Carob tree protection from rats [ไซปรัส]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Michalakis Christoforou
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Προστασία χαρουπόδενδρων απο προσβολές αρουραίων και ποντικών
technologies_1703 - ไซปรัส
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
Governement official:
Costas Michael
Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Environment, Cyprus
ไซปรัส
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Cyprus University of Technology (Cyprus University of Technology) - ไซปรัส1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
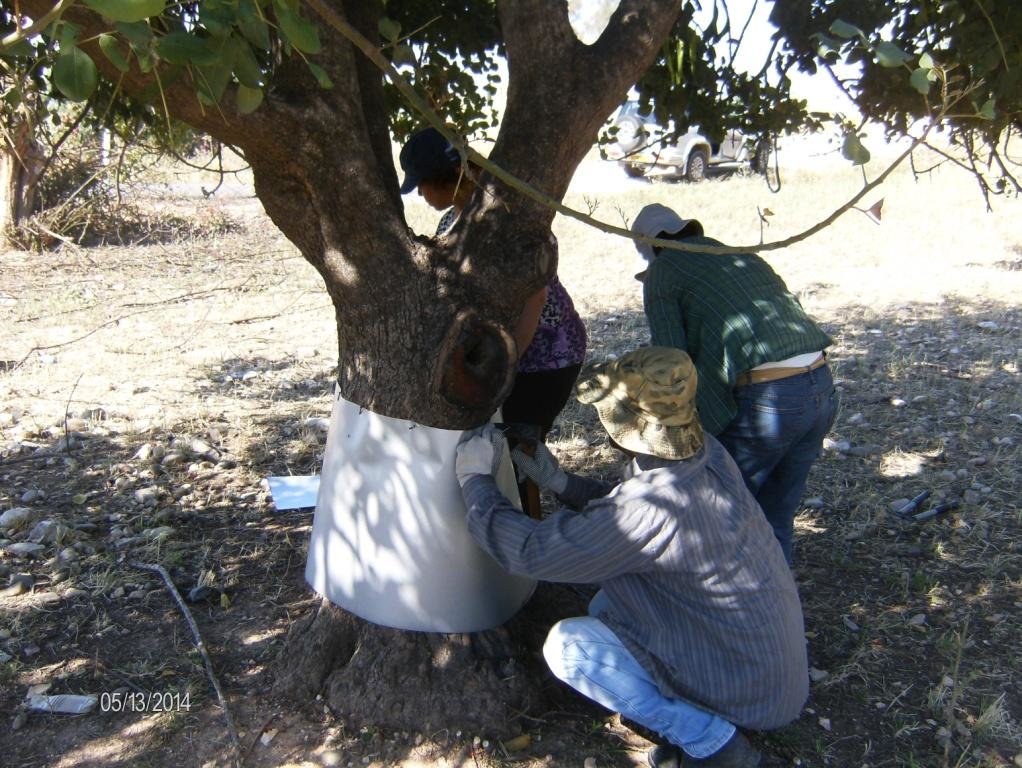
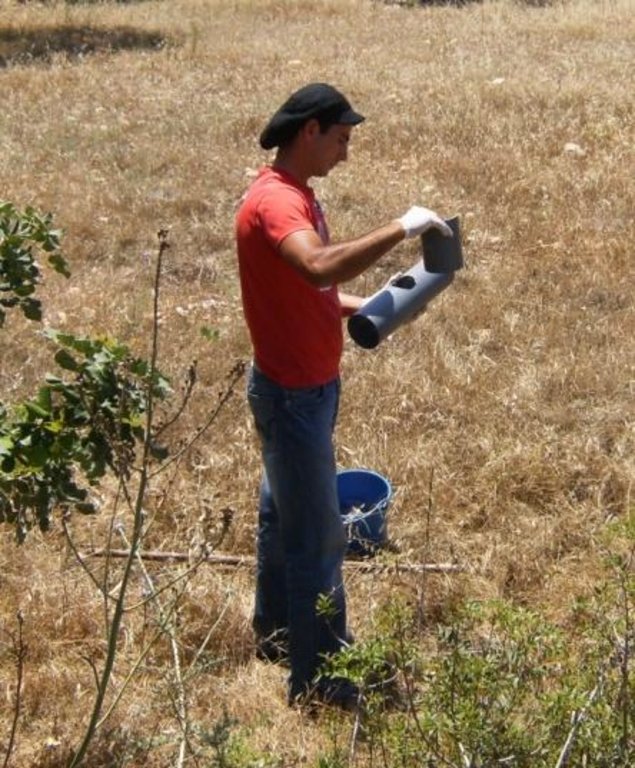
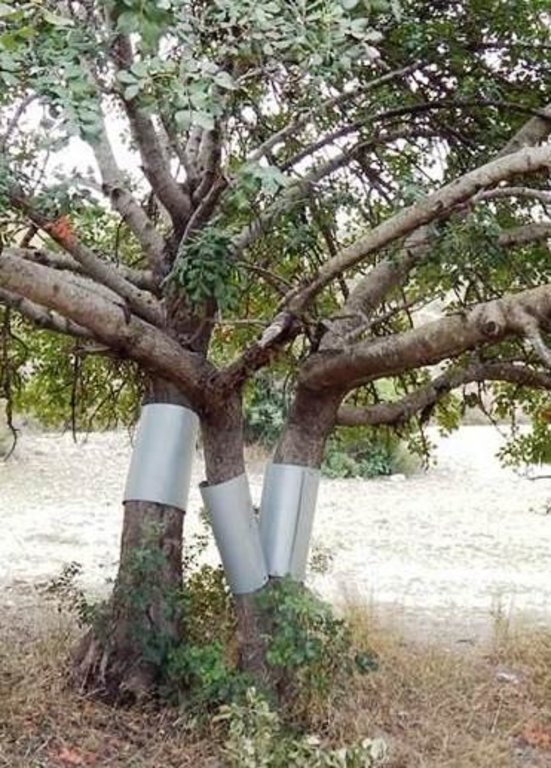
Carrob tree protection from rat attacks include protection of trees directly by using aluminium layers as rings on the neck of the carob trees in order to keep rats away from climbing on the threes and thus causing problens on fruits and new branches. Furthermore, poisonus rat baits are attached on the trees in case the aluminium layers can not be used.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
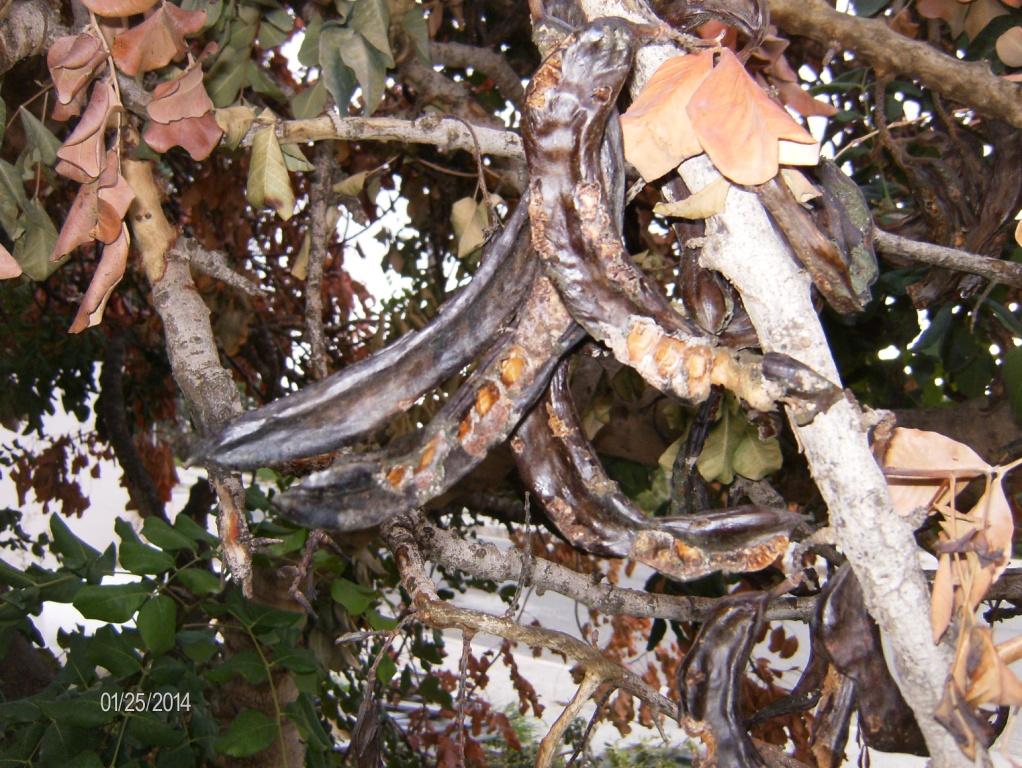
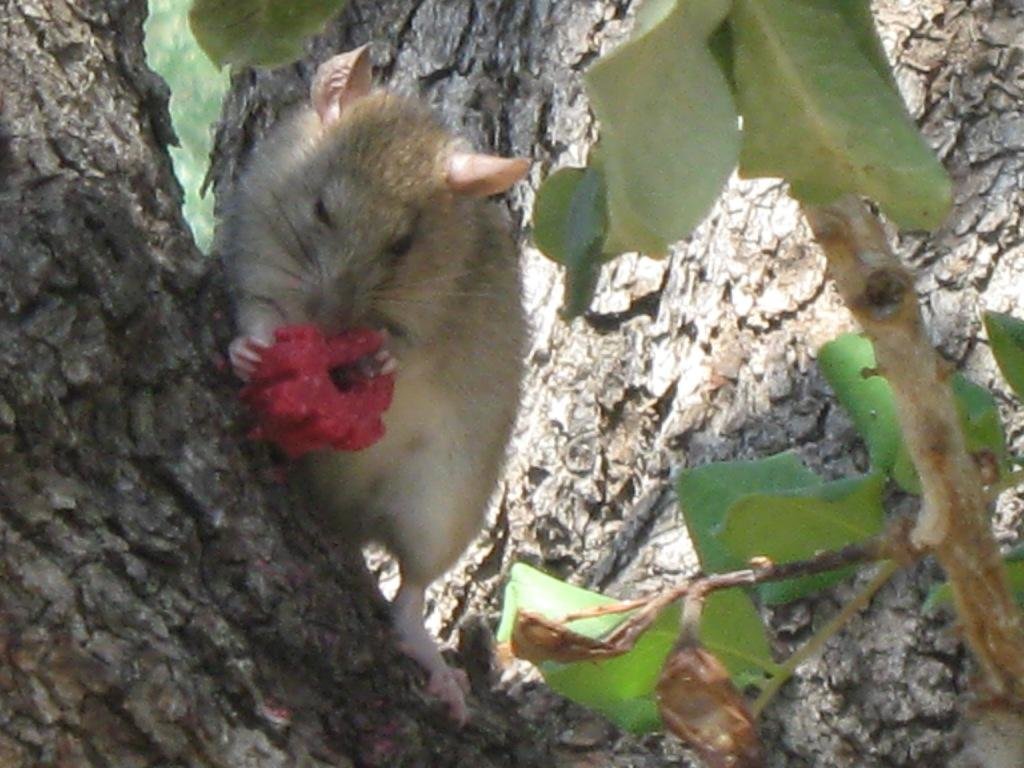
Carob trees are attacked every year by rats who nibble the trunk stem of the tree, remove the bark of the trunk and the branches sucking the juice and eat the mature fruits. Rats nibble the bark of the tree in order to reduce their teeth size which tends to enlarge year by year. This results in the death of the tree branch or even of the entire tree. The tree may also show symptoms of hemiplegia. Rats run on the tree through the trunk. Apart from the direct effect of rat attacks on carob trees, rats also cause other problems to humans and animals. Rats are vectors for serious pest and diseases
Purpose of the Technology: The rat population increases rapidly when there is enough food (such as carobs) available, and the population grows even faster in the absence of natural enemies. . Through interrupting the access from the ground to the tree trunk, or by pruning the branches which are connected to the ground, the rats are hindered from climbing the trees. Rats can also be controlled through the use of chemical baits. However, these baits should only be used by experts who know where and how to place them in order to avoid that other animals come in contact with the baits. Natural enemies such as cats, snakes and birds (e.g. Bam owl (Tyto alba)) should be breeded and established on the carob trees, and farmers, hunters and locals should be informed not to kill the natural enemies of rats.
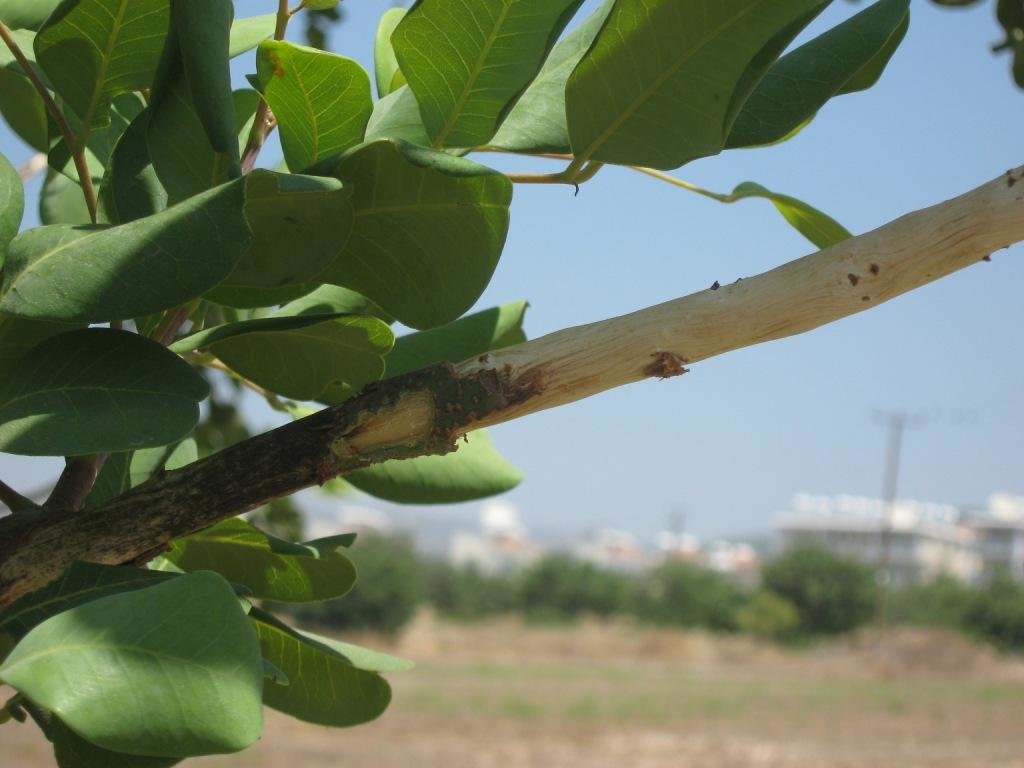
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The carob trees can be protected from rats by covering the tree neck and trunk from the ground up to 1 meter with a hard material such as aluminium with a slippery surface. This way the rats are not able to climb the trees since they will slither on the ring layer.
Natural / human environment: The carob tree protection will increase the production of carobs and therefore the income of the growers. Already established carob trees could provide a good income to growers with low production cost. The population of rats will decrease since the major source of food will not be provided anymore. Educating farmers, hunters and the local population about the benefits of natural enemies will allow that the environment regulates the rat population by itself.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ไซปรัส
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Limassol
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Pissouri
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
50.0
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 km2.
Carob trees are grown in dry lands such as Pissouri and its sorrounding villages. In Cyprus a total of 4000 hectares with 300'000 carob trees are cultivated. The annual production of carobs is around 9000 to 12000 tons. Carob growers use minimum agricultural practices such as mechanical weed control and pest control (insects and rats)
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The use of aluminium layer covering the trunk of carob trees was applied in an EU project called Agrolife which started in 2014, http://agrolife.eu/
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- carob
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: mid October to mid May
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Rat attacks on carob trees cause severe problems for plants health and the fruit quality and production.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Carob growers: Rats are attacking the carob trees causing the death of the trees and damage of fruits.
Locals: The rat population increased during the last 30 years especially in areas where carobs are grown.
Agricultural officer: Rat population increased rapidly causing serious problems in carob production due to heavy rainfall in 2012 and to the hunting and killing of the natural enemies such as snakes and birds by the locals and the farmers.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
- Tree protection
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A7: Others

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M7: อื่นๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: covering the tree trunk with aluminium layer
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Hunting and killing the natural enemies such as snakes and birds)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Rat popuation increases rapidly after rainy year)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Aluminium layers are placed aroud the bark of carob trees as a ring. The aluminium is thin and light thus does not affect the growth of the tree. The hight of the aluminium is more than 50cm so that the rats can not climb or jumb on the bark of the tree
Location: Pafos. Pafos
Date: 10/3/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Agricultural advisors will inform the land users about the rat life cycle and their charactiristics in order to understand the use of the technology)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land users will implement the technology by installing the zinc or alluminium layers around the tree trunk)
Technical knowledge required for wildlife department: low (will release natural enemies such as the bird Tyto alba)
Main technical functions: reduction of rat population, protection of carob trees and fruits
Structural measure: tree trunck cover with aluminium layer
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (other): aluminium layers 1m X 1m X 0,01mm
ผู้เขียน:
Costas Michael
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.91
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
33.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | covering the tree trunk with an aluminium layer | winter, spring |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 265.0 | 265.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Aluminium layer | ha | 1.0 | 1116.0 | 1116.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Iron nails | ha | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1393.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1530.77 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of aluminium layers | once a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: hammer, nails
The costs were calculated for 8 persons working 8 hours per day and per ha. The costs were calculated on the 28th of August 2015.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The costs are affected by the trunk diameter and the plant height
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Total annual rainfall in 2013=255mm
Total annual rainfall in 2014=363mm, and in 2015=300mm from Jan to May
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics. In Jan and Feb the temp can go below 5 C for few hours in one or two days.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l (most of carob trees areas)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (most trees are planted in plateaus. The technology is not affected by landform)
Slopes on average: Flat (most of the plantations), gentle (some fields) and moderate (few plantations, old age carob trees)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (plateaus, flat areas) and shallow (hills with aged carob trees)
Soil texture: mdeium (in plateaus and flat areas) and fine (mostly on the base of the hill)
Soil fertility is medium in plateaus and flat areas and low mostly on the base of the hill
Topsoil organic matter is medium (in plateaus and flat areas) and low (mostly on the base of the hill)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low (due to lack of rainfall, when it rains the water is immediately absorbed by the soil)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table is 5-50m (if a field is near a river) and >50m if a field is far from rivers
Availability of surface water is poor/none (When it rains it does not last long enough in order to cause floods)
Water quality (untreated) is for agriculutral use only ( ground water analysis showed that in some cases the water is contaminated with boron)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Few species grow within the carob trees and those are mostly weeds. Once a year the growers remove the weeds from the fields. Fauna is also poor and consists of rodents, snakes, few birds and insects
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most of the land users are old men and women. Very few young men are involved in the carob tree production.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
80% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Since rat attack is the most damaging factor affecting the growth of carob trees and the quality of the product, the land users who apply the technology have more income with unsignificant yield losses caused by other factors.
Level of mechanization is manual labour (pruning, irrigation and harvesting) and mechanised (cultivating, weeds control, pesticide applications)
Market orientation is mixed (farmers either sell their products individually or sell them as a group)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
35 Kg/tree
หลังจาก SLM:
45-50Kg/tree
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Trunk and branch protection lead to yield increase
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Although other factor like fire, frost, pests and diseases can cause production failure, rat attack is considered as the most damageable
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1,5 euro/tree
หลังจาก SLM:
1 euro/tree
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During pruning, large dead branches should be removed
ภาระงาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50 trees/day
หลังจาก SLM:
65 trees/day
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During pruning,
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Carob fruits are free from infectious diseases transferred by rats
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduction of rat populations within the production area minimizes the risk of man diseases infection like typhos,
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology improved both livelihoods and human health. The growers income has increased more than 10-20% due to the reduction of the damage caused by rats every year. The reduction of the number of rats minimized the risk of human pathogens such as typhus which was very common in these areas.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase of predators in the areas around the carob trees since rats can not climb on carob trees
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Fields with carob trees being attacked by rats are more sensitive to fires since they are abandoned by their owners
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Control of rat population
Quality of carob trees and fruits
Plant growth
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
On small trees the aluminium layer is pressing the trunk in a way the tree can not grow normally. In this case the aluminium layer must be replaced with a layer once every few years
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
rat population around the SLM technology is decreased therefore the damage caused by rats to the neighbours is also decreased
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Decrease in rat population rear farms also decrease the damage caused on the farm infrastructure (wires, wood, plastic equipment), by rats
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The use of aluminium layers covering the trunk of carob trees is not affected by the climatic conditions. Climatic conditions such as heavy rain could affect the use of plastic tubes which include poisonous bait or the direct poisonous cubes placed on the tree branches.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Due to the damage caused on the carob trees by rats already, the trees will need some time (2-3 years) to create new branches able to produce fruits. Furthermore no new damages occur on trees.
During the first 3-5 years the aluminium layer can remain on the trees. After this period the aluminium should be replaced with a larger one due to the enlargement of the tree trunk.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
10
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Due to the lack of effective and cheap ways for controlling rat attack on carob trees the land users are adopting the technology, and so far they get positive results.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Few other land user are interested in adopting the technology. Many other land users are not adopting the technology because they inherited the land and they are not actually working on the land in order to make profit.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| easy to install |
| the technology can be used over a long time |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
the technology can be used over a long time How can they be sustained / enhanced? use of non-oxidizing material |
|
the aluminium layer can be bent easily How can they be sustained / enhanced? both vertical edges should be hold each other by the use of a spur |
| low cost |
| easy installation |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| the aluminium layer can be a target for thieves who steal metal |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| the aluminium layer should be replaced in time because the trees are growing in size | install larger aluminium layers and lold it with spring |
| The aluminium (metal) can overheat during summer time | Spray the layer with white paint |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล