Marshy land transformed into productive land [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Rahatul Islam
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1769 - บังกลาเทศ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
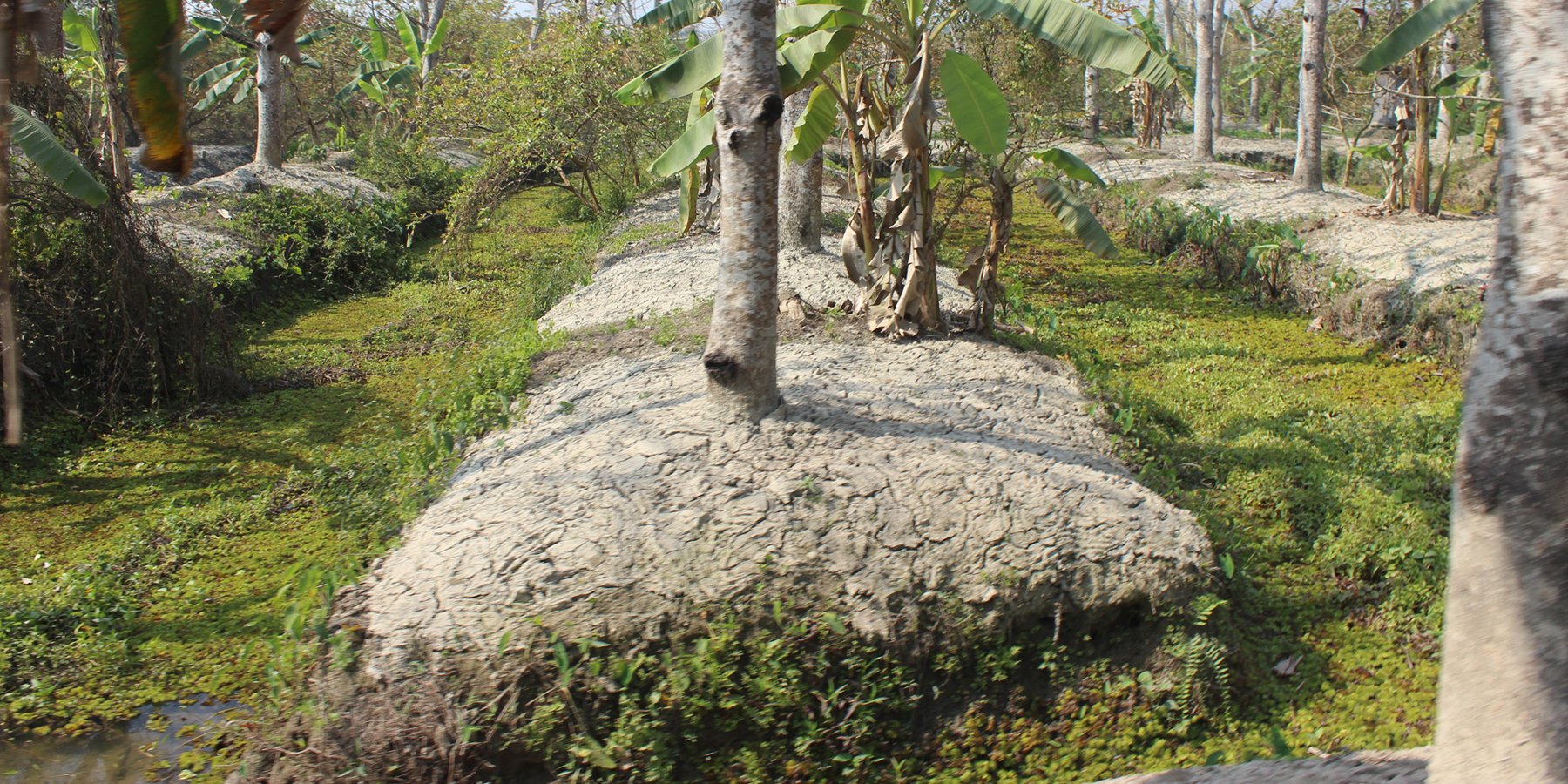
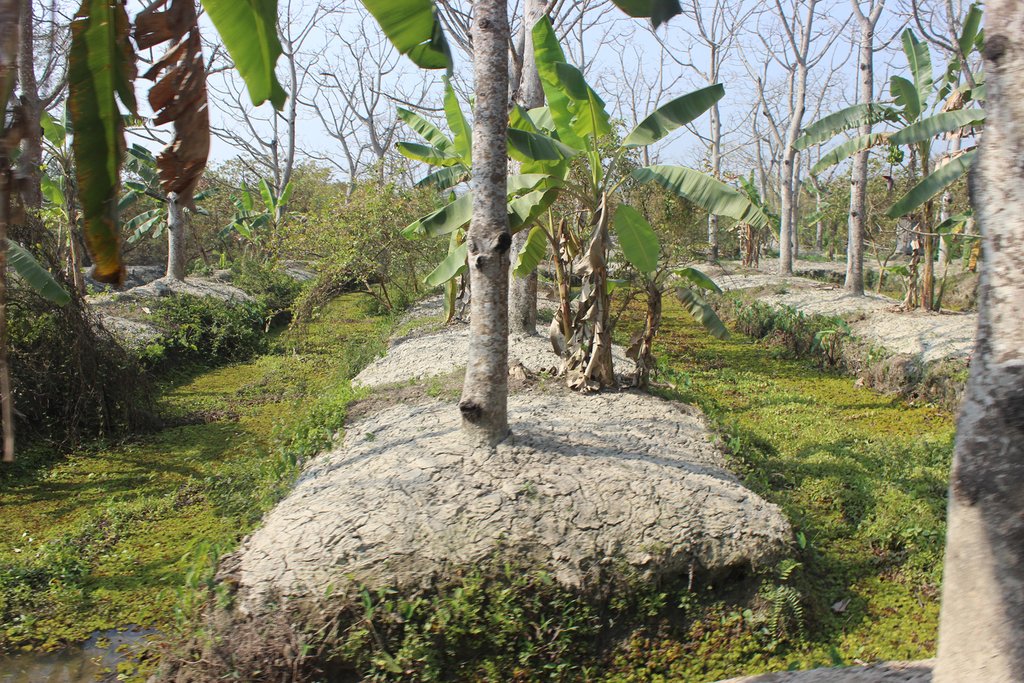
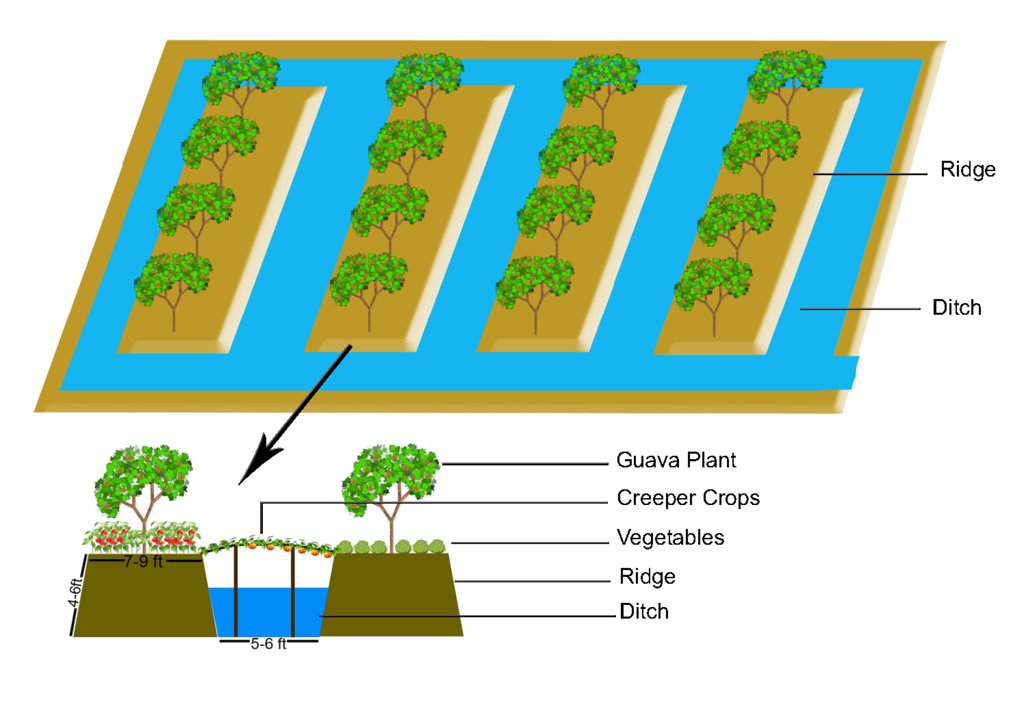
Marshy land is transformed into a ridge and ditch area, where the ridges are wide enough for the nursery of diverse plants and seedlings and where after 6-8 years the yearly management practices the land got strong enough for various agricultural practices (i.e. guava, hog plum, plums and timber wood plantation).
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
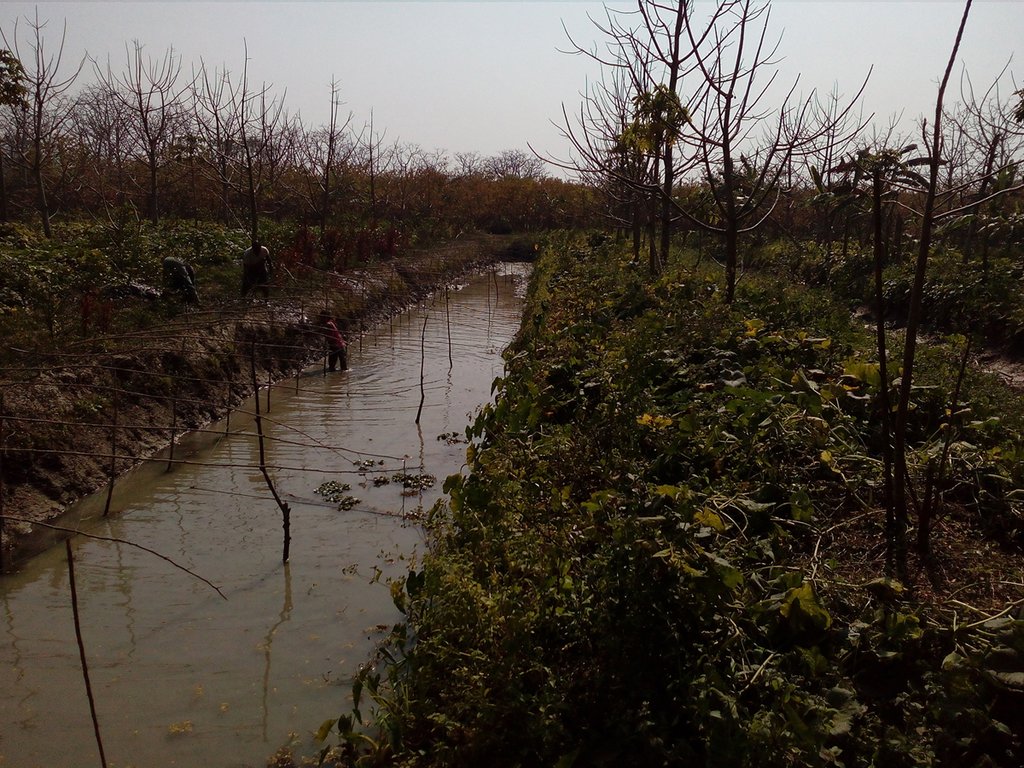
The technology of marshy land convert into ridge and ditch was taken by a community of southern of Bangladesh in order to make that area productive. Long year ago a continuous marshy land covered most of the area of southern Bangladesh like Pirjpur, Jhalokath. This area was flooded more than 9 month and remain perennial wet, that were totally unproductive. So, that technology not only increases agricultural production or economical benefits but also creates a green belt by developing agro-forest. The technology consists of ridge and ditch area. Ridges are elevated beds - land which is 4-6 feet high from surface and 7-9 feet wide. Length of each bed is variable according to size of the land. And ditches are canals - areas that are 5-6 feet wide and deeper than the normal surface area.
At initial stage elevated areas are not strong enough to start cultivating trees like guava, hug plum or other fruit plants. So they use it for nursery of diversified plants, fruit trees such as Banana and Papaya, vegetables, preparation of seedling sapling or as seedbed (rice). Management practices are running every year to develop the ridges and make them strong. Land users are putting soil/muck from the ditches on the ridges to make them higher and to give better protection from flooding water, to increase the fertility, to conserve moisture and reserve organic matter. Though eroded soil and other plant residues are accumulated in the ditches so ultimately they return over the ridge surface. Land become suitable after 4-5 year for planting various trees like guava hog plum, plums, lemons, Areca nuts and various timber producing tress like Teak (Tectona grandis), Mahogany (Swietenia mahagoni). Approximately 7 – 8 year after fruit trees are become appropriate and the physical and biological conditions of the sites have improved. Then land user start to cultivate various vegetables and other agricultural practices. Furthermore, sometime users set up a platform for creeper crops on the canal which works as support for Pumpkins and gourds. Trees and vegetables are irrigated from ditch/canal where water is reserve over the year, even in dry season if necessary. As a result of growing biomass, land degradation from the site has reduced and the fertility of the soil has increased. When fruit trees have reached its harvesting stage, the land users collect fruits for sale with expected income of about 1000USD. Vegetable also provide more than 500USD benefit from each site every year. Approximately 25 years after Mahogany, Teak, and other timber producing trees are getting mature and reach their harvesting stage. Land user cut the trees for selling with expected income of about 10000 USD from each site and size of approximately one hectare.
The technology is working well and is easily manageable by the land users. Nowadays not only farmers but also a large portion of population are interacting with that technology and their lifestyle have changed. Many people are also working to manufacture initial nursery products like seedling bag, earthen pot, creeping materials like bamboo, string, yarn, net, seedling and other material for preparing plant nursery, fruit garden, mixed agro-forest etc. Other people work to transport product from the area to the consumers and some people work to manufacture vehicles like boats, local vans etc. Also locale communities developed the largest floating market of Bangladesh.
The farmers are applying the technology without any extra financial support. According to the land users, they estimate about 200 – 300 family which have applied the technology. Approximately 350 person-day/ha were employed for construction and 50 person – day/ha sufficient for yearly maintenance work. 1600 USD was spending on the construction and most of the cost covered by owner. Farmers have faced some drawback such as undeveloped communication infrastructure and insufficiently developed market places. On the other hand, if they get support from government and related authority, this technology even become more beneficial for them.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Atghar Kuriana Union, Swarupkati, Pirojpur
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Barisal
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
sites are increasing day by day and enter into deep swampy land.
The technology expanding with time.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- vegetables - other
- rice
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- papaya
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
perennial
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Type of tree:
- Tectona grandis
- Swietenia mahagoni
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main crops are guava and hog plum. vegetables are harvested within five to six month. Bananas and papaya stay for several years. woody trees are harvest after they get mature.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การป้องกัน / การจัดการพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- convert marshy land into productive ridge and ditch
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pw (Waterlogging): ภาวะชุ่มน้ำ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land was lower and flooded more than 9 month and remain perennial wet. So the technology helps to overcome waterlogged condition and remain surface water over the year even in dry season at ditch area.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Method of marshy land transform into productive land bases on ridges and ditches. ridges are 7-9 feet wide and 4-6 feet high. Height is variable because yearly management practices increase the height of the ridges. Ditches are connected with each other from the edge/end of the each ridge. This types of connection support water movement and the moving of the boats for crop management and crop harvesting.
ผู้เขียน:
Selim Hossain
วันที่:
03/02/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 hectare
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5 USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Develop ridge and ditch | 7-15 days |
| 2. | vegetative cover with vegetables, seedling, sapling | 2-3 months |
| 3. | fruit trees, timber producing trees | 3-25 years |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Mainly the structural measure are important. But other measures are also important to make the technology stable. At initial stage without vegetative measure, soil will not become stable enough to take further steps of plantation.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | skilled labor | person-days | 300.0 | 5.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seedling (fruit trees) | piece | 500.0 | 0.1 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seedling (timber producing trees) | piece | 300.0 | 0.1 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | seedling bag | 1000.0 | 0.01 | 10.0 | 100.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | earthen pot | 1000.0 | 0.01 | 10.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1600.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1600.0 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
3.0
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | management practice to make ridges and ditches uniform and productive | 3-7days |
| 2. | seasonal vegetable | 2-3 month |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | skilled labor | person-days | 50.0 | 5.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seedling vegetable ( e.g gourd) | pieces | 250.0 | 0.05 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | bamboo | pieces | 50.0 | 1.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | string, ropes | piece | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 317.5 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 317.5 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Basket, spade and other equipment which are needs to develop the site is not carried by land user, these are collecting by laborers. transportation cost also carried by local traders. farmers are represent their product in local market (floating guava market) and then local traders are buy it and transport it to city or capital
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Length of rainy season 5 month that causes water level becoming close to the bed.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
flooding normally occur in rainy season but it is not destructive for the technology
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
This green belt workes as shelter for birds.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Size depends on user capability. Sometime users like to make smaller sites which are easy to maintain. Larger sites reduce waste of land and give extra space to cultivation.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
bare land become productive
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
organic materials are mainly used
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
vegetable and fruit resides can use as animal food
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
timber trees not only fill local demand but also supply in many area of Bangladesh
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop failure by flooding is protected
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Here produce timber, fruit, vegetable, seedling sapling etc
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
production area remarkably increase
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Very easy and local farmers manage it easily.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water is available even in dry season
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
ditch contain enough water in available condition for plant
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Peoples not only depend on agriculture.
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It reduces the economic disparities as it opens new working places.
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Net yearly production of food increases.
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
People get proper nutrient from fruits and vegetable, which are totally chemical free
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not only men but also women are work on site. normally land users family members are always help them every way
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Total amount of water is reduced.
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Good quality water found in all seasons.
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Drainage condition of cultivated ridge area is very good
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetative cover reduces the total evaporation .
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Yearly management practice helps to increase the soil moisture.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Annual and perennial crops cover the area.
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Plant residue.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Release reserved carbon from muck.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
A bare land convert into vegetative cover
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Variety among plants and crops is seem.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The trees serve as nesting habitat
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
ridges are free from flood
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
water reserved in ditch in dry season
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
large vegetation consume huge amount of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases
ความเร็วของลม
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
To develop such kinds of structure requires a huge amount of investment which is not covered in a short time. But in the future it becomes highly beneficial. Yearly maintenance practices not only increase soil fertility, moisture and nutrient availability but land become higher from flooding water as well.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The Technology increase the amount of productive land. |
| Peoples economic condition have changed to the better. This technology creates working place for many people. |
| The Technology increase availability of fresh products. e.g vegetable, fruits. |
| The development of largest floating market of Bangladesh is seen as very positive. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The Technology increase the greenhouse gas consumption. |
| Seedling and sapling are distributed in whole country and increase the vegetation cover. |
| It fulfills the demand of timber and it reduces the deforestation of natural forests. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The communication and transport infrastructure is not very well developped. | Reconstruction of the road. |
| Floating market are temporary and disapear after morning. | Make stable market places. |
| Farmer have no precise knowledge about crop, seeds and hybrid varieties. | Government and non-government organizations services is required. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Water ecosystem is hampered | More research should be taken |
| Huge amount of reserved carbon get released. | Planting enough tree to consume that |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
24/01/2017
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล