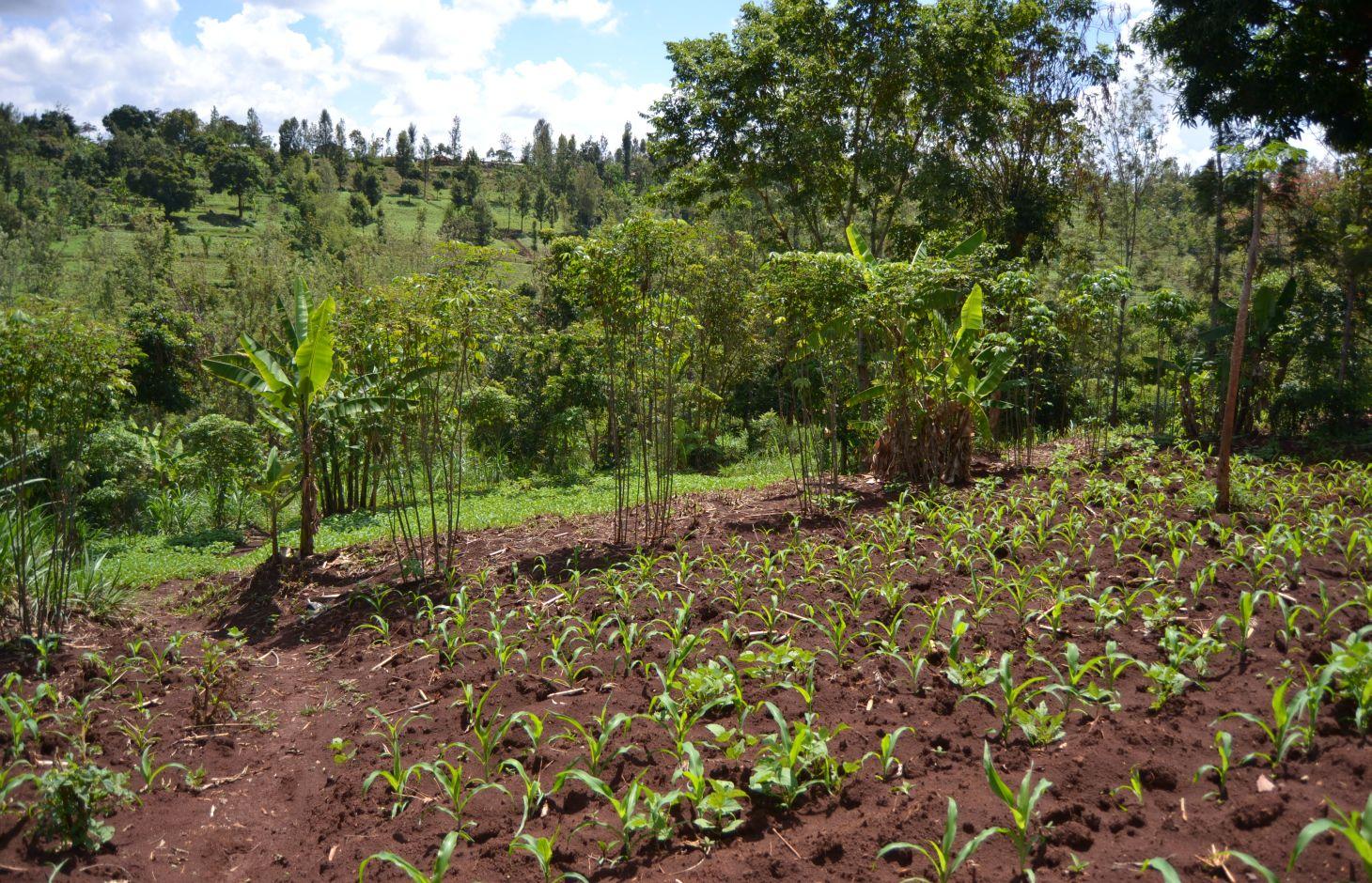
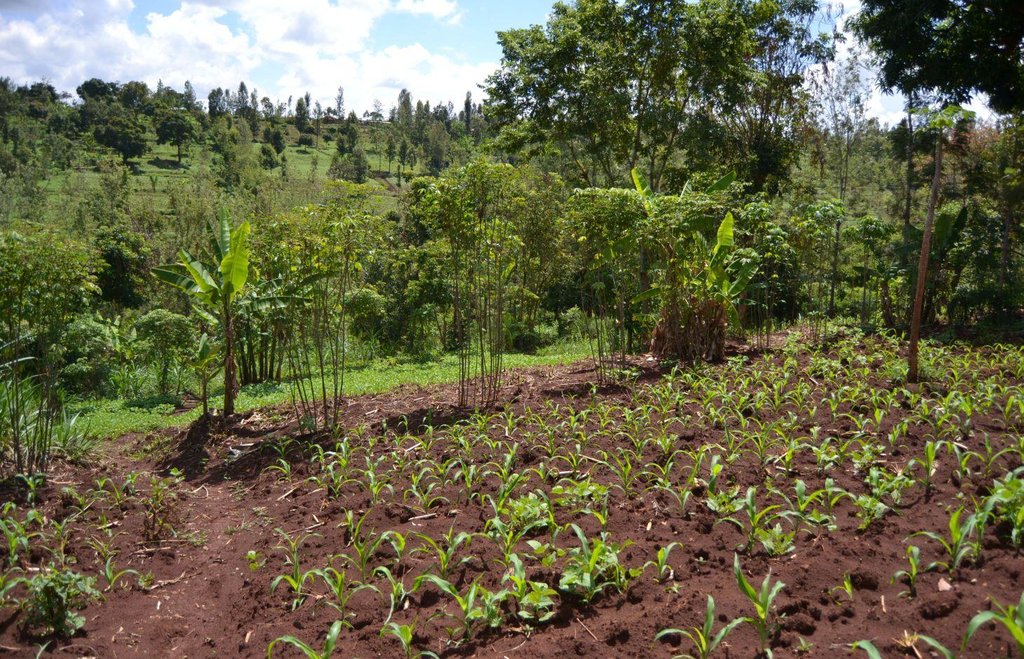
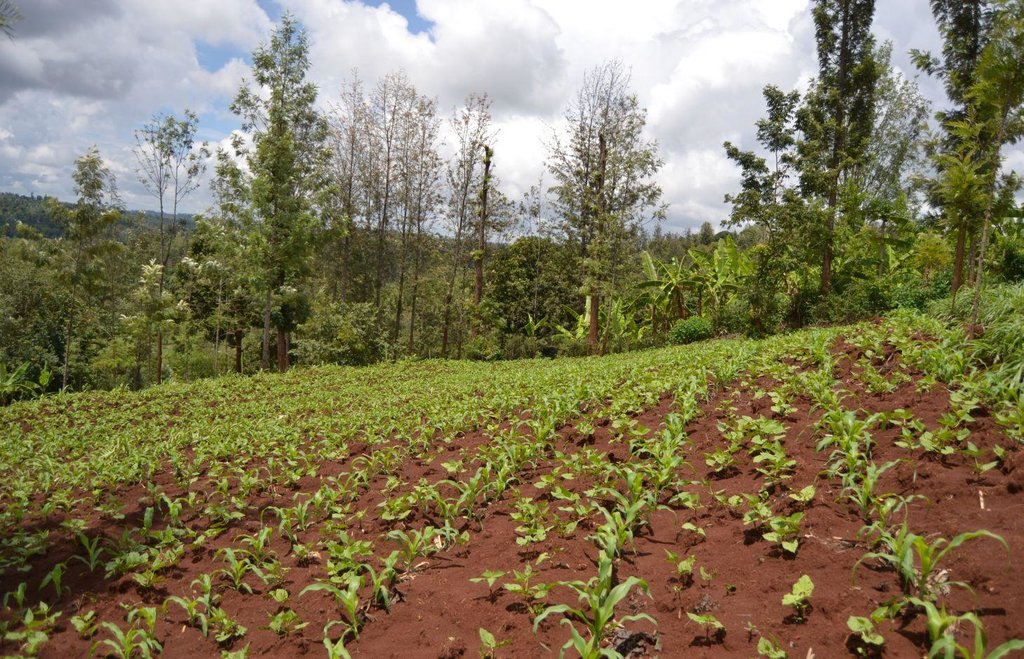
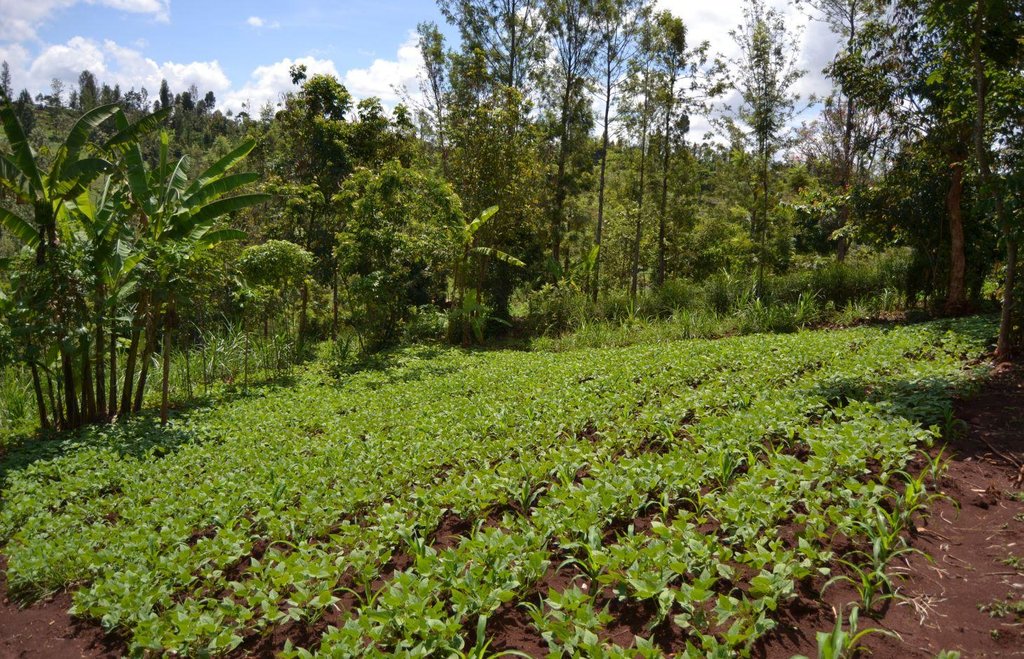
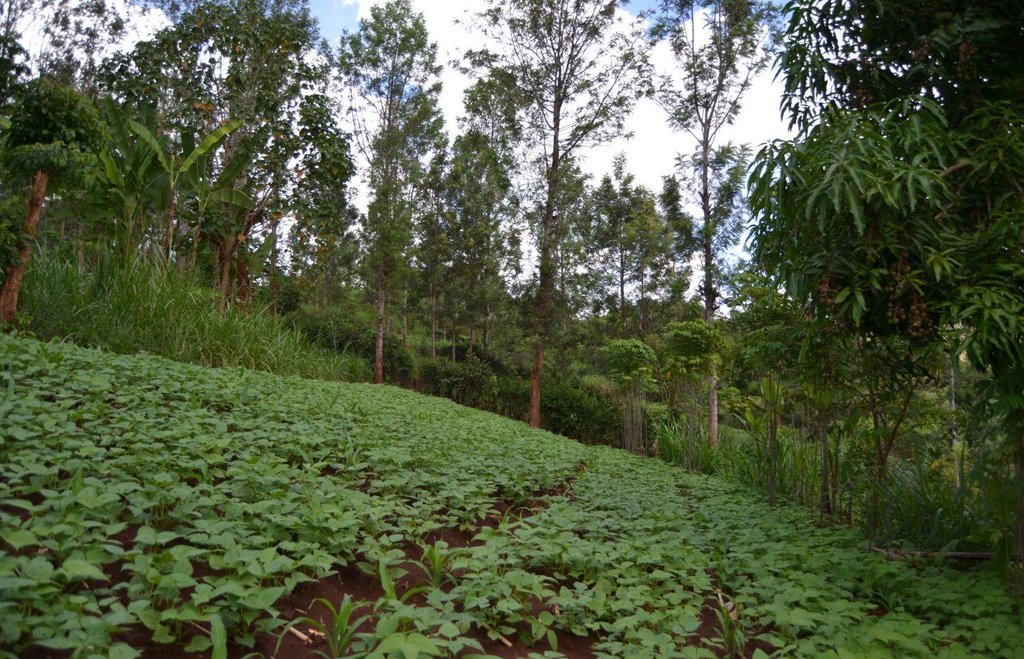
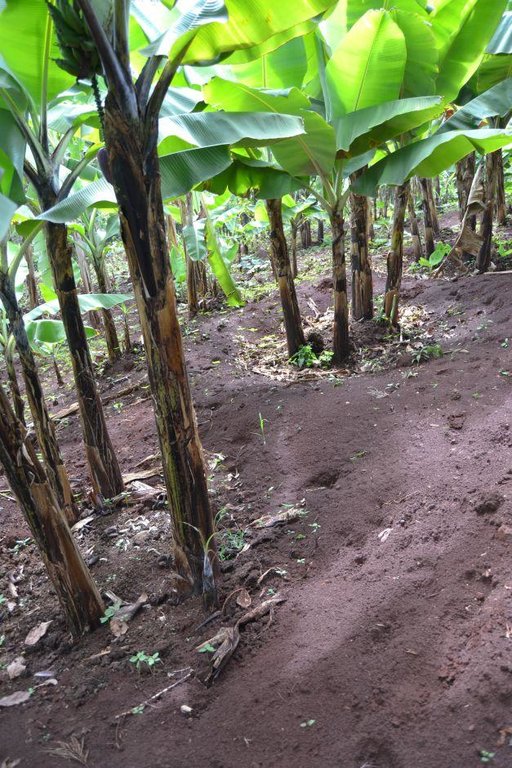
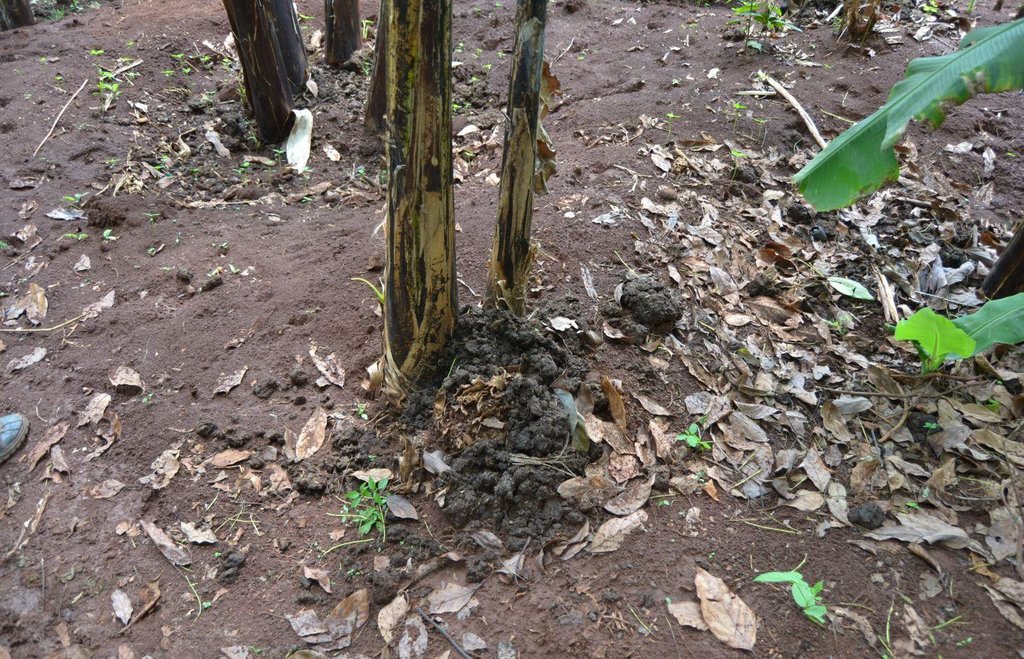
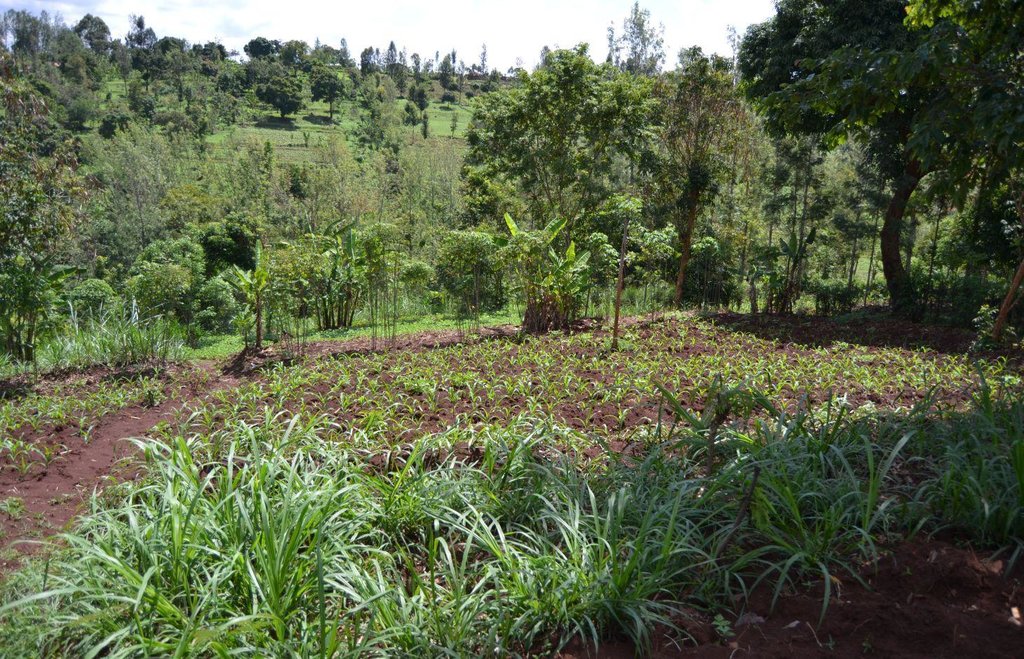
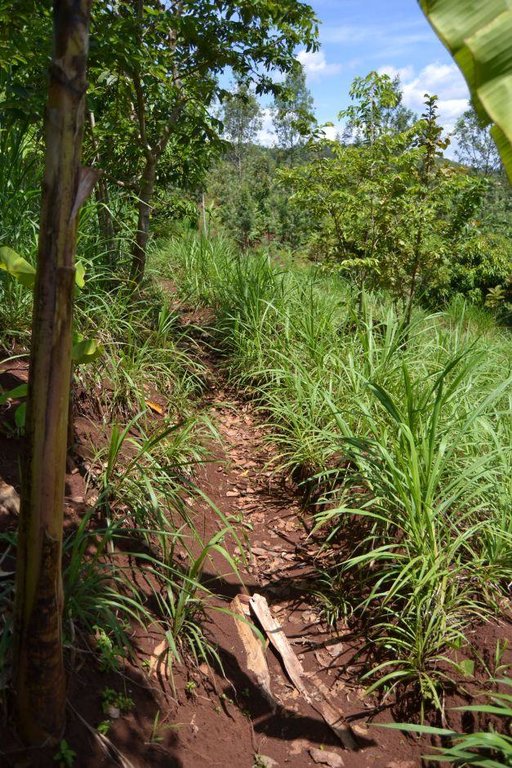
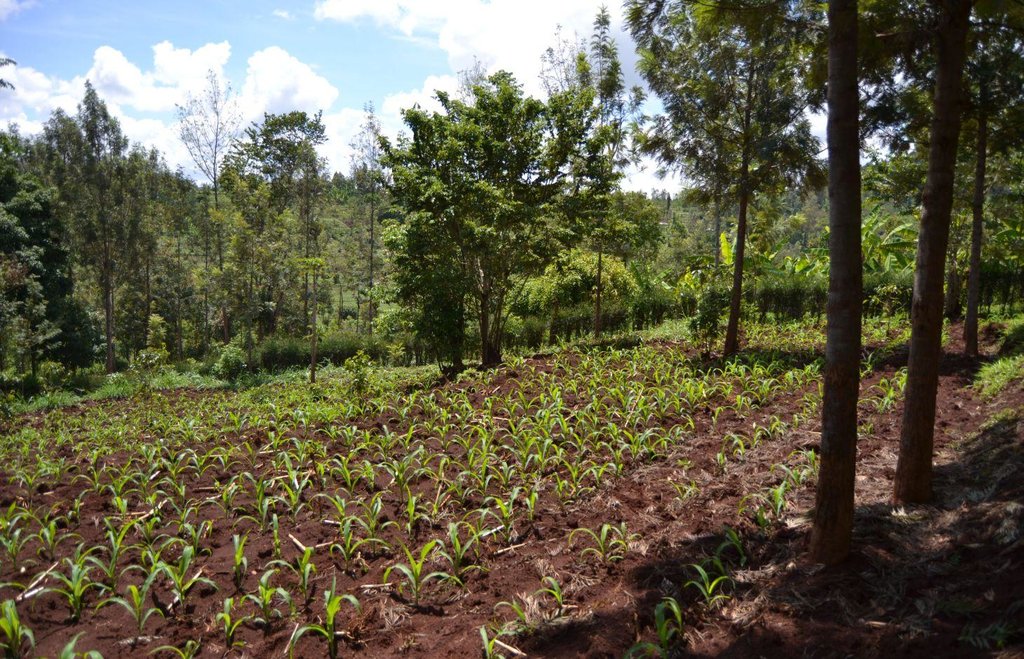
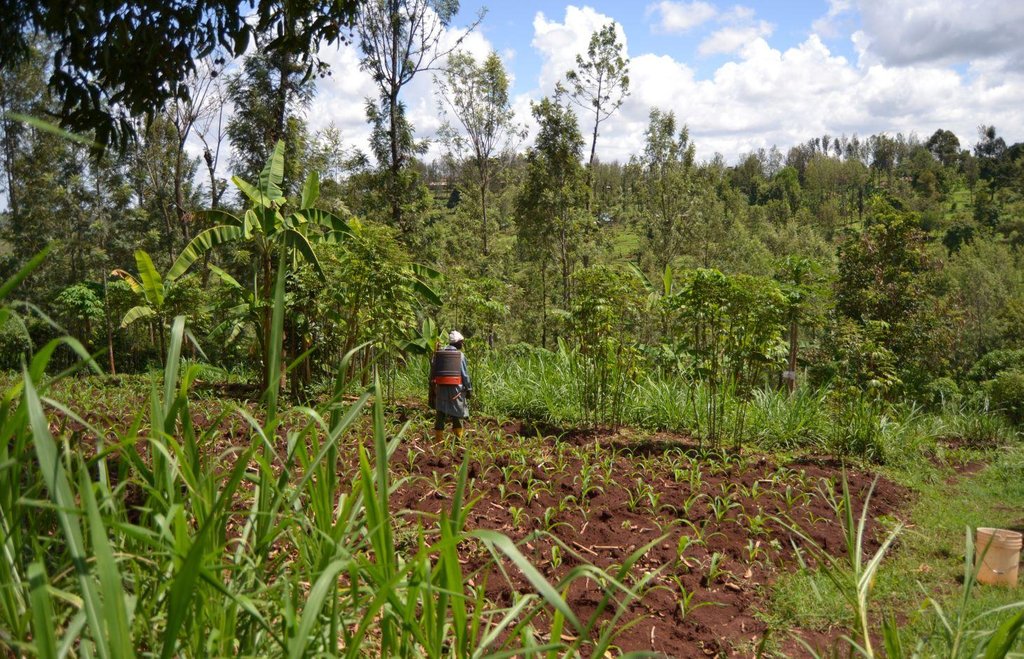
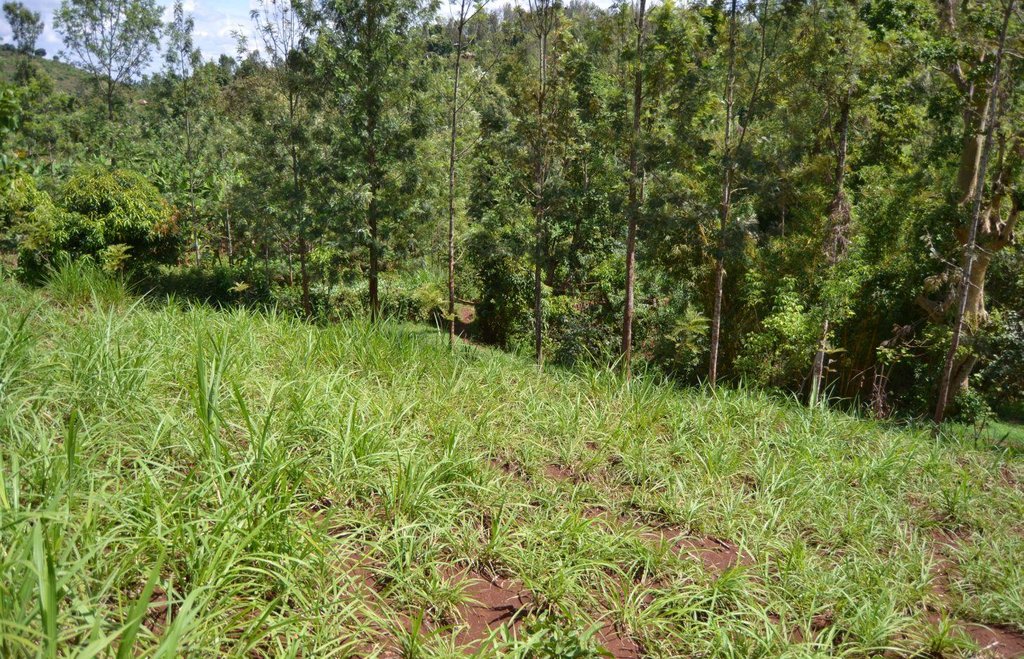
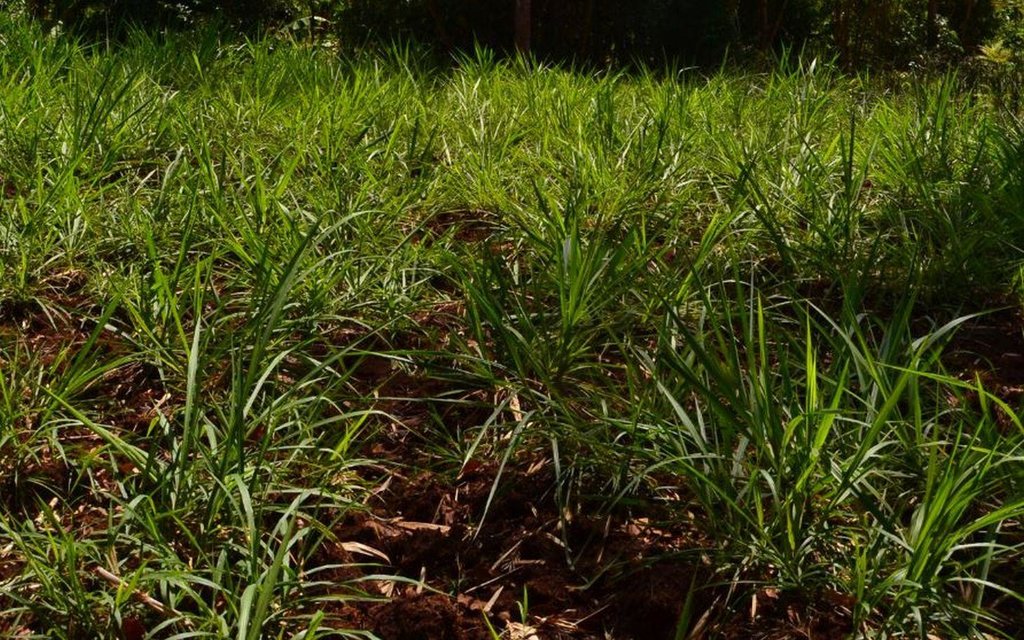
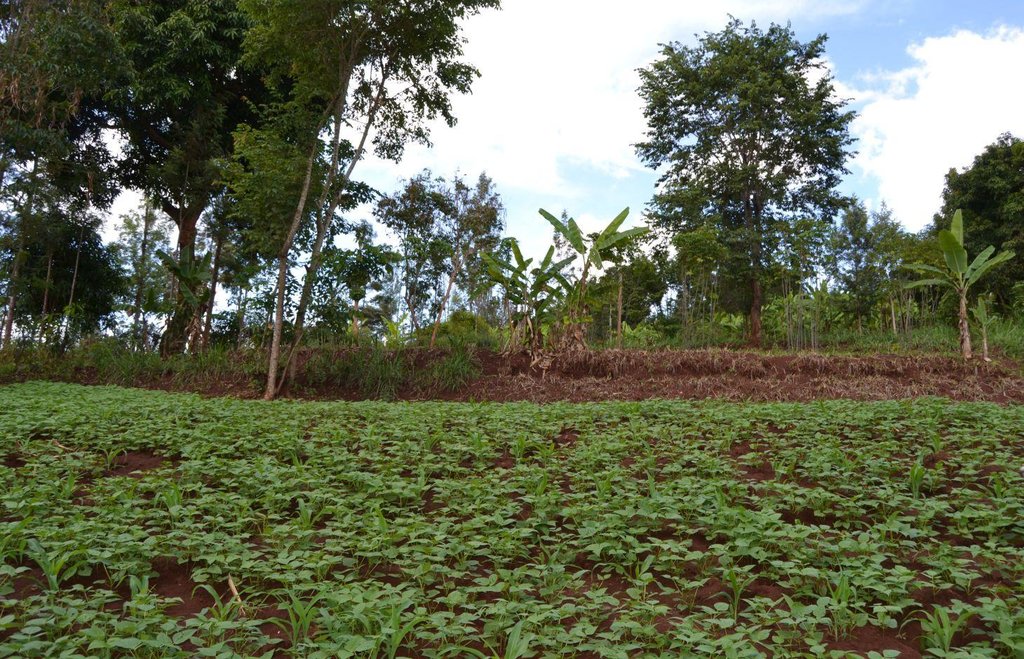
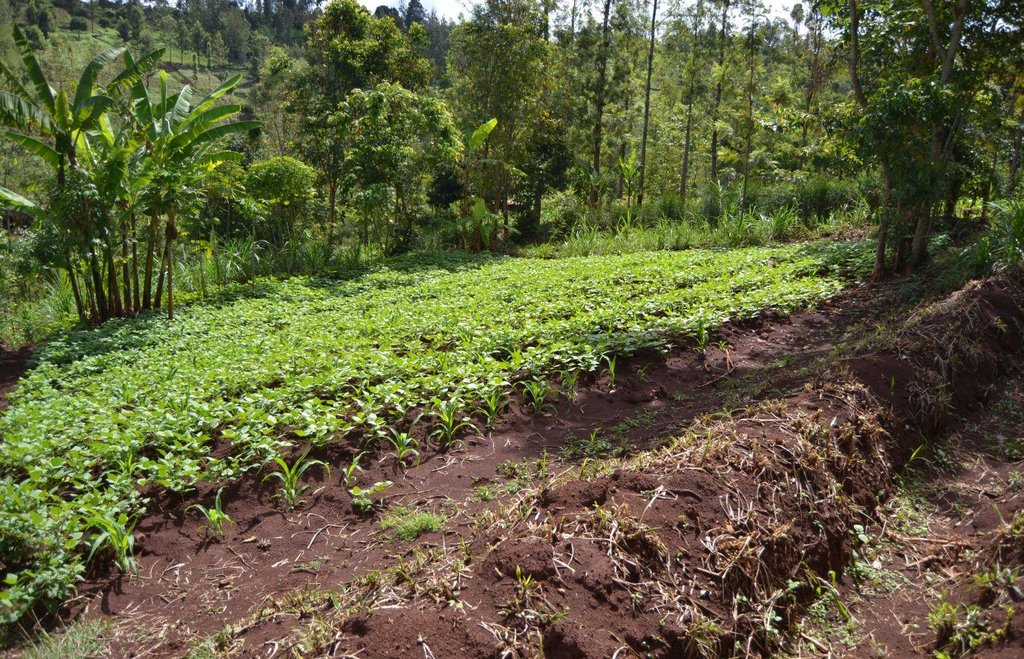
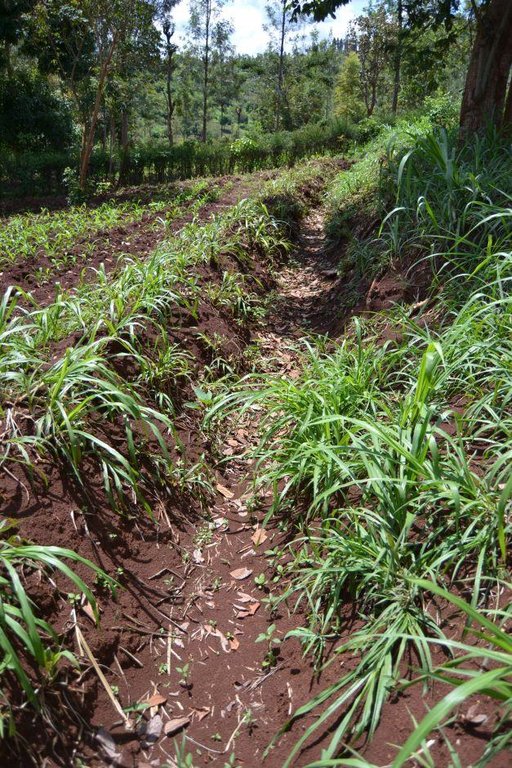
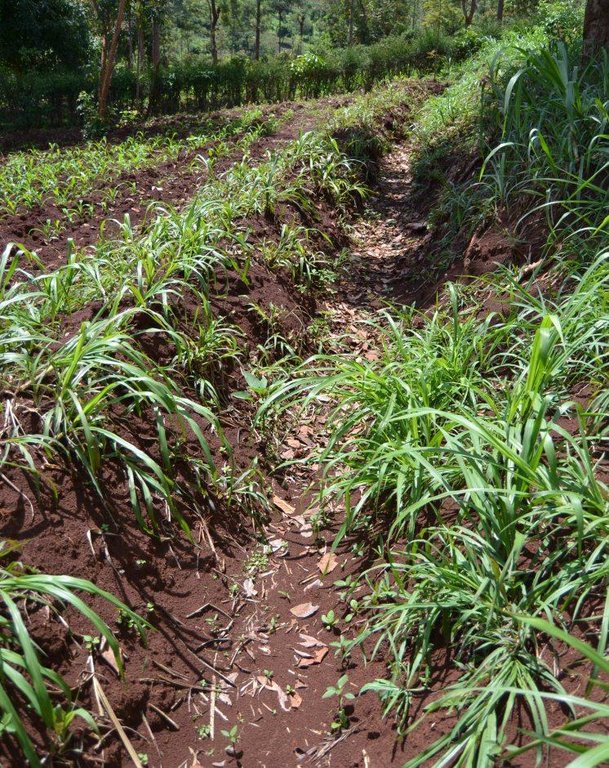
Agroforestry system (intercropping beans/maize) with contour ditches, strips of Napier grass, manure and organic fertilizers. [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Laura D'Aietti
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1146 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Agroforestry system (intercropping beans/maize) with contour ditches, strips of Napier grass, manure and organic fertilizers.: 28 ธันวาคม 2016 (inactive)
- Agroforestry system (intercropping beans/maize) with contour ditches, strips of Napier grass, manure and organic fertilizers.: 5 มิถุนายน 2017 (inactive)
- Agroforestry system (intercropping beans/maize) with contour ditches, strips of Napier grass, manure and organic fertilizers.: 7 พฤษภาคม 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Nyamu Joseph
WRUA Sabasaba
เคนยา
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The technology is a combination of agricultural (e.g. intercropping, manure/compost/mulching), vegetative (e.g. Napier grass strips, trees planting) and structural (e.g. ditches) measures which aim to maximise the overall land yield in a sustainable manner (e.g. reducing soil erosion and increasing soil quality).
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
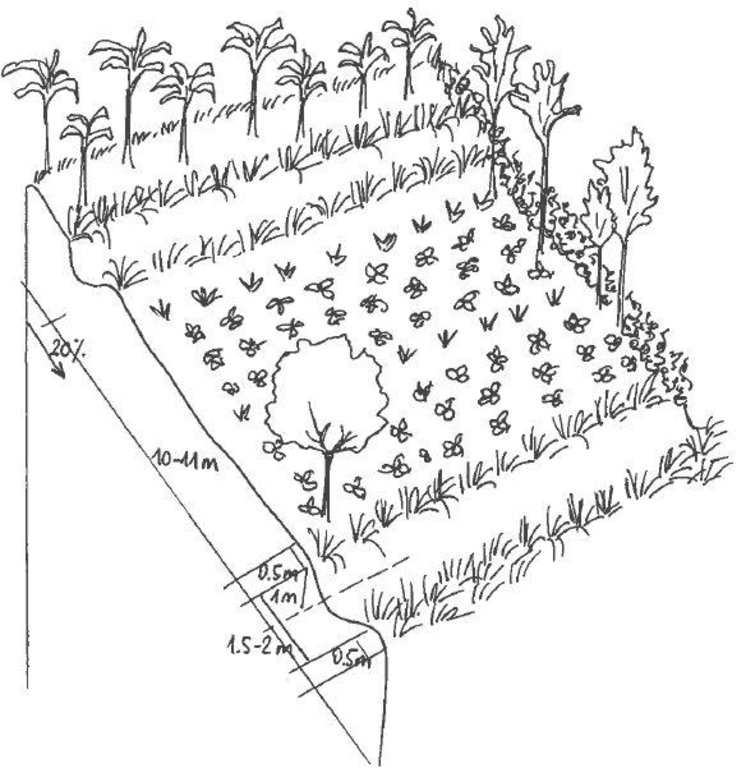
The Agroforestry system combines trees plantation (Bananas, Grevillea and Avocados) for fruits and timber collection with cereal crop, maize (Zea mays). Indeed, in order to increase yields, strip intercropping is practiced: cereal crop (maize) is grown in association with pulse (food legumes): beans. Instead of using expensive commercial fertilizers, beans could facilitate maize growth due to the possible transfer of N during growth or after incorporation of the legume biomass, during the growth period of the cereal (Sangakkara et al., 2003). Furthermore, soil quality (e.g. soil structure) is improved because of the increased amount of humus and organic matter and a better soil cover helps in preventing splash erosion and increase soil moisture content and therefore fertility. Indeed, beans have a beneficial impact for weed control (probably due to the shadow effects) and soil moisture content (Worfswinkel, undated; Odhiambo and Ariga, 2001). Planting different crops helps to diversify production and family food supply. Concerning SWC, hillside ditches have been created at the top of each 'terrace' and trees are also planted nearby and Cassava (a drought resistant plant) at the bottom. Manure/compost and organic fertilizers are supplied regularly both on maize/grass (twice a year) and Bananas (once), as good soil management practice. A higher level of organic matter in the soil indicates reduced bulk density, improved soil structure, aeration and higher water holding capacity (Olabode et al., 2007), which altogether improve the physical, chemical and biological properties of the soil (Haering and Evanylo, 2005). Bananas are planted in lines in the upper part of the land. The ditches, large 1m are excavated along the contour; they break slope into shorter segments 11 m long to intercept surface runoff. Ditches also help to prevent soil erosion and to avoid that nutrients and organic matter flow easily downwards into the river, instead they fall into the ditch. A live barrier of Napier grass is present above and below the edge of the five ditches, in two lines, to capture sediments and stabilize the structure, thus it is adequately protected. To conclude, a small area of the land is used to plant Napier grass only for fodder for grazing
Purpose of the Technology: Maize and beans are cultivated for home consumption while Avocados and Bananas are planted for economic (commercial) purposes. Fruits are sold out to the middle-men directly from the house (not at the market), to reduce costs (e.g. transport) and time. Avocados are sold at about 2.5/3 Ksh and Bananas at 200 Ksh. Grevillea trees are considered as saving, and sold out for timber production when the farmer is in need of cash, earning between 800 up to 1500 Ksh, depending on the size-lenght of the tree and the costs for cutting-transportation (e.g. machine operator). In general the selling of timber occurs per feet (running feet). ‘Whole” or standing tree is the preferred mode of selling trees from farms. Negotiation on sales is per tree ‘standing on farm’, with no processing or conversion. Buyers cut and cross cut, and carry timber from farms. Branches and slabs resulting from timber recoveries are left with the farmer depending on price negotiation; if the buyer carries these products then the price of the tree is adjusted upwards (Carsan and Holding , 2006; Holding et al., undated). Furthermore, the farmer underlined how 'bad prunings' at the top of the trees cause holes inside the trunks and thus a higher risk of fungi attacks and other diseases. The majority of the trees are planted along the boundaries of the land, for demarcation and only few are 'dispersed' on the cropland, to avoid excess of shadow to the cereal crop
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: High initial input to construct ditches and planting crop; manure also requires regular work: feeding cows and collect droppings and distribute them twice during the year, also over Napier grass. Dry planting is the preferred practice and the seeds are soaked the night before planting; this practice is advisable especially when the growing period is very short (Schmidt et al., 1983); organic fertilizers are applied over maize after 1 week and during the growing period (after about 18 days). Further maintenance is necessary after every rainy season to remove the sediments accumulated into the ditch and for pruning Grevillea, every three seasons. As mentioned above, pruning requires skills and knowledge to avoid plant diseases and labour is expensive because it is high risk work. The farmer trees plantation account for: 15 Avocados (from 4 seedlings), 100 Bananas (from cutting new suckers) and 50 Grevillea trees
Natural / human environment: The area is characterized by rolling-hilly slope and highly exposed to erosion and land degradation: planting trees protect the soil from nutrients leaching and create a litter which reduces evaporation during dry seasons. Concerning the variety of the trees, (e.g. Avocado) the farmer by grafting with better quality branches, improve the quality of the stock trees with certified variesties: out of 4 seedlings of Avocado (10 Ksh each), he has now 15 seedlings of the better (certified) variety called HASS, which performs well at 800-2100 m asl with well distributed annual rainfall of 1000-1200 mm (Youth Agro-environmental initiative website)
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Central
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Muthithi location, Kagurumo sublocation
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
0.008
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.008 km2.
GATWAMIKWA village
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Since the year 2000 the farmer adopted SWC practices in respond to the prolonged degraded situation of the land and its low yields.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- fodder crops - grasses
- legumes and pulses - beans
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 122Longest growing period from month to month: from about March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 61Second longest growing period from month to month: from about October to November
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Intercropping of maize and beans: the distance from one line of maize and the other is of 1m.

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- cows

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Type of tree:
- Grevillea robusta
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Trees/ shrubs species: Grevillea (Grevillea robusta)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Avocados (Persea americana- Mũkorobia), Bananas (Musa sapientum- Irigũ)
Grass species: Pennisetum pyramidalis (Napier grass or elephant grass)
Main crop: Maize (Zea mays) and beans
Main animal species and products: Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Fodder is provided to animals (2 cows) confined to a stall.
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Sheet erosion with consequent nutrient leaching which could drain into the river.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of soil fertility.
Grazingland comments: Fig. 10 Annex 3
Plantation forestry: Yes
Type of grazing system comments: Fig. 10 Annex 3
Livestock density: < 1 LU/km2
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Poor vegetation cover, mainly herbaceous), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Steep area (runoff)), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Especially during wet seasons: March-June and October-November), education, access to knowledge and support services (Limited knowledge and training on SWC practices), governance / institutional (Limited or not adequate support)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (From gentle to hilly slope), land tenure (Previous poor management SWC measures, especially in the upper areas)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Agroforestry system, which covers an area of 2 acre. The plot is bordered by Euphorbia tirucalli (Kariaria, milk bush) and Grevillea trees. The ditches are characterized by barriers of Napier grass. Intercropping of maize and beans: the distance from one line of maize and the other is of 1m.
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mulching
Material/ species: Organic residues around Banana trees
Quantity/ density: undefined
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 4 kg
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Leftovers and manure from two cows
Quantity/ density: 8 tonnes
Remarks: (for 1 year). The mix of organic material is left decomposed in a big hole.
Agronomic measure: organic fertilizers
Material/ species: Acid humic and N, P, K, microelements (Biodeposit Elixir: small bags (sachets) of 12 ml)
Remarks: 5 bags (1×12 litre), applied only on maize
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100 a strip
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): few cm
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Trees/ shrubs species: Grevillea (Grevillea robusta)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Avocados (Persea americana- Mũkorobia), Bananas (Musa sapientum- Irigũ)
Grass species: Pennisetum pyramidalis (Napier grass or elephant grass)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 15%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 5-8%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Spacing between structures (m): 1
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40/50
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6/1
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 15-20%
ผู้เขียน:
D'Aietti Laura
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Kenyan Schellings
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
85.9
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging holes (1 feet ×1 feet) and planting trees (e.g. Grevillea trees along the boundaries and in line below the bunds of the ditches) | March (before rains), 1 year |
| 2. | Establishment of the ditches(digging ditch and creating soil bunds donward) and terracing. For 1 (in tot. are 5) : 2 p.d. * 1 day at 200 Ksh a day each. | 2 times per year |
| 3. | Digging the hole (3m×3m×1.5m) where to compost | |
| 4. | Machine to grill/mill maize leftovers (chap cutter) | |
| 5. | Purchase 2 cows | |
| 6. | Purchase generator |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Life span of the machine to grill, the cows and the generator: Several years
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Digging the hole (3m×3m×1.5m) where to compost | person/days | 2.0 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Digging holes (1 feet ×1 feet) and planting trees | person/days | 2.0 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Establishment of the ditches (digging ditch and creating soil bunds donward) and terracing | person/days | 10.0 | 23.3 | 233.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine to grill/mill maize leftovers (chap cutter) | piece | 1.0 | 1164.0 | 1164.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Generator | piece | 1.0 | 582.0 | 582.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Cow | piece | 2.0 | 349.0 | 698.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings Grevillea | pieces | 54.0 | 0.1111 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2697.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 31.4 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare and apply fertilizers (organic) (See Annex 3, Fig. 9&comments) | Ferlizer application: after 1 week and 18 days, on maize only |
| 2. | Prepare manure+compost/mulch (Summary 2.1.2 QT4): Labour (to grill/mill leftovers - 300 Ksh for fuel- leftovers to prepare food for cows-3 person days) rest, the farmer by himself feed cows on daily basis (3 times in a day). Fuel: 1litre×1 day (×3 days) | compost/manure: 2 times/year in the field+grass; once on Bananas (where also added mulch) |
| 3. | Harvesting maize/beans (around Feb/March and Ag/Sept) | 2 times |
| 4. | Apply manure, mulch and compost (during March/April-long rains+Sept) just before the rains, when nutrients infiltrate into the soil with rainwater) (Summary 2.1.2 QT4) | Compost/manure: 2 times/year in the field+grass; once on Bananas (where also added mulch) |
| 5. | Tilling-soil (digging holes to plant maize/beans: 7 inches deep (17cm), spaced 1 feet (0.30 m) in contours: dry planting (before rains starts) | Twice a year, before rainy season (around March/Sept) |
| 6. | Digging planting holes and planting grass (2 persons × 3 days: 200 Ksh) | Every season (March/April and Sept/Oct) |
| 7. | Maintenance (weed control and cutting Napier grass and collecting fodder) (Fig. 11 Annex 3) | Every season (March/Sept); cutting Napier: 3/4 times in a season |
| 8. | Pruning branches and let them dry for firewood | Every 3 seasons (and when shortage of firewood) |
| 9. | Clearing the tree for selling timber (the price depends also of the use of the chainsaw (or saw) or not | When in need of cash (not regularly), not less than 5 years after planting |
| 10. | Repairing the ditches and remove excess of soil/leaves accumulated during the rainy season | After rains (every season) |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Prepare and apply fertilizers (organic) | person/days | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Prepare manure+compost/mulch | person/days | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Digging planting holes and planting grass | person/days | 6.0 | 2.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Maintenance (weed control and cutting Napier grass and collecting fodder) | person/days | 5.0 | 12.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Fuel | l | 3.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings grass (per ha) | pieces | 100.0 | |||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Organic fertilizer (Biodeposit Elixir) from Thika | ml | 12.0 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Pruning branches and let them dry for firewood | person/days | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Clearing the tree for selling timber | person/days | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Repairing the ditches and remove excess of soil/leaves accumulated during the rainy season | person/days | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 112.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1.3 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: the farmer prefers to use fork djembe then just the normal djembe (because it removes better the soil); panga and hoes, shovel, fork djembe, panga, saw, shovels
The costs has been computed during the period of the field visit and it include all the costs for the different structures: agronomic, vegetative and structural measures for 2 acre of land and summarized for 1 year period.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The main environmental constrain is water, in particular during dry season; An important cost is labour required to maintain all the SWC measures.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: subtropics. June, July and August
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is rich because he owns 3 acre of land and livestock, assets (electricity) which are above the average standards of the community. The farmer is retired from an accountancy service position several years ago.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), commercial/ market
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water use rights depend on the use: open access for drinking and domestic uses.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตไม้
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Better yields thanks to the intercropping measures taken. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Intercropping is a commonly known practice which improves the overall conditions of the soil and provide better yields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Besides 'companion planting' there are plants which can be grown as forerunner plants (Storey, 2002). Depending also on the type of soil, attention could be given to some sps. which accumulate concentration of e.g. mineral accumulators, phosporus, potassium, calcium, silica and sulphur . Another way to perhaps enhance the yields is relay intercropping. It is undersowing the next crop into the present crop, so that the present crop is a nurse crop and time and water is saved in the establishment of the following crop (Storey, 2002) Green manure as a way to add organic nutrients and combine more than one green manure and rotate, both legume (e.g. cowpeas, soybeans, annual sweet clover, vetch, sesbania, and velvet beans ) and not legume (e.g. sudangrass, millet, sorghum, and buckwheat). |
|
Agroforestry (Dispersed trees on cropland): The technology is simple to adopt and improves a sustainable land management as well as diversification of income sources and food supply. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be implemented by increasing the number of trees planted (e.g. along the boundaries) and with sps. characterised by deeper root systems, to avoid further water competition. More Avocadoe trees could increase the opportunities for the farmer to be part of a CBO (Community Based Organization) addressed to marketing of Avocadoes for oil production. This could help the farmer to earn more money and invest more in SWC implementation and new methods, in the long run. The option of alley cropping (hedgerow Intercropping) with leguminous plants e.g. Sesbanian sesban (Ramachandran Nair-ICRAF, 1993) could be considered as another option. |
|
Napier grass has very good properties in holding soil; also for ditch stabilization and fodder production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other herbaceous vegetation could be also planted in the field: e.g. Tithonia diversifolia (Mexican sunflower), an excellent (high quality-N, P, K concentration) green manure /nutrient release and medicinal plant, or could be also used as a major component of compost manure. It is an annual weed that can be used for several purposes: fodders, poultry feed, fuel, compost, land demarcation, soil erosion, building materials, shelter for poultry. It is characterized by adaptability to different environment, rapid growth, fast rate of decomposition. Nevertheless, there is the need to ascertain the extent to which this weed sps. could be used for soil improvement and to determine the best mode of application of the weed sps., (Olabode et al., 2007, Olubukola et al., 2013) and the fact that is a invasive weed (with an aggressive growth) it requires a good knowledge in the land management and weed control. |
| The attention to certified varieties give also more value to the production itself and at market level: an increase of the bargaining power creates more opportunities for better income and chances to explore new and bigger markets, (e.g. Avocados for oil production ). |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The technologies in place require maintenance and monitoring, especially during rainy seasons | Eventually subsides or be part of a CBO's (Community Based Organizations) or SHG (Self Help Groups); Still the measures already in place could be improved: diversification of trees (e.g. indigenous) and trainings (e.g. pruning etc) could help the farmer in avoiding tree diseases and allocate more efficiently resources. |
| The amount of work required to carry out all the activities is too much. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Holding C., Carsan S., Njuguna P., 2004. Smallholder Timber Marketing: A Kenyan Experience. FAO/ICRAF/GoK multi-stakeholder programme. International Workshop on small holder timber production.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Odhiambo G.D. and Ariga E. S., 2001. Effect of intercropping maize and beans on Striga incidence and grain yield. Seventh Eastern and Southern Africa Regional Maize Conference. 11th -15 th February, 2001. pp. 183-186.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Olabode O.S., Sola O., Akanbi W.B., Adesina G.O., Babajide P.A., 2007. Evaluation of Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl.) A Gray for Soil Improvement. World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 3 (4): 503-507.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.idosi.org/wjas/wjas3(4)/15.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Olubukola S. A., Aderemi Ojo Ezekiel-Adewoyin O., Dorcas Tinuke D., Akintoye Henry, 2010. Comparing the use of Tithonia diversifolia and Compost as soil amendments for growth and yield of Celosia argentea. New York Science Journal 3 (6).
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.sciencepub.net/newyork/ny0306/20_2680_ny0306_133_138.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ramachandran Nair P. K., 1993. An Introduction to Agroforestry- ICRAF.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.worldagroforestry.org/units/library/books/PDFs/32_An_introduction_to_agroforestry.pdf?n=161
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Sanchez M. A., 2012. Food vs wood: dynamic choices for Kenyan smallholders. A plan B research paper. Master of Science. Michigan State University.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/134024/2/PeraltaSanchezPlanB.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Sangakkara U.R., Richner W., Schneider M. K., Stamp P., 2003. Impact of intercropping beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and sunhemp (Crotalaria juncea L.) on growth yields and Nitrogen uptake of maize (Zea mays L.) grown in the humid tropics during the minor rainy season. Maydica 48: 233-238
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.maydica.org/articles/48_233.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Schmidt H., Swoboda R., Ralph Jätzold R., 1983. Farm Management Handbook of Kenya. Natural Conditions and Farm Management Information. Vol. 2.Part B: Central Kenya
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www2.gtz.de/dokumente/bib/07-1284.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Smith D. M., Jackson N. A., Roberts J.M. and Ong C.K., 1999. Root distributions in a Grevillea robusta-maize agroforestry system in semi-arid Kenya. Plant and Soil 211: 191–205, 1999.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Storey P. J., 2002. The conservation and improvement of sloping land. Volume 1: Practical understanding. Chapter 5: Improving the soil management.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Worfswinkel van M., undated. Intercropping of Annual Foodcrops, Agrobrief (Agromisa), N.4
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.allindiary.org/pool/resources/intercropping.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Carsan S., Holding C., 2006. Growing farm timber: practices, market and policies. The Meru timber marketing pilot programme case studies and reviews. World Agroforestry Centre.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.worldagroforestry.org/downloads/publications/PDFs/b14639.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Chia-Chun Wu, 1998. Effective conservation practices for the cultivation of slopelands, Extension Bulletin (ASPAC/FFTC), No. 449, 7 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/prods/gap/database/gap/files/1272_CONSERVATION_ON_SLOPES.PDF
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Crozier C., 1986. Soil Conservation Techniques for Hillside Farms. A Guide for Peace Corps Volunteers. Appropriate Technologies for Development. Peace Corps Information Collection & Exchange Reprint Series No. R-62. Peace Corps Institution.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
(The Humanity Development Library website: http://www.nzdl.org/gsdlmod?a=p&p=home&l=en&w=utf-8)
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
CSIRO (Baldock J.) Soil carbon: the basics. website (http://www.csiro.au/en/Outcomes/Environment/Australian-Landscapes/soil-carbon.aspx) . Also in: Carbon Farming Fact Sheet: Store carbon for healthy soils and better yields.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.grdc.com.au/uploads/documents/GRDC_CarbonFarming_4pp.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Elemans A., 2011. Thesis report (unpublished): Green water credits program in Saba Saba sub-catchment in the Upper Tana, Kenya.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Gutteridge R. C. and Sheltong H. M., 1998.eridge R. C. and Shelton H. M., 1998. Forage tree legumes in tropical agriculture. (http://www.fao.org/ag/AGP/AGPC/doc/PUBLICAT/Gutt-shel/x5556e00.htm Chapter 5.2
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/ag/AGP/AGPC/doc/Publicat/Gutt-shel/x5556e0q.htm
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
HDRA , undated. Agroforestry in the Tropics.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.thenrgroup.net/member/MRO/AER/AER-560.htm
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Haering, K., Evanylo G., 2005. Composting and Compost Use for Water Quality. In Composting resource directory. Mid-Atlantic Reg. Water Program.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://infohouse.p2ric.org/ref/41/40137.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Holding C., Carsan S., Njuguna P., undated. Smallholder timber and firewood marketing in the coffee and cotton/tobacco zones of eastern Mount Kenya. In: Small-scale forestry and rural development: The intersection of ecosystems, economics and society.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.coford.ie/media/coford/content/publications/projectreports/small-scaleforestryconference/Holding.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล