Water Spreading Weirs [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Biye Baahiwe
technologies_6715 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mohamed Badal
Natural Resource Development Protection and Utilization Department of Somali Region Bureau of Agriculture.
เอธิโอเปีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is soil and water conservation and degraded land rehabilitation technology. Furthermore, the water harvested can be used for spate irrigation and growing food crops and livestock feed.
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [เอธิโอเปีย]
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Water Spreading Weirs are designed to protect the degradation of agricultural fields and rangelands. They contribute to soil and water conservation and enhance the productive use of dry valleys for food crops and livestock fodder production via the harvest and spread of runoff water and fertile soils.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
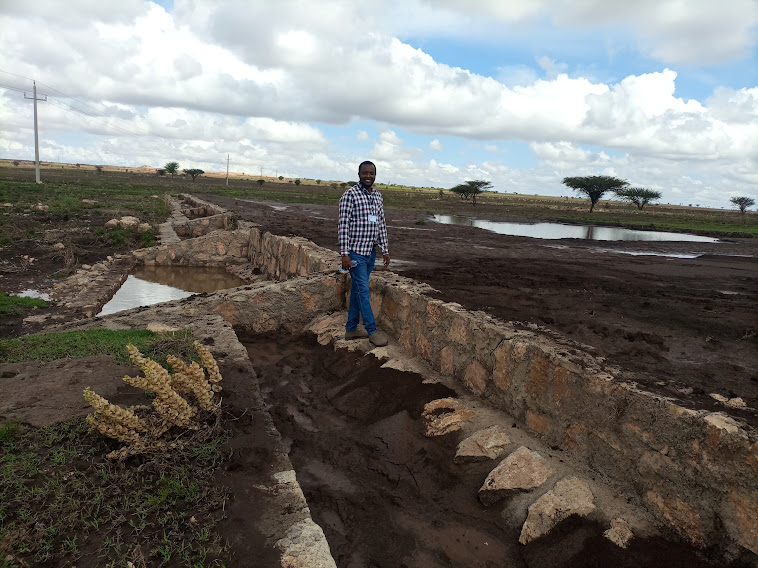
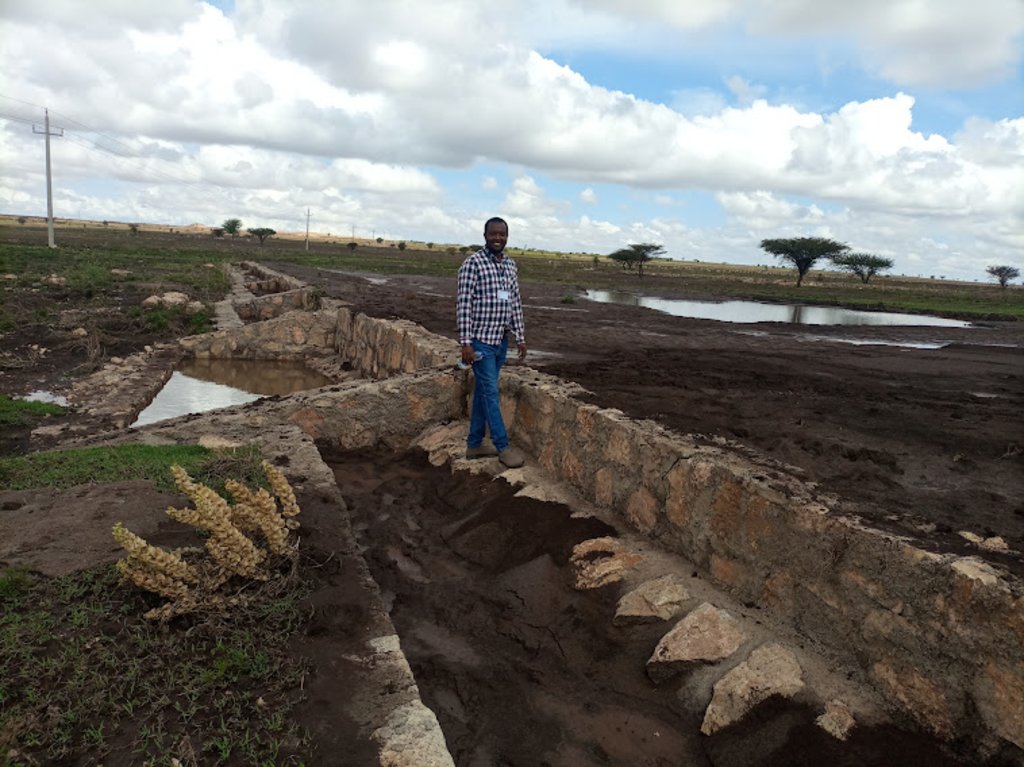
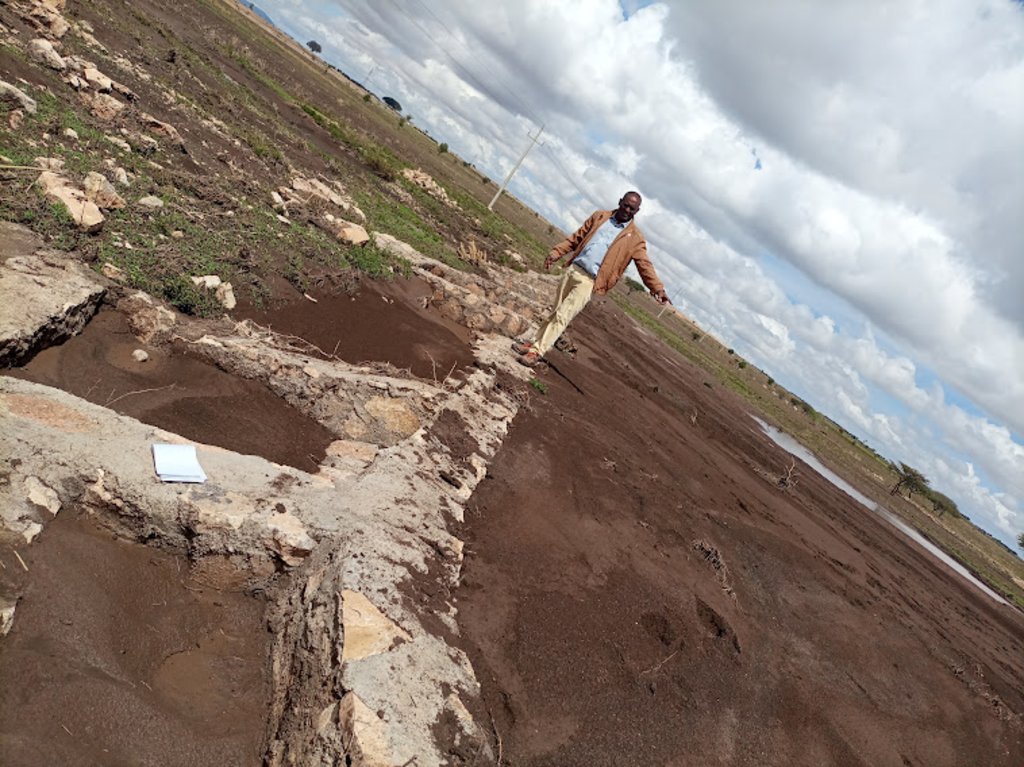
Water Spreading Weirs (WSWs) spread runoff water to the tips of the structure's wings, slowing down the speed of runoff and arresting the sediment pouring downstream. WSWs are applicable both on farmland and rangelands to improve the productive use of the land’s resources. They protect soil erosion and control gully development as well as increasing surface and sub-surface water availability. Activities such as mobilization of the community through awareness creation are among the numerous tasks implemented to put the technology in place. The community participates in site selection and participatory planning. Other stakeholders assist in area delineation, profiling the implementation area, and design. Labour and inputs such as surveying and construction materials, notably stone, sand, water, and cement, and equipment such as line levels, theodolites, spades, hoes, forks, string and measuring tapes etc. are required. On top of these, implementing the technology is supported by satellite images and ground validation exercises.
The main purpose of the technology is to reduce land degradation, harvest and use runoff water for spate irrigation and household uses, improve environmental resilience to the risks of drought, increase the depth and fertility of land behind the structure by capturing sediment washed away, allow infiltration of water and increase overall production of food and fodder crops. Also, the contribution to groundwater recharge is immense. Furthermore, it allows the agropastoral community to grow both cash and food crops which helps to ensure food security. Above all, the water harvested means people can remain in the area and that their livestock have access to drinking water for about three months after interception of rainfall. However, the agropastoralists may be discouraged by the size of the WSWs which can be from one hundred to over two hundred meters across. Care also must be taken that the structures do not cross livestock migration routes.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
The photo is trying to portray the water and soil harvested/stopped from running downstream. The detachment and removal of the topsoil without cover and fragile soil types are easily removed and transported to a long distance beyond the regional territory. The trends denied the productive use of land resources. In contradiction, the structure mitigates the loss of water and soil.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Video for this technology was not captured.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Somali
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Amadle kebele, South Jijiga district
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is located on the farmland used by the extended family and beyond.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2022
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology was put in place in partnership with the government bureau of agriculture and line office with the Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) Project of the GIZ in the Somali Region.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - sorghum
- vegetables - other
- legumes and pulses - soya
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
The legume crop is chickpea. Whereas, the vegetables are tomato and onion.
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Maize is intercropped with chickpeas.
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Cereal crop sorghum rotates with maize and chickpeas. Essentially, crop production suffers from a lack of adequate rainfall. For example, during the last two to three years the area experienced drought. Mainly livestock supports the livelihoods of the inhabitants.

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- Agro-pastoralist
Animal type:
- goats
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- camels
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Essentially, the farming operation is practiced by oxen-plow in which case the animals provide traction force whereas crop residue supply feed to the animals.
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- milk
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- transport/ draught
- meat
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Agro-pastoralism is the common practices in Amadle kebele of south Jijiga district.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The rainfall distribution is erratic with violent erosive feature flooding the plain with severe damage when flowing downstream.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is Water Spreading Weirs, stop the run-off and distribute the water across the farmland.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม
- Eo (Offsite degradation effect): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hq (Decline of groundwater quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology/structure contributes strongly to soil and water management. The tremendous loss of both resources is immensely reduced by the application of water spreading weirs.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology reduces the speed of runoff, stores the sediments, and distributes the water across the structure which creates an opportunity for spate irrigation and the use of residual moisture as supplemental sources of irrigation for growing early maturing crops.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
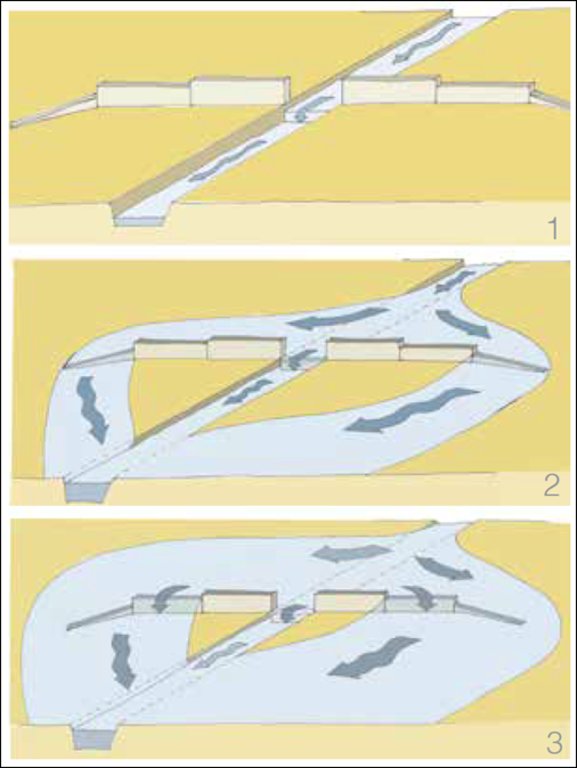
Spate schemes depending on the increase supply flow:
Part i: The flow of small flood rested channel in the river bed
Part ii: A small or medium flood and overflows pours on the lower wings, &
Part iii: A large flood also pours on high wings.
ผู้เขียน:
Anonymous consultant
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
1 WSW
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
Variable ( could be from 100m to over 200m depending on the steepness and width of the farmland.
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
8.414 USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assessing the field (observation) | |
| 2. | Consult the local community along with agricultural partners at different levels | |
| 3. | Surveying and profile data collection | |
| 4. | Develop design and get approval | |
| 5. | Outsource the engineering/masonry works | |
| 6. | Train the masonry workers | |
| 7. | Supply materials | |
| 8. | Implement (execute the excavation and the masonry work) | |
| 9. | Monitor the development (construction supervision) |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Note: 1 USD = 53.481 Ethiopian birr (ETB) when this data is collected.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
27490.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
So far, the project entirely cover the investment and maintenance costs.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
According to the project and regional bureau of agriculture experts, a single structure costs 27, 490 USD. However, in one cascade (dry valley treatment unit) about 8-10 structures are necessary to successfully address the objective of the technology (Soil and Water Management) and ensure productive use of the land from soil arrest and residue of moisture captured in the area. It also enables the use of runoff for spate irrigation.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assess and identify the damage | During the off-season for ease of access to the sites |
| 2. | Estimate the level and cost of damage | During the off-season |
| 3. | Supply materials | |
| 4. | Employ the masonry worker | |
| 5. | Construct /maintain the damaged parts | Before the short/long rainy season. |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Maintenance costs are largely associated with the degree of damage and cost of materials and masonry worker or labor costs that consistently changing in current Ethiopia.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
12154.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The cost is borne by the project.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technical experts give only an estimate of both initial investment and maintenance costs. Variations in materials and labor costs are frequent beyond the imagination. However, maintenance depends on the degree of damage. It seems that maintenance cost estimation takes the highest sides which may dishearten the adoption of the technology in the absence of projects.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Economic crisis and frequently escalating material costs along with rising financial inflation.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
750.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainfall is erratic and erosive. The project site receives rainfall twice a year (Belg- short rain from March to April and Meher- long rain from June to September). However, the number of days on which rain is intercepted is fewer than the ranges stated over here.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Jijiga Meteorology station
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
South Jigjiga district is characterized by hot weather.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The topography where WSW technology/structures are put in place is mostly on gentle slopes across the dry valley drainage line.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
The soil ranges from black silty loam to brown silty and fragile soils that are highly vulnerable to flood. It easily detached and moved away with runoff.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
As the weather of the area is often too hot salinity is not uncommon in the aquifer.
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Rainfall is characterized by erratic and erosive nature. Therefore, flooding is common when heavy rain is intercepted.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Less biodiversity of plant species. Acacias are the common trees, and opuntia and euphorbia species are also common plants in the area. A wild species that may be considered invasive is common in the area. The lower growing weed (wild species) locally known as Weylowed is suggested introduced from Yemen to the Somali part with onion.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
It is the community who are benefiting from the technology. Furthermore, this respondent is a regional SLM specialist. Therefore, specific information on age and gender is not given here though the community was also consulted.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Extended family groups of four households are using the land where the WSW is put in place.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
Land use right is based on clan and extended family.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land is also owned by individuals. However, there is no land measurement and certification in this region.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It is the expert's conviction that crop production in the area increased with water harvest and spread over the farm for use as spate or supplementary irrigation to the seasonal rainfall.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the moisture harvested by the structure is believed to add grain filling period, the crop quality is also expected to increase.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Fodder production also increases with the availability of good soil and moisture conserved in the farm behind the structure.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increases with increasing availability of feed or fodder from either crop residue, natural grass or browse.
การผลิตไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It rather improves crop resilience because of improved soil moisture.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Opportunities can be created to increase the size of land under farming with increasing availability of moisture and fertile soils.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Moisture availability eases the management operation.
การผลิตพลังงาน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Basically, quality is not a priority issue for agro pastoralists in dry valley areas.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the structure reduces the degree of degradation, expense on agricultural inputs is believed to be reduced.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It promotes land users' understanding of SLM through training and exposure to the actual structure and soil and water harvested behind the structure.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
They may manage to access water for livestock drink and/or household consumption.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The structure harvests soil moisture on the farm. It reduces the speed of runoff, stops, and spread over the farm.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased through production of more biomass.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The physical barriers stops the soil and water loss.
การสะสมของดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความเค็ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It is related to a warm climate that triggers evaporation and salinity development in the long run.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความเป็นกรด
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเร็วของลม
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
As the intervention is in its early phase, it is difficult to give an assumption before and after the application of SLM (technology or physical structure). However, a 40 years old woman known as Run Muhamed gave us her insight into the productivity of the land by comparing the hindsight vs the current harvest under highly erratic and erosive rainfall distribution. Accordingly, over the years the harvest per hectare diminished from 0.75 ton/ha to 0.1 ton/ha. This signals the effect of climate change/climate variability and land degradation on crop production. Her household is one of the owners of the land among the other four members of the extended family where the WSW was put in place.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the structure is recently constructed, it is dire to envisage the off-site impacts of the technology at this juncture. However, it has a positive contribution to the availability of groundwater in the adjacent farms.
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Streams are less common in the dry valley.
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It reduces the speed and volume of downstream flooding.
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Need an investigation of its impact on the groundwater.
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Believed to reduce it in the long run.
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
The intervention believed to improve the existing negative consequences of degradation through promoting soil and water management and reducing risks of crop failure.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
| พายุทรายหรือพายุฝุ่นประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ปานกลาง |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
After an extended dry year, like this season, the technology is overloaded with a flash flood. The soil was frequently exposed to the sun and the prevailing heat waves in the area were easily detached by torrential rain. Then the soil and water were partly arrested whereas an immense amount washed away. It seldom could topple the structure if not the cascade comprises eight to ten structures with relatively short intervals to support one another. Furthermore, the dry valley soil is very fragile let alone exposed to a long-term drought that is associated with a heavy shower at the beginning of a short season like this season.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is a technology implemented at the community or extended family level. It is too early to evaluate the adoption trend at this particular time.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology/structure reduce soil and water erosion. |
| Harvest water and make the people and livestock beneficiaries from the still water for crop production, drinking, and household uses. |
| Increase soil moisture and risks of crop failure because of shortage of rainfall. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Rehabilitate both degraded agricultural and grazing lands. |
| Improve agropastoralist access to livestock feed and benefit from the positive impact caused by the technology. |
| Eventually, contributes to the improvement of ecology and overall ecosystem functioning. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost. | Enhance the in-kind contribution of the land users, and increase matching funds from the government as cost-sharing with other projects. |
| Agropastoralist complains about the space it occupies in their farmland regardless of the benefit they accrue over a long period. | Increase the awareness of the community on the productive uses of the degrading land based on the evidence. |
| The structure may fall over the livestock migration/travel routes that are not acknowledged by some members of the community. | During masonry work, precaution is essential to calm down the possible complaints that could emerge because of the raised structure by leveling the crossover roads/paths. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| An inadequate number of structures in a cascade subjected to ineffective soil and water management and distribution of rainwater to support as supplementary sources of moisture for crop production. | Increase the number of structures per conceptual statement and standardize the intervals between the structures. |
| Excessive land users' desire that is unassociated with a tangible contribution to the development of the technology from their side. | Further building land users understanding of SLM technologies and their benefits so that they can build a sense of ownership and accountability to contribute and complement the external efforts. |
| Land users give emphasis mainly on the immediate benefits of the technology (harvesting water for livestock drinking and household use) than the objectives of rehabilitating the dry valley for productive use of it such as crop and livestock feed production. | Acknowledging the immediate benefits, and the mainstreaming work regarding the pillar objectives of the project intervention. |
| The initial investment, as well as maintenance costs, are either expensive or overestimated by local actors. Such a higher cost may discourage land users in the absence of projects or SLM funds. | It would be good to be pragmatic in cost estimation. Furthermore, adapting the technology using local materials may promote the adoption and sustainability of the structure for widespread use. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Three individuals.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
One person.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Four individuals.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
23/03/2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Mekdaschi & Linger, 2013. Freie Universitat Berlin
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.geo.fu-berlin.de/en/v/iwrm/Introduction/Principles/index.html
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Water-spreading weirs
URL:
https://www.unccd.int/best-practice/water-spreading-weirs
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Water Spreading Weir - NATURAL RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
URL:
https://nrmdblog.wordpress.com/2016/12/12/water-spreading-weir/
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire is inclusive and more relevant to evaluate such physical structures as a technology. However, successive drought seasons experienced in the area subject the fragile soil to be easily detached and immensely moved by the early rains past the structure. This may affect the valuation of the efficiency of the technology since dry areas are also characterized by a flash flood that could certainly mask the benefits of such a good technology.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [เอธิโอเปีย]
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล