Herbal leys in an organic dairy rotational grazing system [สหราชอาณาจักร]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Alan Radbourne
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5982 - สหราชอาณาจักร
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Turner Stephen
Perridge Farm Partnership
สหราชอาณาจักร
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Hutchings Nathan
Perridge Farm Partnership
สหราชอาณาจักร
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
European Interreg project FABulous Farmersชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil Association (Soil Association) - สหราชอาณาจักร1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Use of diverse herbal leys in dairy production. Provides resilient forage that improves soil health and provides a habitat for biodiversity within a rotational grazing system
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
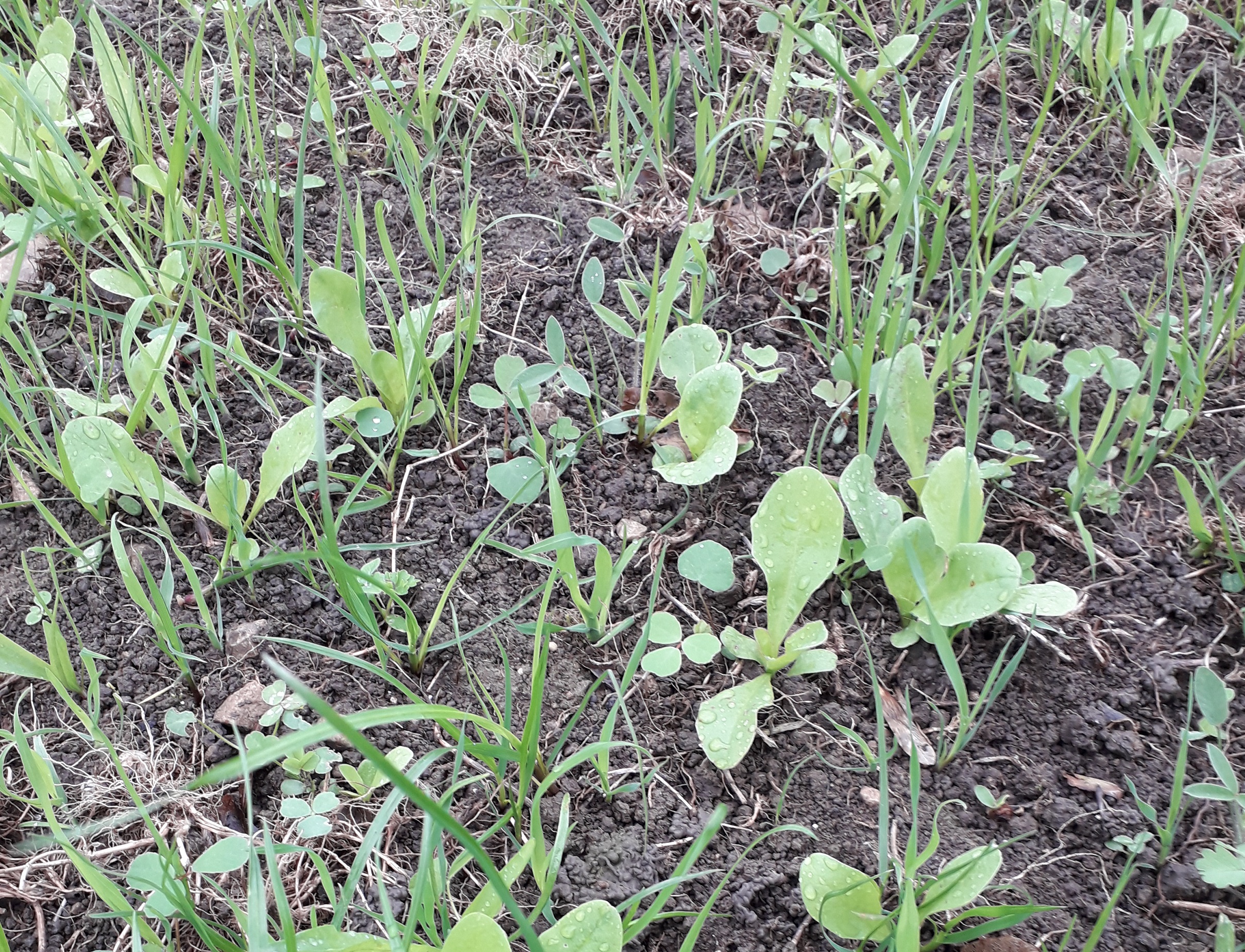
Perridge and Old Burford Farm is a 182 ha organic dairy and beef farm in Somerset. They established 43 ha of diverse herbal leys on their grazing platform between 2018 and spring 2021. There are a further 16 ha to be sown in autumn 2021 with further developments planned thereafter.
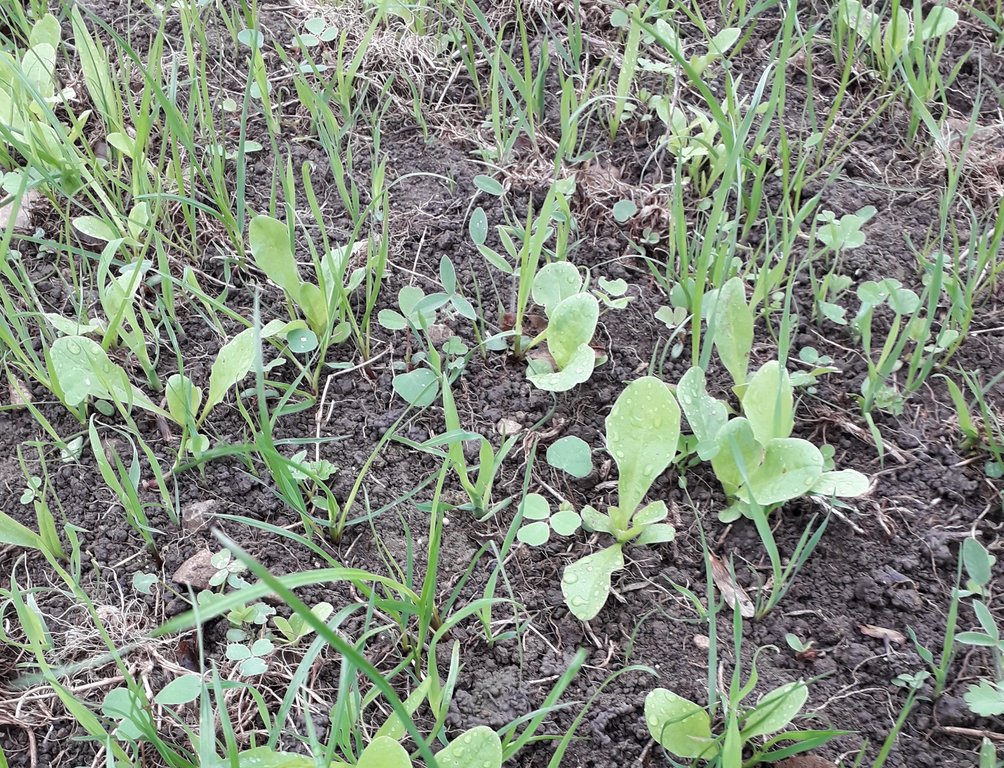
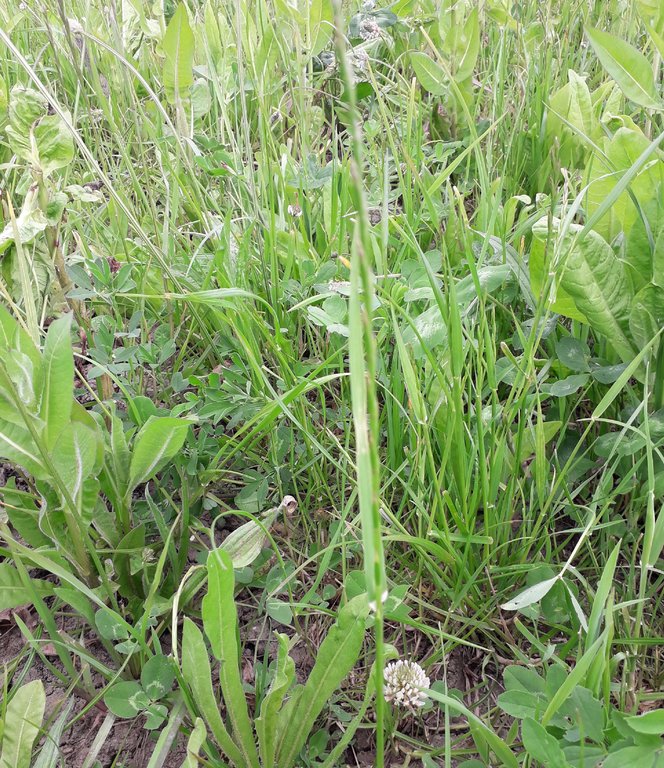
The system initially established a mix of chicory, plantain, ryegrass and clover in Autumn 2018, with further fields including a more complex mix of cocksfoot, Festulolium sp (a natural hybrid of ryegrass and fescue) , ryegrass, timothy, tall and meadow fescue, sainfoin; red, white, alsike and sweet clovers, sainfoin, lucerne, birdsfoot trefoil, burnet, chicory, ribgrass forage herb, yarrow and sheep’s parsley.
The most successful establishment has been from autumn sowing, following ryegrass, into a well prepared seed bed with shallow cultivation. This has led to three to four times more effective germination. To prepare the seed bed, a Cambridge roller was used to form a firm seed-bed and stop seeds going too deep, then seed was sown using a grass harrow and air seeder in August. Soil was rolled again with the Cambridge roller to break up clods of soil and then given a flat-roll to give tight soil-to-seed contact and to conserve moisture. The field is then left untouched until the following spring.
Once established by the following spring, the leys are grazed with 140 organic dairy cows, calves and beef animals. They are grazed using a strip rotation approach where they are moved daily at a target of 4,000kg dry matter (DM)/ha, and graze the herbage down to a residual of 1,800kg DM/ha (minimum residual of 10cm). The minimum full rotation is 35 days but this is often longer.
No artificial inputs are used with these diverse herbal leys, thus adhering to organic standards. The legumes (clover, lucerne, sainfoin and birdsfoot trefoil) are used to fix nitrogen, and with the grazing approach of “a third eaten, a third trampled and a third remaining as residual feed” soil organic matter is built up. In addition, the deep rooting species draw up minerals, improve soil structure and infiltration, and increase soil organic matter (SOM). Increasing SOM can also increase soil bacteria and microbe activity. Furthermore, managing the system with a rotational, cell grazing approach prevents selective grazing and increases species diversity and longevity of the sward.
Benefits:
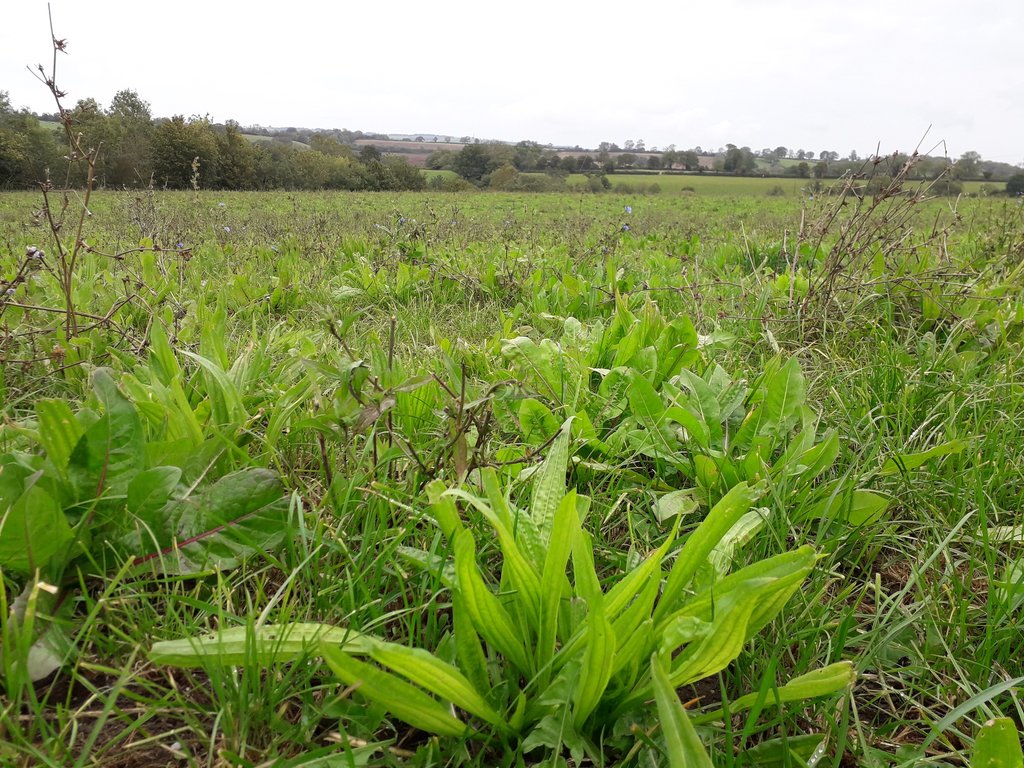
Soil health – deep rooting species improve soil structure and infiltration, and through building up organic matter this improves soil carbon sequestration and leads to greater soil microbial activity and improved nutrient cycling. This is particularly important for this site due to mineral deficiency.
Resilient and persistent forage – deep rooting species bring up moisture from deep in the soil.
Mineral-rich forage – there is a high mineral content in ribwort plantain, chicory, sheep’s parsley, yarrow and burnet. Again, root structure helps, mining more minerals from deeper in the soil profile.
Biodiversity improvements - a wider species diversity of flowing plants is beneficial for biodiversity.
Animal health benefits – Anthelmintic properties of some species with a high tannin content, such as chicory, sainfoin and birdsfoot trefoil, reduce the parasitic worm burden. Also, the way livestock are grazed, with a good residual of forage, reduces soil contact and, therefore, worm risk
There are many positives to herbal leys and these have all been experienced to date, particularly resilient forage production in dry conditions. It currently is too early to see changes in soil structure and health.
The challenge with herbal leys are ensuring successful establishment and selecting the right seed mix. Establishment is reliant on conditions and preparations, with the lifespan of the ley managed through careful grazing by having long rotations and preventing selective grazing. Ensuring you have the correct mix of grasses, herbs and legumes to get the balance of energy and protein is key: there has been some anecdotal experience at this farm of cows not seeming “full” coming off herbal ley, this is thought due to dominance of chicory over grasses.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สหราชอาณาจักร
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Somerset
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Shepon Mallet
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2018
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- cattle - non-dairy beef
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Count:
140
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1ha = 2.47 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
GBP
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.75
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
150
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Shallow cultivator x 4 passes | August |
| 2. | Cambridge Roller | August |
| 3. | Sow seed with grass harrow and air seeder | August |
| 4. | Cambridge Roller | August |
| 5. | Flat Roller | August |
| 6. | Cows let into graze | April |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Shallow cultivator (up to 4 passes) | Ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 50.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Cambridge Roller | Ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 50.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Grass harrow and air seeder | Ha | 1.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 | 50.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Flat roller | Ha | 1.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 50.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Herbal ley seed mix | Ha | 1.0 | 218.0 | 218.0 | 50.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 330.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 440.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Supporting projects such as Fabulous Farmers
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Contract charge provided so includes labour costs. Cost shown represents the cost per ha. This case study applied on 43 ha.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rotational Strip Grazing | 1 day in >35 days April to November |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Maintenance through cattle grazing each year for the remaining life of the ley.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Seed cost, success of establishment. If establishment fails or is patchy then reseeding or over seeding will be required.
Additionally longevity of sward is an important factor in cost – how many years will the sward last before reseeding is required. Aim minimum 4 -5, but can be up to 9 years
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1300.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Good quality and diversity of fodder for grazing cattle. Similar production to grass ley achieved.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Good quality and diversity of fodder for grazing cattle
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cattle remained healthy and well fed on herbal ley
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More resilient and diverse forage
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Up to 16 species have been sown as a very diverse seed mix
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Training and SLM expert support has transferred knowledge to land users
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Deeper rooting and broader leaves have helped maintain soil moisture
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
No heavy machinery used after sowing in August through to grazing in May.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Deep rooting varieties can recharge nurtients from depth, while nitrogen fixers can support nutrient cycling
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Up to 16 species have been sown as a very diverse seed mix
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Plant diversity has attracted a greater abundance of beneficial species
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Deeper rooting and broader leaves have helped maintain soil moisture and recycle from deeper soil water
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | ลดลง | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Improving soil heath and structure, building soil organic matter and improving mineral balance |
| Resilient forage crop that can cope with longer periods of low rainfall |
| Nutritious, high mineral content forage that has additional anthelmintic benefits |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Diverse herbal leys have multiple benefits to soil, also perform well in periods of low rainfall – more evidence of soil benefits is required regarding structure and biological cycling |
| Delivers for biodiversity - through providing flowering plants for pollinators and allowing diverse plants like chicory to go to seed provides important feed for birds |
| More research is required on health impact and production in relation to dairy. Research by Reading University has demonstrated no significant different in growth rate for steers |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Cost and challenge of establishment due to frequent dry springs | Careful timing and flexibility |
| Maintaining species diversity and sward longevity | Rotational grazing and long rotations, allowing plants to seed on a rotational basis |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Have realistic expectations of what plants will thrive on different soil types and select bespoke mixes accordingly | Improved knowledge and support |
| In many cases having to establish a seed bed through ploughing – linked to longevity of sward, want to minimise cultivations and re seeding to reduce soil damage and cost | Improved knowledge and support |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
1
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
1
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
30/09/2020
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล