Dryland watershed management approach [Тунис]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Naceur Mahdi
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2422 - Тунис
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Sghaier Mongi
sghaier.mon@gmail.com
Institut des Régions Arides
4119 Medenine
Тунис
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - Тунис1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП
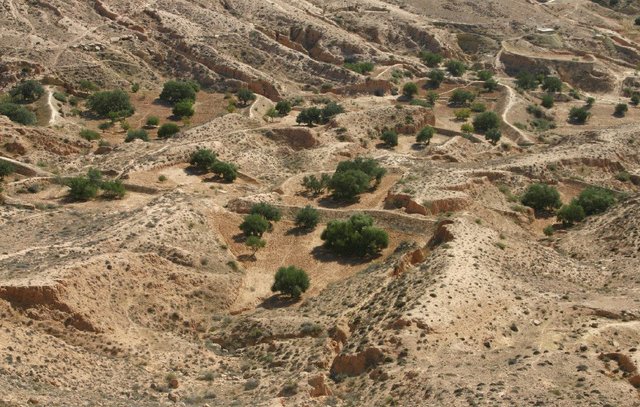

Jessour [Тунис]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- Составитель: Mongi Ben Zaied
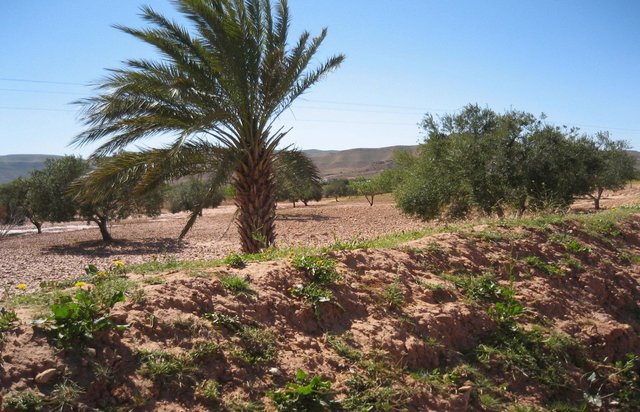

Tabia [Тунис]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- Составитель: Mongi Ben Zaied
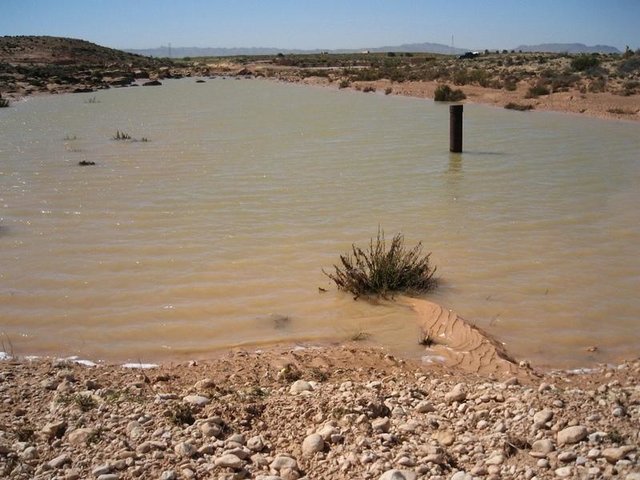

Recharge well [Тунис]
A recharge well comprises a drilled hole, up to 30-40 m deep that reaches the water table, and a surrounding filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer.
- Составитель: Mongi Ben Zaied
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
Integrated land and water management approach, including vegetative, management, and agronomic measure
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
Aims / objectives: The overall purpose of the approach is to prevent soil and water loss by combined measures and to provide a better environment. Soil and water conservation (SWC) technologies, based on harvesting area of surface water and underground water, are implemented to conserve soil and water and to improve the production and the biodiversity.
Methods: This approach is designed for the exploitation of water runoff for agricultural development, particularly for fruit trees cropping (mainly olives).This can be achieved through erosion reduction and aquifer recharge via runoff water infiltration into the terraces, slope angle and length reduction, runoff retaining, infiltration increase and soil loss reduction. The system is based on various runoff water harvesting systems, as jessour, tabias. It is marked by fruit tree development, notably olives. On the terraces, the fruit trees are arranged in inter-rows with the three main species encountered in the study areas. Generally, olive trees are planted, with in between rows almonds and/ or fig trees. SWC technologies play an importance role in arid zones. Since the 1970s, the Tunisian state has encouraged the local population to conserve water and soil in arid zone. Successive programmes and strategies of water and soil conservation have been developed and were implemented in all three natural regions of Tunisia (North, Centre and South).These techniques can be implemented by farmer with governmental subsidies or by government intervention in the projects and programmes of water and soil conservation. During the last decade, the Tunisian government implemented the first national strategy for soil and water conservation (1990-2000) and the second national strategy for soil and water conservation (2001-2011). These strategies mobilized important funds at national and regional levels. About 672.5 ha of SWC technologies were built and about 550 ha of SWC technologies are planned for the second national strategy.
Stages of implementation: 1) Assessment of the current natural resources and socio-economic conditions; 2) Proposition of actions at local and regional level; 3) Aggregation and coherence at the national level; 4) implementation of national action plan at local and regional level.
Role of stakeholders: Different levels of intervention are observed from the individual farm, through the community level, the extension / advisory system, the regional or national administration, or the policy level, to the international framework. The participative approach is usually applied in the construction of SWC technologies.
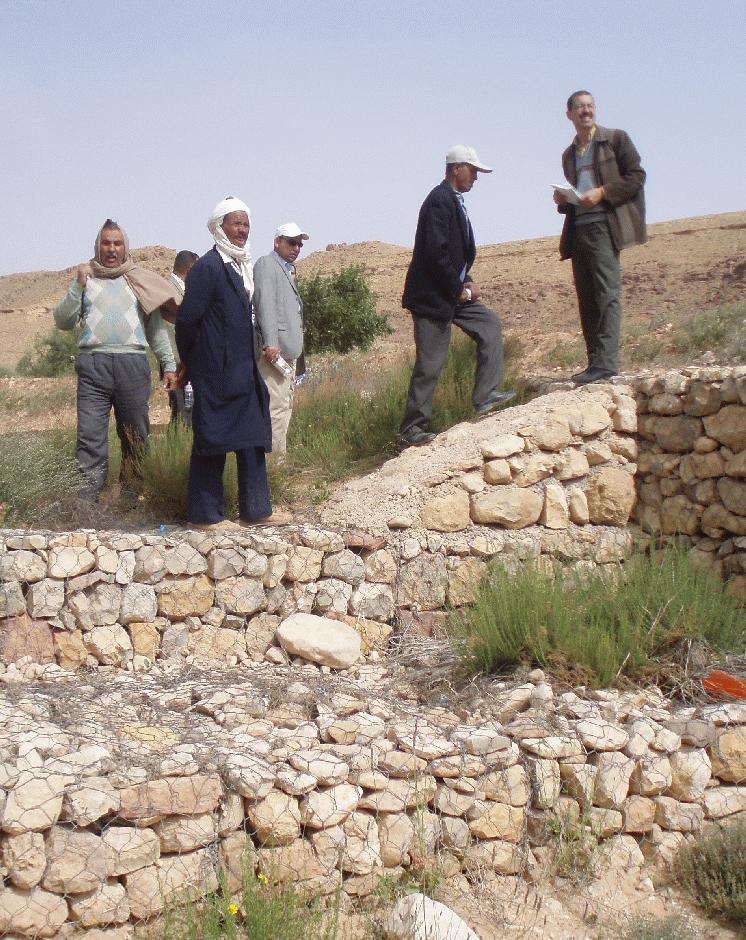
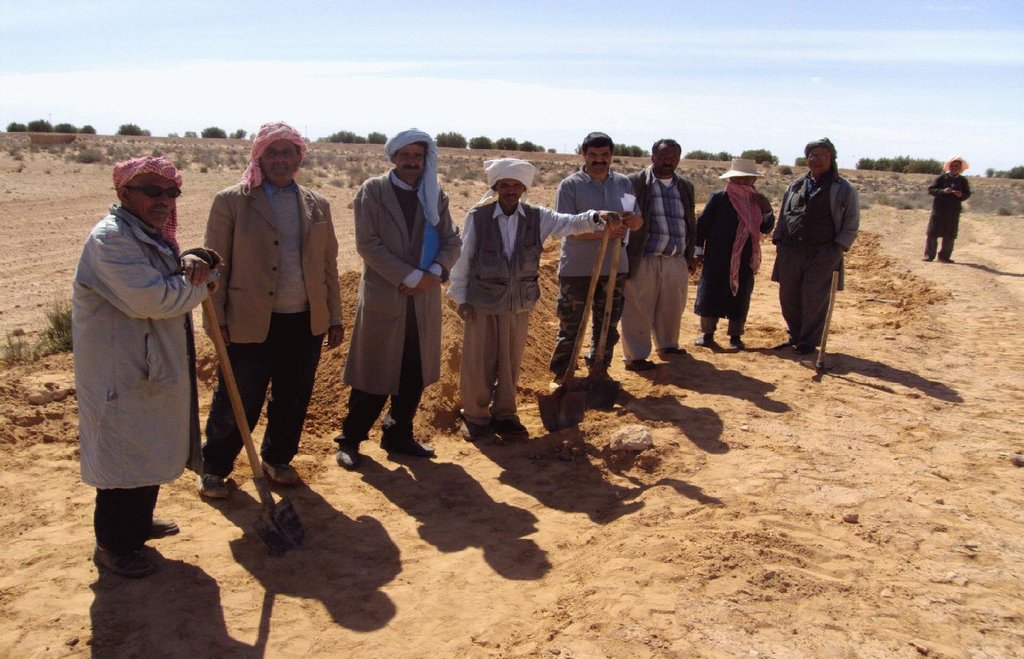
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Тунис
Административная единица (Район/Область):
south-east of tunisia
Более точная привязка места:
Oum Zessar Watershed
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
1960
2.7 Тип Подхода
- недавняя местная инициатива/ инновация
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused on SLM only (production, soil fertility, biodiversity, employement oppourtunities, food self-sufficiency, fixing population and stop farming exodus)
The objectives of the approach are to control soil and water loss to reduce floods and enhance fertility, to enhance rainfed agriculture productivity, to improve the livelihoods of farmers, to contribute to the production increase among farmers and pastoralists, to recharge the groundwater and to extend the area of cropland.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The problems originate in the scarcity of water which is leading to conflicts over resource use between farmers. Oversized techniques leading to prevention of runoff from upstream to downstream reduce agricultural production and therefore the farm income, which causes a lack of cash to invest in SLM. In some cases irreversible land degradation is the result. The problems are mainly related to the lack of technical knowledge, the high costs of investment and the lack of tangible and assessable impacts of SWC activities, technically or socially.
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг
- затрудняют
High cost investment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Public projects (National strategy of SWC), subsidies
Институциональные условия
- затрудняют
Land fragmentation, complexity of land tenure,
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Users organisation, participation
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- содействуют
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The approach helped in the privatization of the land and has therefore greatly reduced the land/water use rights problems. This in turn has rendered the local interventions much more efficient.
Осведомленность в области УЗП, доступность технической поддержки
- затрудняют
Designing parameters
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training , Ehancing SWC specialists guidance
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Working land users were mainly men (Men are the main force for field work.)
Special attention has been paid to make women participate in the approach. Nevertheless, men have much more technical knowledge and skills than women because if SWC technologies have to be constructed by manual labour, men can achieve more. Poor and old people are especially involved through their participation in the special programme against unemployment in rural area. Some unemployed young people may benefit from agricultural development programmes.
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
The choice on the technology to use is made primarily by the technical specialists based on the prevalent type of erosion on each farm and farmers preference.
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
- международные организации
Если участвовало несколько заинтересованных сторон, назовите ведущую организацию:
National and state specialists together with land users.
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | интерактивное | Farmers and local population are very familiar with traditional SWC applied. Therefore the receptiveness to these techniques is very high. There is state encouragement through subsidies. |
| планирование | интерактивное | Workshops/seminars; After a programme is granted, the implementing agency and local communities work together. |
| выполнение | внешняя поддержка | Responsibilities are divided into major steps; In practice, local communities are the major part to manage and carry out. |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | Participative evaluation; Interviews/questionnaires. |
| Research | интерактивное | It can give some suggestions or questionnaires. |
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
Описание:
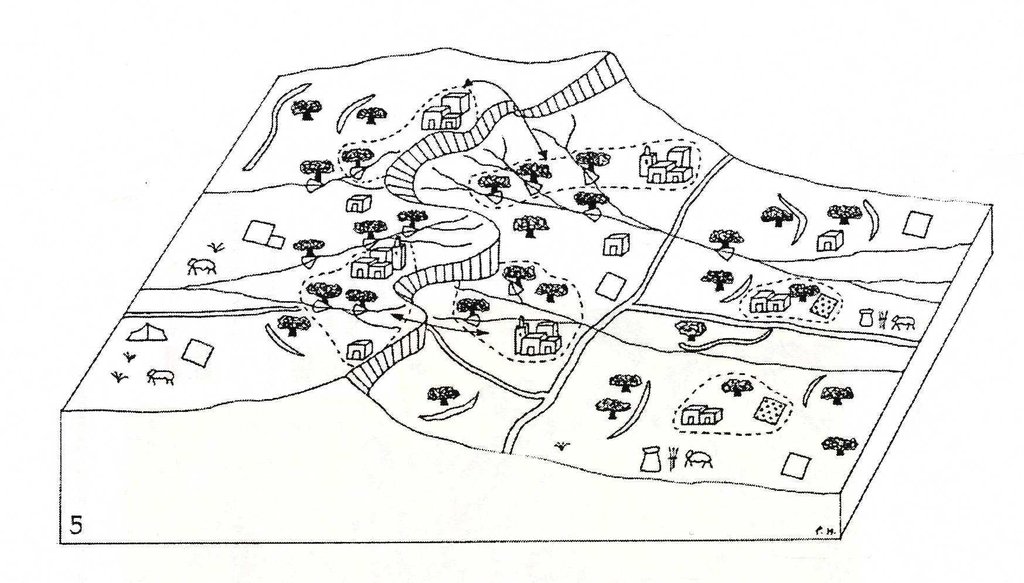
The treatment of the catchment starts from the upstream and continues to piedmont areas, and ends in the downstream section of the catchment. Attention should be given to ensure sufficient water allocation to all the sections of the catchment as well as to the different users (rainfed agriculture and rangelands, irrigated areas, drinking water, industry and tourism).
Автор:
Patricia Home
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- в основном землепользователи при поддержке специалистов по УЗП
Поясните:
consultative,explain
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Decisions are made by politicians/SWC specialists; land users are consulted in the planning phase (experienced farmers may be involved initially).
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
Укажите, кто проходил обучение:
- землепользователи
- местный персонал/консультанты
Если существенно, укажите гендерный и возрастной состав, статус, этническую принадлежность и т.д.
The capacity building programme and activities have benefited farmers representing the diversity of land users (women and men); representatives of NGO; local and external stakeholders, engineers and technicians responsible of the services of agriculture and forest.
Тип обучения:
- обмен опытом между фермерами
- опытные участки
- общие собрания
Рассматриваемые темы:
Training focused on teaching them how to design and build SWC technologies, how to implement these technologies and about the participatory approach.
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Укажите, где именно оказываются консультационные услуги:
- в постоянно функционирующих центрах
Описание/ комментарий:
Name of method used for advisory service: Integrated watershed management; Key elements: Training and demonstration open days, Demonstration plots implemented in private farms, Target farmers groups are visited by specialist to help and advise them.; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system. Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: planners; Activities: training
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The extension system is adequate to ensure continuation of activities. At each governorate level, there is a SWC division which is in charge of SWC activities, including its extension.extension
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, умеренно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Укажите тип поддержки:
- финансовая
Подробнее:
support with financial resources, capacity building, training, institutional support. The financial schema is made of three main components: self-financing from farmers and beneficiaries, subsidies from the government and credit from bank.
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: investigation/ of yield, income of land users, rainfed productivity
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Investigation of land users perceptions of cultural change
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Indicators are runoff loss, sediment load, soil moisture
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through measurements; indicators: Impact assessment
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: for example at the institutional level.
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Укажите темы исследований:
- технология
- approaches
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
Land users have been involved. SWC technologies construction is based on scientific design, according to local conditions.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- 10000-100000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s): 20.0%; national non-government: 5.0%; government: 55.0%; international: 20.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- оборудование
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| техника | профинансированы частично | |
- строительные материалы
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| камень | профинансированы частично | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
Комментарии:
Voluntary but rewarded with in-kind support by government subsidies
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Да
Укажите условия предоставления (процент, окупаемость и т.д.):
repayment conditions: Credit was promoted through agricultural banks with various interest rates, usually lower than market rates.
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Land users can harvest water and irrigate crops in dry seasons. Meanwhile, the cropland area is enlarged.
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности социально и экономически уязвимых групп?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
for disadvantaged women and men, there are employment opportunities and food self-sufficiency
Сумел ли Подход разрешить правовые проблемы землевладения/ землепользования, препятствующие использованию технологий УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
because of increased farm income.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
this appraoch increase farm income, food self-sufficiency and employer opportunities
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- рост продуктивности
increase yield; Food self-sufficiency
- рост прибыли (доходности) и рентабельности
increase farm income
- материальное стимулирование/ субсидии
invest in SWCT
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Employer opportunities
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- нет уверенности
Если нет или нет уверенности, объясните почему:
Can given the recent escalation in payments made to land users for implementation under certain projects it seems that the costs will be too high to sustain. Currently the Ministry of Agricultural is demanding that in-depth cost-benefit analyses are carried out involving environmental, social as well as economic assessments
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Reduction of soil erosion (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: ensure the durability of the works implemented) |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Improvement of livelihood (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: spreading and improvement of a more holistic SLM approach focusing on livelihoods) |
| Many people involved and trained at different levels (pyramid system) (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: participatory approach) |
| More participation and involvement of local population (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Improve participatory approach and increase confidence between partners) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Abandonment of the works, less maintenance | Continue to support farmers and local institution and organisation. Repairing and maintaining in time. |
| Low impact on livelihood conditions | improve efficiency of SWC activities and participatory approach |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Less confidence between partners and less participation | improve dialog and communication; improve efficiency of SWC activities and participatory approach. |
| High costs: farmers depend on external support from the government; they are not willing to invest their labour without payments | New approach should give farmers loans for construction as now they use machines to do the work. In addition, search for cheaper SWC technologies and for improving the benefits. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Genin D., Guillaume H., Ouessar M., Ouled Belgacem A., Romagny B., Sghaier M., Taamallah H. (Eds) 2006. Entre la désertification et le développement : la Jeffara tunisienne. CERES, Tunis; de Graaff J. & Ouessar M. (Eds.) 2002Water harvesting in Mediterranean zones: an impact assessment and economic evaluation.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Water harvesting in Mediterranean zones: an impact assessment and economic evaluation.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Jessour [Тунис]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- Составитель: Mongi Ben Zaied

Tabia [Тунис]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- Составитель: Mongi Ben Zaied

Recharge well [Тунис]
A recharge well comprises a drilled hole, up to 30-40 m deep that reaches the water table, and a surrounding filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer.
- Составитель: Mongi Ben Zaied
Модули
Нет модулей