Dryland watershed management approach [Tunisia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Naceur Mahdi
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2422 - Tunisia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Sghaier Mongi
sghaier.mon@gmail.com
Institut des Régions Arides
4119 Medenine
Tunisia
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - Tunisia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST
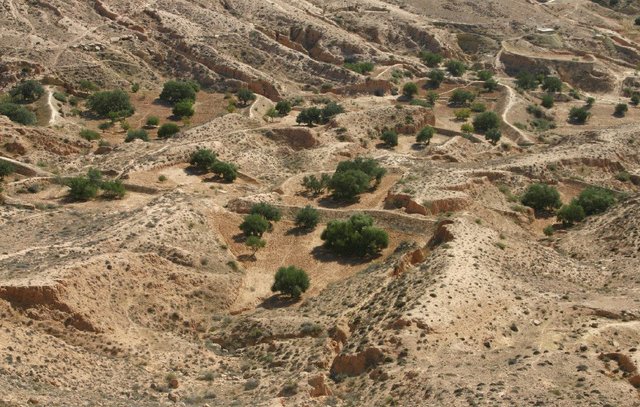

Jessour [Tunisia]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- Compilador: Mongi Ben Zaied
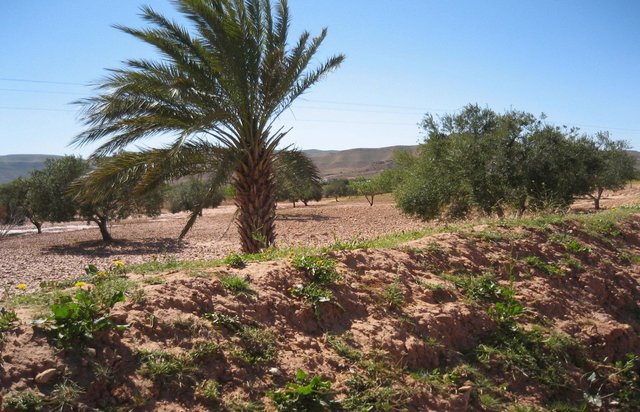

Tabia [Tunisia]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- Compilador: Mongi Ben Zaied
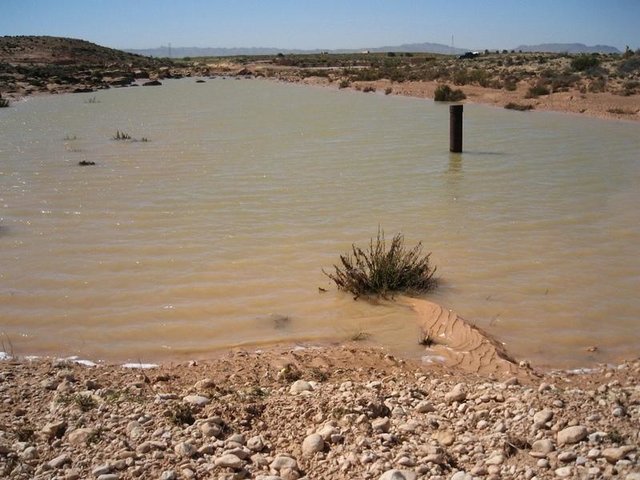

Recharge well [Tunisia]
A recharge well comprises a drilled hole, up to 30-40 m deep that reaches the water table, and a surrounding filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer.
- Compilador: Mongi Ben Zaied
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Integrated land and water management approach, including vegetative, management, and agronomic measure
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: The overall purpose of the approach is to prevent soil and water loss by combined measures and to provide a better environment. Soil and water conservation (SWC) technologies, based on harvesting area of surface water and underground water, are implemented to conserve soil and water and to improve the production and the biodiversity.
Methods: This approach is designed for the exploitation of water runoff for agricultural development, particularly for fruit trees cropping (mainly olives).This can be achieved through erosion reduction and aquifer recharge via runoff water infiltration into the terraces, slope angle and length reduction, runoff retaining, infiltration increase and soil loss reduction. The system is based on various runoff water harvesting systems, as jessour, tabias. It is marked by fruit tree development, notably olives. On the terraces, the fruit trees are arranged in inter-rows with the three main species encountered in the study areas. Generally, olive trees are planted, with in between rows almonds and/ or fig trees. SWC technologies play an importance role in arid zones. Since the 1970s, the Tunisian state has encouraged the local population to conserve water and soil in arid zone. Successive programmes and strategies of water and soil conservation have been developed and were implemented in all three natural regions of Tunisia (North, Centre and South).These techniques can be implemented by farmer with governmental subsidies or by government intervention in the projects and programmes of water and soil conservation. During the last decade, the Tunisian government implemented the first national strategy for soil and water conservation (1990-2000) and the second national strategy for soil and water conservation (2001-2011). These strategies mobilized important funds at national and regional levels. About 672.5 ha of SWC technologies were built and about 550 ha of SWC technologies are planned for the second national strategy.
Stages of implementation: 1) Assessment of the current natural resources and socio-economic conditions; 2) Proposition of actions at local and regional level; 3) Aggregation and coherence at the national level; 4) implementation of national action plan at local and regional level.
Role of stakeholders: Different levels of intervention are observed from the individual farm, through the community level, the extension / advisory system, the regional or national administration, or the policy level, to the international framework. The participative approach is usually applied in the construction of SWC technologies.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Tunisia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
south-east of tunisia
Especifique más el lugar :
Oum Zessar Watershed
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
1960
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- iniciativa local reciente/ innovadora
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused on SLM only (production, soil fertility, biodiversity, employement oppourtunities, food self-sufficiency, fixing population and stop farming exodus)
The objectives of the approach are to control soil and water loss to reduce floods and enhance fertility, to enhance rainfed agriculture productivity, to improve the livelihoods of farmers, to contribute to the production increase among farmers and pastoralists, to recharge the groundwater and to extend the area of cropland.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The problems originate in the scarcity of water which is leading to conflicts over resource use between farmers. Oversized techniques leading to prevention of runoff from upstream to downstream reduce agricultural production and therefore the farm income, which causes a lack of cash to invest in SLM. In some cases irreversible land degradation is the result. The problems are mainly related to the lack of technical knowledge, the high costs of investment and the lack of tangible and assessable impacts of SWC activities, technically or socially.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
High cost investment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Public projects (National strategy of SWC), subsidies
entorno institucional
- impiden
Land fragmentation, complexity of land tenure,
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Users organisation, participation
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The approach helped in the privatization of the land and has therefore greatly reduced the land/water use rights problems. This in turn has rendered the local interventions much more efficient.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
Designing parameters
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training , Ehancing SWC specialists guidance
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Working land users were mainly men (Men are the main force for field work.)
Special attention has been paid to make women participate in the approach. Nevertheless, men have much more technical knowledge and skills than women because if SWC technologies have to be constructed by manual labour, men can achieve more. Poor and old people are especially involved through their participation in the special programme against unemployment in rural area. Some unemployed young people may benefit from agricultural development programmes.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
The choice on the technology to use is made primarily by the technical specialists based on the prevalent type of erosion on each farm and farmers preference.
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
- organización internacional
Si varias partes interesadas estuvieron involucradas, indique la agencia principal:
National and state specialists together with land users.
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | interactivo | Farmers and local population are very familiar with traditional SWC applied. Therefore the receptiveness to these techniques is very high. There is state encouragement through subsidies. |
| planificación | interactivo | Workshops/seminars; After a programme is granted, the implementing agency and local communities work together. |
| implementación | apoyo externo | Responsibilities are divided into major steps; In practice, local communities are the major part to manage and carry out. |
| monitoreo y evaluación | interactivo | Participative evaluation; Interviews/questionnaires. |
| Research | interactivo | It can give some suggestions or questionnaires. |
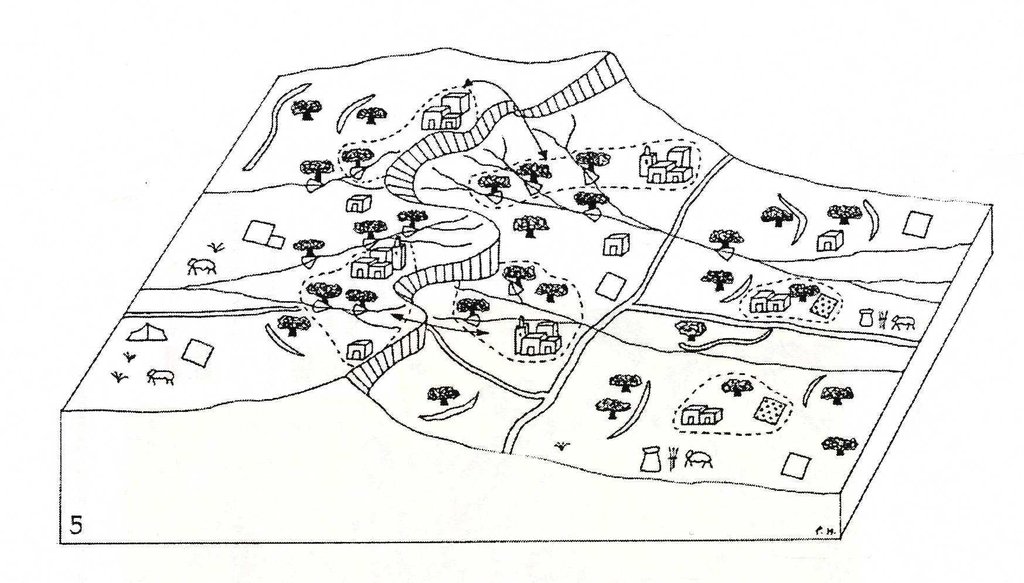
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
Descripción:
The treatment of the catchment starts from the upstream and continues to piedmont areas, and ends in the downstream section of the catchment. Attention should be given to ensure sufficient water allocation to all the sections of the catchment as well as to the different users (rainfed agriculture and rangelands, irrigated areas, drinking water, industry and tourism).
Autor:
Patricia Home
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
Explique:
consultative,explain
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Decisions are made by politicians/SWC specialists; land users are consulted in the planning phase (experienced farmers may be involved initially).
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
Si fuese relevante, también especifique género, edad, estatus, etnicidad, etc.
The capacity building programme and activities have benefited farmers representing the diversity of land users (women and men); representatives of NGO; local and external stakeholders, engineers and technicians responsible of the services of agriculture and forest.
Forma de capacitación:
- de agricultor a agricultor
- áreas de demostración
- reuniones públicas
Temas avanzados:
Training focused on teaching them how to design and build SWC technologies, how to implement these technologies and about the participatory approach.
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en centros permanentes
Describa/ comentarios:
Name of method used for advisory service: Integrated watershed management; Key elements: Training and demonstration open days, Demonstration plots implemented in private farms, Target farmers groups are visited by specialist to help and advise them.; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system. Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: planners; Activities: training
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The extension system is adequate to ensure continuation of activities. At each governorate level, there is a SWC division which is in charge of SWC activities, including its extension.extension
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, moderadamente
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- financiero
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
support with financial resources, capacity building, training, institutional support. The financial schema is made of three main components: self-financing from farmers and beneficiaries, subsidies from the government and credit from bank.
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: investigation/ of yield, income of land users, rainfed productivity
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Investigation of land users perceptions of cultural change
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Indicators are runoff loss, sediment load, soil moisture
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through measurements; indicators: Impact assessment
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: for example at the institutional level.
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Especifique los temas:
- tecnología
- approaches
Proporcione detalles adicionales e indique quién hizo la investigación:
Land users have been involved. SWC technologies construction is based on scientific design, according to local conditions.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 10,000-100,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s): 20.0%; national non-government: 5.0%; government: 55.0%; international: 20.0%
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
Sí
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- equipo
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| maquinaria | parcialmente financiado | |
- construcción
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| piedra | parcialmente financiado | |
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
Voluntary but rewarded with in-kind support by government subsidies
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
Sí
Especifique las condiciones (tasa de interés el apoyo, amortización, etc.):
repayment conditions: Credit was promoted through agricultural banks with various interest rates, usually lower than market rates.
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Land users can harvest water and irrigate crops in dry seasons. Meanwhile, the cropland area is enlarged.
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
for disadvantaged women and men, there are employment opportunities and food self-sufficiency
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
because of increased farm income.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
this appraoch increase farm income, food self-sufficiency and employer opportunities
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
increase yield; Food self-sufficiency
- incremento de la renta(bilidad), proporción mejorada de costo-beneficio
increase farm income
- pagos/ subsidios
invest in SWCT
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Employer opportunities
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- incierto
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
Can given the recent escalation in payments made to land users for implementation under certain projects it seems that the costs will be too high to sustain. Currently the Ministry of Agricultural is demanding that in-depth cost-benefit analyses are carried out involving environmental, social as well as economic assessments
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Reduction of soil erosion (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: ensure the durability of the works implemented) |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Improvement of livelihood (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: spreading and improvement of a more holistic SLM approach focusing on livelihoods) |
| Many people involved and trained at different levels (pyramid system) (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: participatory approach) |
| More participation and involvement of local population (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Improve participatory approach and increase confidence between partners) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Abandonment of the works, less maintenance | Continue to support farmers and local institution and organisation. Repairing and maintaining in time. |
| Low impact on livelihood conditions | improve efficiency of SWC activities and participatory approach |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Less confidence between partners and less participation | improve dialog and communication; improve efficiency of SWC activities and participatory approach. |
| High costs: farmers depend on external support from the government; they are not willing to invest their labour without payments | New approach should give farmers loans for construction as now they use machines to do the work. In addition, search for cheaper SWC technologies and for improving the benefits. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Genin D., Guillaume H., Ouessar M., Ouled Belgacem A., Romagny B., Sghaier M., Taamallah H. (Eds) 2006. Entre la désertification et le développement : la Jeffara tunisienne. CERES, Tunis; de Graaff J. & Ouessar M. (Eds.) 2002Water harvesting in Mediterranean zones: an impact assessment and economic evaluation.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Water harvesting in Mediterranean zones: an impact assessment and economic evaluation.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Jessour [Tunisia]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- Compilador: Mongi Ben Zaied

Tabia [Tunisia]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- Compilador: Mongi Ben Zaied

Recharge well [Tunisia]
A recharge well comprises a drilled hole, up to 30-40 m deep that reaches the water table, and a surrounding filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer.
- Compilador: Mongi Ben Zaied
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos