Emergency infrastructure, shelter and access [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: TUHIN SAMADDAR
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano, Hanspeter Liniger, Nicole Harari
দুর্যোগ সহনশীন অবকাঠামো উন্নয়ন (Durjog-shahonshil abokathamo unnayon)
technologies_664 - บังกลาเทศ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Emergency infrastructure, shelter and access: 28 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure: 2 สิงหาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure: 10 พฤศจิกายน 2017 (inactive)
- Emergency infrastructure including shelter and linked transport infrastructure: 5 มีนาคม 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
Project Staff:
Mustafa Golam
+880 1718770373 / +880 1730799762
pmdrrwash16@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Project Manager, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
บังกลาเทศ
Project staff:
Razzak Abdur
+880 1730 799763 / +880 1730 799763
razzak.pe@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Project Engineer, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
บังกลาเทศ
Project Staff:
Islam Saiful
+880 1730 799746 / +880 1730 799746
saiful644@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Field Officer DRR and Training, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
บังกลาเทศ
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Swiss Red Cross (Swiss Red Cross) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
04/10/2016
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology presented has no direct bearing on land degradation.
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Emergency infrastructure, shelter and access, consists in establishing flood shelters (for people and animals) including flood-proof collective water sources and communication infrastructure as well as health and school facilities cum emergency shelters. The infrastructure is adapted to the specific context of the ‘Char’ land in Bangladesh. Together with improved flood related forecasting measures this allows for a relatively safe and healthy living and has led to increased and timely land use, resulting in adapted livelihoods, reduced health costs and increased income.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The technology applies to the specific context of the ‘char’ land, characterised as riverine sandy island. More than 80% of the land in the intervention area can be classified as Char and is inhabited by 60% of the population served by the project. Every year, especially during floods, the rivers deposit huge amount of silt sediment that makes the land fertile. At the same time, river action washes away some portion of the char which at times can be quite large and has a strong impact on people's lives and livelihoods. The char land is furthermore characterised by its lack of public infrastructure and remoteness to public services.
The technology is applied largely in relation to human environment. It consists of setting up an emergency infrastructure and ensuring access during times of crises/hazards. It has to be understood in close interrelation with approach of setting up an early warning system (for a description of the related approach, see reference in section 1.5 above). The emergency infrastructure includes flood shelters (for people and animals), flood-proof collective water sources and sanitation systems, communication infrastructure such as foot bridges and elevated rural roads, as well as flood-proof health and school facilities that also serve as emergency shelters during hazards. The purpose of the technology is to ensure safety of life and protection of assets during times of emergency and also to mitigate sufferings related to floods. The major activities include facilitating the development of community-led risk reduction action plans and their implementation through community participation and engagement of local governance institutions. This includes maintenance of the built infrastructure as the joint responsibility of the community and the local government.
Land use, especially sowing and harvesting, is increasingly linked to flood related forecasting measures which has led to significant adaptation in the timing of farming activities. This coupled with the creation and access to emergency infrastructure allows for a relatively safe and healthy living. The adopted technology and approach has led to adapted livelihoods, reduced health costs and increased income. The technology has furthermore led to mainstreaming disaster risk management in policies and approach of local government institutions. Increasingly the local goverment’s cash and food for work programmes are targeting establishment and/or reinforcement of emergency infrastructure that can cater to larger population. Increased investments are made especially towards flood shelters and improving communication and access to emergency infrastructure. Since the technology is based on local knowledge and has been developed in consultation with the involved communities, it is generally well accepted with a fair degree of ownership and involvement. However, parts of the region are also prone to river erosion and this has a destructive impact on built infrastructures. The technology does not assure any safeguard against this form of uncertain river action.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
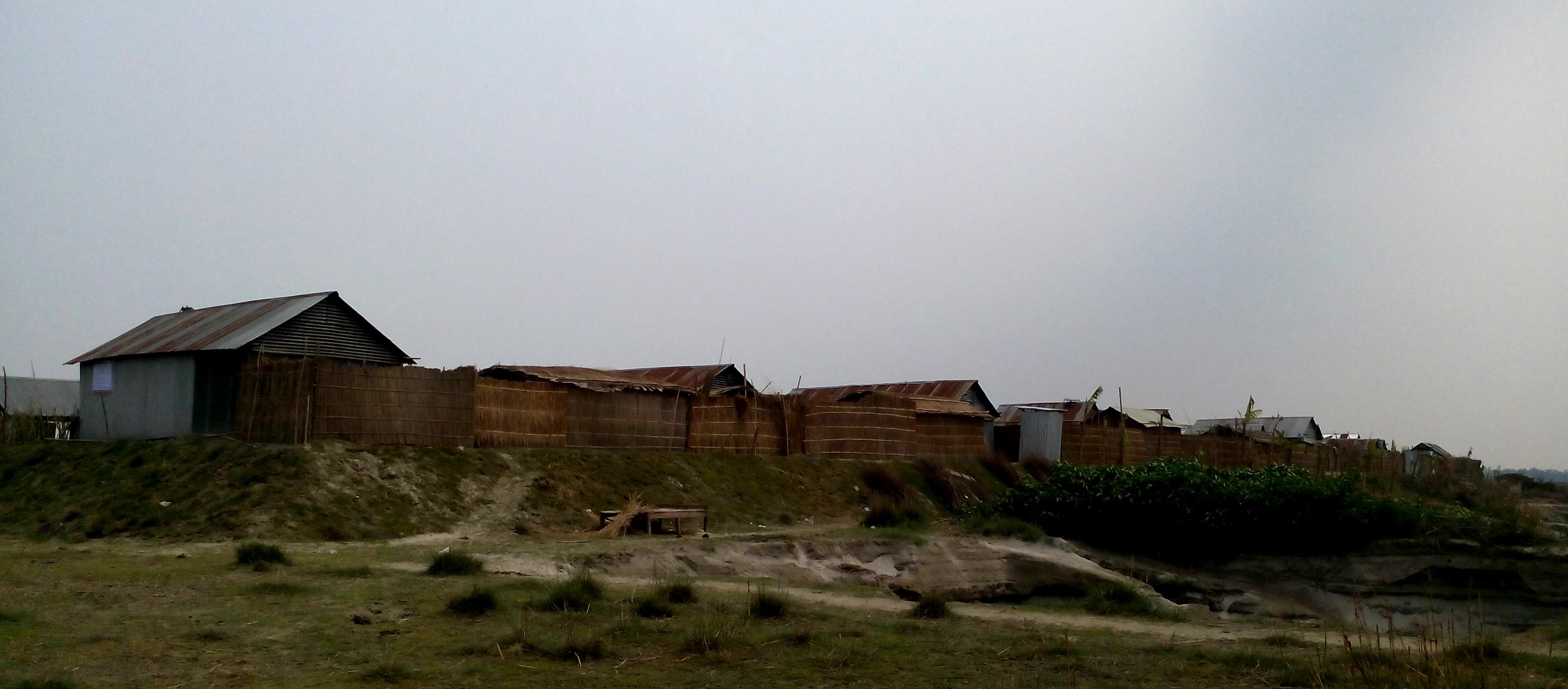
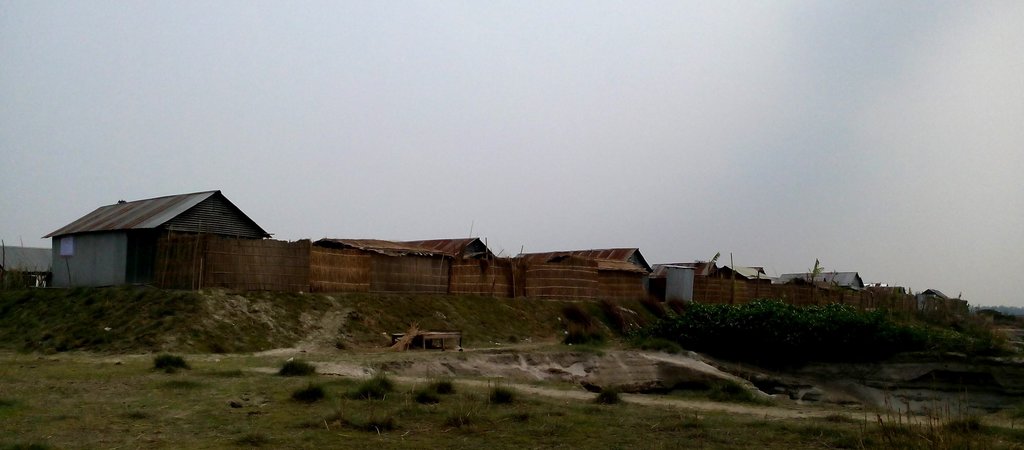
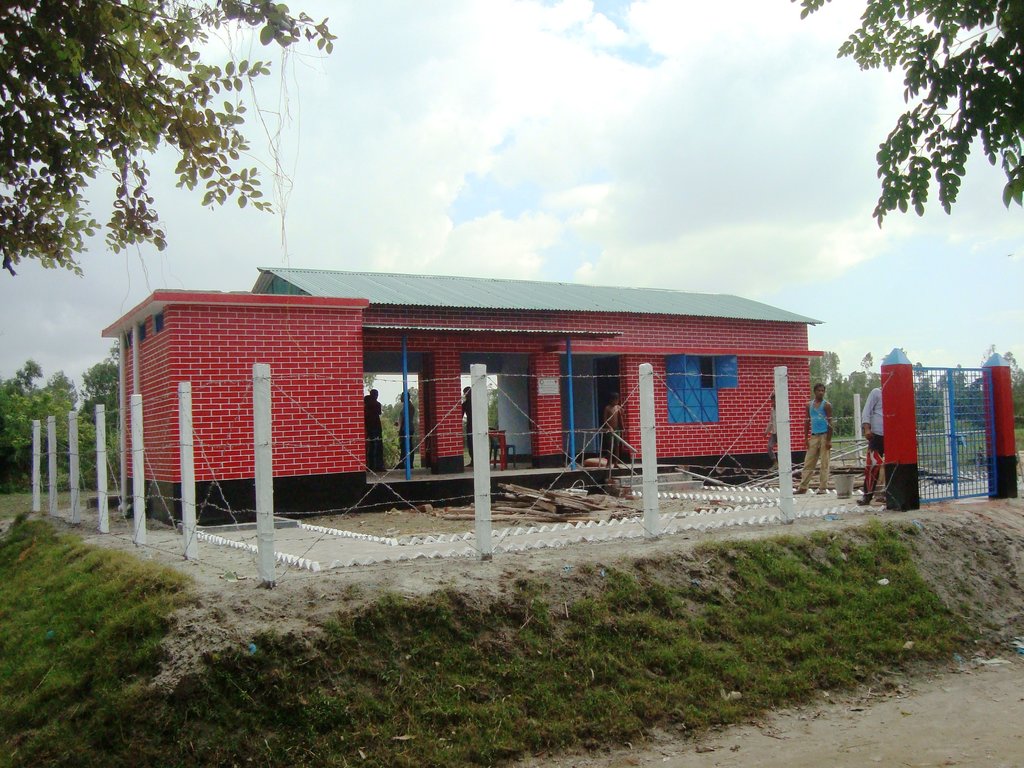
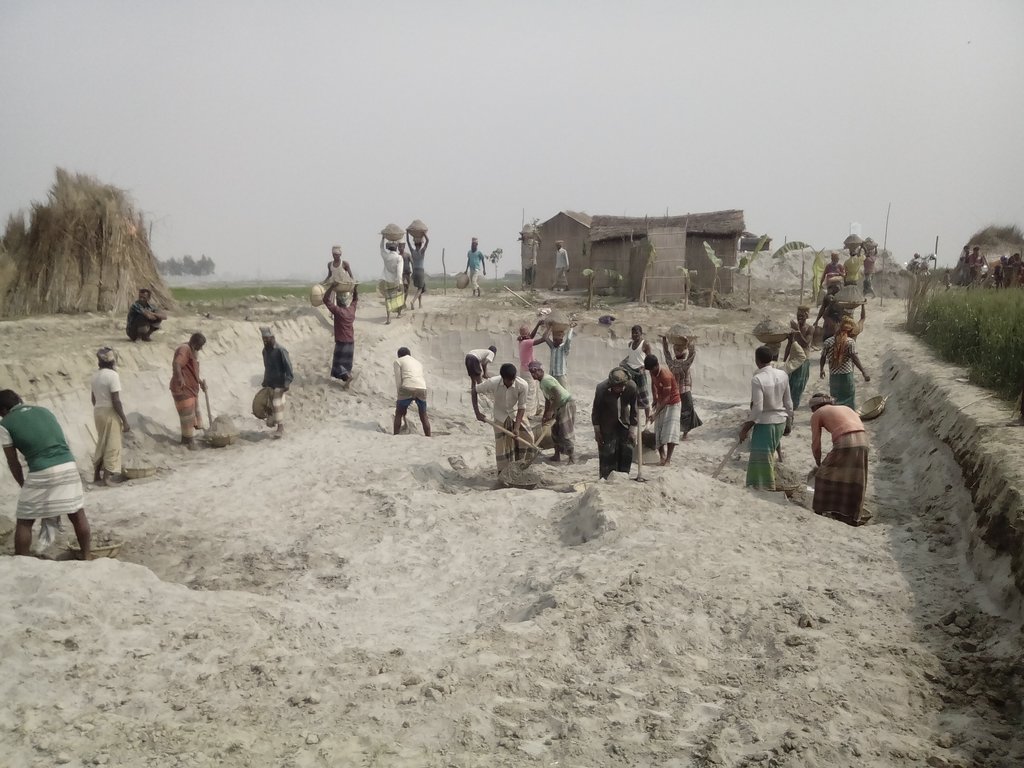
คำอธิบายภาพ:
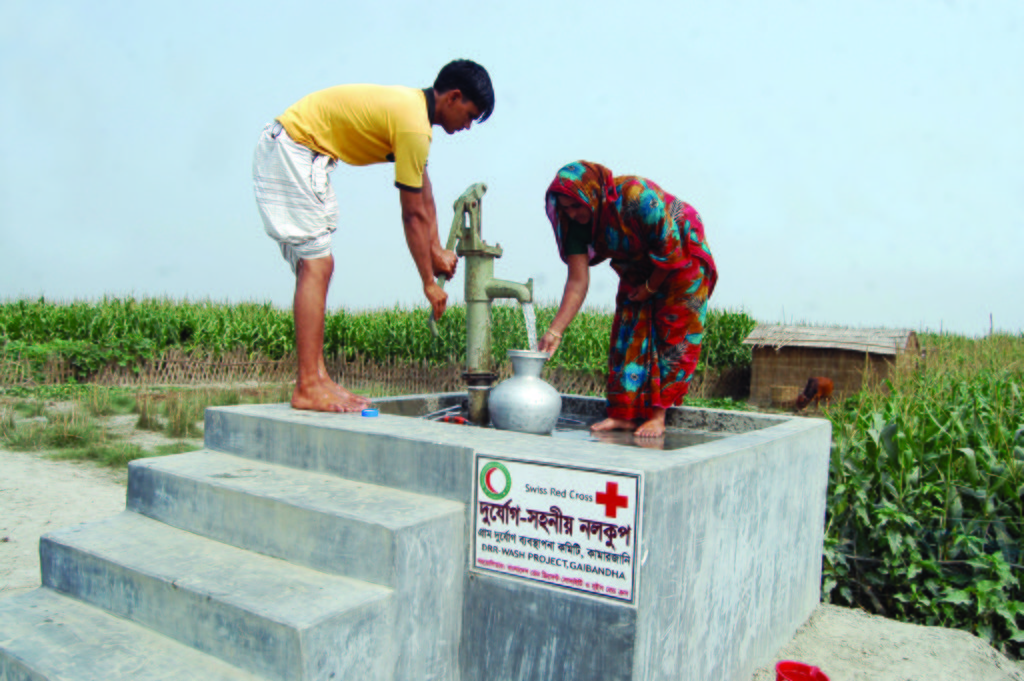
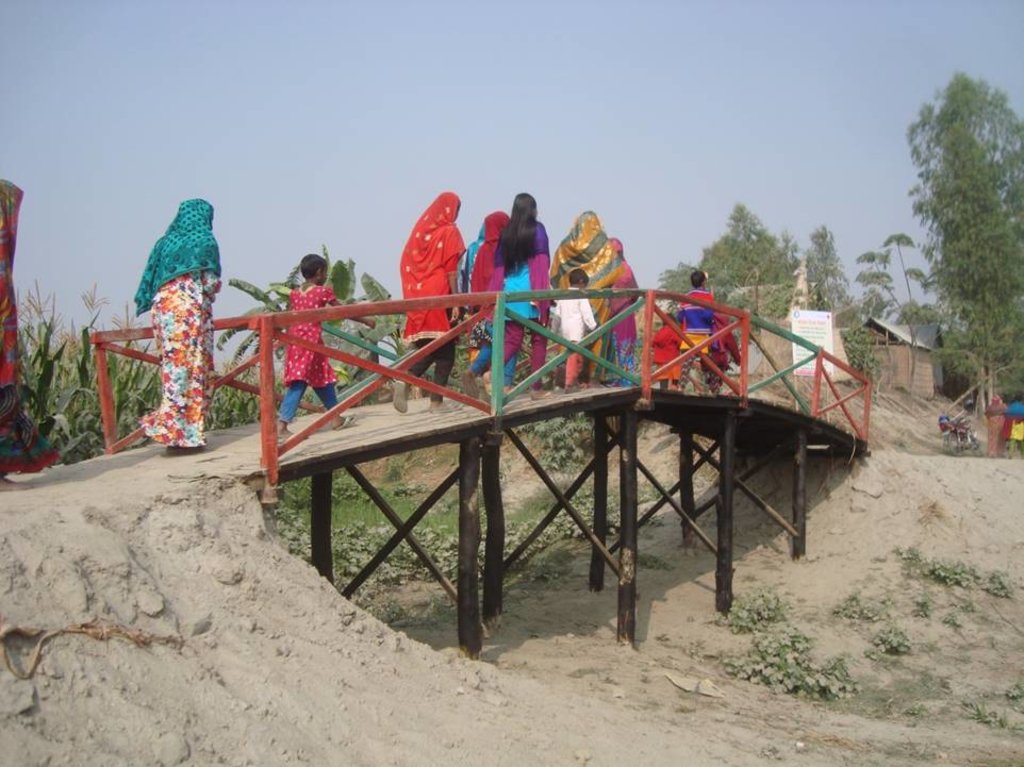
Glimpse of few technologies that served as emergency infrastructure, shelter and access to health and WATSAN facilities.
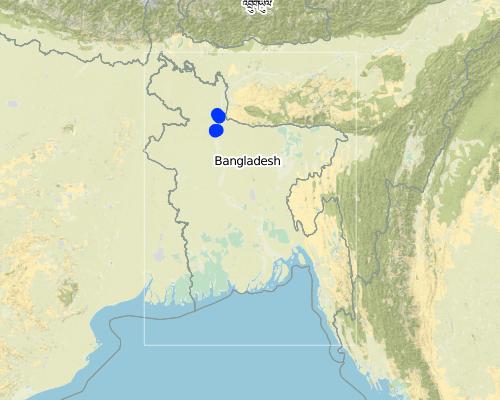
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
North-Bengal
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kamarjani and Mollar Char union in Sadar Upazila and Haldia union in Shaghata Upazila of Gaibandha District
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Since the disaster resilient infrastructure set up by the project is installed at a huge number of sites (as indicated in the description above), only a sample of the various emergency infrastructures are indicated on the map above (If needed a comprehensive GPS reading of all infrastructure built by the project can be provided separately).
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2014
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology has elements of traditional practice (raised plinths for flood protection) and project promoted interventions (emergency shelter and access infrastructure).
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Paddy, Wheat, maize, jute, chilli, pulse, sweet potato

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
- การจราจร ทางถนน รถไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Despite the lack of public infrastructure and services and being exposed to natural hazards people tend to prefer to live in the char as it brings significant economic benefits for them: crops grow rapidly and abundantly with significantly lower input costs than on the mainland.
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Before the intervention, people living on char land depended on their traditional early warning mechanisms and were frequently surprised by floods that destroyed their crops and put their lives in danger. Due to recurring floods, people didn’t have the means to improve their built environment.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply for the land comprises a mix of rainfed, irrigated and post flooding sources.
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 3
ระบุ:
Kharif (monsoon crop), Rabi (winter crop), and Summer/pre-monsoon crop
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
Cow, buffalo, goat, lamb and donkey are very common in the area. People rear these for cultivation, transportation and for having meat. Every household have at least a pair or more of livestock.
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- Emergency infrastructure, shelter and access
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Though emergency infrastructures are built at specific sites, their use and benefits are evenly spread over an expanded area.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
- S9: ที่พักพิงสำหรับพืชและสัตว์

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M4: การเปลี่ยนแปลงช่วงเวลาให้เหมาะแก่การทำกิจกรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In addition to the structural and management measures described above, the technology involves additional elements such as flood-proof collective water supply and sanitation systems and communication infrastructure.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
NA
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
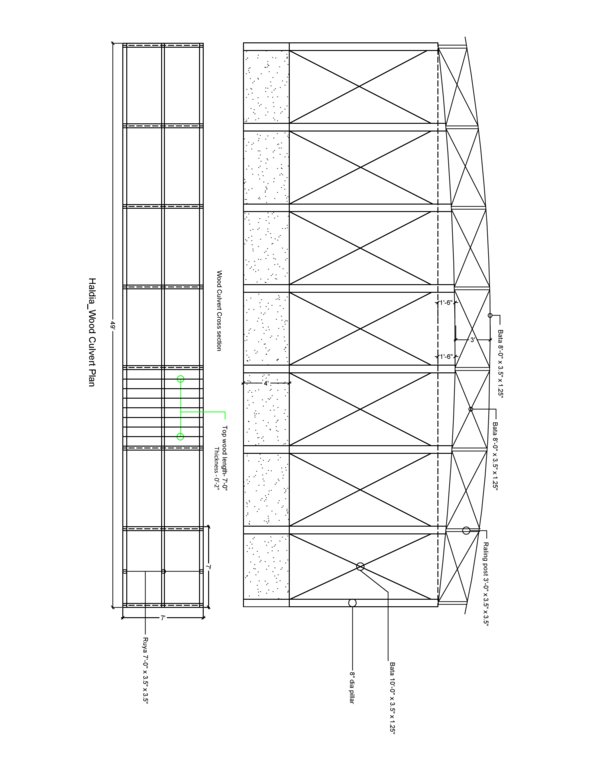
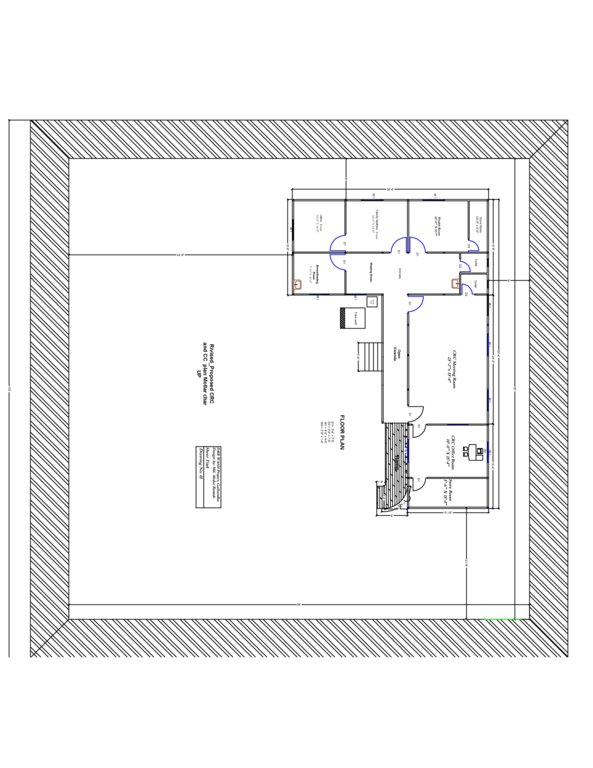
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
The built structural mitigation options have following technical specification:
1. School plinth: Dimension: Length-112' x Width-75' x Height- 5.5', plinth slope- 1:1.5, Capacity: 540 person, Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass)
2. Flood shelter: Dimension: Length-220' x Width-220' x Height- 5.5', plinth slope- 1:1.5, Capacity: 350 families, Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass)
3. Road construction/repair: Dimension: Length-925' x Width-12' x Height- 3' (from existing level), plinth slope- 1:1.5, Capacity: 3 villages (approx:1000 families), Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass).
4. Wooden bridge: Dimension: Length-60' x Width-7' x Height- 12', plinth slope- 1:1.5, Capacity: 600 families approximately, Construction material used: wood, nails, tar, soil and turfing
5. Community Resource Centre cum Community Clinic (CRC-CC): Dimension: Length-110' x Width-80' x Height- 5.6', slop- 1:1.5, (Building size: 100' x 18' x 10') Capacity: 2000 families in 5 village, Construction material used: soil and turfing (grass), bricks, sand, cement, rod, iron angel and CGI sheet.
6. Disaster resilient tube well: Dimension: Length-5' 10" x Width-5' x Height- 3', Boring:100 feet, Capacity: 200 families, Construction material used: bricks, sand, cement, rod, tube well head, pvc pipe, cylinder, piston rod etc. Vertical intervals: 2 in each village.
7. Tube well platform: Dimension: Length-4' 10" x Width-4' x Height- 1', Capacity: 100 families, Construction material used: bricks, sand, cement, pvc pipe
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
School plinth: 125,000BDT, Flood shelter: 496,000BDT, Road construction/repair: 92,000BDT, Wooden bridge: 85,000BDT, CRC-CC: 1800,000 BDT, Disaster resilient tube well: 30,000BDT, Tube well platform: 4,700BDT
ระบุปริมาตร ความยาว เป็นต้น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
Mentioned above
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Bangladeshi Taka (BDT)
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
79.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
350 BDT
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Raising school compound | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of Flood Shelter | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 3. | Road construction above flood level | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 4. | Construction of wooden bridge | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 5. | Construction of Community Resource Center (CRC) house | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 6. | Installation of disaster resilient (DRR) tube well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 7. | Construction of concrete platform of old tube well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As can be seen that all the above activities are structural in nature and can be undertaken efficiently only in dry season.
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
ถ้าเป็นไปได้ให้แจกแจงรายละเอียดต้นทุนการบำรุงรักษาตามตารางข้างล่างดังต่อไปนี้ ให้ระบุลงไปถึงปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่ายต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า ถ้าไม่สามารถแจกแจงรายละเอียดต้นทุนได้ ให้ทำการประมาณค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดในการบำรุงรักษาเทคโนโลยี:
43064900.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
10% of all construction cost (except CRC) is borne by the user. Another 15% (approx) is provided by the local government bodies. Remaining 75% is subsidised by the project.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Defining costs of establishment is bit tricky as the establishments are not same in nature and also size and costs vary from one village to another depending on the geographical location. However, average unit costs of built assets are given below:
1. School plinth: average unit cost: 125,000BDT, Number of unit constructed:4, Total cost: 500,000 BDT
2. Flood shelter: average unit cost: 496,000BDT, Number of unit constructed:4, Total cost:1,488,000 BDT
3. Road construction/repair: average unit cost: 92,000BDT, Number of unit constructed:4, Total cost:20, 368,000 BDT
4. Wooden bridge: average unit cost: 85,000BDT, Number of unit constructed:4, Total cost: 340,000 BDT
5. Community Resource Centre cum Community Clinic (CRC-CC): average unit cost: 1,800,000BDT, Number of unit constructed:3, Total cost:5,400,000 BDT
6. Disaster resilient tube well: average unit cost: 30,000BDT, Number of unit constructed:53, Total cost:1,590,000 BDT
7. Tube well platform: average unit cost: 4,700BDT, Number of unit constructed:790, Total cost:3,713,000 BDT
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Raising school compound | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of Flood Shelter | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 3. | Road construction above flood level | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 4. | Construction of wooden bridge | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 5. | Construction of Community Resource Center (CRC) house | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 6. | Installation of disaster resilient (DRR) tube well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
| 7. | Construction of concrete platform of old tube well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During dry season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The user and local government (UDMC) are mainly responsible for maintenance of all built assets and structures including the CRC. The relevant operation/repair and maintenance training has been provided by the project.. Maintenance manuals and guidelines have been developed and disseminated. Also, repair and maintenance equipment has been provided to cadre of users/caretakers trained in repair/maintenance work.
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
N/A
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Transportation of raw material to sites varies across seasons. In the dry season it is much higher compared to monsoon as the delivery of material is easier in the latter due to extended river outreach.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
2134.80
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Annual average rainfall;
Rainy season: April- October
Occurrence of heavy rain: June-July
Length of dry period: November-March
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
18 Gaibandha Sadar, Gaibandha
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Tropical humid climatic zone.
Temperature: maximum 33.5°C, minimum 10.5°C
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Information on altitudinal zone collected from the website: www.getamap.net
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
N/A
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
In the dry season water crisis occurs. Open defecation and use of pesticide in farming are key pollutants of water sources.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Biodiversity can be rated as moderate or medium both in terms of species and habitat. It is stable and and often self generating.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
N/A
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
People living in Chars have small landholding which often produces enough for subsistence and, in some cases, for market purposes.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เช่า
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land ownership is quite complex as Chars by nature are unstable habitats. In principle land is owned by state but in most cases the politician - musclemen nexus exercises real control. This results in leasing and renting of land which is the predominant form of land ownership in Chars.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
Access to mobile phone and internet:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3600 kg/hectare (maize)
หลังจาก SLM:
1,1400 kg/hectare (maize)
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop production has increased thrice due to stability of household which has led to stable use of land in the chars.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
No safe drinking water source was available
หลังจาก SLM:
More than 40% water source are safe
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Collective water supply systems have groundwater sources and thus no treatment is needed. Further, aspects of availability, easy access and sustainable availability of sufficient water of acceptable quality are well considered. Families can access 10 litres per capita per day (LPCD) during emergencies (which is in line with Sphere standards) and during normal times 40 LPCD is what families can collect from these water sources. All such water sources are within a distance of 50 metres from the settlement as per Bangladesh standards.
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Reliable data not available
หลังจาก SLM:
All households have access to safe drinking water as per govt. standard for rural areas
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The govt. standard for rural areas is approximately 40 LPCD (litres per capita per day): the collective water infrastructure built by the project ensures fulfillment of minimum standards set by the govt for safe drinking water.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
25% families had farm income
หลังจาก SLM:
95% families have farm income
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cattle and poultries are safe during disaster
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The disaster mitigation measures has significantly improved the health situation of the target population.
สถาบันของชุมชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Few credit groups in intervention villages
หลังจาก SLM:
30 CBOs (VDMC) and 3 Local Govt. Committee (UDMC)
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
CBOs and govt mandated institutions have been promoted through project initiatives.
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
CRC is also being used for UDMC office which is an important committee of union parishad.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Widespread
หลังจาก SLM:
Rare
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Conflict sensitive approach has significantly reduced the incidence of conflicts.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Data not available
หลังจาก SLM:
Same
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The disaster resilient tube well ensures year round drinking water.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
95% families were effected from flood
หลังจาก SLM:
47% families are affected from flood
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The above figures are from 2016 when Bangladesh experienced one of the worst floods in recent times.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็นเกี่ยวกับการประเมินผลกระทบ:
N/A
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
| พายุทรายหรือพายุฝุ่นประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ดี |
| คลื่นความหนาว | ดี |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
| ดินถล่ม | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In some cases the appropriate answer would have been "not applicable" but since this is not there, we have selected "well".
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The limited returns that have been generated by the project is highly valued by the users from a cost - benefit perspective; especially when they understand that the project is not directly linked to land management practices. Thus, the indirect benefits are perceived to have high value.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
Out of a total of 8828 HHs targeted by the project, around five thousand HHs in three union have benefitted from the implementation of the technology.
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การมีแรงงานไว้ให้ใช้ (เนื่องจากการอพยพย้ายถิ่นฐาน)
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Dredging machine has been used for building some emergency infrastructure at few sites due to unavailability of labour at the time of construction.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
- Emergency structures have a multipurpose use that includes community meeting, workshop and training - Expanded opportunities of communication during flood |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
- Community is aware and driven to implement flood preparedness and risk reduction measures on its own - Appropriate measures can significantly change people's mindset and behaviour |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
|
- River erosion threatens built structures - High investment needed for building physical structures (e.g. CRC building) in the char which the local government and community find difficult to finance without external support. |
- Careful site selection for construction work through in depth discussion with community people supported by scientific analysis - Install portable semi-permanent structures in the char - Lobby for greater decentralisation of finances to local government |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
|
|
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
3
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
4
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
2
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Latrine and Tube well maintenance manual, SRC-BDRCS-DASCOH
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
SRC
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
N/A
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล