Rehabilitation of degraded communal grazing land [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Nicole Guedel
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kshetigrasta samudayik charan bhumi ko punaruththan (Nepali)
technologies_1492 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/11/2004
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Rehabilitation measures, including eyebrow pits and live fencing, were implemented on degraded communal grazing land to
reestablish a protective vegetative cover
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
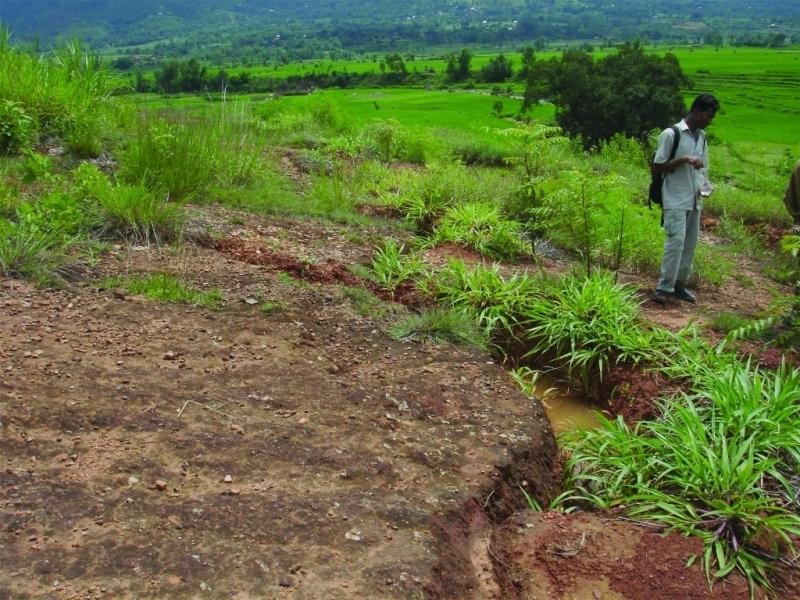
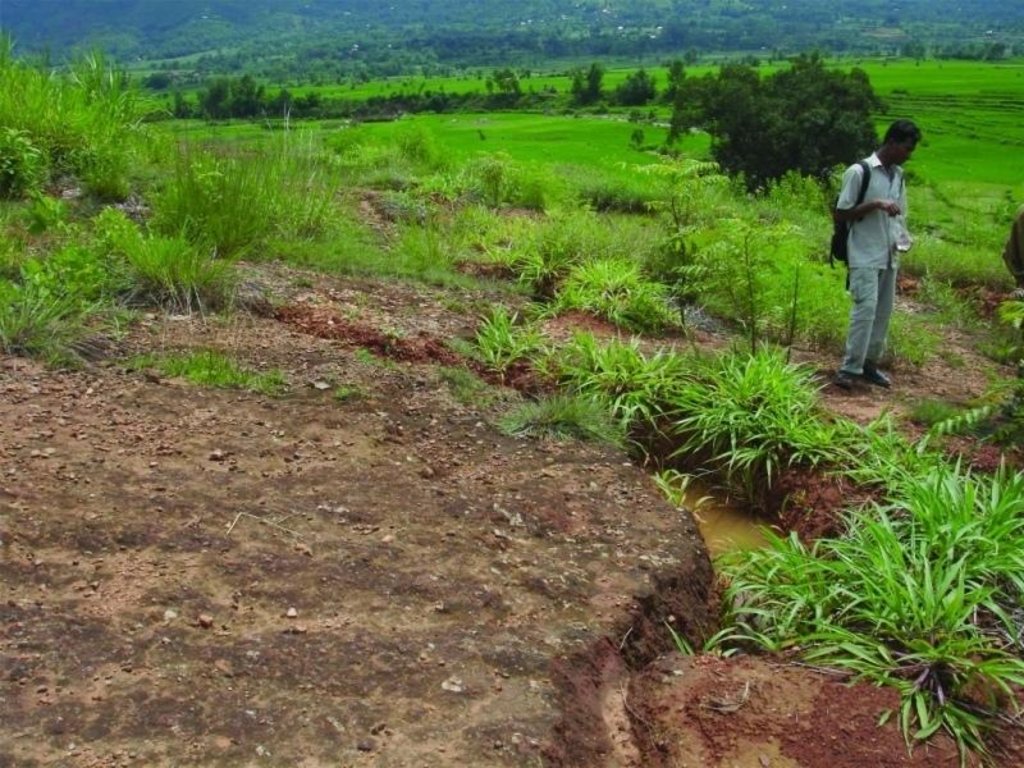
An area of heavily degraded grazing land was rehabilitated by establishing eyebrow pits to control and harvest runoff, planting trees and grasses, and fencing the site to control grazing. The main purpose was to re-establish vegetative cover on the almost bare, overgrazed site. The site is community land of the 40 households (240 people) of Dhotra village in the Jhikhu Khola watershed. These people are very dependent on this area due to the lack of alternative grazing sites. The rehabilitation site is surrounded by irrigated cropland downstream, grazing land, and degraded sal (Shorea robusta) dominated forest. Rainfed forward-sloping terraces immediately adjoin the site.
About 130 eyebrow pits were dug, together with catch drainage trenches. Several species of grass and fodder were planted along the ridges of the eyebrows and drainage trenches. Contour hedgerows were established between the eyebrow pits and trenches, and trees were planted just below the pits. The maintenance is quite easy: the vegetation needs to be cut back from time to time and the pits cleaned before the pre-monsoon period. The remaining bare areas should be revisited each year and replanted.
The area has a distinct dry season from November to May and a wet monsoon period from June to October. Annual rainfall is around 1200 mm. The site has red soils that are highly weathered and, if not properly managed, are very susceptible to erosion.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kavre Palanchok/ Dhotra village, Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The hedgerow technology came from the Philliphines, modified from the SALT (Sloping agriculture land technology) technology. The eye brow pit technology was implemented by the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management in Nepal and was adapted from them. Villagers approached the People and Resource Dynamics Project (PARDYP) for advice. PARDYP assisted, based on experiences made before with rehabilitation experiments under similar conditions. Mainly developed according to theoretical and site specific knowledge.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem is the small per capita landholding size for cropping. These holdings are mostly rainfed, have a low soil fertility status and acidity problems, and are susceptible to erosion. Intense rainfall at the beginning of the rainy season causes considerable soil loss (rill and gully erosion).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Overgrazing leading to lack of vegetation.
Ranching: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 3
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.019 km2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, in blocks
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (insufficient forage supply from the private land.), education, access to knowledge and support services (identification of appropriate SWC technologies and appropriate collaborators)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (for daily household needs ( litter , firewood, timber), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (excessive rainfall during pre-monsoon and monsoon), poverty / wealth (to buy planting materials and for logistics), labour availability (for community level social work)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
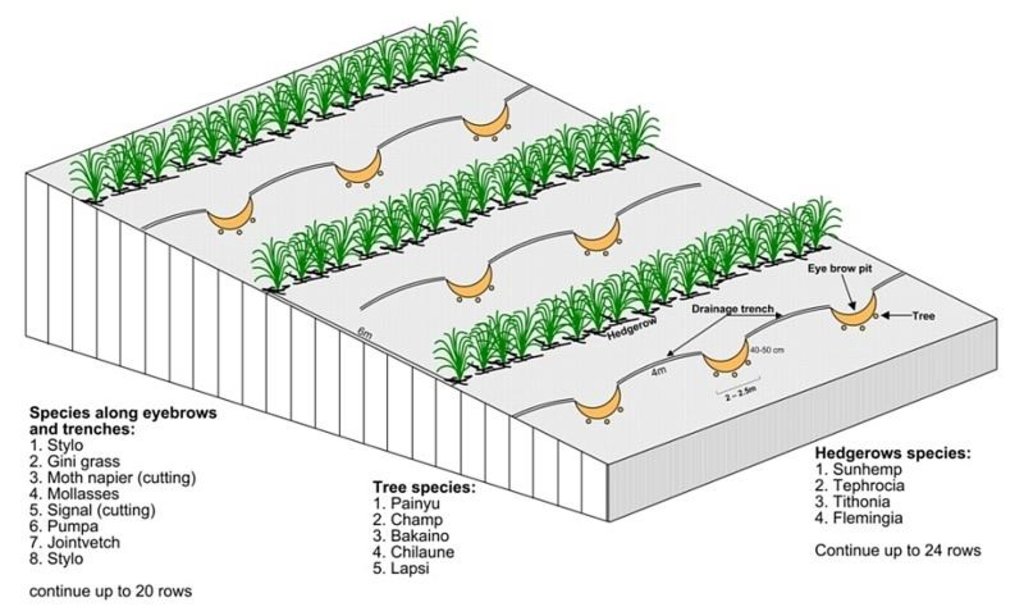
Technical drawing of layout of vegetative and structural measures.
Location: "Dhotra" village, near Dhulikhel. Kabhre Palanchok district
Date: July 2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase in organic matter
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 m
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 120
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4 m
Trees/ shrubs species: Prunus cerasoides, Michelia champaca, Melia azedarach, Schima wallichii,Cherospondias axillaries
Grass species: Stylosanthes guianensis, Panicum maximum, Pennisetum purpureum, Melinis minutiflora, Brachiaria decu
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2.00%
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 5-10 m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-2 m
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5-4 m
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Spacing between structures (m): 6 m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40-50 cm
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1-1.5m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2-2.5 m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-30
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5 m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-2 m
Structural measure: diversion ditch / cut-off drain
Spacing between structures (m): 6 m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0-30 cm
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10-30 cm
Construction material (earth): soil resulting from the digging activities were used to construct eyebrow shaped bunds.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: closing for change of management / intensity level - grazing as well as "symbolic" fencing by small living fence to delineate SWC area.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of tree seedlings and cuttings and sowing of grass seeds. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 2. | Drawing layout of eyebrow terraces, drainage ditches, hedgerows on the bare land | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 3. | Digging holes for eyebrow pits, drainage ditches | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 4. | Making sure that all livestock is stall- fed | ด้วยการจัดการ | All the time |
| 5. | Establishing small live fences with grasses and shrub cuttings | ด้วยการจัดการ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Eyebrow terraces and vegetative measure | Persons/day | 52.0 | 2.0 | 104.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 23.0 | 23.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Transportation | ha | 1.0 | 41.0 | 41.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Lunch, tea for farmers | ha | 1.0 | 47.0 | 47.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 233.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cutting vegetation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | 3 times /year |
| 2. | planting vegetation in any gaps | ด้วยวิธีพืช | before monsun /annual |
| 3. | Cleaning of sediment-filled pits | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | oncea year, before onset of monsoon |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, spade,sickle, hoe, spade
All costs and amounts were roughly estimated by the technicians and authors in 2004.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 900 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Also very steep
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average is variable
Soil texture: red soils with high clay content
Soil fertility was very low before implementation of rehabilitation activities
Topsoil organic matter was low before implementation of rehabilitation activities
Soil drainage / infiltration was poor before implementation of rehabilitation activities
Soil water storage capacity was very low before implementation of rehabilitation activities
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Water quality (untreated): More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
95% of the land users are average wealthy.
3% of the land users are poor.
2% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Only limited grazing area for whole village
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased carrying capacity of land; about $17 was collected from selling grass seeds and grass
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
collected money used for social work
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
At the beginning a few people opposed the activities
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
about 80 percent bare land covered by the various grasses
การสูญเสียดิน
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
into irrigation canal downstream
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The high establishment costs of the technology means that the shortterm benefit for the community only matches the costs involved. In the long-term the environmental benefit of rehabilitated land is high and
economically it is positive.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
40 households in an area of 0.019 sq km
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
40 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No initiative could be seen in the area , but inerst is there.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
The technology already started generating income from the degraded land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In the long run, by selling grass and grass seed, funds can be generated. |
|
The technology is effective against land degradation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More tree and fruit species should be added and grass species multiplied to cover the remaining bare land |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
The technology package is easy to apply as it does not need much knowledge and is cost effective. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure and grasses is required |
|
Improvement can be seen fast and easily; the vegetation cover increased and the loss of top soil decreased. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Nakarmi, G. (2000) Soil Erosion Dynamics in the Middle Mountains of Nepal, a report submitted to PARDYP, ICIMOD, Kathmandu.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ICIMOD
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Schreier, H.; Brown, S.; Shah, P. B.; Shrestha, B.; Merz, J. (2002) Jhikhu Khola Watershed – Nepal, CD ROM. Vancouver: Institute for Resources and Environment, University of British Columbia.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ICIMOD
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Shrestha, B. (2004) Progress Report PARDYP-Nepal. Paper presented at the PARDYP – Access Mid Year Meeting, 19-22 July 2004, ICIMOD, Kathmandu.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล