Adapted combination of technologies in improved cassava production [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: ALLAN BUBELWA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Matumizi ya makinga maji yaloyo imarishwa na mbaazi, samadi, karanga na mbegu bora ya muhogo katika uzarishaji wa muhogo
technologies_1213 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Tibaijuka Eliud
Missenyi District Council
แทนซาเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Rutasingwa Antony
Missenyi District Council
แทนซาเนีย
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - แทนซาเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
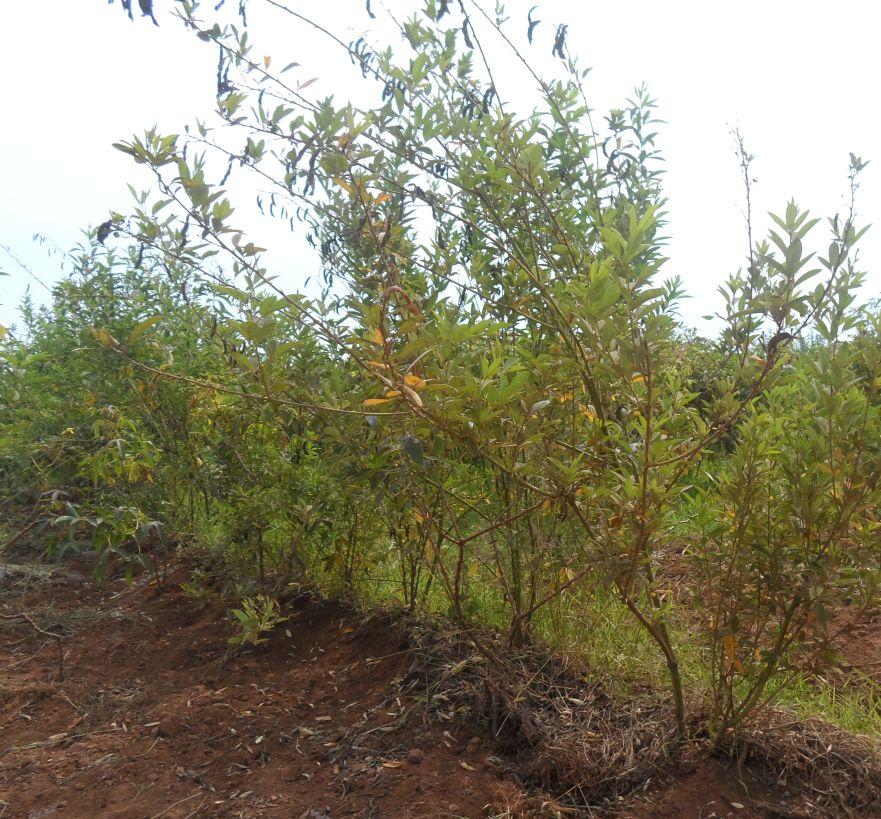
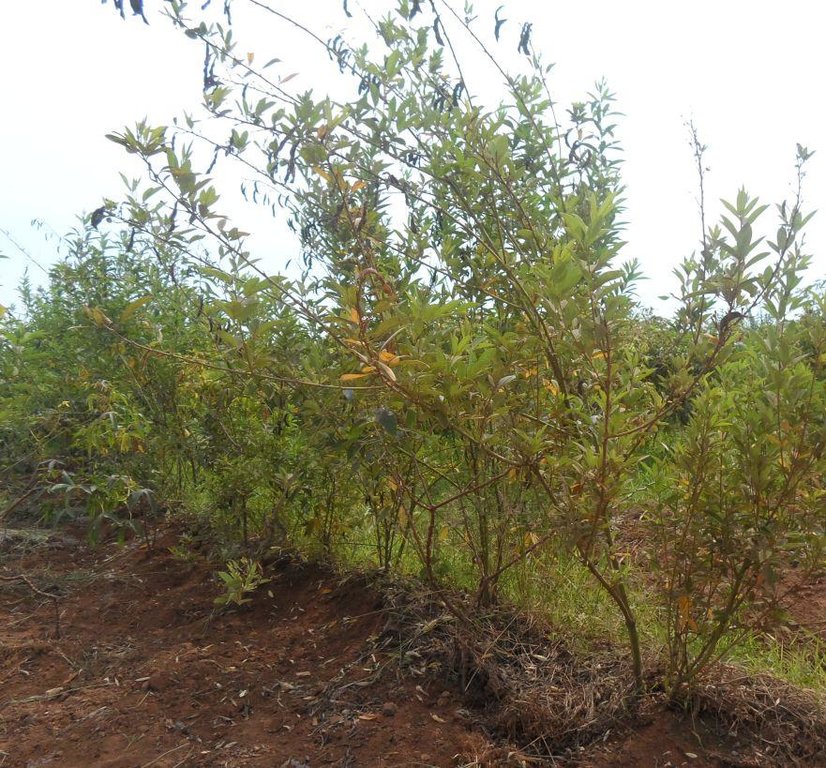
Improved cassava production through the use of contour bund stabilized with cajanus cajan, manure application, cover crops (ground nuts) and improved cassava germplasm.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The technology involves a combination of structural, vegetative and agronomic land use practices aiming at improving production of cassava (Manihot esculenta), improving potential of the soil and environmental function of the land. The technology is among a list of basket of choices of SLM practices recently introduced and adapted to the area by land user and experts working with SCC-Vi Agroforestry an NGO contracted/outsourced by the Tras-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (Kagera TAMP) for provision of SLM advisory and extension services.
Contour bunds are constructed across the sloppy landscapes of average slope 5 – 8 % and are arranged in rows from the top to the bottom of the slope. The average distance between contour bunds is 15 meters. A contour bund is a row of long narrow furrow of average width 90cm and average depth 30cm dug across the slope using simple tools and leveled using A-frame method. Dug soils are piled below the slope to form a long strip earth of fanya chini bund. The average height and width of a bund is 30cm and 45cm respectively. Pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) are planted on contour bund to make them more stronger and productive. A single stand of pigeon pea has two plants and the distance between stands is 30 cm. Improved cassavas (Manihot esculenta) variety (mkombozi) that are resistant to cassava mosaic virus are planted in rows between contour bunds. Within rows, the space between cassavas is 1meter and between rows is 1meter. Manure application is applied before cassava planting at the rate of 2kgs per each plant hole. Cassava is usually planted on May and is harvested after one year. Cassava is planted together with groundnuts (Arachis hypogea) as a cover crop. Despite of having the nutritional advantage to farmers, pigeon pea and groundnuts also diversifies farmers’ livelihood income and have a key role of improving ecosystem through soil water conservation (prevent unproductive loss of green water) and improve soil fertility (through soil nutrient replenishment) and their after harvest remains are sources of organic matter.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to:
1) Increase cassava productivity 2) Improved livelihood of the rural poor through diversification of income sources (cajanus cajan, groundnuts and cassava) and 3) conserve and restore ecosystem through soil fertility improvement (replacement of nutrients lost through uptake by plants), soil moisture improvement (by preventing blue water loss through runoff and green water loss through unproductive evaporation) and control of cassava pests and diseases (use of cassava varieties that are resistant to cassava mosaic virus).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities include land preparation, ploughing and harrowing, contour bund construction and leveling using A-frame, manure procurement and application. Maintenance and recurrent activities involves collection of cassava planting materials and planting, vegetative stabilization of the bunds by planting Cajanus cajan, planting of cover crops (groundnuts within cassava farm), weeding/gap filling and harvesting.
Natural / human environment: The natural environment includes crop land dominated with separate annual crops. A combination of structural and vegetative measure (contour bund strengthened and made more productive with Cajanus cajan). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is moderate lying between 5-8%. Soil texture is gravel sandy loam with medium soil depth.
On human environment, mechanization is dominated by use of handy tools and occasional use of tractors. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, manure, seeds and cassava planting materials with average annual costs of 1033.47 USD per hectare. Land ownership is individual not titles. The expected average annual gross revenue per hectare accrued from cassava alone is 20580 USD.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tanzania/Kagera region
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Missenyi District Council/Minziro village
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
SLM technology was applied in the area under FFS training and partially adopted to some individual farmers fields (FFS members).
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Recently introduced through interventions supported by Tran Boundary Agro-ecosystem management project (Kagera TAMP).
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- legumes and pulses - beans
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
- pigeon pea
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- pineapple
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
- coffee, open grown
- mango, mangosteen, guava
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion caused by rainfall water runoff, low soil fertility due to excessive nutrient plant uptake without replenishment and moisture water stress.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, low moisture and low crop productivity.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: cropping system is largely dominated with annual and perennial cropping and there is also some patches of agroforestry (largely fruit trees like avocados and mangoes).
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V5: อื่นๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Specification of other vegetative measures: vegetative stabilization of bund using cajanus cajan
Specification of other structural measures: Contour bund construction
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (no use of soil fertlization measures), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Nutrient removal by plants without replenishment), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (no use of structural measures to control rainfal runoff and support infiltration), change in temperature (Soil moisture stress to excessive rise in temperature due to climatic change and variability), change of seasonal rainfall (Moisrure stress aring from reduction of the seasonal rainfall (due to climatic change and variability)), droughts (Soil moistrure stress due to unpredicted droughts), population pressure (Continuous use of the land without fallow periods or fertilility replenishment), poverty / wealth (Farmer incapacity to invest in sustainable land managment), labour availability (Migration of the youth to the town leaving behind the less enegetic elders incapable of managing labour intensive SLM), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge about SLM.), governance / institutional (No deriberate institutional support to SLM)
Secondary causes of degradation: inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Water runoff intensified by nearby road construction)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (field staff/agriculture advisers are knowledgeable of the principle behind use of contour bund and manuring and therefore can do with short/simple retraining seminars and learning by doing on the job.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Farmers/land users needs thorough understanding of the principle behind use of contour bund and soil fertility replenishment methods. They also need significant shift of mind set.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Cover cropping
Material/ species: groundnuts
Quantity/ density: 0.2 ton/ha
Remarks: random
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: manure
Quantity/ density: 10ton/ha
Remarks: 1kgs on manure per cassava plant hole
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Trees/ shrubs species: cajanus cajani planted as seeds
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5 - 8%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 5%
Structural measure: Contour bund
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): dug soils are piled down slope (fanya chini) or above slope (fanya juu)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5 -8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tanzanian shillings
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1700.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.17
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting cajanus cajan (perennial shrub) | once |
| 2. | Construction of contour bunds | once |
| 3. | Purchese tools | |
| 4. | Traction hire |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Planting cajanus cajan (perennial shrub) | person/days | 13.0 | 1.7 | 22.1 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction of contour bunds | person/days | 13.0 | 3.46 | 44.98 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor (hired) | pieces | 1.0 | 95.0 | 95.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | pieces | 34.0 | 2.941 | 99.99 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | kg | 6.0 | 27.0 | 162.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 424.07 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.25 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | land preparation for tractor operation/ cleaning/grass slashing (usually occasional depends on land complexity) | November |
| 2. | land manual harrowing (after tractor tilling). | November |
| 3. | manure application | May |
| 4. | Planting of cassava and groundnuts. | May |
| 5. | weeding cassava, groundnuts and pigeon pea (done concurrently) | twice |
| 6. | Harvesting and transportation of groundnuts. | Jully |
| 7. | Harvesting and transportation of cassava (after one year) | May |
| 8. | harvesting cajanus cajan | once |
| 9. | Maintenance of the contour bunds (cleaning of the furrow floor/walls and reshaping of the bunds) | once |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | land preparation for tractor operation/ cleaning/grass slashing (usually occasional depends on land complexity) | person/days | 13.0 | 1.7615 | 22.9 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | land manual harrowing (after tractor tilling). | person/days | 13.0 | 3.55 | 46.15 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | manure application | person/days | 13.0 | 3.55 | 46.15 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planting of cassava and groundnuts. | person/days | 13.0 | 0.88 | 11.44 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Groudnut seeds | kg | 200.0 | 0.4706 | 94.12 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Cassava cuttings | cuttings | 10000.0 | 0.011765 | 117.65 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | tons/ha | 10.0 | 13.235 | 132.35 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: weeding cassava, groundnuts and pigeon pea (done concurrently) | person/days | 13.0 | 3.54 | 46.02 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Harvesting and transportation of groundnuts. | person/days | 13.0 | 0.88 | 11.44 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Harvesting and transportation of cassava (after one year) | person/days | 13.0 | 2.65 | 34.45 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: harvesting cajanus cajan | person/days | 13.0 | 1.76 | 22.88 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Maintenance of the contour bunds (cleaning of the furrow floor/walls and reshaping of the bunds) | person/days | 6.0 | 3.83333 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 608.55 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.36 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, sickles, machete and mattock, hand hoe, spade, sickles and machete
The costs are calculated per unit hectare.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Manure application is the most cost determinant factor
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The area receives bimodal type of rainfall (March to May heavy rainfall and Sep to Dec light rainfall season)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average temperature is 20°C. The average length of growing period is 210 days
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (average attitudinal zonation is 1200 m a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Moderate (average slope is between 5-6%)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (Soil depth is between 30 -50 cm)
Soil texture: Medium (Soil texture is sandy loam)
Soil fertility: Low (There is low soil fertility due to nature of soil and wash by rainfall runoff)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (easy washout of organic matter and nutrients due to the nature of the landscape and soil textural characteristics)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (The area is dominated by sandy loam soil which characteristically have good drainage and infiltration)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (characteristics of sandy loam)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: >50m (is difficult to access ground water table)
Availability of surface water: Also poor/none (There is no surface water in the area. People in the nearby or around the area fetch water from the natural springs found in the lower distant hilly/mountain floors)
Water quality: Good drinking water (water in the lower mountainous floors is in permanent water spring and is good drinking water)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Flora biodiversity is largely dominated by few species of natural grasses dominated by hyperenia rufa and with some limited amount of fauna (ants, earth worms and some insects).
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (own land greater than 5 acres with reliable off farm income).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land (own land not more than 5 acres with some pety business).
30% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land (average land owned is 2 acreas).
15% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (land owned is less than 2 acres and rely on casual labourer).
Off-farm income specification: average rich and poor land users largely use the technology. On the other hand rich land users with reliable off farm income and very poor land users who largely relies on casual labourer seldom use the technology.
Market orientation: Mixed (cassava and groundnuts production are meant for subsistance and commercial use)
Level of mechanization: Manual work (manually using simple hand tools dominated by hand hoe)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Domestic water sources are for the use of all community but are governed by agreed management rules e.g. it is strictly prohibited to water the animals in domestic water sources and there is clear identification and demarcation of areas used for washing and collecting water for drinking and cooking.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1-2 kgs of cassava per crop stand
หลังจาก SLM:
2.5-4 Kgs of cassava per crop stand
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to manure application.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50% risk
หลังจาก SLM:
10-20% risk
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due controll of soil erosion, soil fertility improvement and cantroll of moisture stress.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0 tons/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
20 tons/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Use of farm yard manure.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1 income source (cassava)
หลังจาก SLM:
3 more sources.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
additional income from cajanus cajan, groundnuts and beans
ภาระงาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
6
หลังจาก SLM:
12
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
the technology is labour intensive and heavy labour is needed
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1
หลังจาก SLM:
3
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
incresed no of diets cajanus cajan and beans/protein, cassava/carbohydretes, groundnuts/oil
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
33%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
access to varied food sources and capacity to invest in health services.
สถาบันของชุมชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
1
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
FFS SLM groups
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
5%
หลังจาก SLM:
20%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
% land users aware of improved conservation/erosion knowledge
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
5%
หลังจาก SLM:
40%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
women involvement in SLM activities
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
the technology resulted in increased crop production emanated from improved soil fertility and control of erosion. There is also diversification of income sources from cover crops (groundnuts) and cajanus cajan (cow pea) as well as improved diet due to varied food sources. All these contributed to improved livelihood and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
30%
หลังจาก SLM:
5%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
runoff speed reduced through the use of contour bund and cover crops
การระเหย
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
evaporation reduced from use of civer crops.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
20%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
water stored in soil due to the use of contour bunds and cover crops
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
45%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increased percentage monthly soil coverage with cover crops (ground nuts and beans)
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
controll of soil loss through erosion.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
nutrients generated from the use of beans (phaseola vulgaris)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
following use of farm yard manure
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1
หลังจาก SLM:
3
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
crop varieties planted in different phases on the same land
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farm yard manure is a good medium for increased microbial action and soil fauna
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0%
หลังจาก SLM:
50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increased possibilities for using pest and disease resistant varieties.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Area put uder cultivation are usually protected and less prone to fire burning
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
indirect reduced water loos due to runoff
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
rainfall runoff impeded or trapped by contour bunds
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reduced siltation of the natural water spring in the lower mountain/hilly floors.
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reduced distruction of public roads through eroded soil.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cover crops (groundnuts) where used to provide vegetative cover and to some extent reduce the effect of excessive soil moisture loss due to direct sunlight and by reducing the speed of rainfall runoff.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
At the beginning only slightly positive benefits are realized this is caused by the high investment/establishment costs. But with time benefits are very positive and overcomes establishment costs (non recurrent costs e.g. due to construction of contour bunds).
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
34 households and 100% of the area covered
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
76% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
17 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 13 members groups participated in 0.25 acre plot of cassava as test crop
24% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
17 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: early adopters
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: it is early to give the overall picture of technology adoption as it was recently introduced in April 2013.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Simple to learn/ farmers gained soil fertilization knowledge. |
| Farmers gained soil management skills through learning by doing |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology contributes in improved crop production and productivity. |
| Contour bund are stabilized with cajanus cajani which contributes to farmers nutrition and income. |
| Cover crops (groundnuts) that are grown within cassava are alternative sources of income to farmer before cassava is ready for harvesting and also improves soil fertility and moisture. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High initial investment costs. Farmers are capital strapped and have low investment capacity. | Raise farmers investment capacity through establishment and their direct engagement to rural micro finance institutions (SACCOS and VICOBA). |
| Unintended results due to the negative effects of climatic change and variability | Find means and ways to mitigate adapt climatic change and variability (e.g. use of drought resistant varieties). |
| Contour bund construction is labour intensive and can not be performed by older people who lacks physical strength and energy. | Make sure that FFS groups compose a balance of youth and elders who can play complementary roles to each others. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
11/06/2014
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล