Jessour [ตูนิเซีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli
Jesser, Katra, Tabias (Arabic)
technologies_1013 - ตูนิเซีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mongi Sghaier
+216 75 633 005
Institut des Régions Arides IRA
4119 Medenine - Tunisia
ตูนิเซีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mongi Chniter
+21671 564 939
Commissariats Régionaux au Développement Agricole CRDA
Cité Bouchoucha - le Bardo 2000
ตูนิเซีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ouessar Mohammed
+216 75 633 005
Institut des Régions Arides IRA
4119 Medenine - Tunisia
ตูนิเซีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - ตูนิเซียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Commissariats Régionaux au Développement Agricole (CRDA) - ตูนิเซีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
22/09/2008
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Dryland watershed management approach [ตูนิเซีย]
Integrated land and water management approach, including vegetative, management, and agronomic measure
- ผู้รวบรวม: Naceur Mahdi
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
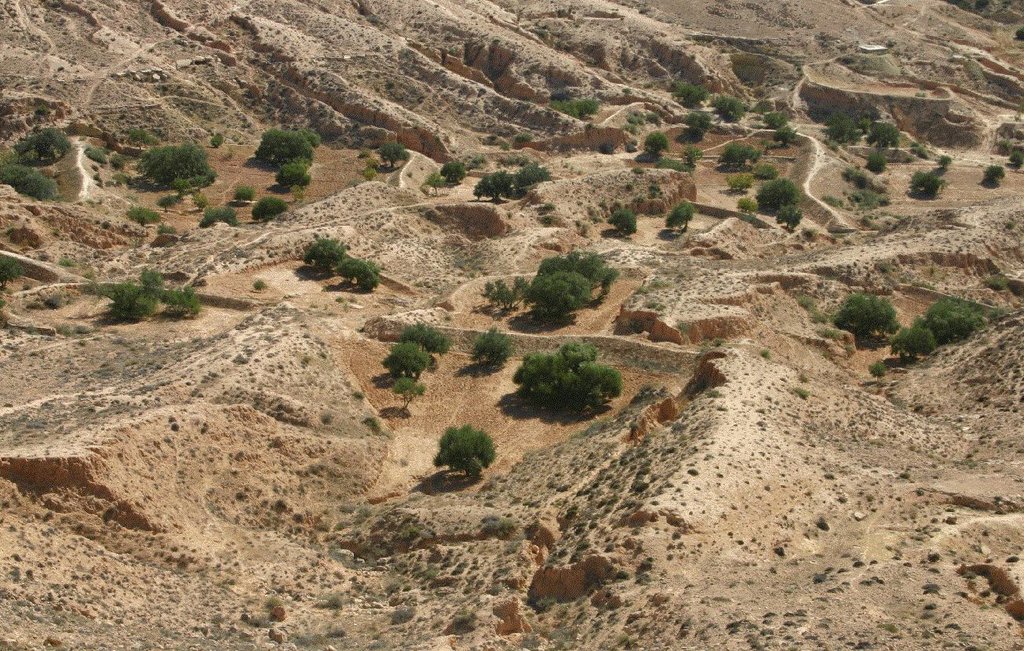
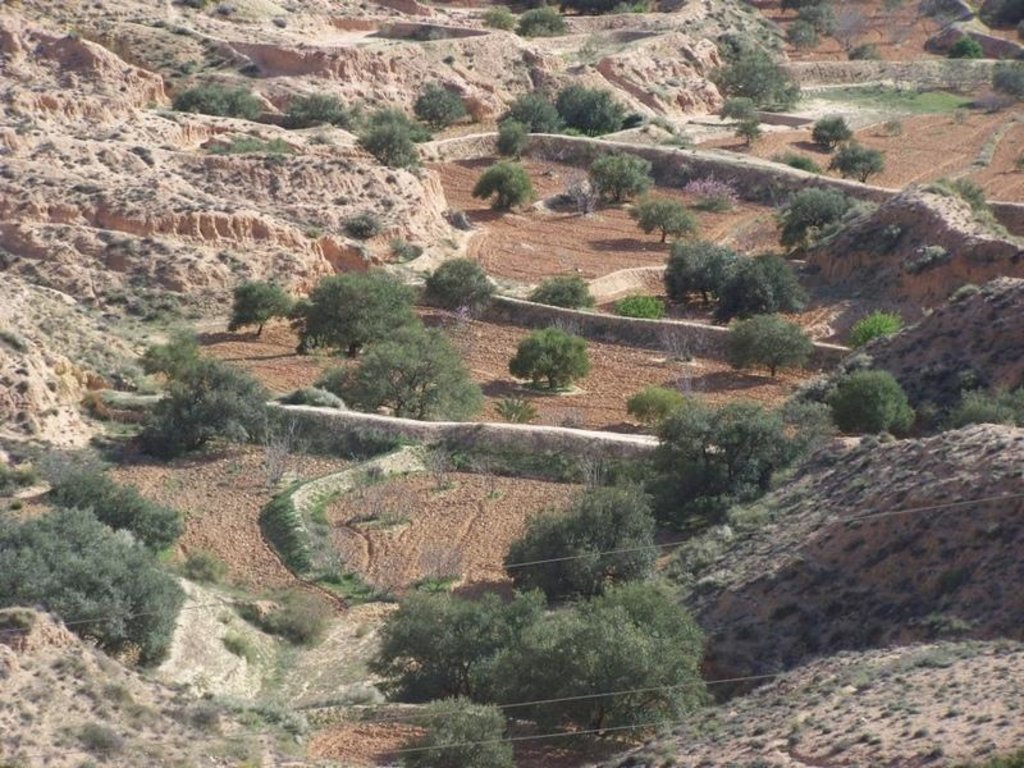
Jessour technology is generally practised in mountain dry regions (less than 200 mm annually) with medium to high slopes. This technology was behind the installation of very old olive orchards based on rainfed agriculture in rugged landscapes which allowed the local population not only to ensure self-sufficiency but also to provide neighbouring areas many agricultural produces (olive oil, dried figs, palm dates, etc.).
Jessour is the plural of jessr, which is a hydraulic unit made of three components: the impluvium, the terrace and the dyke. The impluvium or the catchment is the area which collects and conveys runoff water. It is bordered by a natural water divide line (a line that demarcates the boundary of a natural area or catchment, so that all the rain that falls on this area is concentrated and drained towards the same outlet). Each unit has its own impluvium, but can also receive excess water from upstream units. The terrace or cropping zone is the area in which farming is practised. It is formed progressively by the deposition of sediment. An artificial soil will then be created, which can be up to 5 m deep close to the dyke. Generally, fruit trees (e.g. olive, fig, almond, and date palm), legumes (e.g. pea, chickpeas, lentil, and faba bean) and barley and wheat are cultivated on these terraces.
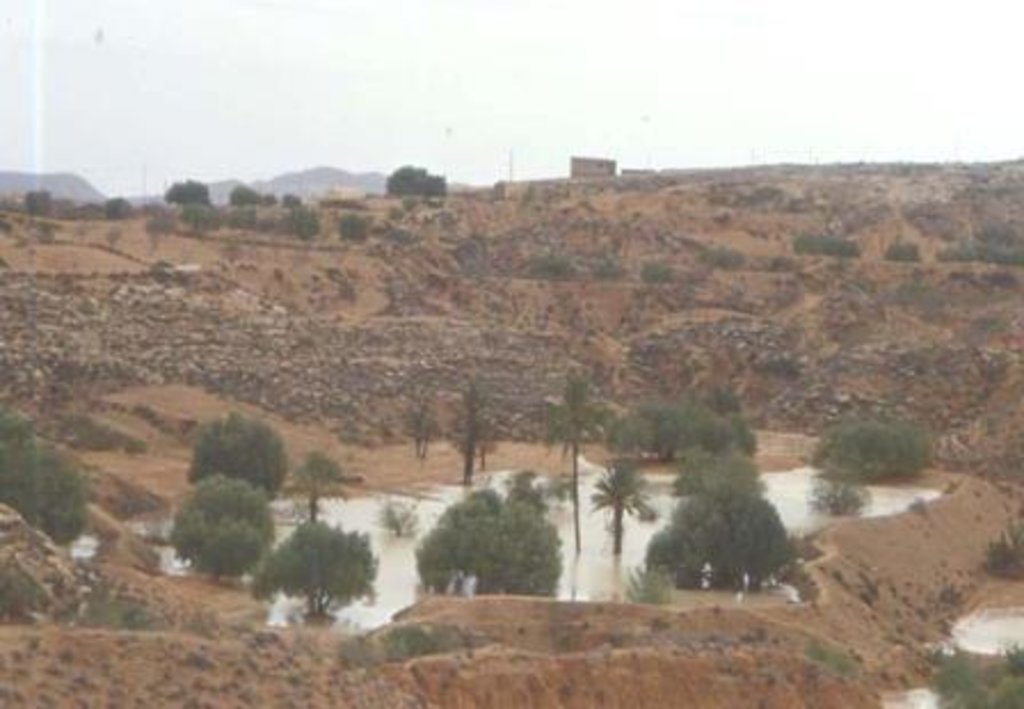
Purpose of the Technology: Although the jessour technique was developed for the production of various agricultural crops, it now also plays three additional roles: (1) aquifer recharge, via runoff water infiltration into the terraces, (2) flood control and therefore the protection of infrastructure and towns built downstream, and (3) wind erosion control, by preventing sediment from reaching the downstream plains, where windspeeds can be particularly high.
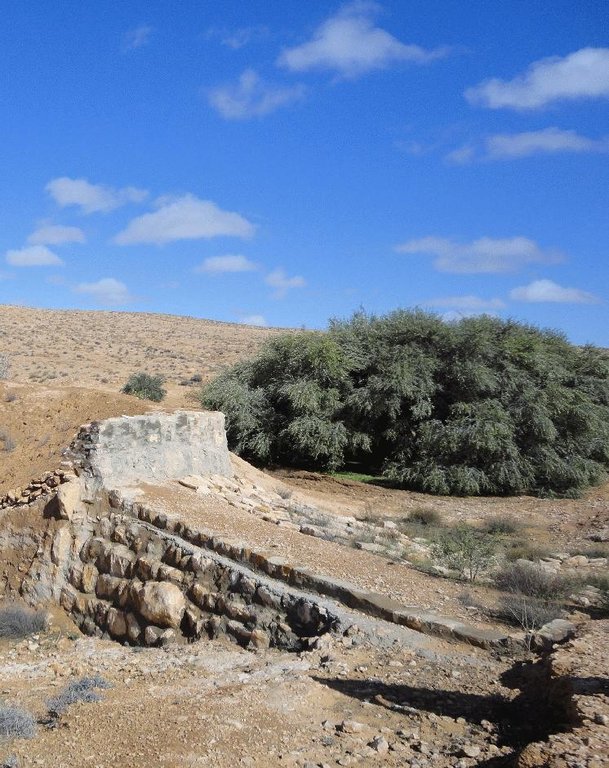
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the Jessour, a dyke (tabia, sed, katra) acts as a barrier used to hold back sediment and runoff water. Such dykes are made of earth, and are equipped with a central and/or lateral spillway (masref and/or manfes) and one or two abutments (ktef), assuring the evacuation of excess water. They are trapezoidal and measure 15-50 m in length, 1-4 m in width and 2-5 m in height. In old units, the dyke is stabilised with a covering of dry stones to overcome the erosive effects of water wave action on the front and back of the dyke. The spillway is made of stones arranged in the form of stairs, in order to dissipate the kinetic energy of the overflow.
This technology is currently encountered in the mountain ranges of Matmata of South Eastern Tunisia where the local agricultural activities are based mainly on rainfed agriculture and livestock breeding. However, high rates of migration to cities may threaten the long-term maintenance of those structures.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ตูนิเซีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Medenine
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Beni Khedache
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology is developed mainly in the upstream areas of the study watershed (mountainous zone of Béni Khédache).
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands, which are dominated by outcroppings of calcareous formations and depositions of quaternary calcareous silt.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crops: Olive oil, fig, cereals
Major food crops: Olive oil, legumes, fig, other fruits
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of surface water (runoff), problems of flooding, water erosion, soil degradation, drought
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology is developed mainly in the upstream areas of the study watershed (mountainous zone of Béni Khédache). This system is based on runoff water harvesting for fruit trees cropping (mainly olives). The cropping areas are relatively small and rarely exceed 0.25 ha.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), poverty / wealth
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, overgrazing, land tenure
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
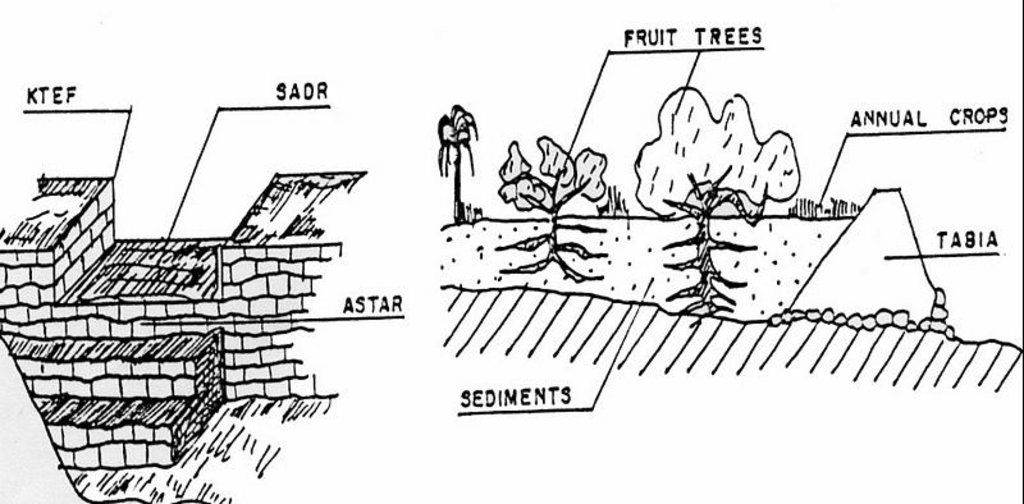
Left: Cross-section of dyke (locally called tabia) and terrace (cropping area).
The Jessour ensure the collection of both runoff water and sediments allowing creating very deep ‘artificial’ soils (terrace) which form a very good reservoir for water and nutrients to be used by fruit trees and annual crops.
Right: The spillway allows the overflow to the other Jessour downstream. It also represents the symbol of water sharing equity between different farmers in the same watershed. (Drawing adapted from El Amami (1984))
Location: Mountainous zone near Beni Khedache. Medenine
Date: 1984
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, harvesting of runoff water / water trapping
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity)
Spillway
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2-5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4-0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 2-6
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2-3
Spacing between structures (m): 30-70
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2-6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-40
Construction material (earth): Main dyke
Construction material (stone): Spillway and in some cases the dyke (external coating)
Construction material (concrete): Occasionally for consolidation of the spillway.
Lateral gradient along the structure: <1%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 300-1000m3
Catchment area: 1-10ham2
Beneficial area: 0.01-1ham2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:5
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
TD
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
1.3
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
10.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dyke construction | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 2. | Plantations | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 3. | Spillway construction | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 1200.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | ha | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | ha | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 3000.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Crop and trees maintenance | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Annually |
| 2. | Dyke and spillway maintenance | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 3. | Repairs | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 4. | Tillage (against soil sealing) | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 5. | Tillage (against soil sealing) | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Annually and after rainy events |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 900.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor, animals and manual works.
The technology establishment and maintenance costs met by the land users are 100% if executed on a private basis, but it can range from 10 to 50% when the site is subject to a publicly-funded programme.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Found in inaccessible and even remote areas, labour is the most determining factors affecting the costs of this system.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (This is the most appropriate location)
Landforms: Mountain slopes (This is the most appropriate location)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth: Very shallow-shallow. Very deep in particular case of loess deposits.
Soil fertility is: Very low
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Medium
Soil water storage: Medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Water quality untreated: Poor drinking water (treatement required) (ground water better than surface water (cisterns))
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Historically, the hard work is done by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
10% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The technique is very ancient and, therefore, ALL the farmers apply this technology. The only difference is the number of the owned units.
Off-farm incomes come from migration, construction works, commerce, tourism sector, administration or informal activities.
Level of mechanization: Manual work and animal traction (Especially in remote areas with difficult access)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The communal rule applies in this region: the farmer owns the terrace (the cropping area) and its impluvium from which the runoff is harvested.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced grazing lands
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
Runoff
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced available runoff for downstream users
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This technique is very ancient and it is therefore already fully adopted/used in the region.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Well known technique by the local population How can they be sustained / enhanced? training of new generations |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
This technique allowed a expansion of cropping lands in the mountain area How can they be sustained / enhanced? encourage maintenance of existing structure |
|
Allows crop production in very dry environments (with less than 200 mm of rainfall) How can they be sustained / enhanced? encourage maintenance of existing structure |
|
Collects and accumulates water, soil and nutrients behind the tabia and makes it available to crops How can they be sustained / enhanced? encourage maintenance of existing structure |
|
Reduced damage by flooding How can they be sustained / enhanced? encourage maintenance of existing structure |
|
Well adapted technology for the ecological environment How can they be sustained / enhanced? ensure maintenance works |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Productivity of the land is very low | Development of alternative income generation activities. |
| Land ownership fragmentation | New land access |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Risks related to the climatic changes | It needs to be combined with supplemental irrigation |
| Risk of local know how disappearence | Trainig of new generations |
| Land ownership fragmentation | Agrarian reform |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
El Amami, S. 1984. Les aménagements hydrauliques traditionnels en Tunisie. Centre de Recherche en Génie Rural (CRGR), Tunis, Tunisia. 69 pp.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ENGREF - Tunis
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ennabli, N. 1993. Les aménagements hydrauliques et hydro-agricoles en Tunisie. Imprimerie Officielle de la République Tunisienne, Tunis, 255 pp.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
INAT - Tunis
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ben Mechlia, N., Ouessar, M. 2004. Water harvesting systems in Tunisia. In: Oweis, T., Hachum, A., Bruggeman, A. (eds). Indigenous water harvesting in West Asia and North Africa, , ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria, pp: 21-41.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ICARDA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Genin, D., Guillaume, H., Ouessar, M., Ouled Belgacem, A., Romagny, B., Sghaier, M., Taamallah, H. (eds) 2006. Entre la désertification et le développement : la Jeffara tunisienne. CERES, Tunis, 351 pp.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA; IRD
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ouessar M. 2007. Hydrological impacts of rainwater harvesting in wadi Oum Zessar watershed (Southern Tunisia). Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 154 pp.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Sghaier, M., Mahdhi, N., De Graaff, J., Ouessar, M. 2002. Economic assessment of soil and water conservation works: case of the wadi Oum Zessar watershed in south-eastern Tunisia.TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands, pp: 101-113.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Dryland watershed management approach [ตูนิเซีย]
Integrated land and water management approach, including vegetative, management, and agronomic measure
- ผู้รวบรวม: Naceur Mahdi
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล