Rip-ploughing, oversowing [แอฟริกาใต้]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Insaai (Afrikaans)
technologies_1372 - แอฟริกาใต้
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
De Wet Saroné
Hattingh Asterid
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
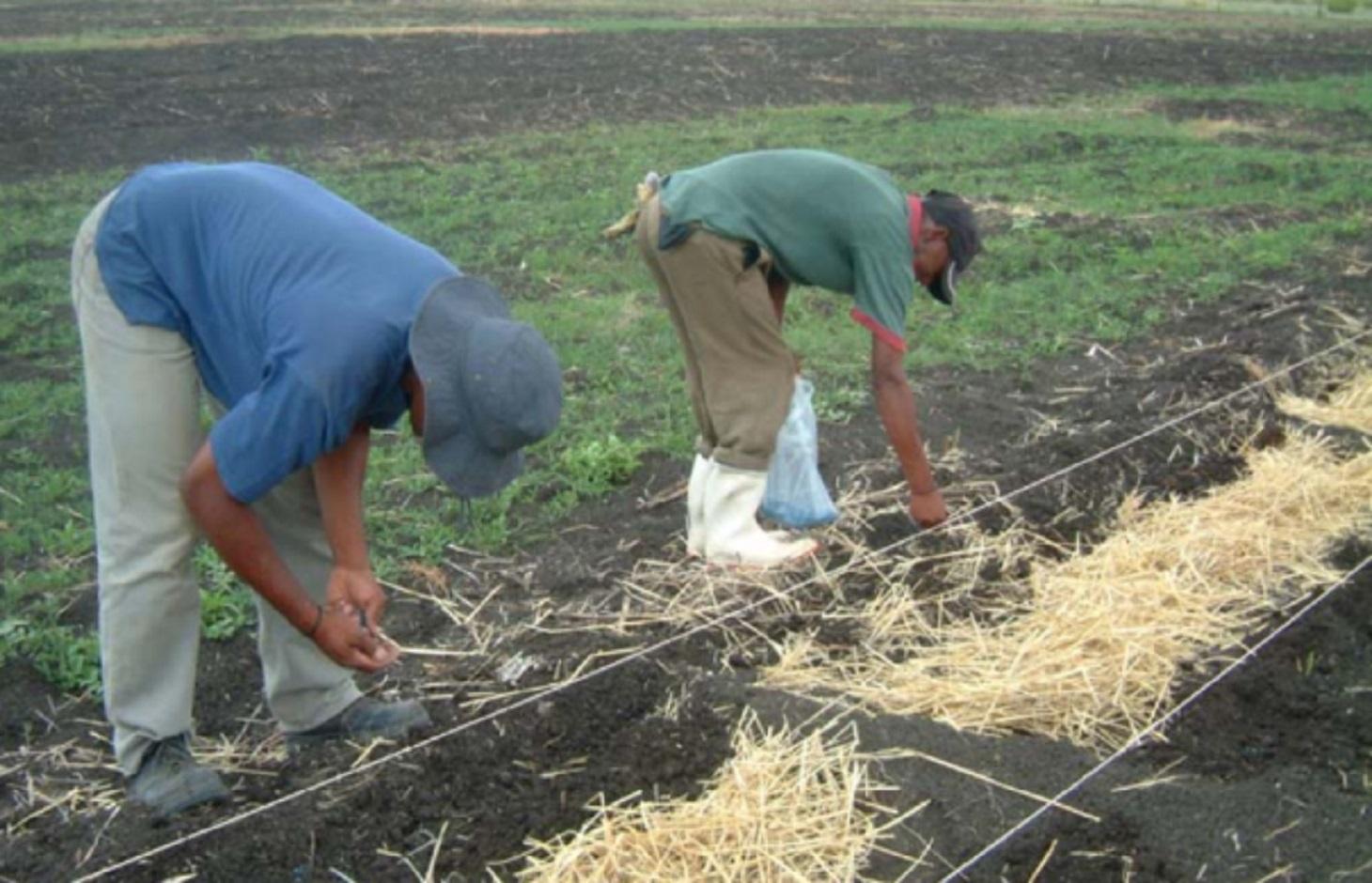
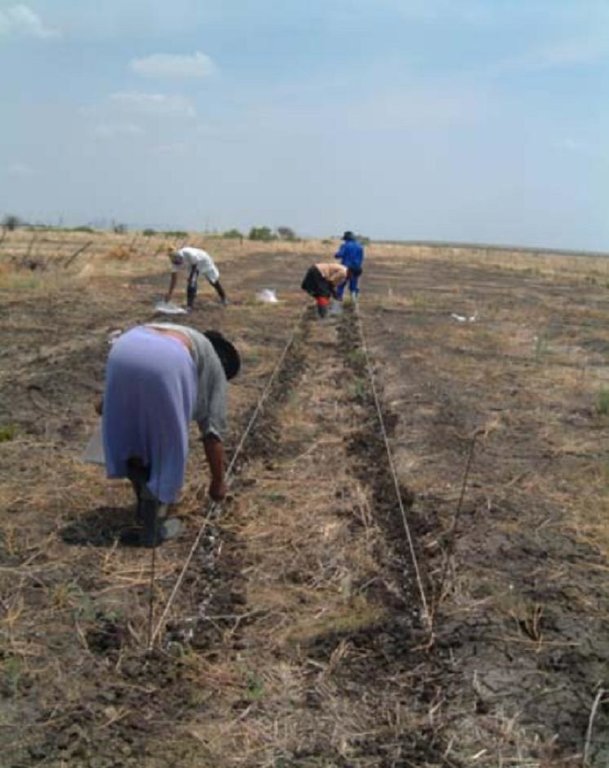
Ripploughing and oversowing (sodsowing) of extensive grazing land in order to improve productivity of a semi-arid rangeland.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
A pasture characterised by the unpalatable Cymbopogen plurinoides grass species was rip-ploughed to a depth of 20, 15, or 7 cm to uproot the unfavourable grass species.
Coated and uncoated seeds of more palatable grass species were hand sown into the furrows and the soil kicked over the seeds.
Grazing has been excluded for the past four years, giving the sown-in grass species the opportunity to establish and credit the soil seed bank.
The purpose of the technology was threefold: First, the success of rip-ploughing as a restoration technology was researched. Secondly, the suitability of coated or uncoated seeds was established. Thirdly, the suitability of the technology for restoration purposes was researched. This was done in the summer of 1995/96. The frequency and density was measured in the following years up to 1999. The density was measured with a 1 x 1 square meter; and tillers, vegetative and reproductive plants were distinguished.
The purpose of the frequency measurement is to establish the percentage a grass species contributes to the grass community. The density measurement gives the amount of rooted plants in a square meter. Distinction between the life stages indicates the self-sustainability of a population. Seed bank analyses are also added.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แอฟริกาใต้
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
North West Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Madikwe, Koster, Potchefstroom
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
0.1
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.1 km2.
The localities are not strictly basin, except Kromspruit & Tweefontein. Davidkatnagel has no slope. Totiuskraal lies between the watershed and basin.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Lennof Reynecke (fellow student) & Klaus Kellner (lecturer)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing or rather mismanagement led to i) dominance of the unpalatable grass species at Koster, and ii) bare soil at Totiuskraal, Davidkatnagel and Krompspruit.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Erosion/overgrazing making area unsuitable for grazing because of lack of vegetation of appropriate palatability and nutrition.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Kromspruit; Davidkatnagel
Ranching: Totiuskraal; Koster
Grazingland comments: Area closure only followed on incentive of researchers. Koster duplicated area enclosure on own initiative afterwards.
Type of grazing system comments: Area closure only followed on incentive of researchers. Koster duplicated area enclosure on own initiative afterwards.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
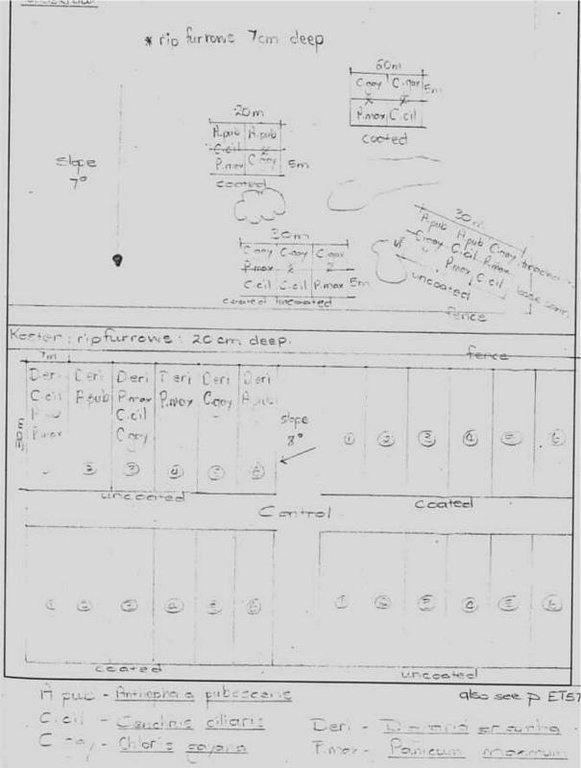
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Site plan for rip-ploughing and hand sowing of palatable grasses.
North West
Date: 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Grass species: Anthephora pubescens, Digitaria erlantha, Chloris gayana, Cenchrus ciliaris, Panicum maximum
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 8.00%
Change of land use type: Area close for plant establishment
Change of land use practices / intensity level: After plant establishment grazing occurs as in 2.4.3.3
ผู้เขียน:
Sarone de Wet
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
8.30
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedbed reparation | Summer |
| 2. | Sowing of seeds | Summer |
| 3. | Enclosing site | Summer |
| 4. | Debushing were necessary | Early Summer |
| 5. | Area enclosure | From start for 2 years |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Constructing seed beds and | persons/day/ha | 36.0 | 8.3 | 298.8 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 308.8 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 308.8 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grazing excluded | /Continuously |
| 2. | Grazing | Spring (Apr-Sept) /After 2 y for a week; then after regrowth |
| 3. | Rotation grazing | Late summer after 2nd year / Once a year for winte |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
For Koster, in terms of seeds and tractors; as well as final credit after 3 years measured in R/ large stock unit.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour and transport; equipment (gasoline).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
430mm and 520 mm
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Hill slopes for Totiuskraal, footslopes for Koster and valley floors for Davidkatnagel; Kromspruit
Altitudinal zone: 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l. for Totiuskraal
Slopes on average: Flat for Davidkatnagel, gentle for Kromspruit and moderate for Koster; Totiuskraal
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture: All sites actually; sandy clay loam: the soil is evenly textured but has a high clay content
Soil fertility is very high
Topsoil organic matter: Medium for Koster and poor for Kromspruit, Davidkatnagel and Totiuskraal.
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium for Koster and poor for Kromspruit, Davidkatnagel and Totiuskraal.
Soil water storage capacity: medium - high
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, very poor
40% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (Koster).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Totiuskraal).
20% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (Kromspruit; Davidkatnagel).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers have extra-farm occupations for the Totiuskraal area
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence for Kromspruit; Davidkatnagel and commercial for Totiuskraal; Koster
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not large enough to be economically viable
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Perennial grass species
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Perennial grass species
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Able to carry more livestock in a sustainable way
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
input constraints
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Labourers expect more money
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Explained beforehand
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Difference in goal
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Compared to none treated site
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation cover binds soil
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
winter forage
Bush encroachment
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Easy establishment
palatability draw animals
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
If not controlled - overgrazing
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation bind soil; denser covering of soil
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation cover ~100%
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
30 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
30 land user families have adopted the Technology
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
25% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: One land user applied the technology to another part of his farm.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Vegetation cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? Rotational grazing |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Establishment of perennial grass cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing management; not graze to seed production stage. |
|
Increase of perennial grass production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing management |
|
Find suitable seed mixtures for different habitats How can they be sustained / enhanced? Literature study on habitat preferences |
|
Seed bed preparation enhance establishment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Know exact depth of sowing of seeds. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Implementation in communal areas mostly | Brainstorm on implementation without gasoline needed. |
| Communication with landuser | Contact on monthly basis built friendship |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Veld management in South Africa, Tainton. 1985.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
From researcher
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล