Water use master plan [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Shreedip Sigdel
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Jal upoyog guru yogana (Main Contributor: HELVETAS Nepal)
approaches_2535 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Jürg Merz
+977 1 5524925; 9851044421 (M)
juerg.merz@helvetas.org.np
HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation Nepal
สวิตเซอร์แลนด์
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
01/03/2013
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
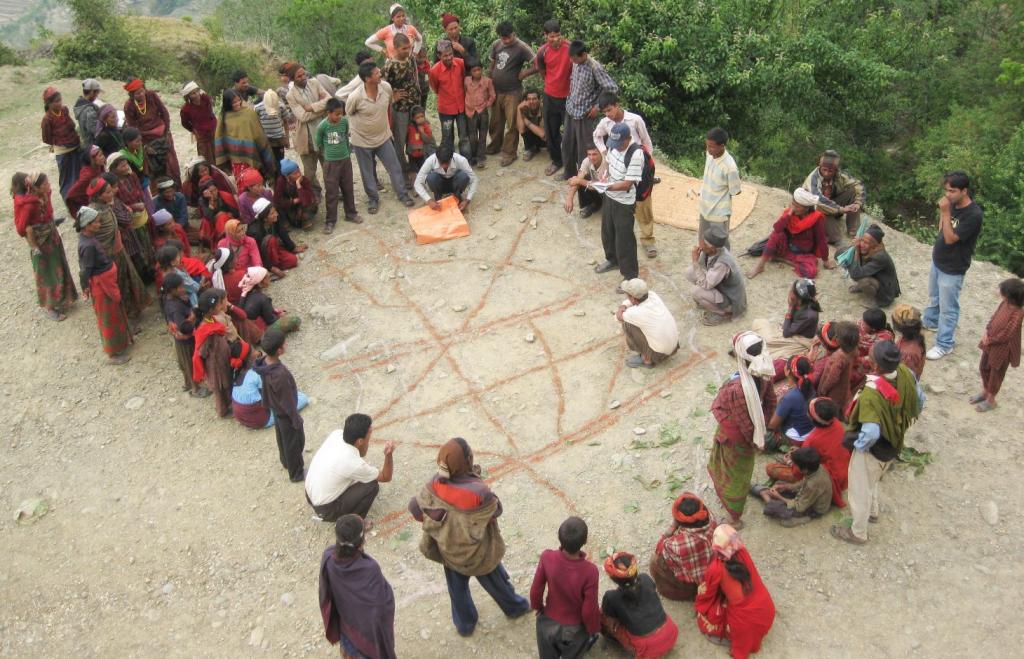
A water use master plan supports the development of integrated water resources at the local level; all stakeholders, including disadvantaged groups, take part in the plan.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: A water use master plan (WUMP) is a holistic, participatory, and inclusive planning process that takes an integrated approach to the management of water resources and uses at the village level. The WUMP specifies the total water budget for its planning unit, the village development committee (VDC), and explores potential uses for it. It empowers marginalized groups to claim their rights to an equitable share of water within and between communities. The WUMP also helps local bodies with annual and periodic planning and project prioritization.
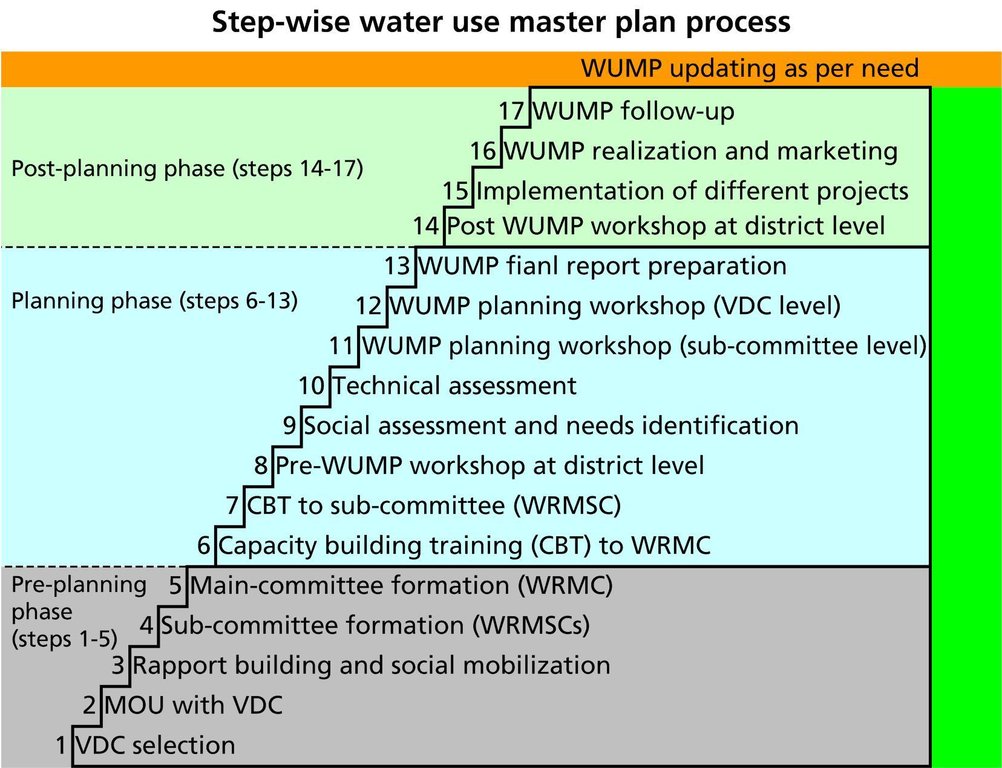
Methods: The WUMP is a 17-step process that includes social mobilization, the formation of inclusive management committees, capacity building for everyone involved in the process, and, as a final step, social assessment using various participatory rural appraisal (PRA) tools. Simultaneously, the technical part of the process evaluates the capacity of all water resources and their potential uses. In a workshop facilitated by NGO staff, the community discusses suggestions formulated by the two participatory assessments, prioritizes possible projects, and formulates plans. The VDC representatives decide which plans can be implemented using their own resources and which need external support. The WUMP then organizes a workshop to present these plans to various organizations in order to get their commitment and support. The prioritized projects are implemented according to the WUMP.
The plan also contains a series of long-term activities and during the course of its implementation, there is sufficient latitude to allow the community to rectify its original plans in order to put into practise lessons learned during earlier phases and to continue to review and modify the plan as needed.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
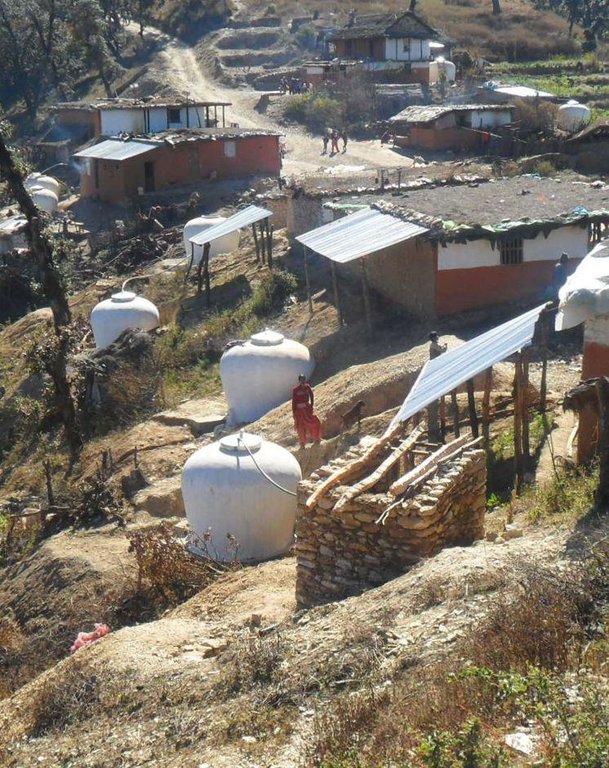
15 districts in the Western, Mid-Western, and Far-Western Development Regions of Nepal
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Water conservation, water sources and catchment area)
• Establish inclusive water planning and water resource management at the community level
• Ensure the optimal use of water resources; see that water is equitably and efficiently distributed
• Promote conservation of water and natural resources linked to water; implement water projects based on the plan agreed by the entire community
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: • Issues on access to water are often contentious, communities often quarrel over water rights
• A lack of coordinated planning at the local level
• A growing demand for water both for domestic and agricultural use
• Water sources are diminishing and the changing climate will further aggravate this
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
บรรทัดฐานและค่านิยมทางสังคม วัฒนธรรม ศาสนา
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Communities are reluctant to share water resources and
hide the sources of water during planning
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Earn everyone's trust through meetings, dialogue, and social mapping that includes all stakeholders including disadvantaged groups.
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
When the WUMP is implemented by the VDC using its
own funds it usually takes a long time.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Collaborate and network with resource organizations such as INGOs and donor funded programmes for funding.
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เป็นอุปสรรค
There is no elected body in the VDC and no one takes permanent ownership of the WUMP.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Create an advisory body consisting of representatives from all political parties.
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
Ensuring equitable use of water resources is a key feature of the WUMP approach.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
When the administrative boundaries of a VDC do not coincide with its physical watershed boundaries, it can be difficult to make technical decisions.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Cluster VDCs into groups in the same sub/watershed.
อื่นๆ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low awareness of the need for conservation and of the
need to use water efficiently
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Intensive awareness raising and capacity building programmes
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
VDC
Equal participation of men and women is encouraged during the social assessment and needs identification phase. During the planning and implementation phases, the participation of women in decision making is ensured through a provision that there be a representation of at least 33% women in the water resource management committees, sub-committees, and users' committees. Disadvantaged groups (Dalit and Janajati among others) are requested to participate in numbers proportional to the percentage they represent in the community in all activities and committees.
- ครู เด็กนักเรียน หรือนักศึกษา
- องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน
HELVETAS
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Community meetings, decision taken by the VDC on how to prepare the WUMP |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Social and resource mapping, social assessments, technical assessments and planning |
| การดำเนินการ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Implementation of the water projects, source protection/conservation |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Review of the plan, community monitoring during the construction phase, follow-up monitoring during routine operation |
| Research | ไม่มี |
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
The step-wise WUMP process
VDC = Village development committee
MOU = Memorandum of understanding
WRMC = Water resource management committee
WRMSC = Water resource management sub-committee
WUMP = Water use master plan
(AK Thaku)
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก โดยการสนับสนุนจากผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
การอธิบาย:
Technologies are selected on the basis of suitability and availability of water sources by local communities with the support of technicians and the VDC.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Since the VDC endorses the WUMP, it decides on implementation.
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
- Local Community
หัวข้อที่พูด:
• Social mobilization and awareness raising orientations, training
• Capacity building and training to WRMC and local service providers
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
- อุปกรณ์
ให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม :
Support is provided to the VDC for the preparation of the WUMP
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
bio-physical aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: Follow-up monitoring to check if the water sources are protected, and if the area is conserved by planting
technical aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: Follow-up monitoring to check water sources and number of water projects implemented
socio-cultural aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: Public hearings and audits to ensure transparency and community participation (especially of disadvantaged groups)
area treated aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: Follow-up monitoring of implementation (as shown in the diagram )
no. of land users involved aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: Public review, final commissioning: community contribution and participation (as shown in the diagram)
management of Approach aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: WUMP follow-up: implementation of WUMP (as shown in the diagram )
Implementation of WUMP aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: WUMP follow-up: implementation of WUMP (as shown in the diagram )
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: • All members of the community, even those with water resources on their own land, are willing to share water resources after participating in the WUMP.
• Disadvantaged groups participate on an equal footing in management committees and have equal access to water resources.
• The community realizes the need to protect water resources and begins to conserve water.
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 2,000-10,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: national non-government: 75.0%; local community / land user(s): 25.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- ไม่มี
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Water, forests, and land are all interlinked. Proper management of water resources, source protection, and conservation are all part of sustainable land management.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Disadvantaged groups participate and share benefits on equal terms.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
This approach has been replicated by the Rural Water Resources Management Project of FINNIDA, the LIVE/EU project, and Nepal Water for Health (NEWAH), a national-level NGO in Nepal. Nepal's Ministry of Local Development, Department of Local Infrastructure and Roads, has expressed an interest in developing WUMPs for all the VDCs in Nepal.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Having access to sustainable water resources improves livelihoods.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Access to water improves hygiene and contributes to better health and to poverty alleviation.
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ไม่แน่ใจ
ถ้าตอบว่าไม่หรือไม่แน่ใจ ให้ระบุและแสดงความคิดเห็น :
In order to ensure sustainability the following issues need to be addressed:
• Social: Coordinated planning in consultation with the local people; capacity building at all levels so that management committees, local service providers, local government, and the community as a whole can participate better, voice their concerns, and be part of the solution.
• Economic: The VDCs take a lead role, the beneficiaries need to be willing to share the costs and need to want to participate in activities such as quality control, and routine operation and maintenance schemes.
• Environment: Conservation of water sources, integrated water resources planning, and the efficient use of water
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Communities appreciate the WUMP approach (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The Ministry of Local Development has expressed an interest in preparing national guidelines for this process in order to scale it up to all the VDCs in Nepal) |
| VDCs own the process both by participating and by contributing to the funding. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Need to simplify the process and make it more cost effective so that it is easier to replicate.) |
| An integrated approach to the use of water resources may help in climate change adaptation. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Strengthen awareness activities and continue to promote water conservation) |
|
The WUMP process is inclusive and is managed by the whole community. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to strengthen the capacity of disadvantaged groups so that they can participate more actively.) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Not all VDCs actively participate in the WUMP | When VDCs contribute funds for the WUMP, they are usually more actively involved. |
| Communities can have high expectations for WUMP but their VDCs may have limited resources. | The VDCs need to communicate clearly with their community so that they can prepare a realistic plan together. |
| Conflicts can arise over the allocation of water resources | The VDC and the management committee must work with the community to see that any contentious issues are resolved equitably |
|
At times it can be difficult to get everyone to agree to a given WUMP. |
The VDC authorities can improve their negotiating skills in order to make their demands heard with donors and district development committees. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Water use master plan preparation guideline. Lalitpur, Nepal: WARM-P/HELVETAS; Rural Village Water Resource Management Project (2011) Proceedings of water use master plan national level experience sharing workshop. Lalitpur, Nepal, HELVETAS (2007)
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล