Strip Tillage Conservation Farming [แซมเบีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Silenga Wamunyima
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
technologies_1187 - แซมเบีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ndandula Sharon
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
แซมเบีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Katoweji Alfred
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
แซมเบีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - แซมเบีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
14/01/2013
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Participatory Research and Development [แซมเบีย]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Arthur Chomba
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
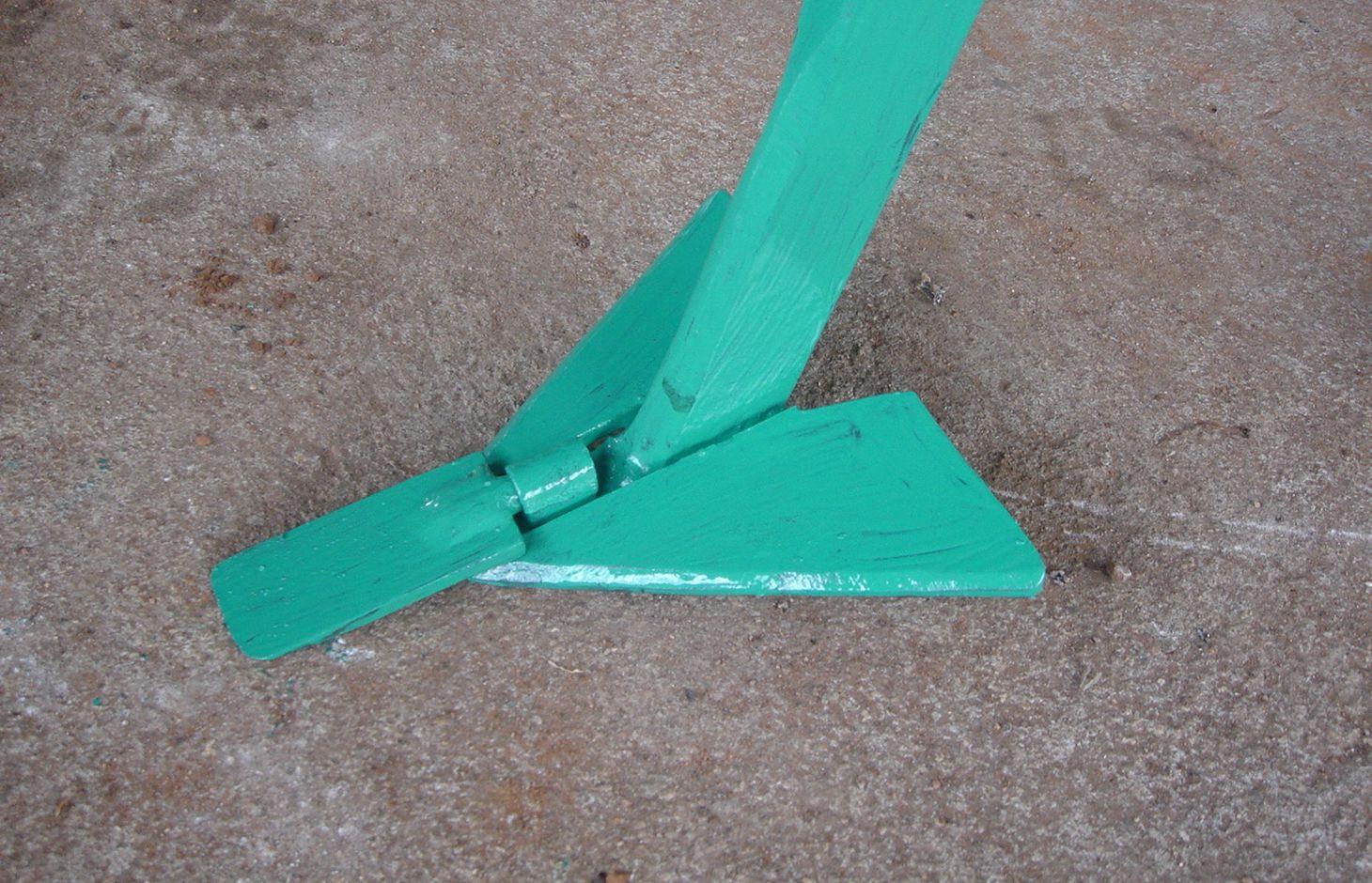
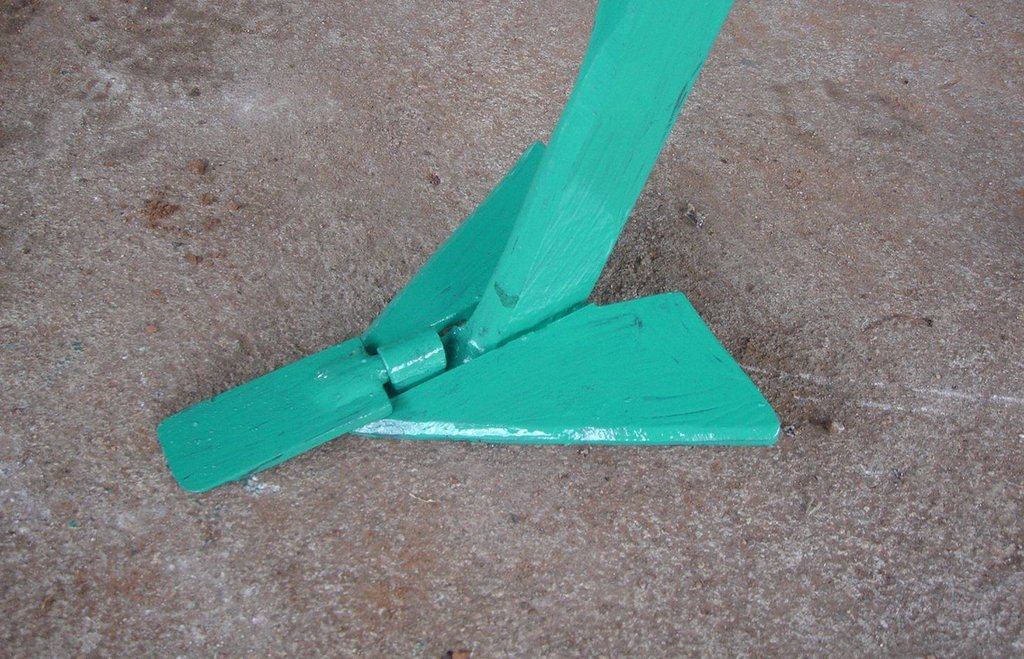
Strip Tillage Conservation Farming is an animal draft reduced tillage method that involves loosening a strip of soil with a strip tillage tool so as to reduce soil disturbance and improve soil and water conservation.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แซมเบีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Zambia/Southern Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mazabuka/Magoye
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Development of the strip tillage technology began in 2008 in response to farmers’ feedback from the promotion of another conservation agricultural technology, the Magoye Ripper. The technology was introduced to the farmers in 2011.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
major cash crop: Cotton and maize
major food crop: Maize
other: Groundnuts

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์ (Agro-pastoralism)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Cattle, goats and chickens
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (opinion du compilateur): perte de structure du sol et perte de fertilité du sol
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): sécheresses et périodes de sécheresse
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 135; Longest growing period from month to month: Mid November to end of March
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The strip tillage technology is only in its second year of promotion and 7 farmers had adopted the technology in the 2011/12 season. The field sizes range from 1ha to 30ha.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A6: อื่นๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Zero till, Crop Residue
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (over ploughing, soil nutrient mining), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping of Maize), overgrazing (overgrazing of crop residues), poverty / wealth (Charcoal burning, under application of fertilizer)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (charcoal burning, openning up new land for agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (high intensity storms resulting in soil erosion and leaching), land tenure (over-exploitation of communal land), governance / institutional (lack of credit facilities)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
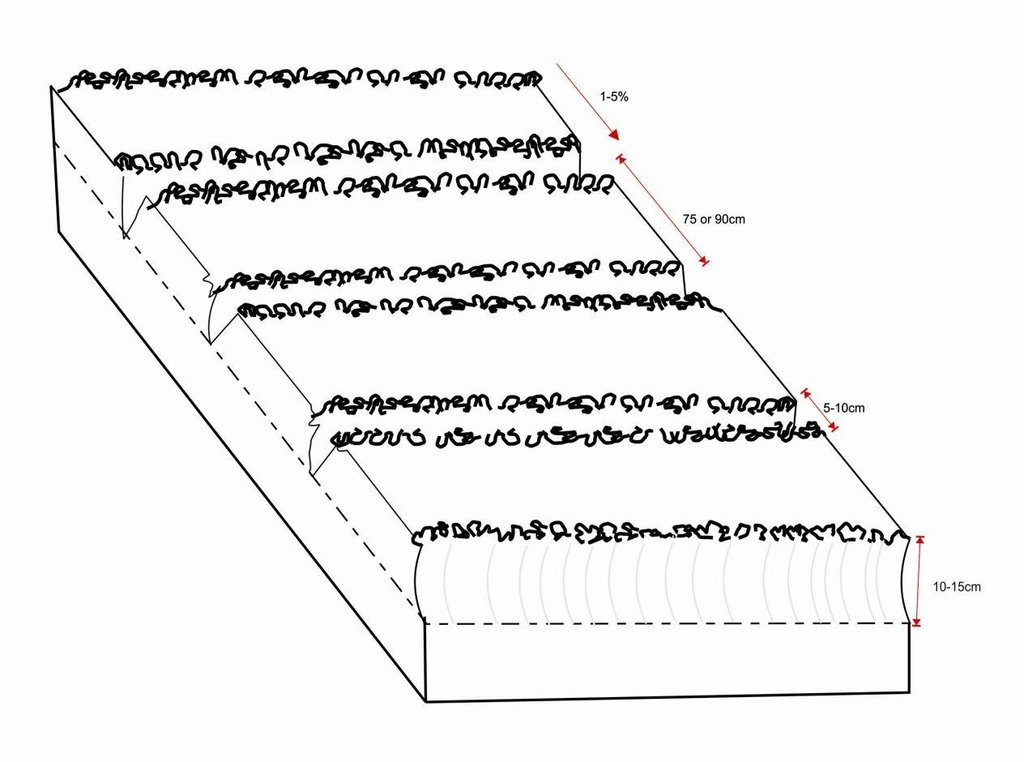
Planting lines are done at a depth of 15-20cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows may be made in the dry season or during the rainy season when the soil is moist.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (must be able to troubleshoot and advise the farmers on how to adapt the technology to fit into their production systems.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge of soil health management required when adopting the practice)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: Maize, Cotton
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row x 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: Crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: Uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 800kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: every 2-3 years
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: rotations of maize, cotton, cowpeas
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Quantity/ density: 20cm deep
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.40
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strip Tillage implement | ||
| 2. | Knapsack Sprayer |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 580.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing and spreading crop residues | จัดการพืช | May-June yearly after harvest |
| 2. | Liming soil | จัดการพืช | Nov-Dec every 3 years |
| 3. | strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | จัดการพืช | Nov-Dec at onset of rain |
| 4. | Chemical weeding | จัดการพืช | 3 times per season |
| 5. | Harvesting | จัดการพืช | April-May |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8.0 | 2.5 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4.0 | 2.5 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24.0 | 1.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | kg/ha | 20.0 | 2.5 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400.0 | 0.8 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Herbicides | l/ha | 5.0 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Lime | kg | 1000.0 | 0.042 | 42.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 4.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 4.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 621.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Strip tillage planter
Calculations are for 1 ha of maize under strip tillage based conservation tillage and costs are for the Zambia situation in Magoye as of August 2012.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The weed control method employed is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides for weeding. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major recurrent cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Summer rains from November to March
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is low - medium and low fertility caused mainly by poor soil management practices, otherwise soils are inherently fertile.
Topsoil organic matter: Due to excessive ploughing and under fertilization
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium. Soils are naturally well drained but become less so after compaction due to ploughing
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Soils mostly loam to sandy loam with medium storage capacity
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: Hand wells are <20m but reliable boreholes are > 50m
Availability of surface water: Mostly seasonal streams and dams
Water quality (untreated):Good when from communal hand-pumps and poor when from hand-dug wells.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology is applied mostly by men since most households are headed males and animal traction operation are reserved for men. Planting and weeding operations are the domain of women and children
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
8% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (own more than 10 cattle).
8% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (own 5 - 10 cattle).
16% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (less than 5 cattle).
68% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (do not own cattle).
Off-farm income specification: sale of rainfed crops makes up about half of their income, the remainder coming from sale of livestock, petty trading, hiring out labour and remittances
Market orientation of production system: Livestock, maize and legumes for home consumption/subsistence and sale of excess maize and cotton, dairy products (mixed).
Level of mechanization: Manual labour only for small backyard fields. Families without cattle borrow or hire
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (families without oxen), 2-5 ha (families with one pair of oxen), 5-15 ha (families with over five oxen)
Grazing land: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3tons/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
5tons/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to early planting
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Residues needed for soil cover
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Better resistance
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2-3ha
หลังจาก SLM:
>10ha
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to increased production area and improved yield
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More time and labour freed for other activities
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to incresed yields
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less time spent on farm operations
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers trained through cooperatives
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to better soil cover
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to better soil cover
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved soil structure
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to good drainage
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to better soil cover
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to better soil cover
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to non-inversion tillage
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to deep tillage
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
ความเค็ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to good drainage
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Resistance to chemical weed control
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Ground water contamination
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only if applied over an extensive area
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only if applied over an extensive area
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only if applied over an extensive area
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only if applied over an extensive area
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Timely and quicker planting enables larger areas to be planted and with less labour in the short term. Improved soil structure and soil fertility leads to higher yields and better resilience to droughts in the long term.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
7 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (field size 1 ha - 30 ha)
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: These farmers heard of the technology by word of mouth and solicited for the technology even before it could be officially promoted
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even before promotion, inquiries to purchase the strip planter have been overwhelming. This is most likely due to the ability to till, plant and fertilizer in one operation.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? acquire more than one strip tillage implement |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and apply the fertilizer in one opperation |
|
Lighter to pull enabling deeper penetration of the tillage tool increasing the rooting depth How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use in moist soils |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant with the first heavy rain in November |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity |
|
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management (No Burning) and use of zero tillage implement |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The purchase price of the strip tillage planter | subsidizing the strip tillage implement |
| Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use | More training on herbicide use |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The purchase price is high making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers | It is already by far the cheapest planter available but mass production can lead to significant reduction in purchase price |
| Benefits are more evident on a scale larger than many farmers capacity especially when used in combination with herbicides | Support farmers to increase capacity |
| Difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides | make herbicides more available at a lower cost |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
FAO
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
INDABA project, Michigan State University
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011
URL:
cfu@zamnet.zm
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Participatory Research and Development [แซมเบีย]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Arthur Chomba
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล