MANGO AND CITRUS TRESS GROWN AS CASHCROPS AND FOR SOIL FERTILITY IMPROVEMENT [ยูกันดา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: betty adoch
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Udo Höggel
Gwoko nyig yen igang
technologies_2319 - ยูกันดา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Okello Vincent
0782954875
okellovincent7@gmail.com
Pagwari Fruit Farmers Association
Pader district, Acoro Sub-County , Acoro parish, Pagwari East village
ยูกันดา
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
09/05/2017
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
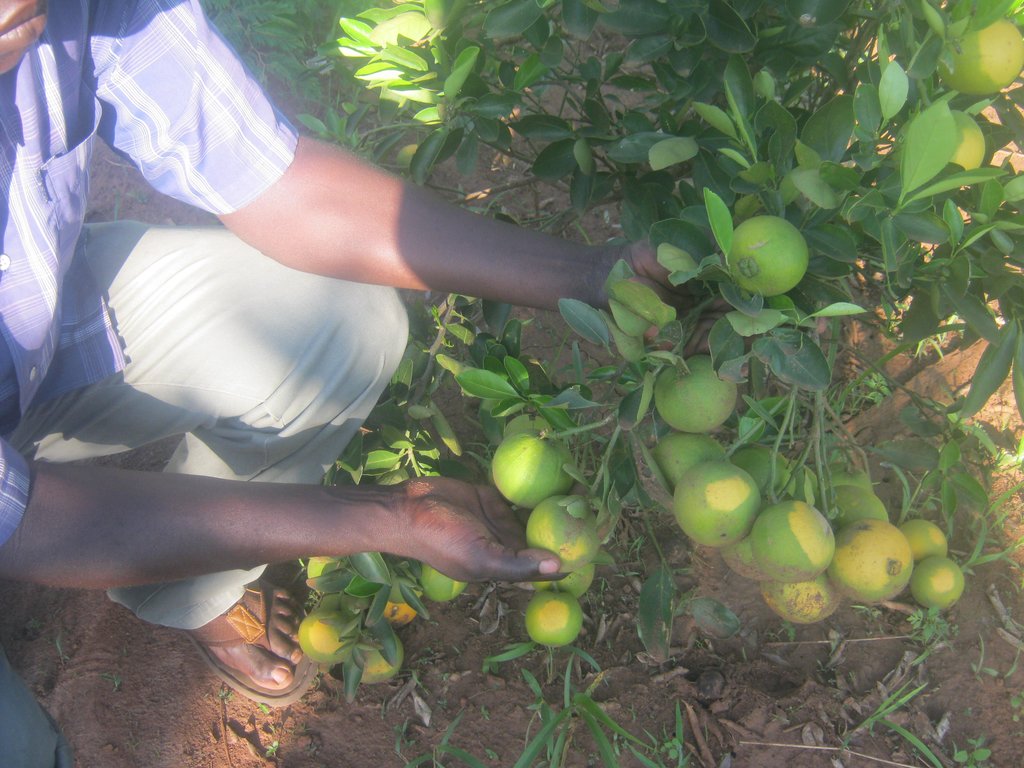
Different varieties of mangoes such as Banganapalle, Alphonso, Kesar, Haden, Bombay, Kent, Keitt, oranges such as Washington Navel, Valencies, Tangarine, jack fruits and avacados are grown for purposes of household income and soil fertility improvement.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
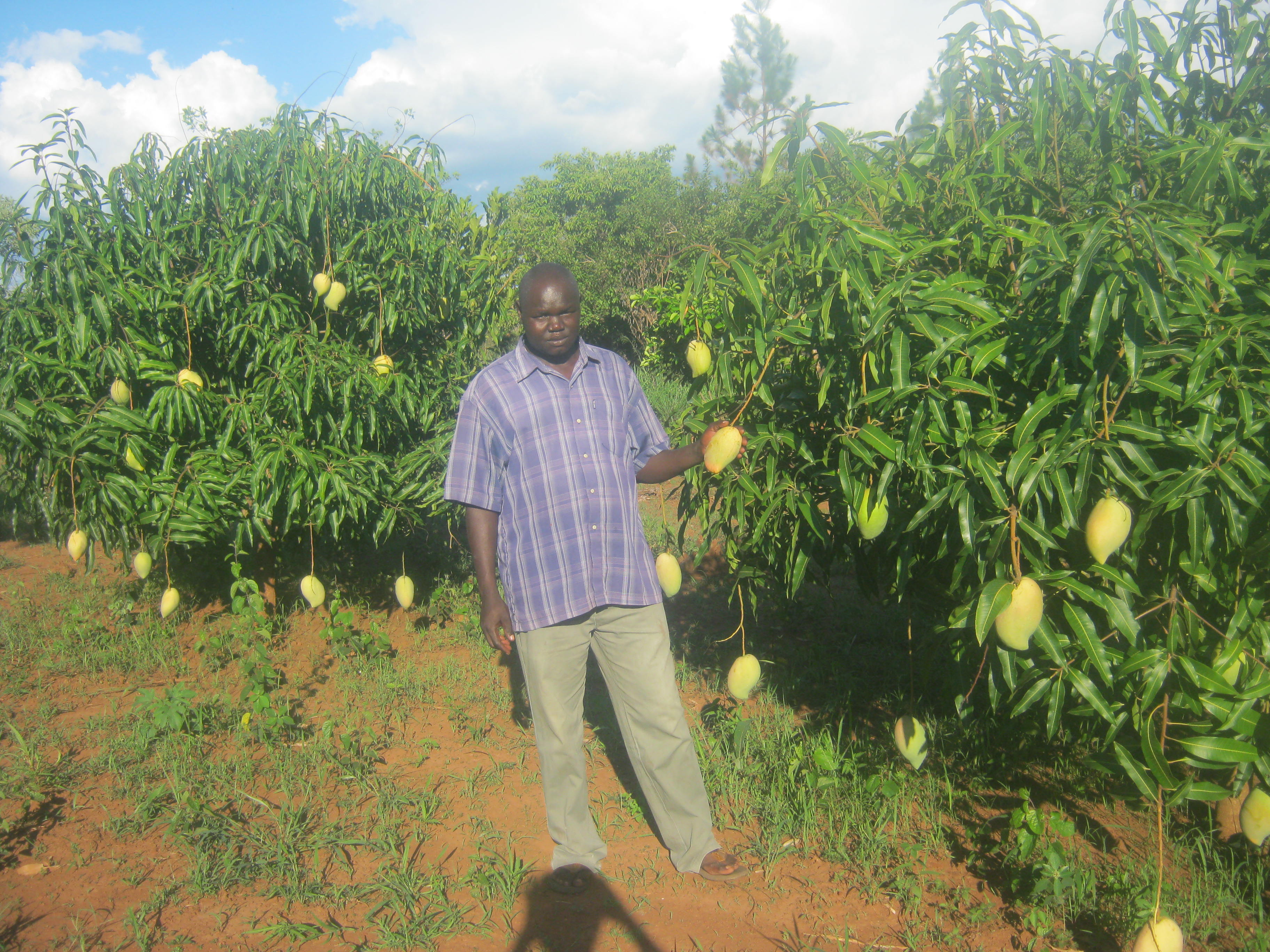
Home fruit tree groves of grafted mango (mangifera indica) and citrus (citrus aurantium) is a farming practice that farmers practice in Northern Uganda to diversify their economic activity, for soil fertility improvement and household income.
Northern Uganda has tropical savanna climate which receives moderate amount of rainfall ranging from 750-1000mm per annum. The soils are moderately fertile with less organic matters coupled with soil erosion, which leads to low crop productions hence low incomes. The moderate rainfall is also unreliable which makes the region to experience drought. Farmers grow fruits as an alternative source of income.
This land user generates over 90% of his household income from fruit growing. The planted fruit trees increase the organic matter content in the soil when dry leaves decompose, rooting prevents soil erosion, pruned brunches are a source of fuel wood and trees acts as wind breaks. Major fruits grown include jack fruits, grafted mangoes, oranges and avocados.
For all these fruits, seeds are first planted in a nursery bed for a period for about two months with the following required inputs: hoes, pangas, spades, wheelbarrows, and shovels. Afterwards, transplanting into the gardens is done. Selection and clearing of the field is done and the planting holes are marked. Excavation is done in accordance to the slope direction: the top soil is put on the hillward side of the planting hole then the sub-soil is put on the downward side of the planting hole. The planting holes are dug in a square shape at 60*60 cm. Composite manure is mixed with top soil and applied into the hole to speed up the seedling establishment and to enhance growth. When planting, the hole is not fully filled but ends 5 cm below the surface so to enable water harvesting, moisture retentions and infiltration. This ensures ample soil moisture and water supply to plants.
The spacing for avocados is 8 × 8 m (65 seedlings/acre), jack fruits is 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre), mangoes 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre) and oranges 4 × 5 m (200 seedlings/acre). After planting, mulching is done by saw dust, kitchen waste like groundnut husks, vegetables and so on. 75 mangoes, 150 oranges, 20 avocados, 20 jack fruits and 4 grapes trees are spread evenly over the planting area. To realize maximum production, the land user needs to have constant water for irrigation.
On the other side, fruit tree growing has brought negative feelings from neighbors who don't promote this practice. Fruit farmers' lifestyle has changed due to revenues realised from growing fruit trees. To maintain this technology, weeding, pruning and creating fire lines during dry seasons to protect the farm is very critical . The technology is highly susceptible to pests and diseases that may require support from the local extension worker from time to time to be able to obtain high yields.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
Fruit trees protect the soil from environmental degradation and its effects such as soil erosion and landslides.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
วันที่:
19/05/2017
สถานที่:
Pader District, Acoro parish, Pagwari East village.
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Betty Adoch
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ยูกันดา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Northern Uganda.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Pader District, Acoro parish,Pagwari East village.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
GPS point indicating the land user fruits garden
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2013
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Land user needs to generate income.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้:
- การปลูกหลายพันธุ์รวมกัน
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
The land was use for brick making
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Drip irrigation is done during dry seasons
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
Cows: 5, Goats:7. Improved breeds of goat and cattle which are high yielding
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
- สวนครัว
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The fruits gardens covers 2 acres of land.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Fruit growing promotes soil conversation.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Fruit growing conserves the environment by preventing tree cutting.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area initially was severly degraded by brick making work but after putting it under fruit growing, it became very fertile.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เขียน:
Betty Adoch
วันที่:
19/05/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
The fruit trees are planted on a generally flat average land size of 2 acres of land with following spacing: mangoes 10X10msq, jack fruits 10X10msq because it forms a big canopy, oranges 5X5 msq.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
2 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
UGX
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
3500.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3000 UGX
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing for nursery bed | จัดการพืช | dry season |
| 2. | Raising the nursery | จัดการพืช | dry season |
| 3. | Digging planting holes | จัดการพืช | dry season |
| 4. | Applying composite manure | จัดการพืช | dry season |
| 5. | Transplanting at 15 to 30cm seedling high | จัดการพืช | onset of rain |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Different fruit species have different nursery beds
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Site clearing for nursery bed | Meters | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Raising the nursery | Meters | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Transplanting | Acres | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Pitting for fruit tree planting | Acres | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Pangas | Pieces | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoes | Pieces | 15.0 | 10000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Axes | Pieces | 5.0 | 10000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Wheelbarrows | Pieces | 4.0 | 95000.0 | 380000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | String | Pieces | 4.0 | 5000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Dipper | Pieces | 4.0 | 45000.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Watering can | Pieces | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Spray pump | Pieces | 4.0 | 75000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Bamboo | Pieces | 10.0 | 10000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Dry grass | Bundles | 5.0 | 3000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1535000.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is technically easy to maintain once established and can be replicated by other land users.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | จัดการพืช | after every 3 months |
| 2. | Pest control | จัดการพืช | dry season use cow dung and driny use season pesticide |
| 3. | Stray animal control | จัดการพืช | dry season |
| 4. | Thieves control | จัดการพืช | rainy season |
| 5. | Prunning branches | จัดการพืช | rainy season |
| 6. | Buying pesticides | จัดการพืช | rainy season |
| 7. | Transportation to market | จัดการพืช | season of harvest |
| 8. | Buying mulching materials | จัดการพืช | onset of rain |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Hired labour | Man day | 4.0 | 3000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spray pump | Piece | 4.0 | 75000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Irrigation during dry season | Litres | 10000.0 | 200.0 | 2000000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Syringe pipe | Piece | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedings | Pieces | 269.0 | 3500.0 | 941500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Composite manures | Wheelbarrows | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Stringes for making holes in a stright line | Rolls | 4.0 | 5000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Peg for setting holes | Boundle | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Pesticides (dythen m45) | kg | 1.0 | 40000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 3331000.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user has knowledge on agronomic practices.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
High costs of labor
High transportation cost
Purchase of pesticides
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
950.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Heavy rains in April, May, August and September
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Pader weather station
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Savanna climate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Loamy, silty soil at the top and deep down there is gravel. Soil pH is neutral and less saline.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Very low water table
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The land user is a typical farmer who is contented with his lifestyle as a fruit grower due to the income derived from sale of fruits.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user bought the land from the community members.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user has fenced his land and put marked stones.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the litter from the leaves, increased soil fertility leading to increased production.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the nutrients from the soil.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Especially from the jack fruits wastes
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased level of nutrients in the soil.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Because of the different fruit trees species planted.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The land user recently acquired additional plot of land (0.5 acres) from the sale of fruit trees.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Fruit trees reduce soil erosion and increase soil fertility due to leaves litter.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Fruit trees dont require alot of inputs once established; minimal costs for reducing pests and diseases; minimized by the role of extension workers during trainings.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
From the sale of fruits and reduced expenses on farm in puts
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
From the sale of diverse fruit types (mangoes, oranges, jack fruits and others)
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only labour for maintenance and monitoring against thieves
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Income from sale of fruits is used to buy other household income.
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Daily portion of fruits within diet.
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Community bye-laws on controlled grazing and encroachment were put in place.
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Local bye-law committee (LBC) was put in place and supported by the Sub-County and District Council.
Bye-law on controlled grazing and encroachment passed at Sub-County Level.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Trainings conducted by extension workers and fellow champion farmers, also integrating exposure learning events.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The presence of the local bye-law committee and bye-laws reduced conflicts: no encroachment, no grazing on fruit gardens and no thieves.
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Integrating people with disabilities (PWDs) in fruit tree growing trainings and exposure learning events.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Planted fruit trees control soil run off/soil erosion.
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
การสะสมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to planted fruit trees and soil&water conservation bye-law on tree planting.
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Planted trees reduce drought.
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to firelines to control bush burning during dry season.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to presence of strict community bye-laws.
ความคิดเห็นเกี่ยวกับการประเมินผลกระทบ:
The technology is rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by any farmer in any climatic region especially tropical regions.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | ลดลง | ดีมาก | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูฝน | ลดลง | ดีมาก |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดีมาก |
| ไฟป่า | ดีมาก |
| ไฟบนบก | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ดินถล่ม | ดีมาก |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology is drought resistant and manageable by any farmer who has the interest to practice it.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The fruits are locally sold expensively at 1000 UGX@ and raise much income to the farmer.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 10-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
20 household
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user uses the little resources he has to establish the technology.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Constant supply of fruits provides high income to the land user. To realize maximum production, there is need for irrigation to have a constant fruit supply with support from extension workers who are readily available with the extension workers for technical advice. |
| The fruit trees modify the micro-environment making it conducive. |
| The technology is very rewarding, cost effective once established and can easily be replicated by other land users. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology is good for small , medium and large scale farmers due to its ability to improve soil fertility, increase production and household income. |
| Can easily be replicated by other land users. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Before establishment the technology requires some knowledge and skills on fruit growing which can be extended by the extension worker who are located far from the land user. Associated with high costs in terms of transport and allowances to the land user. |
Training and capacity building of local land users / experts. Training champion farmers. Establishment of learning sites / demonstrations. |
| Prone to climate change | Irrigation during the dry season |
| Requires water supply | Irrigation during dry seasons |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High establishment costs associated with reduced maintenance costs both in the short, medium and long term. | Adapt low cost practices for those starting and integrate with time and for those with low incomes. |
| Associated with high prevalence of pests and diseases. Risky to spray during flowering season. |
Close monitoring of the field all the time. Seek technical advice from the extension worker. |
| Labour intensive at the time of establishment. | Supplement with family labour. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
1
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
1
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
1
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Do Trees on Farms Improve Household Well-Being? Evidence From National Panel Data in Uganda, Daniel, C.Miller,September 2020.2020.0010
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
On-line. Free of cost.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล