Dryland watershed management approach [ตูนิเซีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Naceur Mahdi
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2422 - ตูนิเซีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Sghaier Mongi
sghaier.mon@gmail.com
Institut des Régions Arides
4119 Medenine
ตูนิเซีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - ตูนิเซีย1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
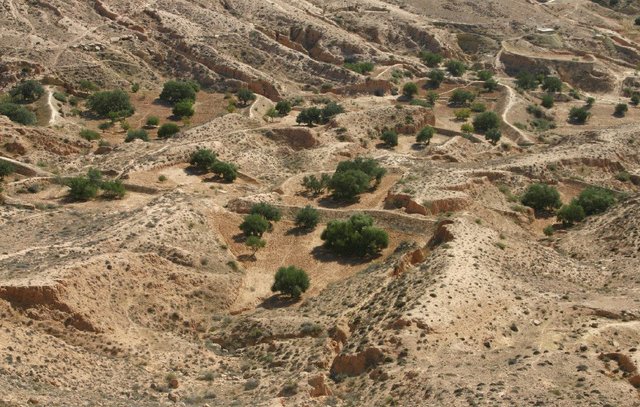

Jessour [ตูนิเซีย]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied
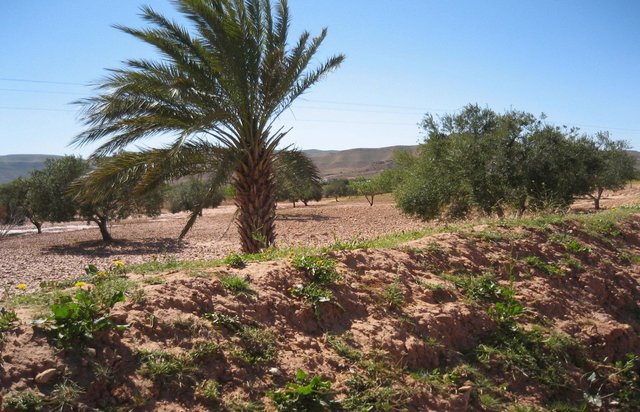

Tabia [ตูนิเซีย]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied
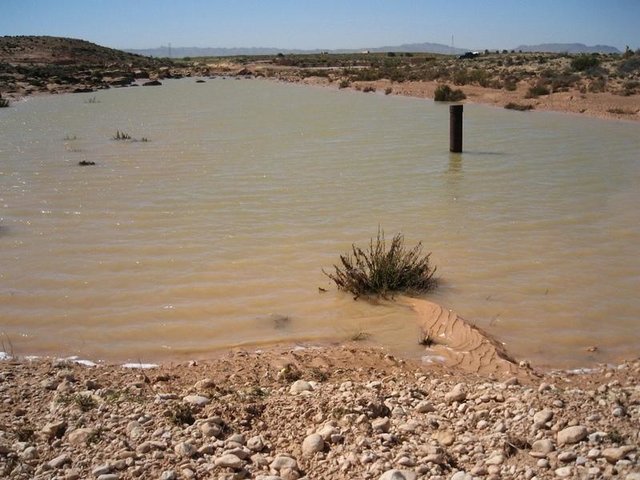

Recharge well [ตูนิเซีย]
A recharge well comprises a drilled hole, up to 30-40 m deep that reaches the water table, and a surrounding filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Integrated land and water management approach, including vegetative, management, and agronomic measure
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: The overall purpose of the approach is to prevent soil and water loss by combined measures and to provide a better environment. Soil and water conservation (SWC) technologies, based on harvesting area of surface water and underground water, are implemented to conserve soil and water and to improve the production and the biodiversity.
Methods: This approach is designed for the exploitation of water runoff for agricultural development, particularly for fruit trees cropping (mainly olives).This can be achieved through erosion reduction and aquifer recharge via runoff water infiltration into the terraces, slope angle and length reduction, runoff retaining, infiltration increase and soil loss reduction. The system is based on various runoff water harvesting systems, as jessour, tabias. It is marked by fruit tree development, notably olives. On the terraces, the fruit trees are arranged in inter-rows with the three main species encountered in the study areas. Generally, olive trees are planted, with in between rows almonds and/ or fig trees. SWC technologies play an importance role in arid zones. Since the 1970s, the Tunisian state has encouraged the local population to conserve water and soil in arid zone. Successive programmes and strategies of water and soil conservation have been developed and were implemented in all three natural regions of Tunisia (North, Centre and South).These techniques can be implemented by farmer with governmental subsidies or by government intervention in the projects and programmes of water and soil conservation. During the last decade, the Tunisian government implemented the first national strategy for soil and water conservation (1990-2000) and the second national strategy for soil and water conservation (2001-2011). These strategies mobilized important funds at national and regional levels. About 672.5 ha of SWC technologies were built and about 550 ha of SWC technologies are planned for the second national strategy.
Stages of implementation: 1) Assessment of the current natural resources and socio-economic conditions; 2) Proposition of actions at local and regional level; 3) Aggregation and coherence at the national level; 4) implementation of national action plan at local and regional level.
Role of stakeholders: Different levels of intervention are observed from the individual farm, through the community level, the extension / advisory system, the regional or national administration, or the policy level, to the international framework. The participative approach is usually applied in the construction of SWC technologies.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
ตูนิเซีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
south-east of tunisia
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Oum Zessar Watershed
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
1960
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- เป็นนวัตกรรมท้องถิ่นล่าสุด/ นวัตกรรมใหม่
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused on SLM only (production, soil fertility, biodiversity, employement oppourtunities, food self-sufficiency, fixing population and stop farming exodus)
The objectives of the approach are to control soil and water loss to reduce floods and enhance fertility, to enhance rainfed agriculture productivity, to improve the livelihoods of farmers, to contribute to the production increase among farmers and pastoralists, to recharge the groundwater and to extend the area of cropland.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The problems originate in the scarcity of water which is leading to conflicts over resource use between farmers. Oversized techniques leading to prevention of runoff from upstream to downstream reduce agricultural production and therefore the farm income, which causes a lack of cash to invest in SLM. In some cases irreversible land degradation is the result. The problems are mainly related to the lack of technical knowledge, the high costs of investment and the lack of tangible and assessable impacts of SWC activities, technically or socially.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
High cost investment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Public projects (National strategy of SWC), subsidies
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Land fragmentation, complexity of land tenure,
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Users organisation, participation
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The approach helped in the privatization of the land and has therefore greatly reduced the land/water use rights problems. This in turn has rendered the local interventions much more efficient.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Designing parameters
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training , Ehancing SWC specialists guidance
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Working land users were mainly men (Men are the main force for field work.)
Special attention has been paid to make women participate in the approach. Nevertheless, men have much more technical knowledge and skills than women because if SWC technologies have to be constructed by manual labour, men can achieve more. Poor and old people are especially involved through their participation in the special programme against unemployment in rural area. Some unemployed young people may benefit from agricultural development programmes.
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
The choice on the technology to use is made primarily by the technical specialists based on the prevalent type of erosion on each farm and farmers preference.
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
- องค์การระหว่างประเทศ
ถ้ามีผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียหลายคนที่เกี่ยวข้องให้ระบุหน่วยงานตัวแทน:
National and state specialists together with land users.
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Farmers and local population are very familiar with traditional SWC applied. Therefore the receptiveness to these techniques is very high. There is state encouragement through subsidies. |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Workshops/seminars; After a programme is granted, the implementing agency and local communities work together. |
| การดำเนินการ | จ่ายเงินหรือสนับสนุนจากภายนอก | Responsibilities are divided into major steps; In practice, local communities are the major part to manage and carry out. |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Participative evaluation; Interviews/questionnaires. |
| Research | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | It can give some suggestions or questionnaires. |
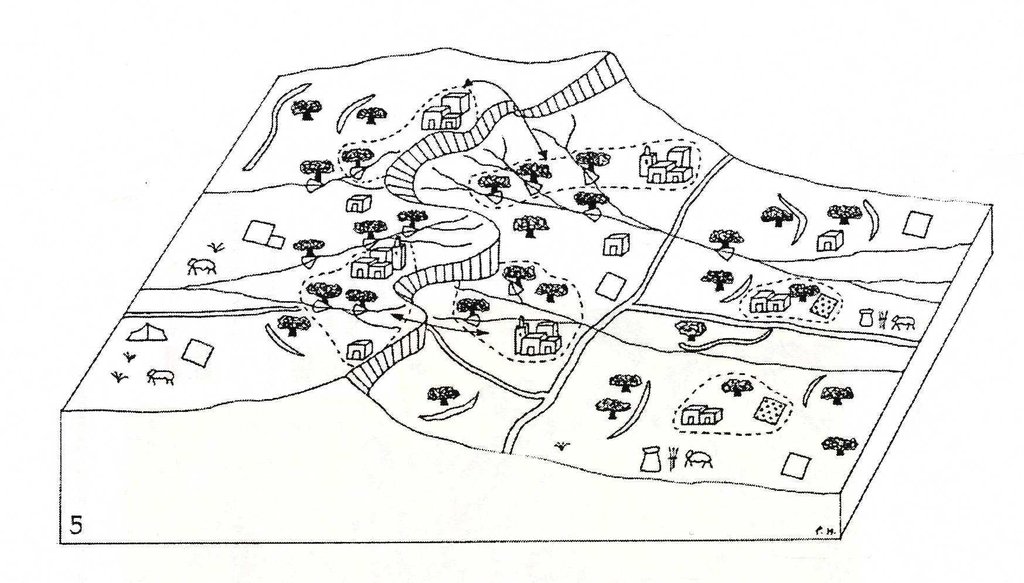
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
The treatment of the catchment starts from the upstream and continues to piedmont areas, and ends in the downstream section of the catchment. Attention should be given to ensure sufficient water allocation to all the sections of the catchment as well as to the different users (rainfed agriculture and rangelands, irrigated areas, drinking water, industry and tourism).
ผู้เขียน:
Patricia Home
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก โดยการสนับสนุนจากผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
การอธิบาย:
consultative,explain
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Decisions are made by politicians/SWC specialists; land users are consulted in the planning phase (experienced farmers may be involved initially).
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง ให้ระบุ เพศ อายุ สถานภาพ ชาติพันธุ์ เป็นต้น:
The capacity building programme and activities have benefited farmers representing the diversity of land users (women and men); representatives of NGO; local and external stakeholders, engineers and technicians responsible of the services of agriculture and forest.
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- เกษตรกรกับเกษตรกร
- ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
- จัดการประชุมสู่สาธารณชน
หัวข้อที่พูด:
Training focused on teaching them how to design and build SWC technologies, how to implement these technologies and about the participatory approach.
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ที่ศูนย์ถาวร
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Name of method used for advisory service: Integrated watershed management; Key elements: Training and demonstration open days, Demonstration plots implemented in private farms, Target farmers groups are visited by specialist to help and advise them.; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system. Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: planners; Activities: training
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The extension system is adequate to ensure continuation of activities. At each governorate level, there is a SWC division which is in charge of SWC activities, including its extension.extension
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- ด้านการเงิน
ให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม :
support with financial resources, capacity building, training, institutional support. The financial schema is made of three main components: self-financing from farmers and beneficiaries, subsidies from the government and credit from bank.
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: investigation/ of yield, income of land users, rainfed productivity
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Investigation of land users perceptions of cultural change
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Indicators are runoff loss, sediment load, soil moisture
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through measurements; indicators: Impact assessment
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: for example at the institutional level.
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เทคโนโลยี
- approaches
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
Land users have been involved. SWC technologies construction is based on scientific design, according to local conditions.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s): 20.0%; national non-government: 5.0%; government: 55.0%; international: 20.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- อุปกรณ์
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เครื่องจักร | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
- วัสดุสำหรับการก่อสร้าง
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| หิน | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
ความคิดเห็น:
Voluntary but rewarded with in-kind support by government subsidies
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุเงื่อนไข (อัตราดอกเบี้ย การชำระคืน):
repayment conditions: Credit was promoted through agricultural banks with various interest rates, usually lower than market rates.
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Land users can harvest water and irrigate crops in dry seasons. Meanwhile, the cropland area is enlarged.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
for disadvantaged women and men, there are employment opportunities and food self-sufficiency
ปรับปรุงประเด็นของการถือครองที่ดินหรือสิทธิในการใช้ ซึ่งขัดขวางการนำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้ให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
because of increased farm income.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
this appraoch increase farm income, food self-sufficiency and employer opportunities
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
increase yield; Food self-sufficiency
- กำไร (ความสามารถ) อัตราส่วนค่าใช้จ่ายต่อผลประโยชน์ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
increase farm income
- การจ่ายเงินหรือการช่วยเหลือ
invest in SWCT
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Employer opportunities
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ไม่แน่ใจ
ถ้าตอบว่าไม่หรือไม่แน่ใจ ให้ระบุและแสดงความคิดเห็น :
Can given the recent escalation in payments made to land users for implementation under certain projects it seems that the costs will be too high to sustain. Currently the Ministry of Agricultural is demanding that in-depth cost-benefit analyses are carried out involving environmental, social as well as economic assessments
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Reduction of soil erosion (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: ensure the durability of the works implemented) |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Improvement of livelihood (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: spreading and improvement of a more holistic SLM approach focusing on livelihoods) |
| Many people involved and trained at different levels (pyramid system) (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: participatory approach) |
| More participation and involvement of local population (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Improve participatory approach and increase confidence between partners) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Abandonment of the works, less maintenance | Continue to support farmers and local institution and organisation. Repairing and maintaining in time. |
| Low impact on livelihood conditions | improve efficiency of SWC activities and participatory approach |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Less confidence between partners and less participation | improve dialog and communication; improve efficiency of SWC activities and participatory approach. |
| High costs: farmers depend on external support from the government; they are not willing to invest their labour without payments | New approach should give farmers loans for construction as now they use machines to do the work. In addition, search for cheaper SWC technologies and for improving the benefits. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Genin D., Guillaume H., Ouessar M., Ouled Belgacem A., Romagny B., Sghaier M., Taamallah H. (Eds) 2006. Entre la désertification et le développement : la Jeffara tunisienne. CERES, Tunis; de Graaff J. & Ouessar M. (Eds.) 2002Water harvesting in Mediterranean zones: an impact assessment and economic evaluation.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Water harvesting in Mediterranean zones: an impact assessment and economic evaluation.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Jessour [ตูนิเซีย]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied

Tabia [ตูนิเซีย]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied

Recharge well [ตูนิเซีย]
A recharge well comprises a drilled hole, up to 30-40 m deep that reaches the water table, and a surrounding filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล