sources and grazing land.
The project has enabled to address the following points:
1. Support mobility in pastoralism by enhancing the access to water (rehabilitation and construction of 160 wells; digging of 31 ponds for pastoral use);
2. Maintain or build processes of consultation and restoring security (joint committees for consultation and prevention of conflicts during transhumance);
3. Promote the proper use of water supply structures, in time and space (rehabilitated and new wells, excavated ponds) by context-specific management (strengthening of traditional management systems) and encourage the maintenance of infrastructure.
The pastoral ponds should be constructed in locations of existing water sources (natural ponds in suitable places, i.e. with a clayey soil capable to retain water). The existing water source is enlarged and improved by rural engineering (enlargement of the surface, deepening).
The wells are rehabilitated. Most wells were constructed several decades ago and are severely damaged. The water supply structures all have different and complementary functions. The deep wells in the pastoral zone are generally used throughout the year, and are overexploited. The way in which these structures are managed is strongly anchored in the region. The District officer delegates the management to 'Heads of Wells'. These old wells, which are used day and night, are often in a poor condition. Rehabilitating degraded wells is given priority over digging new wells because of the substantial potential for conflict. The water supply structures in areas of dry forest are less old and smaller in number. These wells are less frequently used and function as an alternative water source when the traditional ponds, water reservoirs and wells have dried up. They allow to delay the movement of the herds towards grazing areas in the Sahelian zone.
The strip between these two zones is used for agropastoralism. Herds cannot remain there. Therefore the project has facilitated the movement of the herds to the zones further south. The pastoral ponds close to the livestock routes for the transhumance were created in a way to be easily used by the herders, but also to encourage short stays.
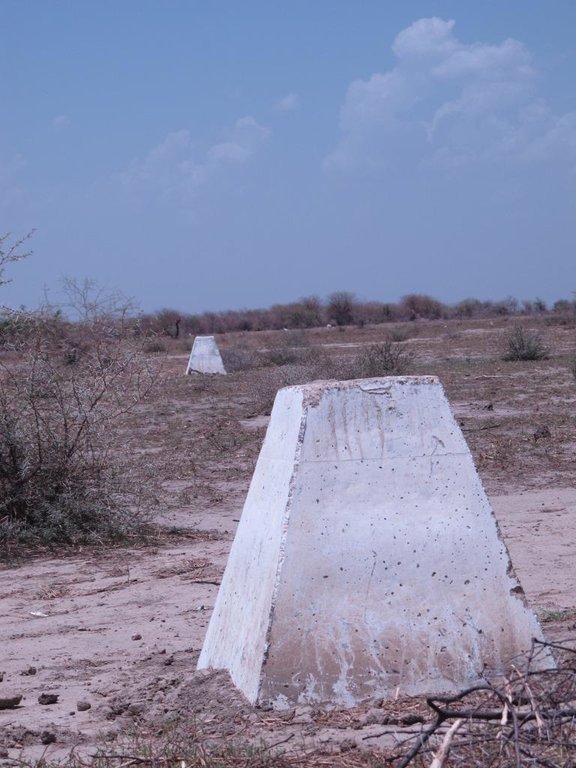
The approach was combined with consultation through joint committees for the prevention of conflicts, and at a later stage by marking of sections of the livestock routes for the transhumance. Many meetings were held with the users of the land management structures and policy makers, with the aim to identify and negotiate the target sites and to anticipate methods for the management and maintenance of the structures. This has enabled to maintain an atmosphere of social stability conducive to cooperation. Along almost 550 km of the livestock routes for the transhumance, sections were marked ('mourhals' in Chadian Arabic). The demarcation was not intended to enclose the herds in the livestock corridors (from which they can move freely outside the growing seasons for agricultural crops), but rather to implement the results of the consultations on the land use on the ground. The committees for the prevention of conflicts, which were supported by the project, also played a major role.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Chade
Região/Estado/Província:
Regions of Batha and of Guéra
Especificação adicional de localização:
Although the sites where the technology was applied are at the local scale, the project has considered pastoralism and the relationships between the two regions at the broader landscape scale.
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
Main towns of the two relevant regions (Ati for the region of Batha and Mongo for the region of Guéra).
The water sources constitute an anchorage point for the herds. The surrounding grazing land is controlled by the access to the water supply points (impact zone with a radius of 15 to 20 km around the wells). Apart from the area directly influenced by the technology, complementary relationships between the zones provide an added value: hence the zone targeted by the decision-making process of the herders is very large.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Projects on pastoral water resources like the project Almy Al Afia primarily focus on the development of water sources for pastoralism. The phases preceding the implementation are extremely important, because they are based on consultation and on the appreciation of local management systems. These phases include registration, selection of construction sites and the development of guidelines.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Nomadismo
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Tipo de animal:
- camelos
Comentários:
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density: Variable depending on zones and seasons.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
In these zones, rainfall is erratic in terms of spatial distribution and in quantity. Hence, grazing areas are not uniformly covered from year to year. The mobility of herds is the only way to adapt to this variability.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
- Gestão do lençol freático
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S8: Saneamento/estruturas de águas residuais

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M3: Disposição de acordo com o ambiente natural e humano
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
- Eo: efeitos de degradação externa

Deteriorização física do solo
- Ps: Subsidência de solos orgânico, sedimentação do solo

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The wells (new and rehabilitated) and the demarcation of the livestock routes are the outcome of a long process of outreach. The communications between the local level (taking account of the views of future users) and the level of decision-making (administration) enable social agreements to be formalized. These agreements set the rules for the selection of the locations of the water supply structures, their management and maintenance.
Autor:
Project Almy Al Afia
Data:
2016
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Structure (new well, rehabilitation or km of markings)
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
FCFA
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1000 FCFA
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Outreach / awareness raising | Four to six meetings prior to the signing of the social agreements |
| 2. | Construction of the facilities | Four to six months, depending on the type of structure and its depth |
| 3. | Monitoring the management | Regular visits of the project team to support the implementation of adapted management practices |
Comentários:
The implementation of the different phases varies greatly in terms of the location of the outreach activities and the duration of the construction work.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material de construção | Rehabilitated wells (mean depth 56 m) | 1 | 93,0 | 10497939,0 | 976308327,0 | |
| Material de construção | Geophysical assessment for new wells | 1 | 158,0 | 17979914,0 | 2840826412,0 | |
| Material de construção | Exploration drilling for new wells (mean depth 96 m) | 1 | 220,0 | 6005415,0 | 1321191300,0 | |
| Material de construção | New wells (mean depth 45 m) | 1 | 62,0 | 45145740,0 | 2799035880,0 | |
| Material de construção | Pastoral ponds (6000 m3 on average) | 1 | 31,0 | 23008065,0 | 713250015,0 | |
| Material de construção | Markers (8 signs / km) | 1 | 492,0 | 1069203,0 | 526047876,0 | |
| Outros | Outreach on new wells (/site) | 1 | 62,0 | 213428,0 | 13232536,0 | |
| Outros | Outreach on rehabilitation (/site) | 1 | 93,0 | 248695,0 | 23128635,0 | |
| Outros | Outreach on marking (/km) | 1 | 492,0 | 52088,0 | 25627296,0 | |
| Outros | None | None | ||||
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 9238648277,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 9238648277,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The context of pastoralism has taken the project approach to not ask compensation from users: if the users are never the same, then who should be charged? Who will collect the payments and manage the collected funds? In addition, most of the water supply structures are far from financial institutions, which causes problems in securing these funds. Therefore the users contribute in terms of day-to-day maintenance of structures, by mobilizing labour in particular.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mobilising indigenous groups for day-to-day maintenance of structures (dredging, cleaning) | Depending on the type of structure (generally monthly) |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Support missions for the management and maintenance of the water supply structures (2 missions per structure for the entire project) | 1 | 155,0 | 53000,0 | 8215000,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Support mission for the management and maintenance of the markings | 1 | 100,0 | 53000,0 | 5300000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 13515000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 13515000,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The amount of financial support varied with the type of structure (more support for management and maintenance is needed for new structures than for rehabilitated structures) and with their location or specific problem (in the case of structures located in the agropastoral zones). Financial support to the markings of the livestock corridors was indirectly provided through the committees for the prevention and management of conflicts.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The costs of the constructions are highly dependent on their location (costs for the supply and disposal of equipment and materials), on the price of inputs (cement, etc.), and especially on the type of structure (depth of the wells, geological environment). The costs of the supply and disposal of equipment and materials include costs for the installation of the structures (water, cement, labour, machinery) on the construction sites (which are often far away from routes and towns), and costs for the disposal of the equipment after the construction is completed. The costs of supply and disposal can be significant with respect to the costs of the structure itself.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
One rainy season per year (from June to September)
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Ati
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
- Árido
The target region includes large areas extending over important gradients (encompassing boundaries of the desert zone, the forested zone and the cotton-growing zone).
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Sim
Especifique:
Depending on the zones: presence of sodium carbonate.
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
- Nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
Transhumance, and more generally pastoral mobility, applies to large geographical scales and long periods. The areas involved are very large, far above 10.000 ha.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Grupo
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Quantidade anterior à GST:
n/a
Quantidade posterior à GST:
n/a
Comentários/especificar:
Expansion of the areas covered by water supply points. Reduced closure of water supply points (rehabilitation), opening-up of new grazing land, securing the movement of livestock and people.
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Quantidade anterior à GST:
n/a
Quantidade posterior à GST:
n/a
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Preserving the capacity of herders and their families to move, to choose their trajectories rather than responding to imposed conditions.
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
n/a
Quantidade posterior à GST:
n/a
Comentários/especificar:
Upgrading of traditional management systems of water supply structures.
Instituições comunitárias
Atenuação de conflitos
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Reduction of the impacts of the concentration of livestock and people in small areas. Promotes the complementary relations between the zones (pressure relief in some zones and use and maintenance of other zones), and over the seasons.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Diversidade vegetal
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
n/a
Quantidade posterior à GST:
n/a
Comentários/especificar:
Increased access to groundwater through the rehabilitation of wells and the construction of new wells.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
As explained above, in these zones with low rainfall and scarce natural water sources of temporary character (ponds), it is essential to combine the use of surface water with the use of water from deep permanent groundwater bodies. When they have the choice, herders almost exclusively choose sources with surface water (avoiding effort to extract the water). But when these sources run dry, they fall back on using wells (and deep groundwater). The rehabilitation of old wells and the construction of new wells in zones without wells contributes to increasing the availability of water.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | não bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | redução/diminuição | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The profitability is considered in relation to the number of animals/herds involved. The costs of construction and rehabilitation are certainly significant, but the water supply structures are used for thousands of animals (in case of the most heavily used wells); most animals drink every two days. Therefore the costs per head of livestock are limited. The wells are long lasting, and therefore the returns are positive in the short and the long term.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
The technology responds to a substantial need, but also corresponds to the capacity of land users to use and maintain the structures. The energy supply is provided by animal traction, and does not require external energy sources.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
Access to water is such a large problem that it requires all the land users who enter the zone to be informed when a water supply structure is rehabilitated or constructed. The involvement of traditional leaders in the management of the structures, and the system of representatives of the traditional leadership in the various other zones (Khalifas) contributes to the spontaneous dissemination of the information.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Permanent access to water. |
| Reopening of water supply structures and consolidation of access to water at some degraded sites. |
| Agencies and authorities for conflict prevention. |
| Marking of sections of livestock corridors with conflict situations. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Full commitment of groups (access to water is a major problem). |
| Continuation of the approach through the development of other projects and inclusion at the national level. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Interventions are limited with regard to the needs (rehabilitation in particular). | By larger investments and better integration of the approach in public action. |
| There is a need to extend the approach, in particular the support to the consultative bodies. | Formalize support to the consultation process. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
|
Recognition of the experiences, the approach and the methodology in other interventions. Outreach and awareness raising are performed during the project, but at the end the management of the infrastructure is no longer supported. The government should be able to follow up on the support (mechanism for monitoring and maintenance). |
Formalize support to the consultation process. |
| There is a need to mainstream outreach and consultation (lengthy process). | Formalize support to the consultation process. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Progress reports and thematic reports of the project Almy Al Afia
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Follow-up and evaluation of the project activities (logbook, annual update)
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Creating value from lessons learned in the project Almy Al Afia (Republic of Chad, Ministry of Water)
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
2016
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Capitalisation des enseignements de la deuxième phase du projet Almy Al Afia, Main document, DHP, Antea/Iram, March 2016
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Document de Suivi-Evaluation des activités du PHPTC II, tableau de bord des activités du projet, DHP, Antea/Iram, mars 2016
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Note Entretiens Techniques du PRAPS, Accès et gestion durable des espaces pastoraux (chemins de transhumance, aires de pâturages et de repos), PRAPS, 2016, B. Bonnet, A. H. Dia, P. Ndiaye, I. Touré
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Evaluation et capitalisation de 20 ans d’intervention du Groupe AFD portant sur le secteur de l’Hydraulique Pastorale au Tchad, IIED, May 2013, S. Krätli, M. Monimart, B. Jallo, J. Swift, C. Hesse
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Platform on pastoralism in Chad
URL:
www.plateforme-pastorale-tchad.org/
Título/ descrição:
Website of PRAPS-TD
URL:
www.praps.cilss.int/index.php/praps-pays-tchad/
Título/ descrição:
Website of Iram
URL:
https://www.iram-fr.org/elevage-pastoralisme-et-hydraulique-pastorale.html
Título/ descrição:
AFD in Chad
URL:
http://www.afd.fr/fr/page-region-pays/tchad
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos