Agroforestry with Acacia senegal [เซเนกัล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Julie Zähringer
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1119 - เซเนกัล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CSE (CSE) - เซเนกัล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
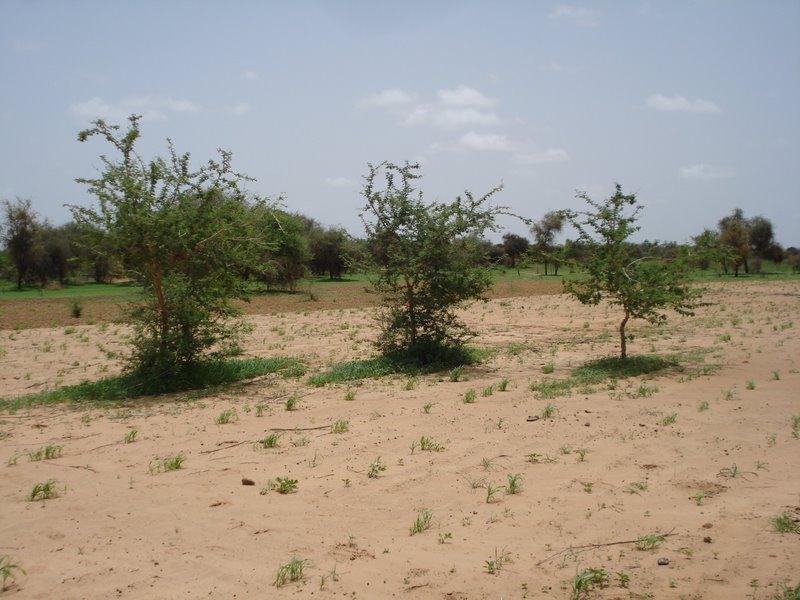
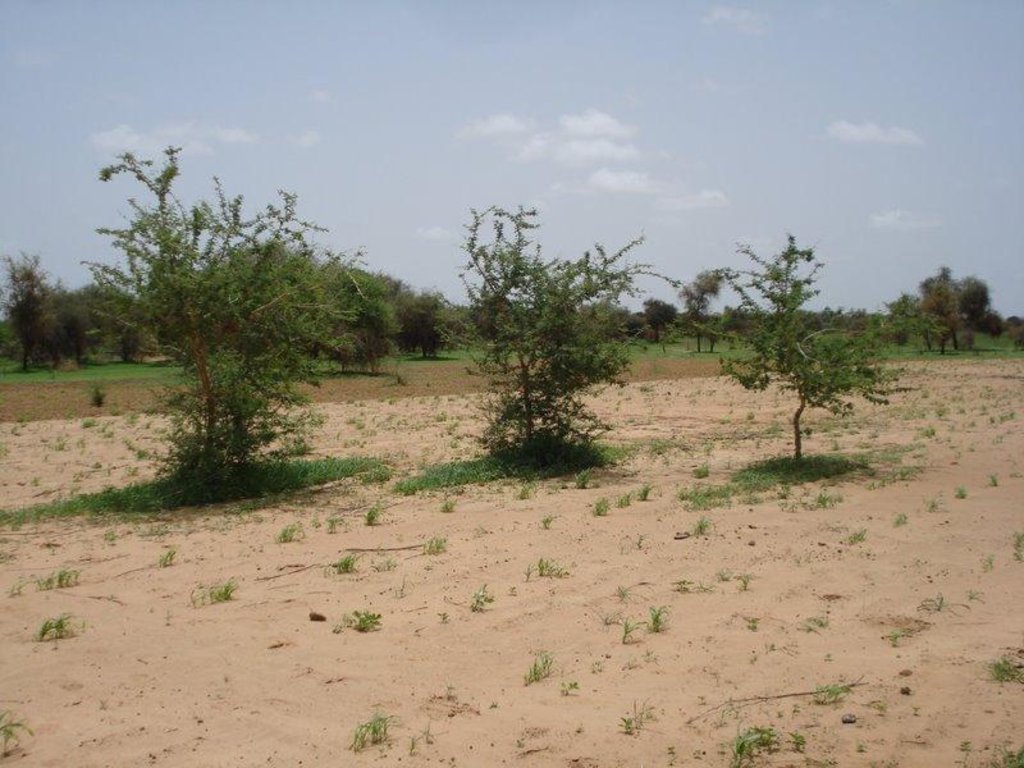
An agroforestry system, dominated by Acacia senegal, developed through protection of all naturally regenerating trees with improvement of soil properties through presence of trees, application of manure and a fallow rotation.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Acacia senegal is the dominating woody species in this agroforestry system. To improve soil properties and crop production, organic manure is applied and a fallow system practiced. One part of the field is being cultivated with either millet (Pennisetum typhoides), cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) or maïz (Zea mais] whereas the other part is left fallow for two years before rotation.
Purpose of the Technology: Initially, the main objective of the land user applying the technology was to improve soil properties and crop production in his fields by maintaining any tree and protecting natural regeneration when preparing his land for cultivation. With the start of exploiting Acacia senegal for the exudates, gum arabic, the potential of revenue increase through gum exploitation became evident and the objective shifted from soil protection to gum exploitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Because of knowledge his father passed on to him, the land user applying this agroforestry practice believes that any tree in his fields is useful and should be protected.Through the technique of assisted natural regeneration, trees naturally growing in the field are protected to reach mature age instead of being cut to clear area for cultivation. The only inputs related to this technology are those for seeds for crop cultivation. During the 3-4 months of gum Arabic exploitation, the land user is obliged to survey his fields day and night, as intruders try to tap the Acacia senegal trees illegally. However, this task is fulfilled by the landuser himself and does not involve expenses for payed manpower.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. The main land use type in the area is extensive pastoralism followed by rainfed agriculture. Pastoralism is primarily practiced by transhumant Fula (Peulh) herders and further by Mauritanian Moor herders with herds of dromedaries. Vegetation cover in the area has been largely degraded due to cutting for domestic uses and cattle feeding, bushfires and overgrazing. The soil is exposed to wind erosion which carries away nutrients in the topsoil and therefore declines soil fertility. During intense rains in the rainy season, surface runoff is accelerated and leads to the formation of gullies and ravines.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เซเนกัล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Louga
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Barkédji
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.35 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
family tradition: the father taught the sons not to cut any trees in their fields, as they have beneficial properties
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - millet
- legumes and pulses - peas
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: July to October

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Type of tree:
- Acacia senegal
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major cash crop: Acacia senegal
Major food crop: Millet, groundnut, cowpea
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): degradation of vegetation cover, wind erosion, increased surface runoff, formation of gullies and ravines, management of natural water sources (people doing laundry and personal hygiene in temporal ponds used as sources of drinking water)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): wind erosion, water erosion, reduction of vegetation cover
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (absence of inorganic fertilizers, reduction of fallow period), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (domestic uses), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (oversized herds of cattle and dromadaires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (during rainy season), population pressure (need for pasture and cultivable land), poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: organic manure (untreated)
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Get all the seeds |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds for millet | ha | 1.0 | 1.68 | 1.68 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds for groundnut | ha | 1.0 | 5.25 | 5.25 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds for cowpeas | ha | 1.0 | 7.85 | 7.85 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 14.78 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 14.78 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of crops | beginning of growing season once a year |
| 2. | Application of manure | several times during growing season |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The landuser has to spend 90-120 person days for surveillance of his Acacia senegal trees every year during the exploitation of gum arabic. No costs incur to the landuser because of this activity, as he or somebody from his family is undertaking the task.The protection of natural regeneration in the fields does not have any costs, as the young trees are not enclosured.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
seeds for crop planting
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
300.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
During one rainy season (july-september), dry period from october-mai
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: tropics, in the sylvopastoral zone of the Ferlo
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: High (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, ranked 1, groundwater from borehole during dry season) and for agricultural use only (irrigation, ranked 2, water from temporary ponds during the rainy season)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Compared to the sudano-guinean zones of the country, this zone is not very species rich
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: women do not have the right to ask for land to cultivate, it can only been attributed to them by their husbands
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
22% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: no off-farm income (if income generated through gum exploitation is seen as farm income)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1) and Mixed (ranked 2, only gum from Acacia senegal is sold)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The single landuser applying the technology exploits cropland of about 35 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the land user can count on income from gum exploitation he is less vulnerable to crop failure
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Applies especially for fallow part, cultivation might be entirely given up
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Income from gum arabic exploitation
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Biological N-fixation (A.senegal), but amount questionable
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through plant litterfall, application of manure
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mainly applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part only little
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Applies for the cultivated part only
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Birds building nests in trees on fields
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
the landuser is expecting a rise in income through increased gum production
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
1
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
increase of crop production How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain or increase number of trees in fields |
|
increase of income How can they be sustained / enhanced? assist natural regeneration of Acacia senegal |
|
provision of shade for cattle and increased availability of manure as consequence How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain or increase number of trees in fields |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
increase of soil fertility increase of soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase the number of trees with positive impact on soil fertility improve manure application and increase number of trees in cultivated part |
|
reduction of wind erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase tree abundance |
| maintenance of woody species diversity |
|
improvement of soil cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase tree abundance |
| little to no costs of establishment |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| surveillance of Acacia senegal trees during exploitation season required | establish a fence |
| crop damaging birds find a habitat to build nests in trees | put scarecrows |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| tendency towards a monoculture of Acacia senegal (in the part of the field left fallow) | encourage natural regeneration of other local species as well |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล