Local Rabbit Keeping for Manure Production and Household Income [ยูกันดา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: betty adoch
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson, Bernard Fungo
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Drake Mubiru, Udo Höggel
Gwoko Apwoyo pi cetgi me medo moc ngom
technologies_2890 - ยูกันดา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Onen Geoffrey
0793874904 / 0776492280
onen@yahoorocket.com
Ongako Farmers group
Omoro District, Ongako Subcounty, Kal Parish, Kal Village
ยูกันดา
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - ยูกันดา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
24/05/2017
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
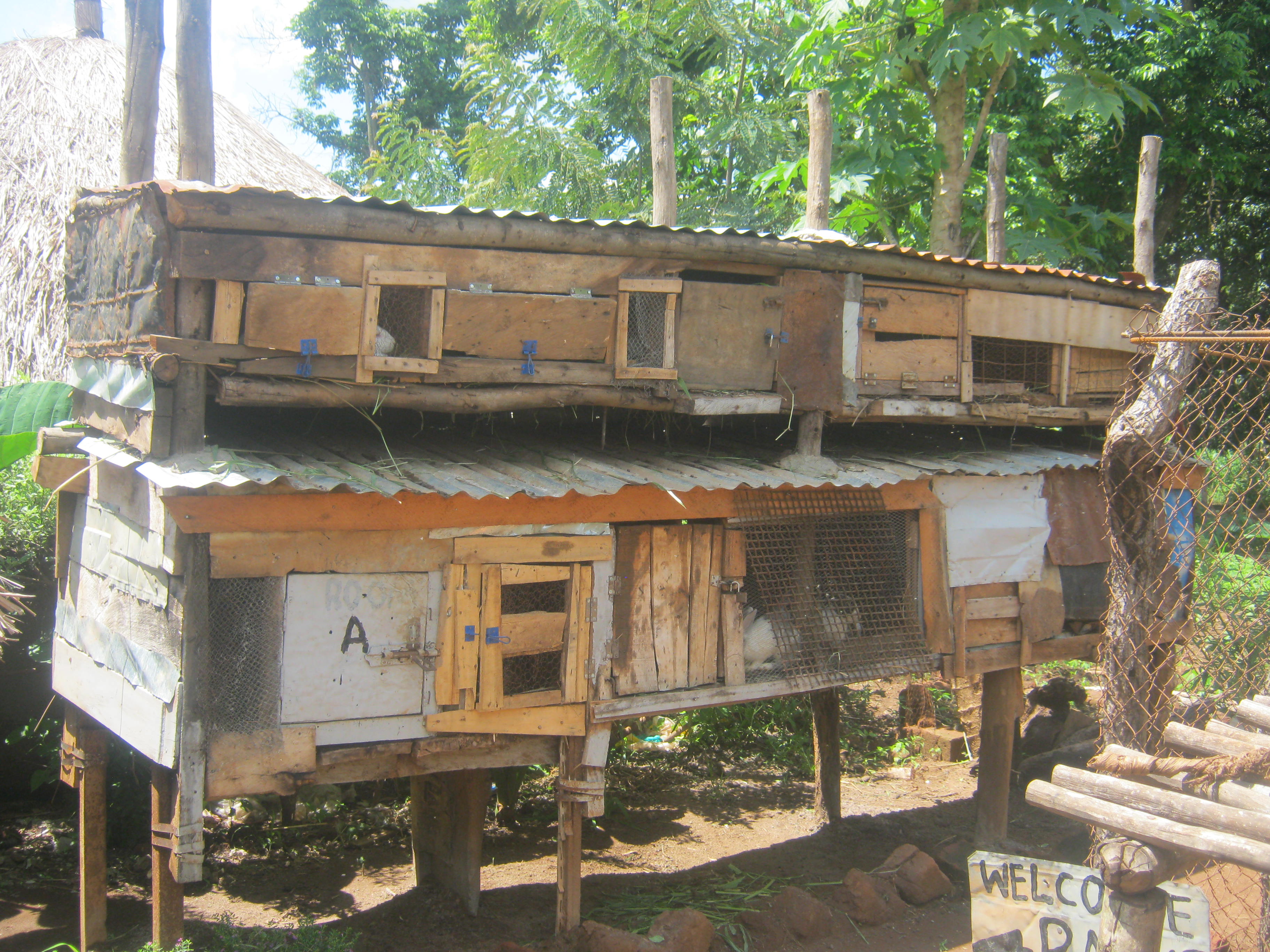
Local rabbits are kept in a shade made of wood, iron sheet and wire mesh for manure production with the aim of obtaining animal manure for soil fertility improvement thus increasing vegetable and fruits production and household income.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Local rabbit keeping for manure production is a common practice promoted by farmers in Northern Uganda with the aim of obtaining animal manure for soil fertility improvement, increasing agricultural production and for securing household income.
Through the promotion of this technology the farmer uses animal manure because soils have low fertility, coupled with low productivity and hence low crop yields caused by degradation due to mono-culture, overgrazing and bush burning.
To obtain animal manure, local rabbits are kept within the compound for easy monitoring, minimum protection against predators and easy collection of manure. After manure is collected, it is filled into a decomposing pit. From there the manure is later applied to agricultural fields, vegetable and fruit gardens.
Important to note is that this technology is appropriate for small scale farmers with land size holding of 0.5-2 acres. it requires little amount of money at the time of establishment, it is not labour intensive and provides high nutrient manure since the rabbits are fed mainly on local feeds.
Usually manure is collected around the rabbit house on a weekly basis to be used as compost manure which is then applied to the garden. Following steps are required : Site clearing, collecting manure and digging compost pits for manure decomposition and manure application to the garden. Material required is timber, wheel barrows, hoes, nails, wire mesh and iron sheets. The compost manure pit is dug to 1 meter depth and 1 meter width. Rabbit dung is collected to fill up the pit.
To maintain the technology, land users need to clear the bush around the house for easy collection of the dung and turning the decomposing manure weekly for proper decomposition.
Usually it takes one month for a pit to fill up and the decomposition period is three months. The compost manure is then collected using a wheelbarrow and spread into the vegetables and fruits gardens of lemon grass, green peas, green pepper and fruits (tangerine, oranges).
After applying on his garden, the farmer continues to collect the surplus manure which he sells to other farmers at a rate of 2,000 shillings per spade of organic manure. This practice is usually appreciated by land users because it enhances soil fertility, increases crop production and rehabilitates badly degraded land by adding manure nutrients to the soil.
What is not liked about this technology is that the manure takes somewhat a long time to accumulate due to the small number of rabbits kept in addition to long time to decompose for application on the garden.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Video showing rabbit keeping for increased manure production and household income.
วันที่:
24/05/2017
สถานที่:
Kal Village , Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty,Omoro District, Northern Uganda
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Betty Adoch
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ยูกันดา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Northern Uganda.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kal Village, Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty,Omoro District, Northern Uganda
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Kal Village, Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty, Omoro District, Northern Uganda
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2016
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Local rabbit keeping project for animal manure
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Vegetables, fruits

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
Degraded lands
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Cereals cropland and grazing fields.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- การเลี้ยงผึ้ง การเพาะเลี้ยงสัตว์น้ำ สัตว์ปีก ฟาร์มกระต่าย ฟาร์มหนอนไหม
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S9: ที่พักพิงสำหรับพืชและสัตว์

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pu (Loss of bio-productive function): การสูญเสียหน้าที่การผลิตทางชีวภาพอันเนื่องมาจากกิจกรรม อื่นๆ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The application of this technology helps repairing the soil from human-induced degradation.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
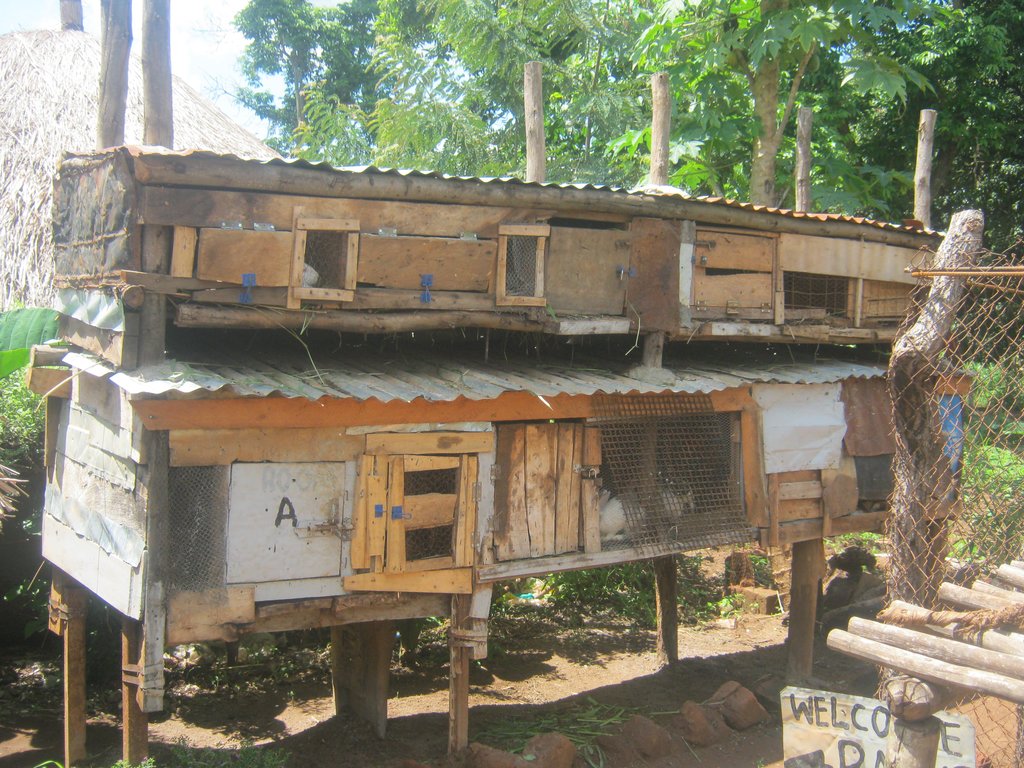
The technical drawing shows a rabbit house (hutch). This hutch was made simple and affordable to the farmer. The hutch was constructed around the compound for easy monitoring from danger by the farmer. The farmer constructed the hutch out of wood, iron sheets for the roofing and a wire mesh door that can be opened and closed.
However, when constructing a hutch, the measurements tend to vary depending on the number of rabbits a farmer wants to rear.
The technical drawing shows that the width of the hutch is six (6) meters and having a depth of 1,5 metres. The wall of the hutch is made of wood of about 1 meter high supported by a raised platform. That platform offers protection against dangerous reptiles such as snakes that prey on rabbits.
The hutch has lower and upper levels, partitioned into smaller rooms big enough to accommodate a pair of rabbits. The sizes of the rooms are four times bigger than the size of the rabbit's length. This is to provide ample space for the rabbit to run around and stretch as well as a place to hide while playing.
A hutch is constructed in a way that protects the rabbit from adverse weather conditions such a too windy weather that usually kills or makes the rabbit to become too sick as well as to provide shade to the rabbits.
However, hutches can be difficult to clean and also rabbits may be able to escape if the wire mesh isn't tightly secured.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
2 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
UGX
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
3500.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3000shs
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing | จัดการพืช | Dry and wet season |
| 2. | Digging pits | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry and wet season |
| 3. | Collecting rabbit dung | ด้วยการจัดการ | Dry and Wet season |
| 4. | Pilling the dung in the pit | ด้วยการจัดการ | Dry and Wet season |
| 5. | Applying manures to the garden | จัดการพืช | Wet season |
| 6. | Constructing the hutch | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry and Wet season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Easy to establish the technology because it requires less capital.
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | persons day | 2.0 | 3500.0 | 7000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoes | piece | 3.0 | 12000.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Wheelbarrows | piece | 1.0 | 90000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spade | piece | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Nails | pics | 30.0 | 500.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Poles | pics | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wire mesh | Roll | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Iron sheets | pics | 2.0 | 32000.0 | 64000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Timber | pics | 10.0 | 12000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 442000.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land user can afford to pay the workers during during construction, compost manure making and labour for transporting the manures to the garden.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turning the compost | ด้วยการจัดการ | During dry and wet season |
| 2. | Cleaning the hutch | ด้วยการจัดการ | During dry and wet season |
| 3. | Digging around the hutch | ด้วยการจัดการ | During dry and wet season |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Clearing around the hutch | perso per dayn | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Cleaning the hutch | person per day | 4.0 | 3000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Clearing around the manure pit | person per day | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Adding manure to the garden | persons per day | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoe | pic | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spade | pic | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Wheelbarrow | pic | 1.0 | 150000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hard broom | pic | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 213500.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Maintenance activities do not require much capital.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Inputs such as timber, wheel barrows, hoes, nails , wire mesh and iron sheets affect costs most.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1500.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainy seasons from april, may, june, july, august, september and october. Dry seasons from november, december, january, febuary and march.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Gulu weather station.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Tropical savanna climate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Manure adds nutrients into the soil thus increasing crop productions
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Manure add nutrients to the soil fertile soils improving crop quality
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to application of manure which is locally obtained.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Some of the surplus manure is sold to generate income @ spade at UGX 2000 to the neighbourhood
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low quantity before SLM
หลังจาก SLM:
high quantity after SLM
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetable crop growing improved due to manure applications into the soil.
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Dense vegetation cover provides above ground carbon sink.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Improved rabbit species being reared by the farmers that fetch high market prices.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology is good at providing locally available materials such rabbit dung/animal manure that is less cost intensive and locally obtained. |
| Good at improving soil fertility by applying manure, rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by other small scale farmers in other areas. |
| Provides income after sale of manure. |
| Very appropriate for men and children/youth since it does not involve a lot of moving from one place to another for feeds. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology is multipurpose (good at improving soil fertility by applying manure, provides income after sale of manure). |
| Easy to replicate. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Leaching due to excessive rainfall. | Dig the manure pit under shade/shelter. |
| Liked by thieves. | Fencing, provision of security. |
| Rabbits consume lots of feeds. | Grow relevant local feeds near the homestead such as grass, maize plant. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Negative attitude by other community members. | Involve them in the process of manure preparation and hutch constructions. |
| Long period required for manure to decompose. | Dig pit under shade for fast cooling of the compost and enhancement of decomposition. |
| Low rabbit dung collection for manure since they are kept in less numbers. | Expand the number of rabbits to generate manure. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
1
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
1
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
The potential of rabbit production in improving household incomes in Nankoma Sub-county, Bugiri District, Uganda E K Ndyomugyenyi and O D Otiengino
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289674867_Ndyomugyenyi_E_K_and_Otiengino_O_D_2013_The_potential_of_rabbit_production_in_improving_household_incomes_in_Nankoma_Sub-county_Bugiri_District_Uganda_Livestock_Research_for_Rural_Development_25_8_htt
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Rabbit Farming In Uganda, Rearing Tips, Farmers Association, Market, Urine, Feeds & Cages
URL:
https://www.aboutuganda.com/agriculture/rabbit-farming-in-uganda
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล