Water points for livestock in daily pastures [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Nicole Stolz
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Boris Orlowsky, Sa'dy Odinashoev
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Nicole Harari, Alexandra Gavilano, Alvin Chandra
Нуқтаи обнушии чорво
technologies_623 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Pasture User Union [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Livestock holders at village level join a pasture user union to access different rights provided under the national law "About pastures" passed in 2013. Among others, the Paster User Unions (PUUs) are able to obtain onwership of a communal collective pasture land, have the right to collect fees to improve …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Boris Orlowsky
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
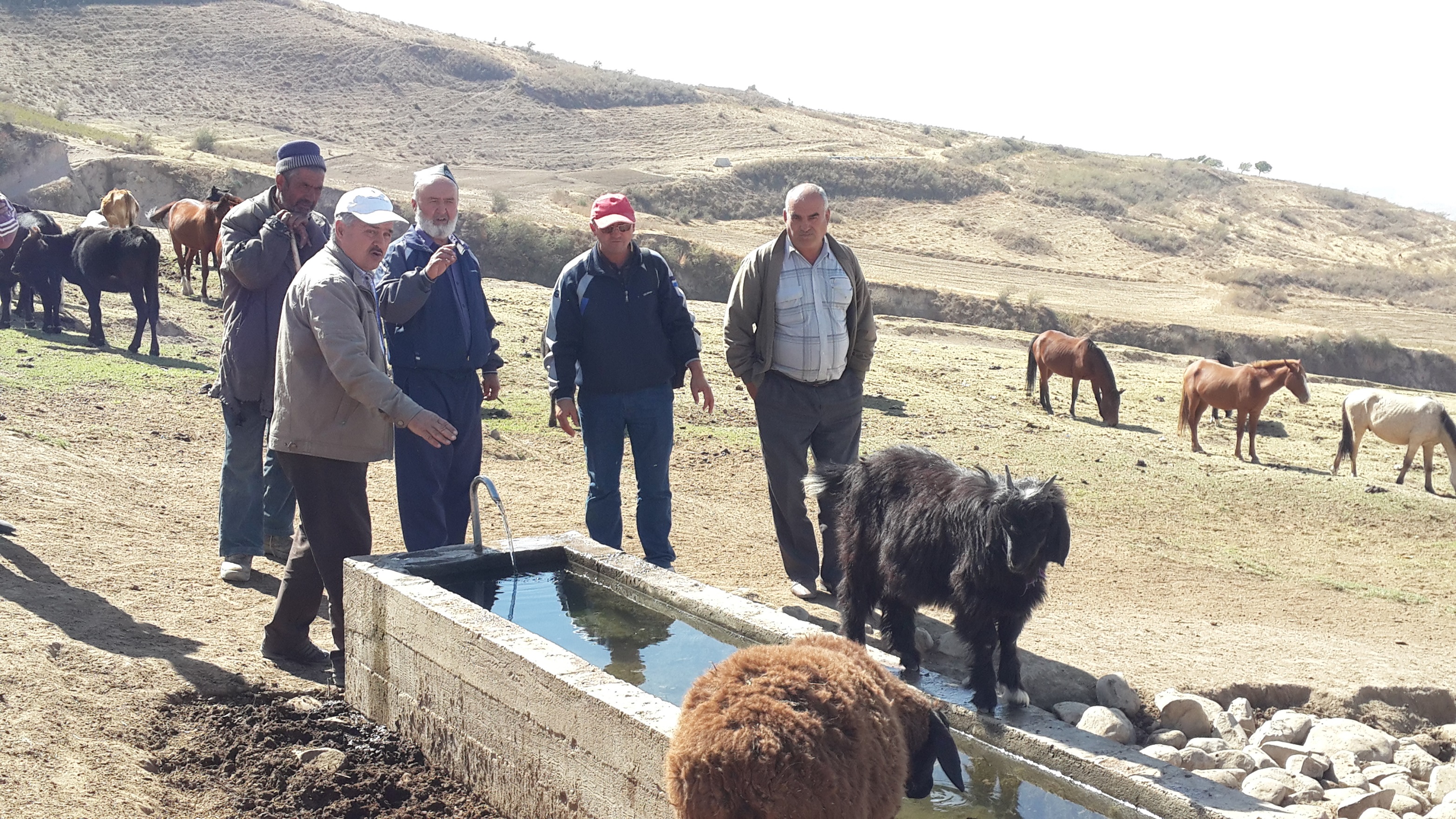
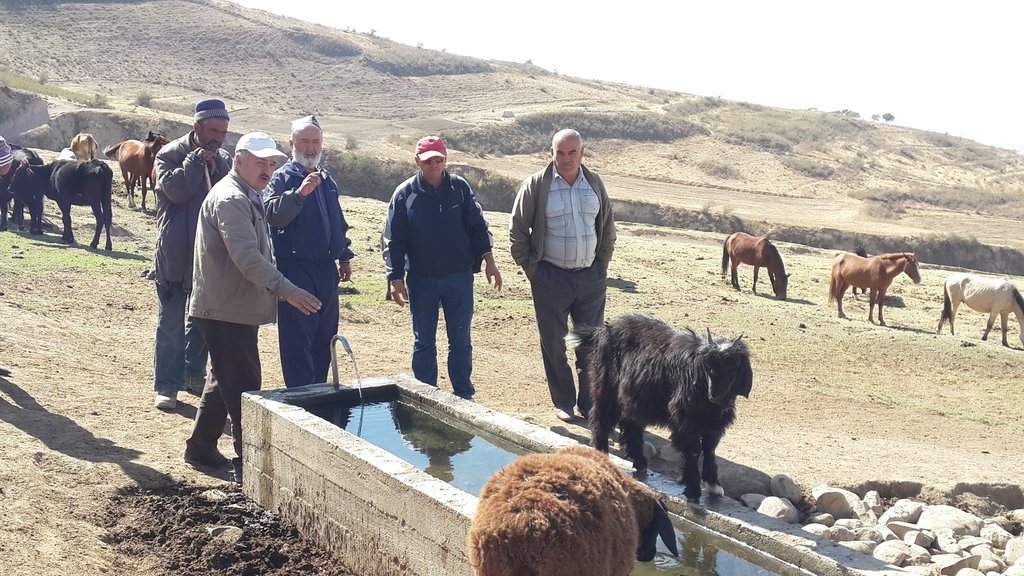
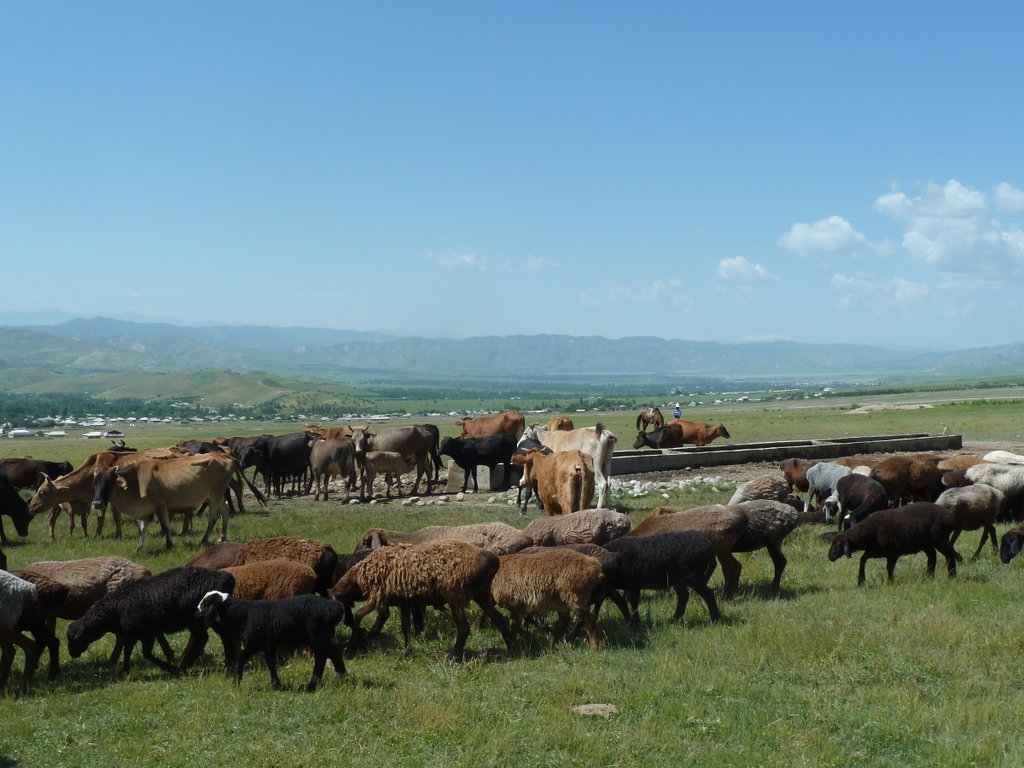
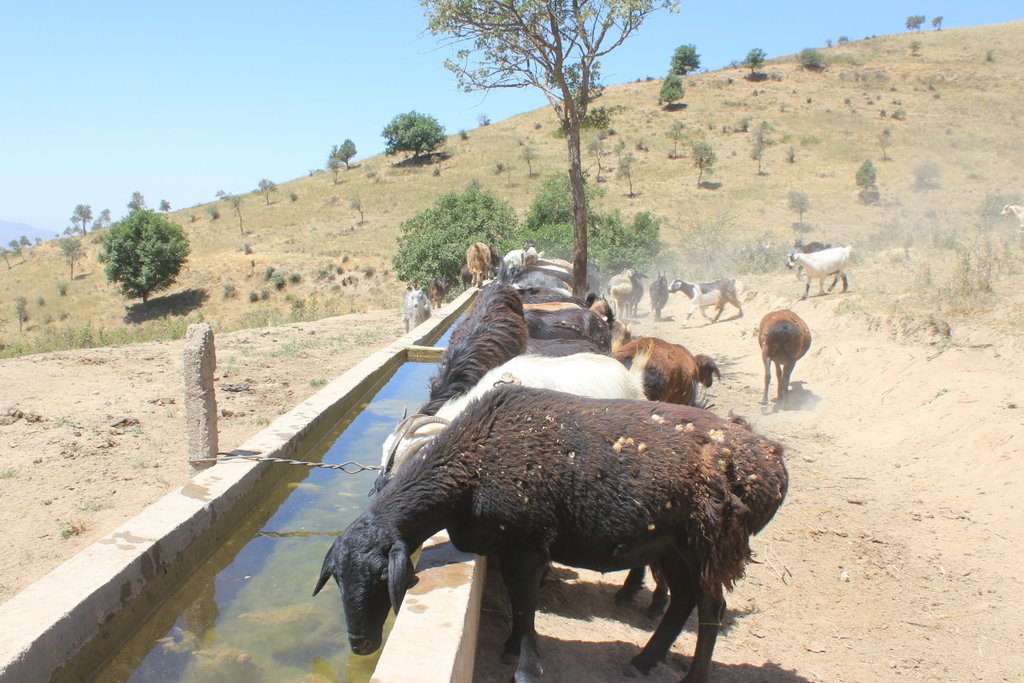
Water points for daily use in pastures, reducing erosion and enhancing productivity of cattle and other livestock.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Bringing water from springs or other sources to water points in pastures greatly increases livestock productivity and improves reproductive performance. Difficult and distant access to water exhausts the animals, reducing production of meat and milk and reproductive capacities by up to 50%.
By providing water points in pastures, negative effects on livestock productivity can be reduced to a minimum. In order to implement the technology, water sources with perennial flow have to be identified with the shortest possible distance to and from the different grazing grounds. As a next step, in Tajikistan, water and land ownership and user rights must be regulated. Rights to pasture users are either given by the community or individual land and water owners. If the water source and a location for construction are found within a reasonable distance of the different pasture grounds, a drinking water system for livestock can be designed and constructed. Construction involves spring water collection , laying of pipes
and finally installation of the water point. Besides the direct benefits (i.e. increased productivity and reproduction), the water points in the pastures reduce erosion from cattle tracks in often critical locations such as steep slopes surrounding springs. Water points also protect springs from being destroyed or spoiled by the animals. Thus the technology has a risk reduction benefit. A potential negative effect of the technology is a reduction of biodiversity, as extracting water from catchment springs may result in fewer natural fauna and flora in the micro-environments around the springs.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
สถานที่:
Muminabad district
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Khatlon
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Muminabad, Dehbaland
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2014
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
By a Caritas Switzerland project
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Livestock density (if relevant):
high
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Number of growing seasons per year:
2
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pu (Loss of bio-productive function): การสูญเสียหน้าที่การผลิตทางชีวภาพอันเนื่องมาจากกิจกรรม อื่นๆ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water points in daily pastures lead to less movements of herds from and to natural water sources, as water is brought to the animals. Densitiy of animals around natural water sources lead to damages by tampling through compaction of land, while overgrazing leads to vegetation losses, that lead to increased washing or blowing out of soil. Trampling can as well destroy a natural water source and make it unusable.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
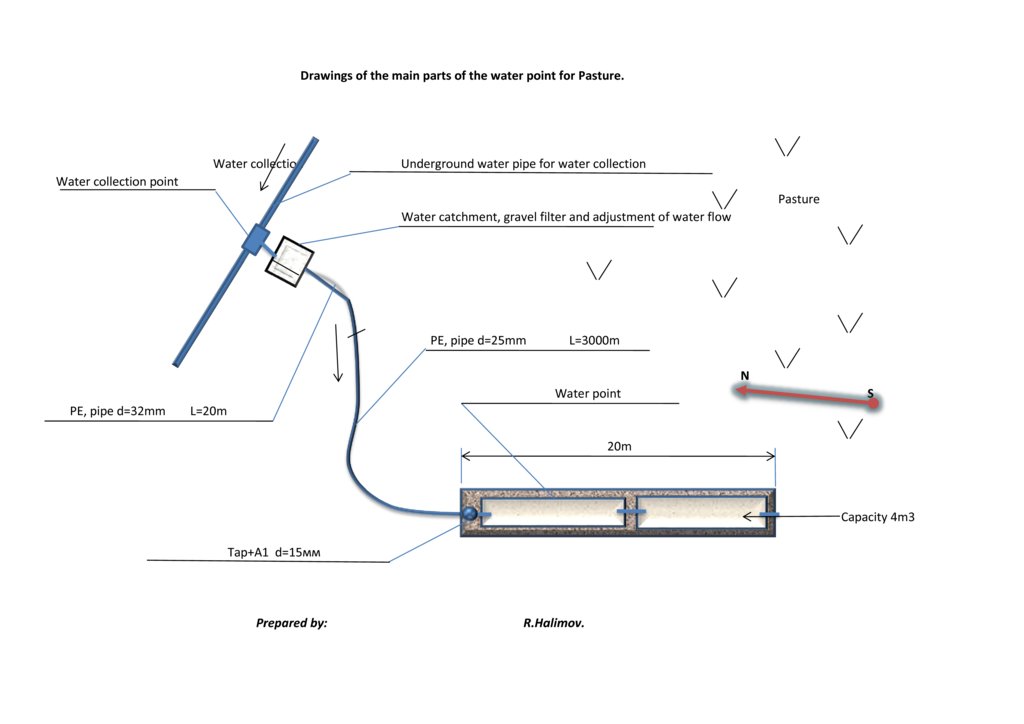
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Water is collected in underground pipes and from surface runoff, passes through a filter which additionally regulates the flow and is led to the water point structure. The length of the tubes (see drawing) allows for collecting water from a surface of several hectars. The structure is made of concrete and consists of two basins, holding together approx. 4m3 of water.
ผู้เขียน:
R. Halimov
วันที่:
16/03/2015
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
one water point
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
18m, 4,5m3
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tajik Somoni
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
45 Somoni (5.5 USD per day)
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identify water sources (spring detection) | early spring and late autumne (observe at least over two years) |
| 2. | Identify where a potential water point should be placed in the pasture area | N/A |
| 3. | Identify the land ownership | N/A |
| 4. | Design of the system | N/A |
| 5. | Tapping and protecting the spring | summer |
| 6. | Digging trenches and lay pipes | Spring |
| 7. | Connecting the tubes to spring catchment | N/A |
| 8. | Construct water point | N/A |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | person/days | 77.0 | 45.0 | 3465.0 | 20.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Material Transport Dushanbe-Muminabad | trips (truck with diver) | 1.0 | 3050.0 | 3050.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Transport in the district Center to construction place | trips (truck with driver) | 3.0 | 150.0 | 450.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Tubes | m | 1820.0 | 4.0 | 7280.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Cement | kg | 1800.0 | 1.06 | 1908.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Gravel | m3 | 6.0 | 180.0 | 1080.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Tubes | m | 1820.0 | 4.0 | 7280.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Cement | kg | 1800.0 | 1.06 | 1908.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gravel | m3 | 6.0 | 180.0 | 1080.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 27501.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 3437.63 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
15000.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Integrated Watershed Management Project, Caritas Switzerland
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Close/open water point during winter time / spring | twice per year |
| 2. | Small repairs | twice per year |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water points from cement are not that intensive for maintenance, Herders will take care of the water points as they are daily there. It is important that the tube system is fully covered with soil so that the animals will not destroy any open laying tubes.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Clean outlet of water point to reduce erosion | days | 2.0 | 45.0 | 90.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Control spring catchment (illegal cutting of trees, any other changes in vegetation to assess output of spring) and line | days | 2.0 | 45.0 | 90.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Control water line - walk along the tubes and control for leackeges) | days | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | showel | item | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Water Tab | item | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gravel bed around water point | kg | 20.0 | 20.0 | 400.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Replacement of tubes | m | 200.0 | 4.0 | 800.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 2075.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 259.38 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
2075.0
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Cost for pipes and cement, i.e. the distance of the next suitable spring to the pasture area;
land ownership: state owned land rented to the Pasture Union
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
800.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Spring and autumne rainfall
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
continental climate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
cattle and livestock grazing is a male task, animals at home are taken care by women
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
range land at community level is about 300 ha, single farmers have about 1 ha cropland
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
water is owned by the pasture user union
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
more meat, milk (avarage 1 l before, after 3 liter) and higher productivity (every second year, now every year)
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
permanently availible
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is no water availible before the intervention in the pasture area, but animals need to walk for several km to reach water down in the valley or even back at the villages
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Animals have access to improved water quality (i.e. tab water).
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
หลังจาก SLM:
30% increase
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Animals are healthier. Farmers have more milk and meat due to improved access to water and less movement during the day.
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Work for herders got easier, as they have to walk less with the animals to find water.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Negative side effect, as water beyond the need of animals runs off unused.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Erosion reduced due to improved land cover as anmials do not go into spring atchments. Reduced movements of animals reduce as well trampling and loss of vegetation cover in watershed areas.
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Tabbed water remains accesible in droughts.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
none
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความหนาว | ไม่ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water points need to be closed during winter time, otherwise the tubes will get destroyed due to freezing.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land users did not bear the full costs they benefit strongly from the beginning
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
20 water points have been established that are used by more than one village herds
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The project subsidized the construction of water points. Livestock breeders from other districts have participated by observing the use of technology
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Improved water management has improved livestock production by controlled grazing and access to water at daily pasture points. |
| Transporting livestock from steep valley locations to water drinking points was previously labour intensive, a farming activity which has improved due to dedicated water points. |
| Water quality at drinking points is good enough to be used by farmer and herders as well. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Erosion by livestock has been reduced as livestock grazing is more controlled and distributed compared to before the project interventions. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Water points and farms are remote, and construction requires machinery and a challenging transport of materials to upper pasture zones. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Investment costs are still considered to be too high to be fully borne by pasture users | Pasture User Union have been formed which collects fees. The unions help to save money for technology investments. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
3 informations, 1 engineer and 1 SLM specialist
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
3 Herders
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
11/10/2016
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
n/a
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Disaster RIsk Management in Tajikistan
URL:
https://www.caritas.ch/de/was-wir-tun/engagement-weltweit/klimaschutz-und-katastrophenpraevention/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Pasture User Union [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Livestock holders at village level join a pasture user union to access different rights provided under the national law "About pastures" passed in 2013. Among others, the Paster User Unions (PUUs) are able to obtain onwership of a communal collective pasture land, have the right to collect fees to improve …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Boris Orlowsky
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล